一、简单了解什么是 CSS
CSS 的工作就是将网页中元素的排版进行精确的控制,实现美化页面的效果。
CSS的基本语法规则如下:
选择器 + {一条 / N条声明}
<p>这是内部样式</p>
<!--内部样式-->
<style>
p {
color: red;
font-size: 30px;
}
</style>

<p style="color: green; font-size: 40px;">
内联样式
</p>

p {
color: blue;
font-size: 50px;
}
<!--这里是外部样式的引入方式-->
<link rel="stylesheet" href="style.css">
<p>
外部样式的测试
</p>

二、CSS 选择器
1.标签选择器
在 style 标签中使用 {},在 { 前面写上标签名称。 此时,就意味着会选中当前页面中所有指定的标签。
<style>
p{
color: blueviolet;
}
</style>
<p>
这是 css 选择器测试
</p>
<div>
<p>
这是div中 css 选择器测试
</p>
<p>
这是div中 css 选择器测试
</p>
这是一个 div
</div>

2.类选择器
<style>
/* 此处定义一个 css 类,名字为 one */
.one{
color: aqua;
}
.two{
color: gray;
}
.three{
color: fuchsia;
}
.four{
font-size: 30px;
}
</style>
<div class ="one">
这是第一个div
</div>
<div class="two">
这是第二个div
</div>
<div class="three">
这是第三个div
</div>

到这里,我们已知类选择器的使用方式,但是,还需要注意:
一个类,可以被一个元素引用,也可以被多个元素引用。
一个元素可以引用一个类,也可以引用多个类。
<div class ="one four">
这是引用了多个类的div
</div>

3.ID 选择器
html 中的每个元素,都是可以设置一个唯一的 id 作为元素的身份标识。
<style>
#oneDiv{
color: darkred;
}
#twoDiv{
color: darkorange;
}
</style>
<div id="oneDiv">
这是一个测试ID选择器的div
</div>
<div>
这是一个测试ID选择器的另一个div
</div id="twoDiv">

总结,类选择器 和 ID选择器 两者的特点。
类选择器, 是可以让多个元素应用用一个类的。
ID 选择器,只能针对唯一元素生效,一个页面中只能有唯一的 ID。
4.后代选择器
<style>
ul li {
color: red;
}
</style>
这里代码的含义是,先在页面中找到所有的 ul,然后在这些 ul 中找到所有的 li。
<ol>
<li>aaa</li>
<li>bbb</li>
<li>ccc</li>
</ol>
<ul>
<li>aaa</li>
<ul>
<li>111</li>
</ul>
<li>bbb</li>
<li>ccc</li>
</ul>

5.子选择器
只是找到匹配的单一的子元素,不找其他孙子元素之类的。
<style>
.test>ul{
color: rgb(223, 92, 5);
}
</style>
这里的代码含义是,只在 .test 的子元素中找到 ul 标签。
<div class="test">
<ul>
<li>aa</li>
<li>bb</li>
<li>cc</li>
</ul>
</div>

6.伪类选择器
前面 的选择器是选中某个元素。
伪类选择器选中的是某个元素的特定状态。
:hover 鼠标悬停时的状态。
:active 鼠标按下时的状态。
<style>
.one1:hover{
color: green;
font-size: 30px;
}
.one1:active{
color: greenyellow;
font-size: 50px;
}
</style>
<div class="one1">
这是一个测试伪类选择器的div
</div>



三、字体属性
1.设置字体家族
<style>
.one{
font-family: 宋体;
}
</style>
<div class="one">
这是一个div
</div>
2.设置字体大小
<style>
.one{
font-size: 40px;
}
</style>
<div class="one">
这是一个div
</div>
3.设置字体粗细
font – weight
实际设置是有两种设置风格。
1.使用单词

<style>
.one{
font-weight: bold;
}
</style>
<div class="one">
这是一个div
</div>

2.使用数字
<style>
.one{
font-weight: 100;
}
</style>
<div class="one">
这是一个div
</div>
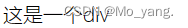
4.文字倾斜
/* 设置倾斜 */
font-style: italic;
/* 取消倾斜 */
font-style: normal;
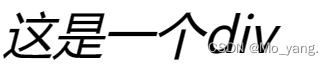
四、文本属性
1.文本对齐
对齐方式有下面三种:
center:居中对齐
left:左对齐
right:右对齐
<style>
.one{
text-align: center;
}
</style>
<div class="one">
这是一个div
</div>

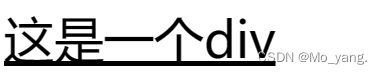
2.文本装饰
装饰的常用取值有下面几个:
underline 下划线
none 什么都没有,可以给 a 标签去掉下划线
overline 上划线
line – through 删除线
<style>
.one{
text-decoration: underline;
}
</style>
<div class="one">
这是一个div
</div>
<style>
a{
text-decoration: none;
}
</style>
<br>
<a href="#">百度</a>
<br>

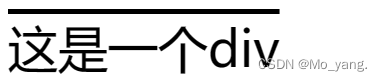
overline 上划线
<style>
.one{
text-decoration: overline;
}
</style>
<div class="one">
这是一个div
</div>
line – through 删除线
<style>
.one{
text-decoration: overline;
}
</style>
<div class="one">
这是一个div
</div>

3.文本缩进
text – indent 每个段落首行缩进两个文字。
这里常用的单位是 em 。这个单位表示的是一个相对的量。是以问字尺寸为基础进行设置的。
<style>
.one{
font-size: 40px;
text-indent: 2em;
line-height: 60px;
}
</style>
<div class="one">
文本缩进
</div>
4.背景设置
设置背景分为两种:
1.设置背景颜色: background – color 设定单一颜色。
2.设置背景图片: background – image:url(图片路径);
<style>
.one{
background-image: url(touxiang.png);
/* 这里设定一个较大的高度便于观察 */
height: 1000px;
}
</style>
<div class="one">
这是背景
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet consectetur adipisicing elit. Labore nemo, necessitatibus beatae voluptatibus rem esse, quam unde voluptatem excepturi impedit pariatur nulla nobis facilis voluptates odit delectus, incidunt qui deleniti.
</div>
background – repeat: no–repeat 这段代码可以解决图片在页面平铺的问题。
<style>
.one{
background-image: url(touxiang.png);
/* 这里设定一个较大的高度便于观察 */
background-repeat: no-repeat;
height: 1000px;
}
</style>
<div class="one">
这是背景
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet consectetur adipisicing elit. Sit vel soluta cupiditate laborum ipsa ex voluptatibus obcaecati, esse quisquam nisi, nulla facilis saepe consectetur voluptates repellendus magnam voluptas nostrum optio.
</div>

此时,我们有会发现一个问题,就是背景图片出现在了左上角。如果我们想将图片转移到中间,呢么,background-position:
center center; 这串代码可以解决问题。
这里就不在演示。
background – size 设置背景图的尺寸。
由此,来实现背景图片的页面全覆盖。
<style>
.one{
background-image: url(touxiang.png);
/* 这里设定一个较大的高度便于观察 */
background-repeat: no-repeat;
height: 1000px;
background-position: center center;
background-size: cover;
}
</style>
<div class="one">
这是背景
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet consectetur adipisicing elit. Sit vel soluta cupiditate laborum ipsa ex voluptatibus obcaecati, esse quisquam nisi, nulla facilis saepe consectetur voluptates repellendus magnam voluptas nostrum optio.
</div>
五、圆角矩形
在我们编辑页面时,可以使用 div 通过限制其高度,宽度。以此来实现一个矩形。
但是,有时需要通过圆角矩形来让页面更加美化。
对此,使用 border–radius: 可以实现需求。
<style>
.one{
/* 通过设置宽高来限制范围 */
width: 200px;
height: 100px;
/* 设置矩形的背景颜色 */
background-color: black;
color: white;
text-align: center;
line-height: 100px;
/* 设定矩形的角的弧度像素数 */
border-radius: 10px;
}
</style>
<div class="one">
<p>
这是一个测试圆角矩形的div
</p>
</div>

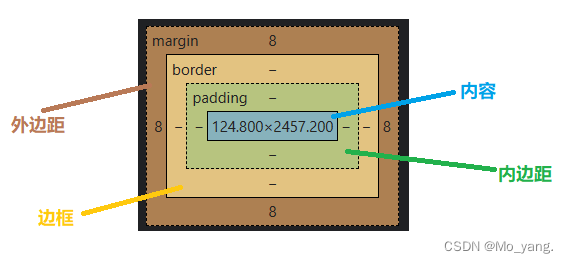
六、CSS 盒子模型
1.介绍边框与外边框
默认情况下,直接使用 border 是直接设置了四个方向。
要实现准确的设置还有下面的操作:
border – left: 设置左边框
border – right:设置右边框
border – top:设置顶部边框
border – bottom:设置下方边框
margin–bottom: 这个关键字是控制外边距,即,控制盒子与盒子之间的距离。
<style>
.one{
width: 300px;
height: 100px;
background-color: cadetblue;
color: blue;
text-align: center;
line-height: 100px;
border: 10px black solid;
/* 控制外边距让两个元素之间有间隙 */
margin-bottom: 5px;
}
/*这是对比元素*/
.contrast{
width: 300px;
height: 100px;
background-color: chartreuse;
color: black;
text-align: center;
/* 控制外边距让两个元素之间有间隙 */
margin-bottom: 10px;
}
</style>
<div class="eight">
这是一个测试边框属性的div
</div>
<div class="contrast">
这是对比的div
</div>

如上图所示,我们发现边框的添加,会导致盒子的撑大。
对此,这里再引入一个属性 box-sizing: border-box;
.one{
width: 300px;
height: 100px;
background-color: cadetblue;
color: blue;
text-align: center;
line-height: 100px;
border: 10px black solid;
box-sizing: border-box;
/* 让两个元素之间有间隙 */
margin-bottom: 5px;
}

2.介绍内边框
这里使用第二种形式解释:
<style>
.one{
width: 300px;
height: 100px;
background-color: aquamarine;
color: blueviolet;
text-align: left;
/* line-height: 100px; */
border: 10px rgb(168,168,0) solid;
box-sizing: border-box;
padding: 10px 20px;
margin-bottom: 15px;
}
</style>
<div class="nine">
这是一个测试内边距属性的div
</div >

七、弹性布局
<style>
div{
width: 100%;
height: 150px;
background-color: red;
}
div>span{
background-color: green;
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
}
</style>
<div>
<span>1</span>
<span>2</span>
<span>3</span>
</div>

要给水平排列的父元素,设置 flex。这样水平方向上的尺寸边距就会变得比较可控。
这里的排列方式的值,常用的有下面几条:
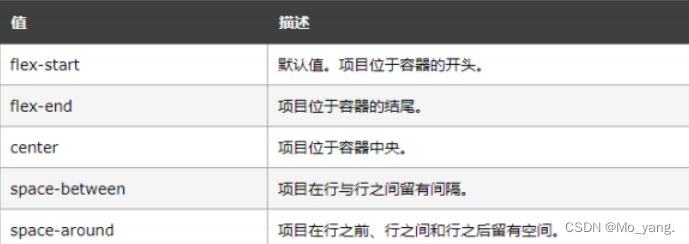
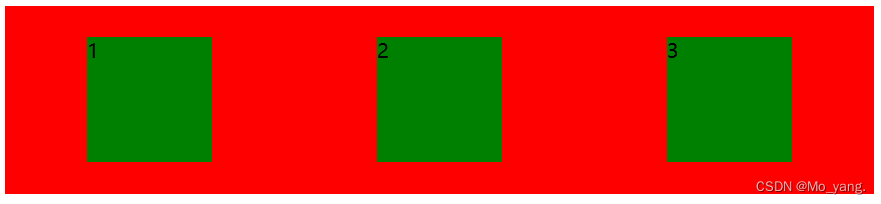
<style>
div{
width: 100%;
height: 150px;
background-color: red;
display: flex;
justify-content: space-around;
align-items: center;
}
div>span{
background-color: green;
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
}
</style>
<div>
<span>1</span>
<span>2</span>
<span>3</span>
</div>
码子不易,您小小的点赞是对我最大的鼓励!!!
原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_62905847/article/details/130179242
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。
如若转载,请注明出处:http://www.7code.cn/show_19579.html
如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系代码007邮箱:suwngjj01@126.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!