一、base的用法
使用要求:仅允许用于访问基类的构造函数、实例方法或实例属性访问器。从静态方法中使用 base 关键字是错误的。所访问的基类是类声明中指定的基类。 例如,如果指定 class ClassB : ClassA,则从 ClassB 访问 ClassA 的成员,而不考虑 ClassA 的基类。
例子1、访问基类方法
public class animal
{
public virtual void sound()
{
Console.WriteLine("动物的叫声:wowowow");
}
}
public class dog:animal
{
public override void sound()
{
base.sound();
Console.WriteLine("dog:wowowowo");
}
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
dog dog = new dog();
dog.sound();
Console.ReadKey();
} 基类 Person 和派生类 Employee 都有一个名为 Getinfo 的方法。 通过使用 base 关键字,可以从派生类中调用基类的 Getinfo 方法。
例子2、调用基类构造函数
public class animal
{
public animal()
{
Console.WriteLine("发现未知动物");
}
public animal(int a)
{
Console.WriteLine("发现{0}只未知动物",a);
}
public virtual void sound()
{
Console.WriteLine("动物的叫声:wowowow");
}
}
public class dog:animal
{
public dog() : base()
{
Console.WriteLine("未知动物为小狗");
}
public dog(int a) : base(a)
{
Console.WriteLine("小狗的数量为{0}",a);
}
public override void sound()
{
base.sound();
Console.WriteLine("dog:wowowowo");
}
}
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
dog dog = new dog(2);
dog.sound();
Console.ReadKey();
}
}运行结果为:

从例子中我们也可以看的出对于继承类的构造函数,访问顺序是父类构造函数,再访问子类的构造函数。(base 用于用户父类构造函数,this 用于调用自己的构造函数。)
二、this的用法
1、限定类似名称隐藏的成员(用 this 区别类成员和参数)
public class Employee
{
private string alias;
private string name;
public Employee(string name, string alias)
{
// Use this to qualify the members of the class
// instead of the constructor parameters.
this.name = name;
this.alias = alias;
}
}
2、将对象作为参数传递给方法
public class animal
{
public void leg_count(dog dog)
{
Console.WriteLine("狗腿的数量为:"+dog.leg);
}
public void leg_count(duck duck)
{
Console.WriteLine("鸡腿的数量为:" + duck.leg);
}
}
public class dog
{
public int leg = 4;
public animal animal;
public void count()
{
animal = new animal();
animal.leg_count(this);
}
}
public class duck
{
public int leg = 2;
public animal animal;
public void count()
{
animal = new animal();
animal.leg_count(this);
}
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
dog dog = new dog();
duck duck = new duck();
dog.count();
duck.count();
Console.ReadKey();
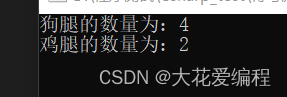
}运行结果为:
3、声明索引器
索引器类似于属性。 很多时候,创建索引器与创建属性所使用的编程语言特性是一样的。 索引器使属性可以被索引:使用一个或多个参数引用的属性。 这些参数为某些值集合提供索引。
使用 this 关键字作为属性名声明索引器,并在方括号内声明参数。
namespace ConsoleApp1
{
public class IndexExample
{
private string[] nameList = new string[10];
public string this[int index]
{
get { return nameList[index]; }
set { nameList[index] = value; }
}
public int this[string name]
{
get
{
for(int i = 0; i < nameList.Length; i++)
{
if(nameList[i] == name) return i;
}
return -1;
}
}
}
public class Program
{
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
IndexExample indexExample = new IndexExample();
indexExample[0] = "Tom";
indexExample[1] = "Lydia";
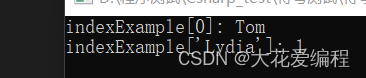
Console.WriteLine("indexExample[0]: " + indexExample[0]);
Console.WriteLine("indexExample['Lydia']: "+ indexExample["Lydia"]);
}
}
}
运行结果为:
4、串联构造函数
namespace ConsoleApp1
{
public class Test
{
public Test()
{
Console.WriteLine("no parameter");
}
public Test(string str) : this()
{
Console.WriteLine("one parameter: " + str);
}
public Test(string str1, string str2): this(str1)
{
Console.WriteLine("two parameters: " + str1 + " ; " + str2);
}
}
public class ProgramTest
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Console.WriteLine("Test t1 = new Test();");
Test t1 = new Test();
Console.WriteLine("Test t2 = new Test('str1');");
Test t2 = new Test("str1");
Console.WriteLine("Test t3 = new Test('str2', 'str3');");
Test t3 = new Test("str2", "str3");
}
}
}
运行结果为:
Test t1 = new Test();
no parameter
Test t2 = new Test('str1');
no parameter
one parameter: str1
Test t3 = new Test('str2', 'str3');
no parameter
one parameter: str2
two parameters: str2 ; str3
5、扩展方法
- 定义包含扩展方法的类必须为静态类
- 将扩展方法实现为静态方法,并且使其可见性至少与所在类的可见性相同。
- 此方法的第一个参数指定方法所操作的类型;此参数前面必须加上 this 修饰符。
- 在调用代码中,添加 using 指令,用于指定包含扩展方法类的 using。
- 和调用类型的实例方法那样调用这些方法。
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System;
namespace CustomExtensions
{
// Extension methods must be defined in a static class.
public static class StringExtension
{
// This is the extension method.
// The first parameter takes the "this" modifier
// and specifies the type for which the method is defined.
public static int WordCount(this string str)
{
return str.Split(new char[] {' ', '.','?'}, StringSplitOptions.RemoveEmptyEntries).Length;
}
}
}
namespace Extension_Methods_Simple
{
// Import the extension method namespace.
using CustomExtensions;
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
string s = "The quick brown fox jumped over the lazy dog.";
// Call the method as if it were an
// instance method on the type. Note that the first
// parameter is not specified by the calling code.
int i = s.WordCount();
System.Console.WriteLine("Word count of s is {0}", i);
}
}
}
第二步、对扩展类定义

代码:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using classextension;
namespace 符号测试
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Test test = new Test();
test.method();
test.methodextension();
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
public class Test
{
public void method()
{
Console.WriteLine("这是原始类内的方法");
}
}
}
扩展类/
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using 符号测试;
namespace classextension
{
public static class TestExtension
{
public static void methodextension(this Test test)
{
Console.WriteLine("这是扩展类的方法");
}
}
}
运行结果为:

C# – base 关键字用法_c#中base的用法-CSDN博客
C# – this 的用法_c# 静态函数 子类this参数_wumingxiaoyao的博客-CSDN博客
原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/qiaodahua/article/details/134604440
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。
如若转载,请注明出处:http://www.7code.cn/show_28612.html
如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系代码007邮箱:suwngjj01@126.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!