本文介绍: 之前我们介绍过了redis的五中基本类型以及在可视化界面进行操作,那么在开发中(在代码中)我们通常使用,jedis进行操作redis,要是springboot 项目,我们通常使用redisTemplte进行操作首先将redis启动。
前言
之前我们介绍过了redis的五中基本类型以及在可视化界面进行操作,那么在开发中(在代码中)我们通常使用,jedis进行操作redis,要是springboot 项目,我们通常使用redisTemplte进行操作
方式一 Jredis
<dependency>
<groupId>redis.clients</groupId>
<artifactId>jedis</artifactId>
<version>3.2.0</version>
</dependency>
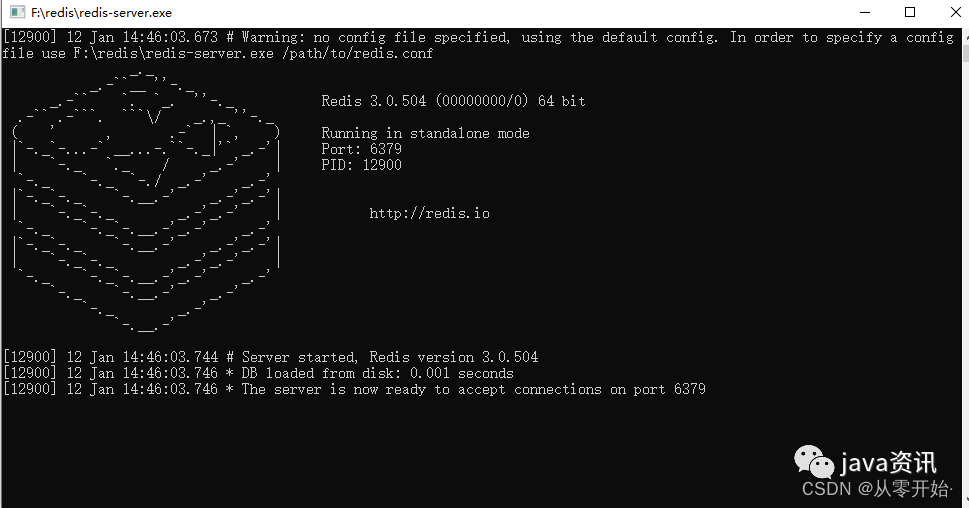
1. 测试连接
@Test
public void test11() {
//测试连接
Jedis jedis = new Jedis("localhost", 6379);
String ping = jedis.ping();
System.out.println(ping);
}
2. 基本操作
String
- 设置值
jedis.set("name","张三");
- 获取值
jedis.get("name")
@Test
public void test11()
{
//连接
Jedis jedis = new Jedis("localhost", 6379);
//设置值
jedis.set("name","张三");
//获取
String name = jedis.get("name");
System.out.println(name);
}

jedis.del("name");
```java
@Test
public void test11() {
//测试连接
Jedis jedis = new Jedis("localhost", 6379);
jedis.del("name");
System.out.println(jedis.get("name"));
}
List
jedis.rpush("redisList","a","b","aa");
jedis.lpush("redisList","la","lb","laa");
List<String> list = jedis.lrange("redisList", 0, -1);
返回value集合,从0开始 到最后一个(-1)【包含最后一个】
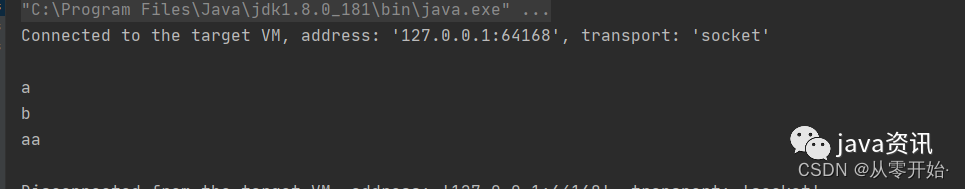
@Test
public void test11() {
//测试连接
Jedis jedis = new Jedis("localhost", 6379);
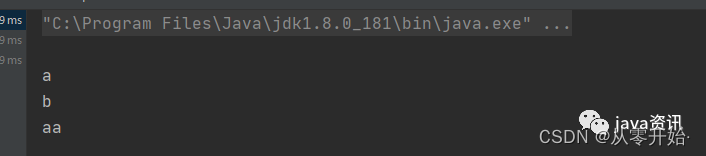
jedis.rpush("redisList","a","b","aa");
List<String> list = jedis.lrange("redisList", 0, -1);
list.forEach(System.out::println);
}
jedis.del("redisList");
//测试连接
Jedis jedis = new Jedis("localhost", 6379);
jedis.del("redisList");
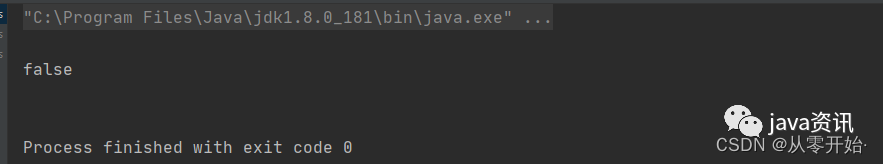
//判断key是否存在
Boolean redisList = jedis.exists("redisList");
System.out.println(redisList);
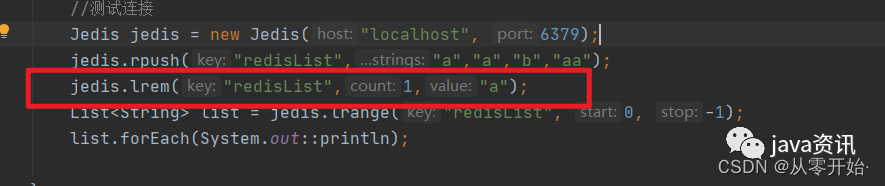
jedis.lrem("redisList",1,"a");
jedis.lrem(“key”,删除几个,要删除的元素);
set
- 添加元素
jedis.sadd("redisSet","a","bb","ccc");
Set<String> redisSet = jedis.smembers("redisSet");
Jedis jedis = new Jedis("localhost", 6379);
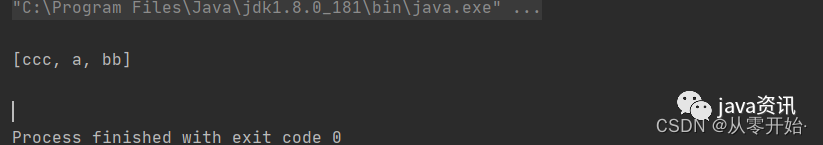
jedis.sadd("redisSet","a","a","bb","ccc");
Set<String> redisSet = jedis.smembers("redisSet");
System.out.println(redisSet);
删除key同理
//测试连接
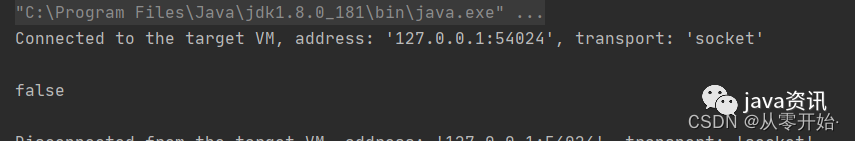
Jedis jedis = new Jedis("localhost", 6379);
jedis.del("redisSet");
System.out.println(jedis.exists("redisSet"));
删除指定元素
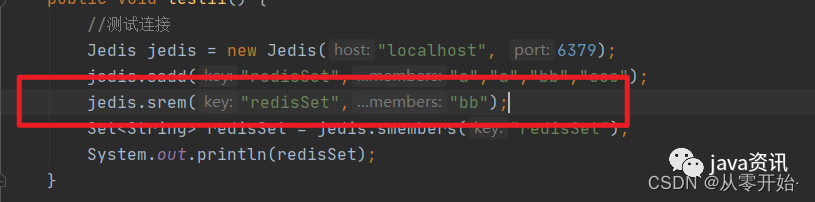
删除元素 “bb”
zset
- 添加元素
jedis.zadd("redisZSet",10,"aa");
jedis.zadd(“key”,score排序序号,“值”);
不太理解,可以回看 redis——基本介绍以及 五种 数据类型 (重要)
- 获取元素
Set<String> zSet = jedis.zrange("redisZSet",0,-1);
Hash
- 设置值,
因为存储的是hsah首先需要new 一个hashMap ,往我们new 出来的hash 存储数据,再将整个数据存储进redis hash 中
Jedis jedis = new Jedis("localhost", 6379);
Map<String,String> hashMap = new HashMap<String,String>();
hashMap.put("name","zhangsan");
hashMap.put("age","18");
jedis.hmset("redisHash", hashMap);
- 获取值
List<String> hmget = jedis.hmget("redisHash", "name", "age");

这边不太明白的,还是先去理解redis——基本介绍以及 五种 数据类型 ,这边不再过多赘述,都是些api的使用
这边介绍一个判断key是否存在
jedis.exists("key")
方式二 redisTemplate
依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redis</artifactId>
</dependency>
注入对象
@Resource
private RedisTemplate redisTemplate;
使用
可以看到有很多种方法,这边直接贴出一个通用工具类,仔细看代码中的注释就知道每个方法对应的数据类型使用了
package com.test1.demo;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.BoundSetOperations;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.HashOperations;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.ValueOperations;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
import java.util.*;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
/**
* spring redis 工具类
**/
@SuppressWarnings(value = { "unchecked", "rawtypes" })
@Component
public class RedisCache
{
@Resource
public RedisTemplate redisTemplate;
/**
* 缓存基本的对象,Integer、String、实体类等
*
* @param key 缓存的键值
* @param value 缓存的值
*/
public <T> void setCacheObject(final String key, final T value)
{
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set(key, value);
}
/**
* 缓存基本的对象,Integer、String、实体类等
*
* @param key 缓存的键值
* @param value 缓存的值
* @param timeout 时间
* @param timeUnit 时间颗粒度
*/
public <T> void setCacheObject(final String key, final T value, final Integer timeout, final TimeUnit timeUnit)
{
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set(key, value, timeout, timeUnit);
}
/**
* 设置有效时间
*
* @param key Redis键
* @param timeout 超时时间
* @return true=设置成功;false=设置失败
*/
public boolean expire(final String key, final long timeout)
{
return expire(key, timeout, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
}
/**
* 设置有效时间
*
* @param key Redis键
* @param timeout 超时时间
* @param unit 时间单位
* @return true=设置成功;false=设置失败
*/
public boolean expire(final String key, final long timeout, final TimeUnit unit)
{
return redisTemplate.expire(key, timeout, unit);
}
/**
* 获取有效时间
*
* @param key Redis键
* @return 有效时间
*/
public long getExpire(final String key)
{
return redisTemplate.getExpire(key);
}
/**
* 判断 key是否存在
*
* @param key 键
* @return true 存在 false不存在
*/
public Boolean hasKey(String key)
{
return redisTemplate.hasKey(key);
}
/**
* 获得缓存的基本对象。
*
* @param key 缓存键值
* @return 缓存键值对应的数据
*/
public <T> T getCacheObject(final String key)
{
ValueOperations<String, T> operation = redisTemplate.opsForValue();
return operation.get(key);
}
/**
* 删除单个对象
*
* @param key
*/
public boolean deleteObject(final String key)
{
return redisTemplate.delete(key);
}
/**
* 删除集合对象
*
* @param collection 多个对象
* @return
*/
public boolean deleteObject(final Collection collection)
{
return redisTemplate.delete(collection) > 0;
}
/**
* 缓存List数据
*
* @param key 缓存的键值
* @param dataList 待缓存的List数据
* @return 缓存的对象
*/
public <T> long setCacheList(final String key, final List<T> dataList)
{
Long count = redisTemplate.opsForList().rightPushAll(key, dataList);
return count == null ? 0 : count;
}
/**
* 获得缓存的list对象
*
* @param key 缓存的键值
* @return 缓存键值对应的数据
*/
public <T> List<T> getCacheList(final String key)
{
return redisTemplate.opsForList().range(key, 0, -1);
}
/**
* 缓存Set
*
* @param key 缓存键值
* @param dataSet 缓存的数据
* @return 缓存数据的对象
*/
public <T> BoundSetOperations<String, T> setCacheSet(final String key, final Set<T> dataSet)
{
BoundSetOperations<String, T> setOperation = redisTemplate.boundSetOps(key);
Iterator<T> it = dataSet.iterator();
while (it.hasNext())
{
setOperation.add(it.next());
}
return setOperation;
}
/**
* 获得缓存的set
*
* @param key
* @return
*/
public <T> Set<T> getCacheSet(final String key)
{
return redisTemplate.opsForSet().members(key);
}
/**
* 缓存Map
*
* @param key
* @param dataMap
*/
public <T> void setCacheMap(final String key, final Map<String, T> dataMap)
{
if (dataMap != null) {
redisTemplate.opsForHash().putAll(key, dataMap);
}
}
/**
* 获得缓存的Map
*
* @param key
* @return
*/
public <T> Map<String, T> getCacheMap(final String key)
{
return redisTemplate.opsForHash().entries(key);
}
/**
* 往Hash中存入数据
*
* @param key Redis键
* @param hKey Hash键
* @param value 值
*/
public <T> void setCacheMapValue(final String key, final String hKey, final T value)
{
redisTemplate.opsForHash().put(key, hKey, value);
}
/**
* 获取Hash中的数据
*
* @param key Redis键
* @param hKey Hash键
* @return Hash中的对象
*/
public <T> T getCacheMapValue(final String key, final String hKey)
{
HashOperations<String, String, T> opsForHash = redisTemplate.opsForHash();
return opsForHash.get(key, hKey);
}
/**
* 获取多个Hash中的数据
*
* @param key Redis键
* @param hKeys Hash键集合
* @return Hash对象集合
*/
public <T> List<T> getMultiCacheMapValue(final String key, final Collection<Object> hKeys)
{
return redisTemplate.opsForHash().multiGet(key, hKeys);
}
/**
* 删除Hash中的某条数据
*
* @param key Redis键
* @param hKey Hash键
* @return 是否成功
*/
public boolean deleteCacheMapValue(final String key, final String hKey)
{
return redisTemplate.opsForHash().delete(key, hKey) > 0;
}
/**
* 获得缓存的基本对象列表
*
* @param pattern 字符串前缀
* @return 对象列表
*/
public Collection<String> keys(final String pattern)
{
return redisTemplate.keys(pattern);
}
/**
* 生成唯一编号,没有过期时间
*/
public String getCode() {
Long serialNum = redisTemplate.opsForValue().increment("JG", 1L);
return "JG" +String.format("%06d",serialNum);
}
}
原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_42482058/article/details/131384348
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。
如若转载,请注明出处:http://www.7code.cn/show_33268.html
如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系代码007邮箱:suwngjj01@126.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
声明:本站所有文章,如无特殊说明或标注,均为本站原创发布。任何个人或组织,在未征得本站同意时,禁止复制、盗用、采集、发布本站内容到任何网站、书籍等各类媒体平台。如若本站内容侵犯了原著者的合法权益,可联系我们进行处理。