《The effect of spatial resolution on decoding accuracy in fMRI multivariate pattern analysis》
一、简介
论文的基本信息
标题: The effect of spatial resolution on decoding accuracy in fMRI multivariate
pattern analysis
作者:
Anna Gardumi a,b,
⁎, Dimo Ivanov a,b
, Lars Hausfeld a,b
, Giancarlo Valente a,b
, Elia Formisano a,b
, Kâmil Uludağ a,b
机构:
a Department of Cognitive Neuroscience, Faculty of Psychology and Neuroscience, Maastricht University, Maastricht, The Netherlands
b Maastricht Brain Imaging Center, Maastricht University, Maastricht, The Netherlands
摘要
fMRI中的多变量模式分析(MVPA)已被用于从分布的皮层激活模式中提取信息,这在传统的单变量分析中可能无法检测到。然而,对于fMRI中MVPA的物理和生理基础以及空间平滑对其性能的影响知之甚少。一些研究已经解决了这些问题,但他们的调查仅限于3岁时的视觉皮层,结果相互矛盾。在这里,我们使用超高场(7 T)功能磁共振成像来研究空间分辨率和平滑对语音内容(元音)解码和说话者身份的影响。为此,我们获得了高分辨率(1.1 mm各向同性)的fMRI数据,并从原始k空间数据中以2.2和3.3 mm的平面内空间分辨率重建了它们。此外,每个分辨率下的数据都用不同的三维高斯核尺寸进行空间平滑(即不平滑或1.1、2.2、3.3、4.4或8.8 mm核)。对于所有空间分辨率和平滑核,我们证明了使用支持向量机(SVM) MVPA在7 T下解码语音内容(元音)和说话人身份的可行性。此外,我们发现高空间频率对元音解码具有重要的信息作用,并且在两种解码任务中,高空间频率和低空间频率的相对贡献是不同的。适度平滑(高达2.2 mm)提高了元音和扬声器解码的精度,可能是由于减少了噪声(例如残余运动伪影或仪器噪声),同时仍然保留了高空间频率的信息。总之,我们的结果表明,即使在相同的刺激和相同的大脑区域,fMRI中MVPA的最佳空间分辨率取决于感兴趣的特定解码任务。
Multivariate pattern analysis (MVPA) in fMRI has been used to extract information from distributed cortical activation patterns, which may go undetected in conventional univariate analysis. However, little is known about the physical and physiological underpinnings of MVPA in fMRI as well as about the effect of spatial smoothing on its performance. Several studies have addressed these issues, but their investigation was limited to the visual cortex at 3 T with conflicting results. Here, we used ultra-high field (7 T) fMRI to investigate the effect of spatial resolution and smoothing on decoding of speech content (vowels) and speaker identity from auditory cortical responses. To that end, we acquired high-resolution (1.1 mm isotropic) fMRI data and additionally reconstructed them at 2.2 and 3.3 mm in-plane spatial resolutions from the original k-space data. Furthermore, the data at each resolution were spatially smoothed with different 3D Gaussian kernel sizes (i.e. no smoothing or 1.1, 2.2, 3.3, 4.4, or 8.8 mm kernels). For all spatial resolutions and smoothing kernels, we demonstrate the feasibility of decoding speech content (vowel) and speaker identity at 7 T using support vector machine (SVM) MVPA. In addition, we found that high spatial frequencies are informative for vowel decoding and that the relative contribution of high and low spatial frequencies is different across the two decoding tasks. Moderate smoothing (up to 2.2 mm) improved the accuracies for both decoding of vowels and speakers, possibly due to reduction of noise (e.g. residual motion artifacts or instrument noise) while still preserving information at high spatial frequency. In summary, our results show that – even with the same stimuli and within the same brain areas – the optimal spatial resolution for MVPA in fMRI depends on the specific decoding task of interest.
二、论文主要内容
语音刺激的解码任务
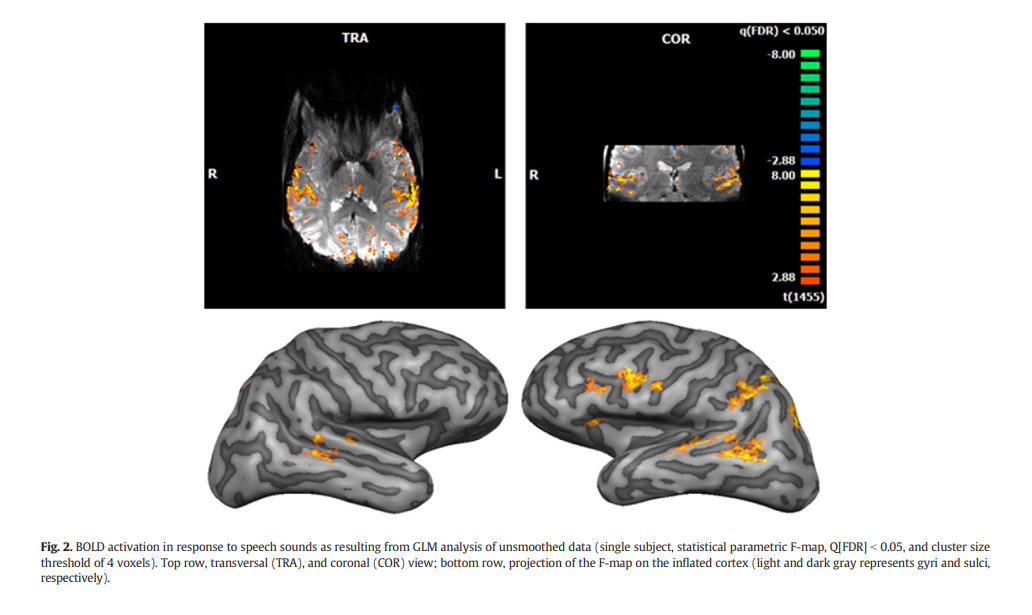
作者使用了一个实验范式和一组刺激,这些刺激在之前的3 T fMRI研究中被使用过(Formisano et al., 2008)。他们呈现了不同说话者的语音刺激(元音),并考虑了从听觉皮层反应模式中解码元音和说话者的单试验。
本文使用了超高场(7T)fMRI技术,从听觉皮层的反应模式中对语音刺激(元音)和说话者进行单次解码。具体来说,本文采用了以下步骤:
多变量模式分析(MVPA)
多变量模式分析中的多变量指的是多个变量之间的关系。它是一种基于机器学习的方法,用于从fMRI数据中提取空间模式信息,并用这些信息来解码不同的认知过程。多变量模式分析可以同时考虑多个脑区的活动模式,从而提高解码的准确性和稳定性。它是一种相对于单变量分析和双变量分析更加复杂和全面的数据分析方法。
多变量模式分析(MVPA)是一种用于从fMRI数据中提取空间分布的激活模式的信息的方法。
这是一种用于从功能磁共振成像(fMRI)数据中提取空间分布的激活模式的信息的方法,它可能在传统的单变量分析中无法检测到。
本文的MVPA主要包括以下几个方面: