nginx版本: 1.18.0
1. 结论
location命中后
如果是root,会把请求url的 ip/域名+port替换为root指定的目录,访问资源
如果是alias,会把请求url的ip/域名+port+匹配到的路径替换为alias指定的目录,访问资源
2. 详解root
2.1 基本用法
以请求http://example.com/foo/bar/hello.html 为例,location配置如下
location /foo {
root /home/hfy/;
}
匹配到/foo,url的域名+port替换为root指定的目录,即url中的examp.com被替换为了/home/hfy,所以实际访问的路径为/home/hfy/foo/bar/hello.html
为了更好理解,再来一个例子,请求的url不变,location配置更改为
location /foo/bar {
root /home/hfy/;
}
匹配到/foo/bar,url的域名+port替换为root指定的目录,即url中的examp.com被替换为了/home/hfy,所以实际访问的路径仍然为/home/hfy/foo/bar/hello.html。root在替换时不会替换匹配到的路径。
2.2 location的最左匹配原则
location会从url最左边的路径匹配,如果一致则命中该location。只有中间匹配到不会命中。
比如请求的url为http://example.com/foo/bar/hello.html ,location为
location /bar {
root /home/hfy/;
}
不会命中该location,因为从url中的/foo开始匹配,与location /bar不一致,不会命中,如果url更改为http://example.com/bar/hello.html 才会命中该规则
2.3 index
在location内部其实默认配置了一条规则index index.html,补全后的规则如下
location /foo {
root /home/hfy/;
index index.html;
}
假设我们访问的url为http://example.com/foo/bar ,匹配到/foo,实际访问的路径为/home/hfy/foo/bar。如果我们的bar是一个文件夹,其中如果包含index.html文件,则会把该文件返回。所以index的作用是,当实际访问的是一个目录时,会返回该目录中index指定的文件,如果该目录中不存在index指定的文件,则会返回403。
在访问http://example.com/foo/bar ,时我们打开浏览器的控制台,查看发送的请求,会发现发生了一个301重定向,http://example.com/foo/bar 被重定向为http://example.com/foo/bar/ ,由此引发了新的问题,为什么会发生重定向,url末尾的/,location 匹配路径末尾的/,以及root 指定目录末尾的/都表示什么意思
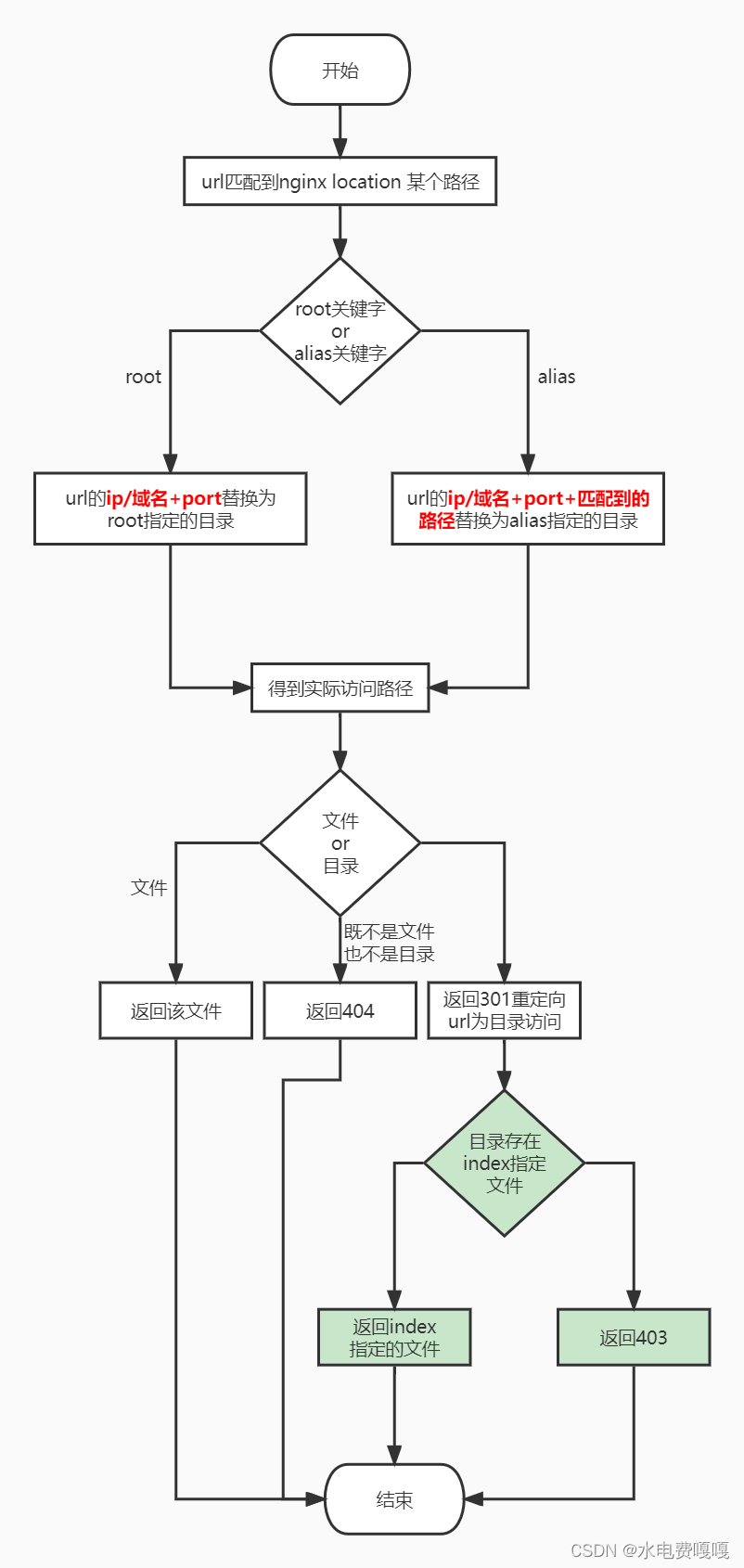
2.4 nginx location解析url工作流程
上述的工作流程,假设了url末尾没有加/,如果末尾包含/,解析流程为上图中绿色部分。例如url为http://example.com/foo/ ,如果foo不存在或者是文件,则直接返回404,如果是foo是目录,则进入到绿色部分流程。如果foo目录中存在index指定的文件,则返回该文件。如果不存在返回403。从这个例子可以看出,url末尾加/表示要访问一个目录,如果实际是个文件,nginx会返回404。
根据上述的流程图,我们看一下2.3中的重定向问题,在访问http://example.com/foo/bar 为什么发生了301重定向。
首先命中如下规则
location /foo {
root /home/hfy/;
index index.html;
}
根据上述的流程图,先替换域名+port,实际访问的路径为/home/hfy/foo/bar,然后nginx发现bar不是文件而是个目录(文件夹),所以重定向为了http://example.com/foo/bar/ 访问bar这个目录中的index.html文件
2.5 末尾’/’
然后再看一下2.3中的另一个问题,末尾的/分别是什么含义
事先声明,仅是我个人粗浅的理解,根据对不同情况的测试,尝试总结 ‘/’的含义
- url末尾/的含义
http://example.com/foo/bar 表示我们把bar当成一个文件,想要访问bar文件
http://example.com/foo/bar/ 表示我们把bar当成一个目录,想要访问bar目录下index指定的文件
location /foo {
root /home/hfy/;
index index.html;
}
/foo 既能匹配http://example.com/foo 也能匹配 http://example.com/foo/
location /foo/ {
root /home/hfy/;
index index.html;
}
/foo/只能匹配http://example.com/foo/
- root 指定目录末尾/的含义
location /foo {
root /home/hfy/;
index index.html;
}
/home/hfy 表示把hfy当成目录或者文件
/home/hfy/ 表示只把hfy当成目录
root后面指定的都应该是目录 (不过alias有种特殊情况,后面会提到)
- url末尾不加/,如果需要带/时依靠nginx自动帮我们重定向加/
- location 路径不加/,这样末尾有无/的url都能匹配到
- root或者alias指定的目录后面加/,明确表示root指定的是目录,增强配置的可读性
3. 详解alias
3.1 基本用法
以请求http://example.com/foo/bar/hello.html为例,location配置如下
location /foo {
alias /home/hfy/;
}
匹配到/foo,url的ip/域名+port+匹配到的路径替换为alias指定的目录,即url中的example.com/foo被替换为了/home/hfy,所以实际访问的路径为/home/hfy/bar/hello.html
同样再来一个例子,请求的url不变,如果location配置更改为
location /foo/bar {
alias /home/hfy/;
}
匹配到/foo/bar,url的ip/域名+port+匹配到的路径替换为alias指定的目录,即url中的example.com/foo/bar被替换为了/home/hfy,所以实际访问的路径为/home/hfy/hello.html。alias在替换时会替换匹配到的路径。
alias其余特性,最左匹配、index、location解析url工作流程、末尾’/’与root一致。
4. 特殊情况
4.1 alias指定文件
- case 1
url http://example.com/foo
/home/hfy/foo是一个文件
location配置如下
location /foo {
alias /home/hfy/foo;
}
实际访问路径/home/hfy/foo,nginx返回foo文件。
这就是上面说的特例,alias也可以指定文件,并且正常返回了要访问的文件。但是实际一般不会用alias指定文件。
- case 2
url http://example.com/foo
/home/hfy/foo是一个文件
location配置如下
location /foo {
alias /home/hfy/foo/;
}
实际访问路径/home/hfy/foo,alias指定 /home/hfy/foo/是一个目录,而foo是一个文件,返回404。
- case 3
url http://example.com/foo/
/home/hfy/foo是一个文件
location配置如下
location /foo/ {
alias /home/hfy/foo;
}
实际访问路径/home/hfy/foo/要访问目录,alias指定/home/hfy/foo是目录或文件,而foo是一个文件,返回了500。
- case 4
url http://example.com/foo/
/home/hfy/foo是一个文件
location配置如下
location /foo/ {
alias /home/hfy/foo/;
}
实际访问路径/home/hfy/foo/,alias指定/home/hfy/foo/是一个目录,而foo是一个文件,返回了404。
- case 5
url http://example.com/
/home/hfy/foo是一个文件
location配置如下
location / {
alias /home/hfy/foo;
}
实际访问路径/home/hfy/foo,但是返回了500。
- case 6
url http://example.com/
/home/hfy/foo是一个文件
location配置如下
location / {
alias /home/hfy/foo/;
}
实际访问路径/home/hfy/foo,返回404。
4.2 root指定文件
- case 1
url http://example.com/foo
/home/hfy/foo是一个文件
location配置如下
location /foo {
root /home/hfy/foo;
}
实际访问路径/home/hfy/foo/foo,不存在,返回404。
- case 2
url http://example.com/foo
/home/hfy/foo是一个文件
location配置如下
location /foo {
root /home/hfy/;
}
实际访问路径/home/hfy/foo,返回foo文件。
- case 3
url http://example.com/foo/
/home/hfy/foo是一个文件
location配置如下
location /foo {
root /home/hfy/;
}
或
location配置如下
location /foo/ {
root /home/hfy/;
}
实际访问路径/home/hfy/foo/要访问目录,/home/hfy/foo是文件,返回404。
- case 4
url http://example.com/
/home/hfy/foo是一个文件
location配置如下
location / {
root /home/hfy/foo;
}
实际访问路径/home/hfy/foo,foo是一个文件,但是却返回404。
- case 5
url http://example.com/
/home/hfy/foo是一个文件
location配置如下
location / {
root /home/hfy/foo/;
}
实际访问路径/home/hfy/foo,foo是一个文件,但是却返回404。
原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_44387339/article/details/128114151
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。
如若转载,请注明出处:http://www.7code.cn/show_27422.html
如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系代码007邮箱:suwngjj01@126.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!