Kotlin 是一门现代但已成熟的编程语言,旨在让开发人员更幸福快乐。 它简洁、安全、可与 Java 及其他语言互操作,并提供了多种方式在多个平台间复用代码,以实现高效编程。
https://play.kotlinlang.org/byExample/01_introduction/02_Functions
引出
1.kt里的委派模式Delegation;
2.kt里的特性,productivity boosters生产力助推器;
kt里的委派模式
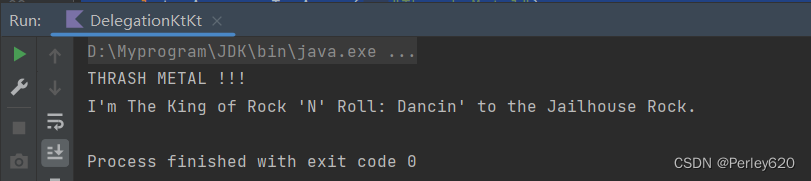
Delegation Pattern 委派模式 by关键字
Kotlin支持在本地级别轻松实现委派模式,而无需任何样板代码。
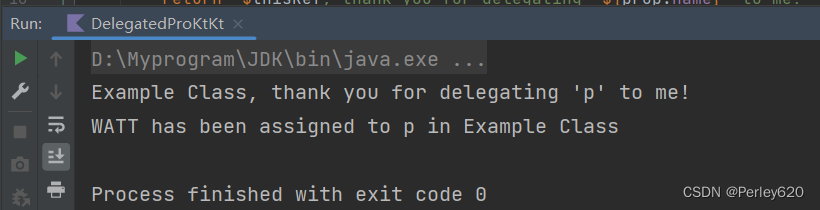
Delegated Properties 属性委派
lazy懒加载
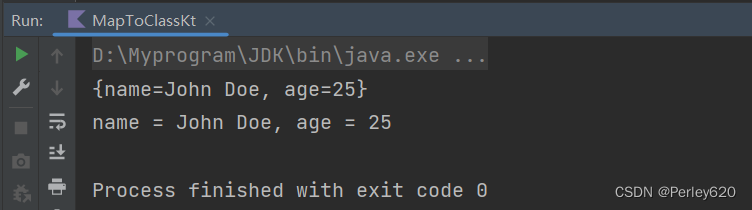
map中存储属性
productivity boosters生产力助推器
Named Arguments命名参数
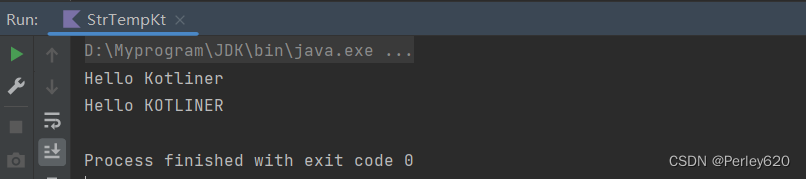
$占位符在String中
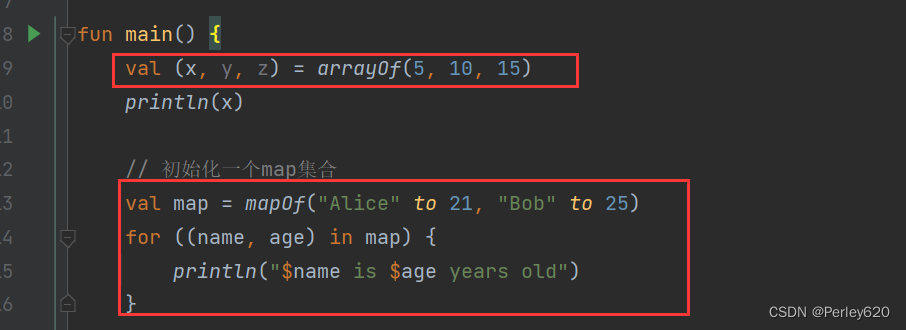
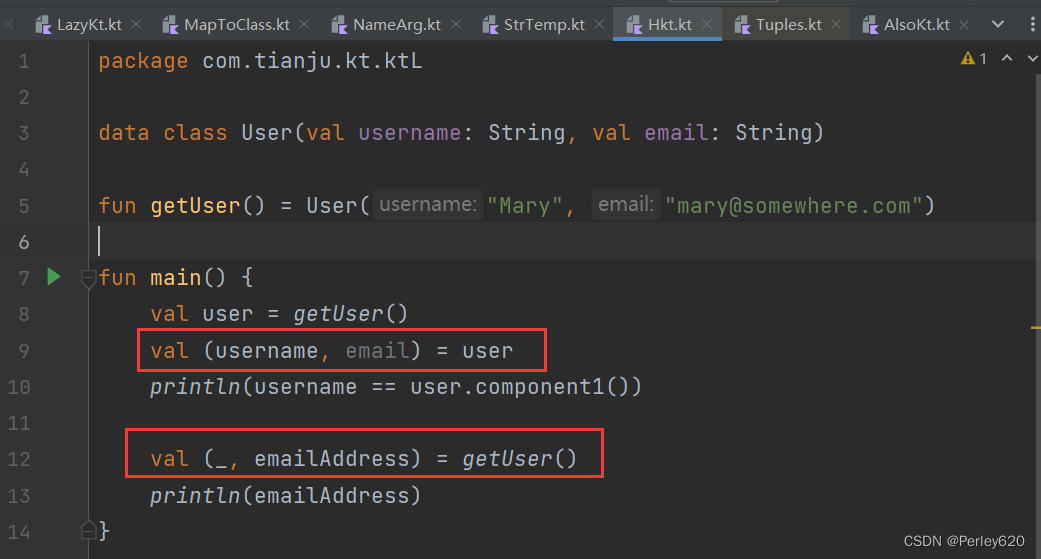
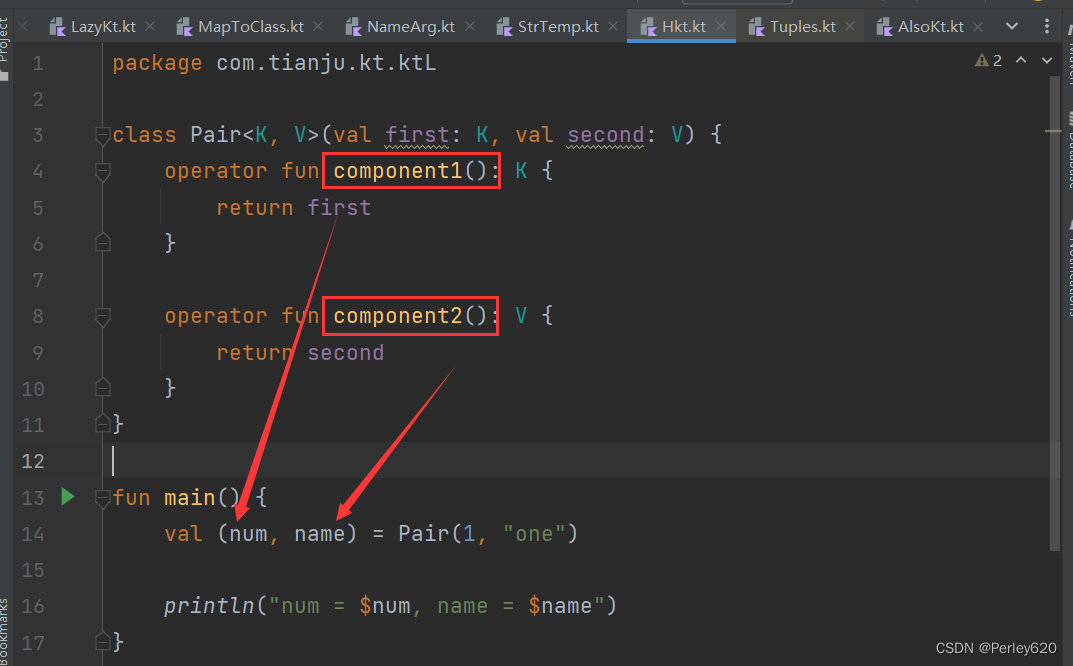
Destructuring Declarations 破坏声明语法
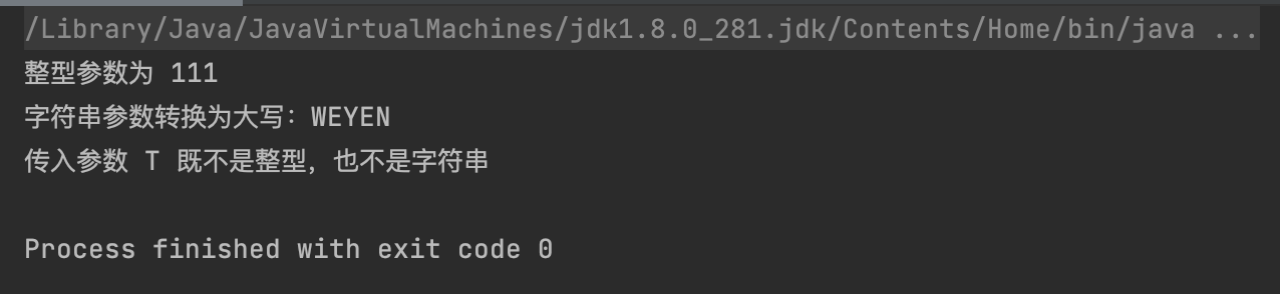
Smart Casts 聪明的编译器
总结
声明:本站所有文章,如无特殊说明或标注,均为本站原创发布。任何个人或组织,在未征得本站同意时,禁止复制、盗用、采集、发布本站内容到任何网站、书籍等各类媒体平台。如若本站内容侵犯了原著者的合法权益,可联系我们进行处理。