一、概念
常见概念
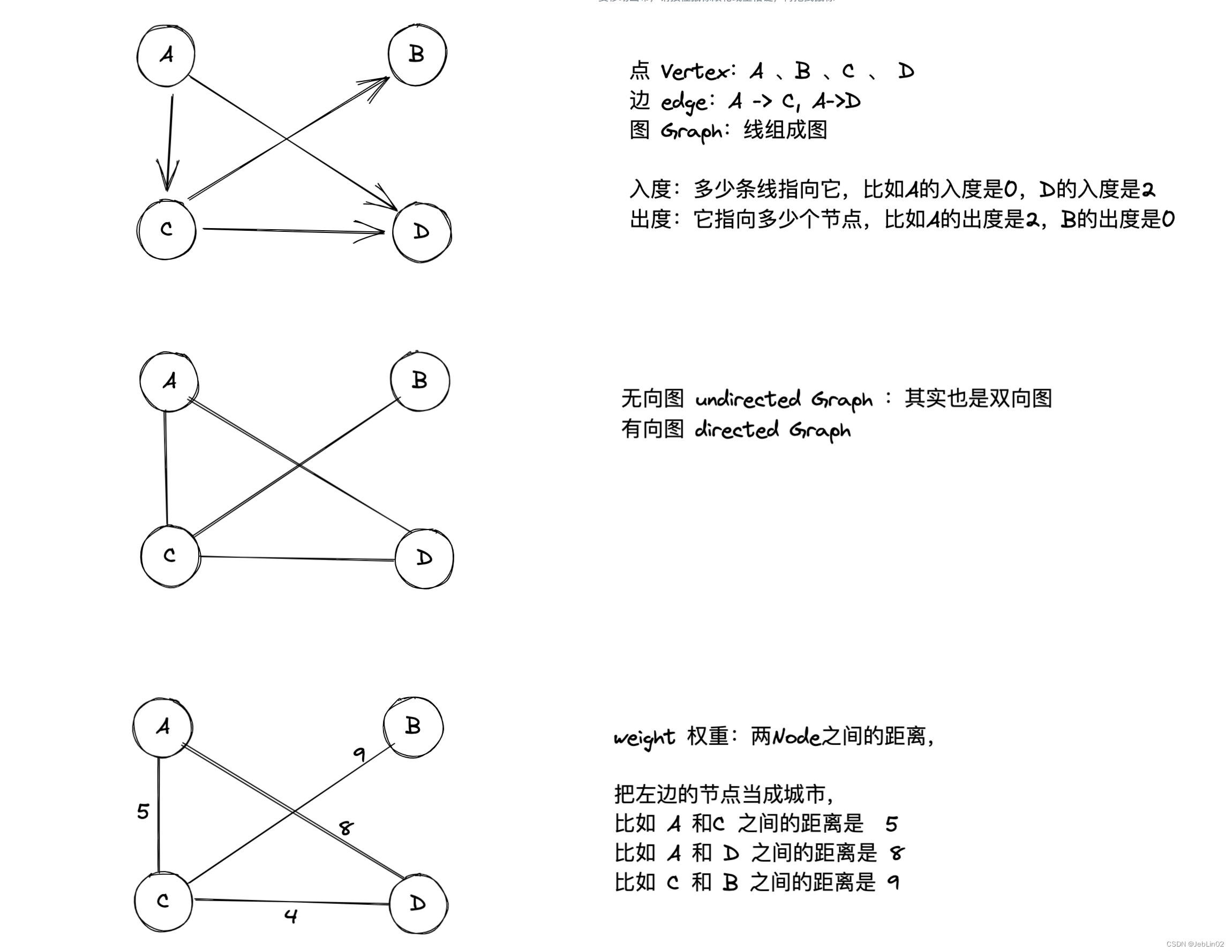
- 顶点(Vertex): 图中的节点或点。
- 边(Edge): 顶点之间的连接线,描述节点之间的关系。
- 有向图(Directed Graph): 边具有方向性的图,边有箭头表示方向。
- 无向图(Undirected Graph): 边没有方向性的图。
- 路径(Path): 顶点序列,通过边连接的顶点序列。
- 回路(Cycle): 闭合的路径,起点和终点相同的路径。
- 连通图(Connected Graph): 图中任意两个顶点之间都存在路径的图。
- 强连通图(Strongly Connected Graph): 有向图中任意两个顶点之间都存在双向路径的图。
- 连通分量(Connected Component): 无向图中的极大连通子图。
- 树(Tree): 无环连通图,任意两个节点都有唯一路径。
- 森林(Forest): 多个不相交树的集合。
- 度(Degree): 顶点的度是指与该顶点相关联的边的数量。
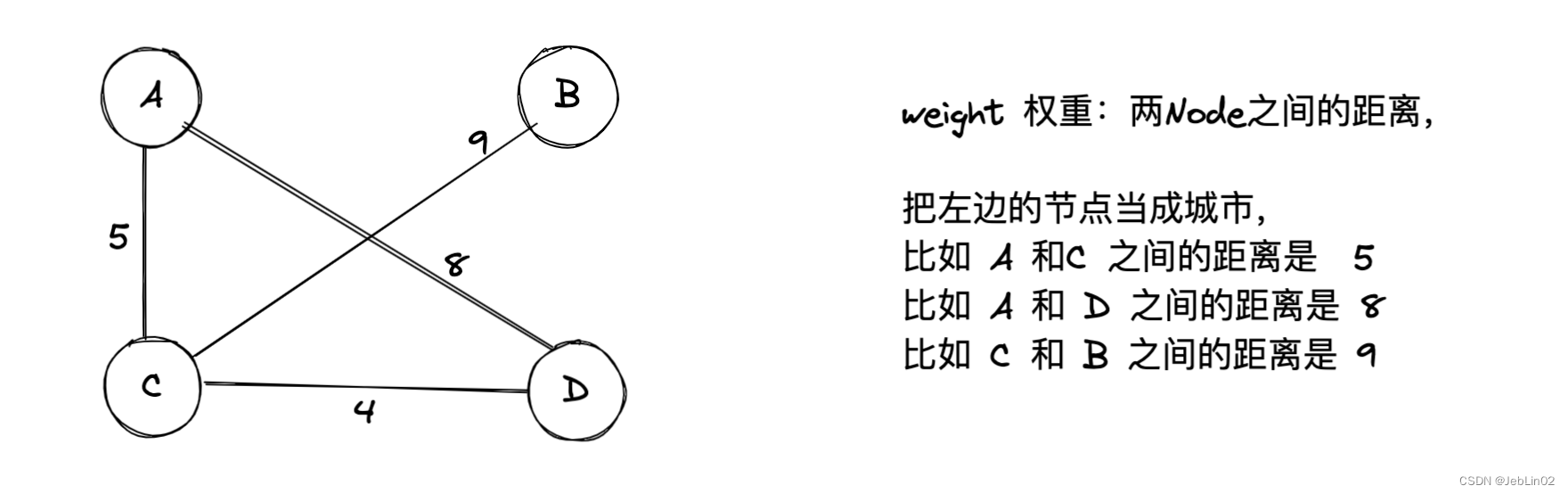
- 权重(Weight): 边或者顶点上的数值,表示边的代价或者顶点的属性。
邻接矩阵
邻接表法
| Node | weight | |
| A | C | 5 |
| A | D | 8 |
| C | B | 9 |
| C | D | 4 |
| B | C | 9 |
| D | A | 8 |
| D | C | 4 |
二、算法题
1、套路模板
/**
* @author jeb_lin
* 22:27 2023/11/29
*/
public class Node {
public int value; // 可以改成 String
public int in;// 入度
public int out;// 出度
public ArrayList<Node> nexts; // 多个后继节点
public ArrayList<Edge> edges; // 多条边,该节点指出去的
public Node(int value){
this.value = value;
this.in = 0;
this.out = 0;
this.nexts = new ArrayList<>();
this.edges = new ArrayList<>();
}
public int getValue() {
return value;
}
public void setValue(int value) {
this.value = value;
}
public int getIn() {
return in;
}
public void setIn(int in) {
this.in = in;
}
public int getOut() {
return out;
}
public void setOut(int out) {
this.out = out;
}
public ArrayList<Node> getNexts() {
return nexts;
}
public void setNexts(ArrayList<Node> nexts) {
this.nexts = nexts;
}
public ArrayList<Edge> getEdges() {
return edges;
}
public void setEdges(ArrayList<Edge> edges) {
this.edges = edges;
}
}
/**
* @author jeb_lin
* 22:27 2023/11/29
*/
public class Edge {
public Node from;
public Node to;
public int weight;
public Edge(Node from, Node to, int weight) {
this.weight = weight;
this.from = from;
this.to = to;
}
// 复写下面这俩,是为了放入Set的时候能正确去重
@Override
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
if (this == obj) {
return true;
}
if (obj == null || !(obj instanceof Edge)) {
return false;
}
Edge edge = (Edge) obj;
return this.weight == edge.weight && Objects.equals(edge.from, this.from) && Objects.equals(edge.to, this.to);
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return this.weight * this.from.hashCode() * this.to.hashCode();
}
public Node getFrom() {
return from;
}
public void setFrom(Node from) {
this.from = from;
}
public Node getTo() {
return to;
}
public void setTo(Node to) {
this.to = to;
}
public int getWeight() {
return weight;
}
public void setWeight(int weight) {
this.weight = weight;
}
}
/**
* @author jeb_lin
* 22:26 2023/11/29
*/
public class Graph {
public HashMap<Integer,Node> nodes; // 该图上面的所有Node,nodeVal -> Node
public HashSet<Edge> edges; // 该图上面的所有边
public Graph(){
this.nodes = new HashMap<>();
this.edges = new HashSet<>();
}
public HashMap<Integer, Node> getNodes() {
return nodes;
}
public void setNodes(HashMap<Integer, Node> nodes) {
this.nodes = nodes;
}
public HashSet<Edge> getEdges() {
return edges;
}
public void setEdges(HashSet<Edge> edges) {
this.edges = edges;
}
}
2、二维数组转化成图
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 备注 | |
| 0 | 0 | 1 | 5 | Node0->Node1 ,weight=5 |
| 1 | 1 | 2 | 3 | Node1->Node2 ,weight=3 |
| 2 | 0 | 2 | 7 | Node0->Node2 ,weight=7 |
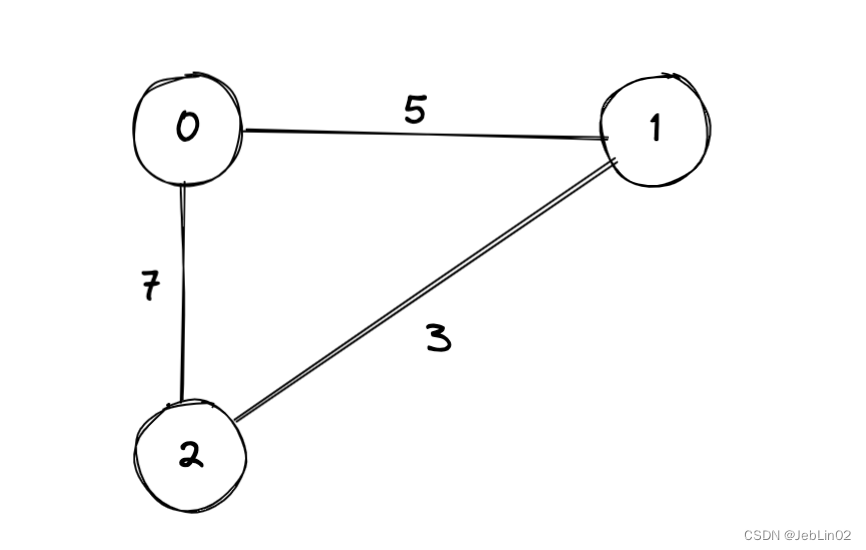
/**
* 把二维数组转换成图
* [
* [0,1,5], // 表示 node0 -> node1 ,weight = 5
* [1,2,3],
* [0,2,7]
* ]
*
* @param matrix
* @return
*/
public static Graph createGraph(int[][] matrix) {
Graph graph = new Graph();
HashMap<Integer, Node> nodes = new HashMap<>(); // 该图上面的所有Node,nodeVal -> Node
HashSet<Edge> edges = new HashSet<>(); // 该图上面的所有边
graph.setEdges(edges);
graph.setNodes(nodes);
for (int i = 0; i < matrix.length; i++) {
int[] row = matrix[i];
if (!nodes.containsKey(row[0])) {
nodes.put(row[0], new Node(row[0]));
}
if (!nodes.containsKey(row[1])) {
nodes.put(row[1], new Node(row[1]));
}
Node from = nodes.get(row[0]);
Node to = nodes.get(row[1]);
from.setOut(from.getOut() + 1);
to.setIn(to.getIn() + 1);
from.getNexts().add(to);
Edge edgeTemp = new Edge(from, to, row[2]);
from.getEdges().add(edgeTemp);
if(!edges.contains(edgeTemp)){
edges.add(edgeTemp);
}
}
return graph;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[][] arr = {{0, 1, 5}, {1, 2, 3}, {0, 2, 7}};
Graph graph = createGraph(arr);
System.out.println("ok");
}3、图的深度优先遍历DFS

private static void testBreadthFirstSearch() {
Node node1 = new Node(1);
Node node2 = new Node(2);
Node node3 = new Node(3);
Node node4 = new Node(4);
Node node5 = new Node(5);
node1.getNexts().add(node2);
node1.getNexts().add(node3);
node1.getNexts().add(node4);
node2.getNexts().add(node1);
node2.getNexts().add(node3);
node3.getNexts().add(node1);
node3.getNexts().add(node2);
node3.getNexts().add(node4);
node3.getNexts().add(node5);
node4.getNexts().add(node1);
node4.getNexts().add(node3);
node4.getNexts().add(node5);
node5.getNexts().add(node3);
node5.getNexts().add(node4);
breathFirstSearch(node1);
}
private static void breathFirstSearch(Node head) {
System.out.println(" === breathFirstSearch ===");
if(null == head){
return;
}
Set<Node> nodeSet = new HashSet<>();
LinkedList<Node> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(head);
nodeSet.add(head);
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
Node temp = queue.poll();
System.out.print(temp.value + ",");
for (int i = 0; i < temp.getNexts().size(); i++) {
Node nextTemp = temp.getNexts().get(i);
if(!nodeSet.contains(nextTemp)){
queue.offer(nextTemp);
nodeSet.add(nextTemp);
}
}
}
System.out.println();
}4、 图的广度优先遍历BFS

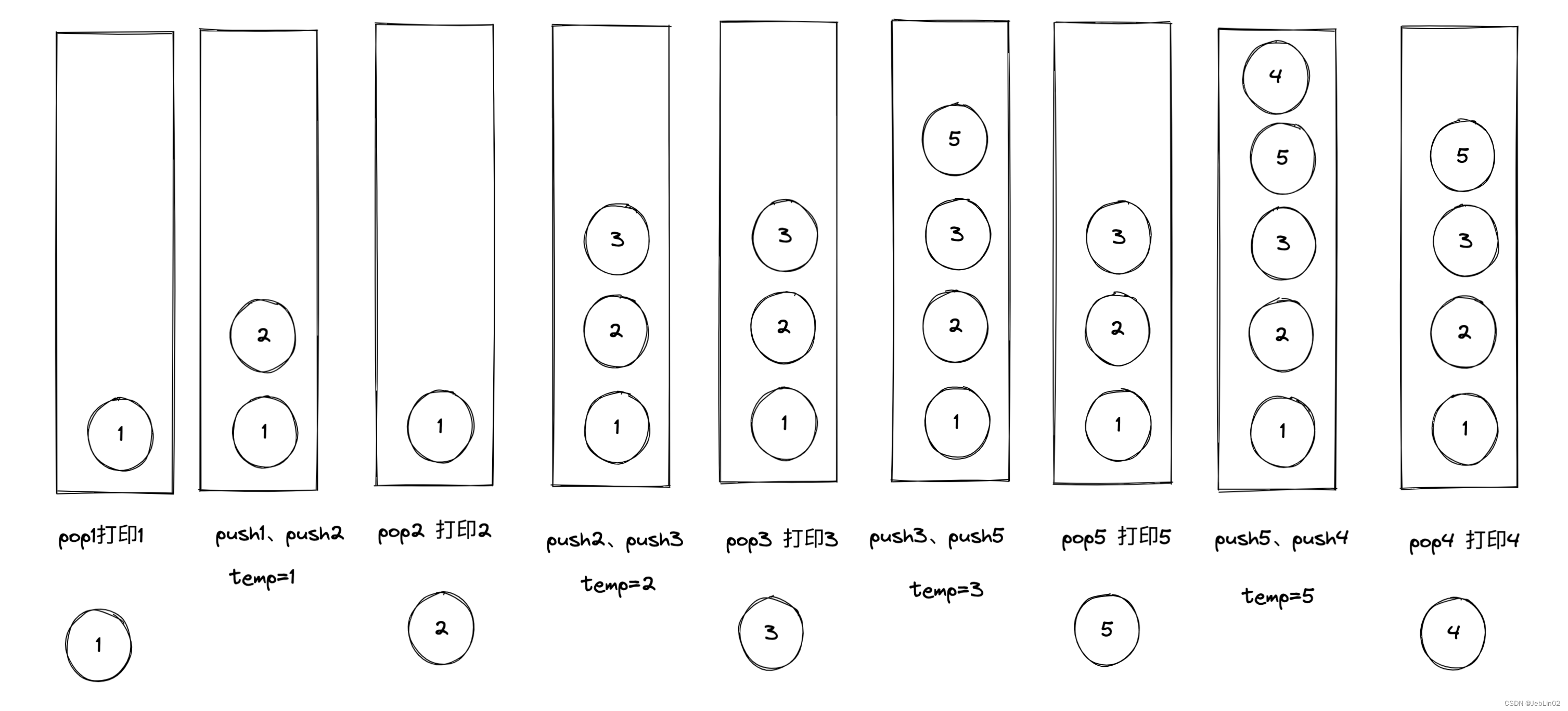
private static void testDepthFirstSearch() {
Node node1 = new Node(1);
Node node2 = new Node(2);
Node node3 = new Node(3);
Node node4 = new Node(4);
Node node5 = new Node(5);
node1.getNexts().add(node2);
node1.getNexts().add(node3);
node1.getNexts().add(node4);
node2.getNexts().add(node1);
node2.getNexts().add(node3);
node3.getNexts().add(node1);
node3.getNexts().add(node2);
// node3.getNexts().add(node4);
node3.getNexts().add(node5);
node4.getNexts().add(node1);
node4.getNexts().add(node3);
node4.getNexts().add(node5);
node5.getNexts().add(node3);
node5.getNexts().add(node4);
depthFirstSearch(node1);
}
private static void depthFirstSearch(Node head) {
if(null == head){
return;
}
System.out.println(" === depthFirstSearch ===");
Stack<Node> stack = new Stack<>();
stack.push(head);
Set<Node> nodeSet = new HashSet<>();
nodeSet.add(head);
System.out.print(head.value + ",");
while (!stack.isEmpty()){
Node tempNode = stack.pop();
for (int i = 0; i < tempNode.getNexts().size(); i++) {
Node nextTemp = tempNode.getNexts().get(i);
if(!nodeSet.contains(nextTemp)){
stack.push(tempNode);
stack.push(nextTemp);
nodeSet.add(nextTemp);
System.out.print(nextTemp.value + ",");
break;
}
}
}
System.out.println();
}
private static void testBreadthFirstSearch() {
Node node1 = new Node(1);
Node node2 = new Node(2);
Node node3 = new Node(3);
Node node4 = new Node(4);
Node node5 = new Node(5);
node1.getNexts().add(node2);
node1.getNexts().add(node3);
node1.getNexts().add(node4);
node2.getNexts().add(node1);
node2.getNexts().add(node3);
node3.getNexts().add(node1);
node3.getNexts().add(node2);
node3.getNexts().add(node4);
node3.getNexts().add(node5);
node4.getNexts().add(node1);
node4.getNexts().add(node3);
node4.getNexts().add(node5);
node5.getNexts().add(node3);
node5.getNexts().add(node4);
breathFirstSearch(node1);
}原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/Sword52888/article/details/134699844
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。
如若转载,请注明出处:http://www.7code.cn/show_13143.html
如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系代码007邮箱:suwngjj01@126.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
声明:本站所有文章,如无特殊说明或标注,均为本站原创发布。任何个人或组织,在未征得本站同意时,禁止复制、盗用、采集、发布本站内容到任何网站、书籍等各类媒体平台。如若本站内容侵犯了原著者的合法权益,可联系我们进行处理。