数据库-Oracle
链接: oracle常见面试题_ocrale面试题-CSDN博客
链接:Oracle 面试题汇总_oracle面试-CSDN博客
〇、Oracle用户管理
1、创建用户
概述:在oracle中要创建一个新的用户使用create user语句,一般是具有dba(数据库管理员)的权限才能使用。
create user 用户名 identified by 密码;
注意:oracle有个毛病,密码必须以字母开头,如果以数字开头,它不会创建用户
eg、create user xiaoming identified by oracle;
2、给用户修改密码
概述:如果给自己修改密码可以直接使用
SQL> password 用户名或passw
如果给别人修改密码则需要具有dba的权限,或是拥有alter user的系统权限
SQL> alter user 用户名 identified by 新密码
3、删除用户
概述:一般以dba的身份去删除某个用户,如果用其它用户去删除用户则需要具有drop user的权限。
比如drop user 用户名 【cascade】
注意:在删除用户时,如果要删除的用户,已经创建了表,那么就需要在删除的时候带一个参数cascade,即把该用户及表一同删除;
4、权限
权限分为系统权限和对象权限。
何为系统权限?
用户对数据库的相关权限,connect、resource、dba等系统权限,如建库、建表、建索引、建存储过程、登陆数据库、修改密码等。
何为对象权限?
用户对其他用户的数据对象操作的权限,insert、delete、update、select、all等对象权限,数据对象有很多,比如表,索引,视图,触发器、存储过程、包等。
执行SELECT * FROM Dba_Object_Size;语句可得到oracle数据库对象。
6、用户管理的综合案例
概述:创建的新用户是没有任何权限的,甚至连登陆的数据库的权限都没有,需要为其指定相应的权限。给一个用户赋权限使用命令grant,回收权限使用命令revoke。
为了讲清楚用户的管理,这里我给大家举一个案例。
SQL> conn xiaoming/oracle
ERROR:
ORA-01045: user XIAOMING lacks CREATE SESSION privilege; logon denied
警告: 您不再连接到 ORACLE。
SQL> show user
USER 为 “”
SQL> conn system/oracle
已连接。
SQL> grant connect to xiaoming;
授权成功。
SQL> conn xiaoming/oracle
已连接。
注意:grant connect to xiaoming;在这里,准确的讲,connect不是权限,而是角色。
现在说下对象权限,现在要做这么件事情:
* 希望xiaoming用户可以去查询emp表
* 希望xiaoming用户可以去查询scott的emp表
grant select on scott.emp to xiaoming
* 希望xiaoming用户可以去修改scott的emp表
grant update on scott.emp to xiaoming
* 希望xiaoming 用户可以去修改/删除,查询,添加scott的emp表
grant all on scott.emp to xiaoming
* scott希望收回xiaoming对emp表的查询权限
revoke select on scott.emp from xiaoming
一、Oracle数据库操作
2、删除数据库
-
完全备份
exp demo/demo@orcl buffer=1024 file=d:back.dmp full=y
demo:用户名、密码
full: 是否导出全部文件
-
导出指定的表
exp demo/demo@orcl file=d:backup2.dmp tables=(teachers,students)
-
按过滤条件,导出
exp demo/demo@orcl file=d:back.dmp tables=(table1) query=” where filed1 like ‘fg%’”
4、数据库还原
-
完整还原
imp demo/demo@orcl file=d:back.dmp full=y ignore=y log=D:implog.txt
指定log很重要,便于分析错误进行补救。
-
导入指定表
imp demo/demo@orcl file=d:backup2.dmp tables=(teachers,students)
二、Oracle表操作
1、创建表
- 学生表
create table student (
Id number(4) primary key,
xh number(4) , --学号
xm varchar2(20), --姓名
sex char(2), --性别
birthday date, --出生日期
sal number(7,2) --奖学金
);
- 班级表
create table class(
classid number(2),
cname varchar2(40)
);
–修改表
–添加一个字段
alter table student add (classid number(2));
–修改一个字段的长度
alter table student modify (xm varchar2(30));
–修改字段的类型或是名字(不能有数据) 不建议做
alter table student modify (xm char(30));
–删除一个字段 不建议做(删了之后,顺序就变了。加就没问题,应该是加在后面)
alter table student drop column sal;
–修改表的名字 很少有这种需求
rename student to stu;
–创建自增列
create sequence student
increment by 1 – 每次加几个
NOMAXvalue – 不设置最大值 (maxvalue 99999999 等同于maxvalue 99999999 )
cache 10; —设置缓存cache个序列,如果系统down掉了或者其它情况将会导致序列不连续,
一旦定义了S_Test,你就可以用currval,nextval
currval=返回 sequence的当前值
nextval=增加sequence的值,然后返回 sequence 值
比如:
S_Test.CURRVAL
S_Test.NEXTVAL
insert into student(id,xh, xm, sex) values (student.Nextval,‘a003’, ‘john’, ‘女’);
create table tabname(col1 type1 [not null] [primary key],col2 type2 [not null],…)
根据已有的表创建新表:
A:select * into table_new from table_old (使用旧表创建新表)
B:create table tab_new as select col1,col2… from tab_old definition only<仅适用于Oracle>
2、删除表
drop table tabname
3、重命名表
说明:alter table 表名 rename to 新表名
eg:alter table tablename rename to newtablename
4、增加字段
说明:alter table 表名 add (字段名 字段类型 默认值 是否为空);
例:alter table tablename add (ID int);
eg:alter table tablename add (ID varchar2(30) default ‘空’ not null);
5、修改字段
说明:alter table 表名 modify (字段名 字段类型 默认值 是否为空);
eg:alter table tablename modify (ID number(4));
6、重名字段
说明:alter table 表名 rename column 列名 to 新列名 (其中:column是关键字)
eg:alter table tablename rename column ID to newID;
7、删除字段
说明:alter table 表名 drop column 字段名;
eg:alter table tablename drop column ID;
8、添加主键
alter table tabname add primary key(col)
9、删除主键
alter table tabname drop primary key(col)
10、创建索引
create [unique] index idxname on tabname(col….)
11、删除索引
drop index idxname
12、创建视图
create view viewname as select statement
13、删除视图
三、Oracle操作数据
1、数据查询
select <列名> from <表名> [where <查询条件表达试>] [order by <排序的列名>[asc或desc]]
2、插入数据
insert into test values(1,‘zhangsan’,20);
insert into 表名(列) values(对应的值);
insert into test(id,name) values(2,‘lisi’);
3、更新数据
update 表 set 列=新的值 [where 条件] –>更新满足条件的记录
update test set name=‘zhangsan2’ where name=‘zhangsan’
4、删除数据–delete与truncate 区别
-
delete from 表名 where 条件 –>删除满足条件的记录
delete from test where id = 1;
rollback; –>回滚数据
-
truncate table 表名
-
drop table 表名
删除所有数据,包括表结构一并删除,不会记录日志,数据不能恢复–>删除很快
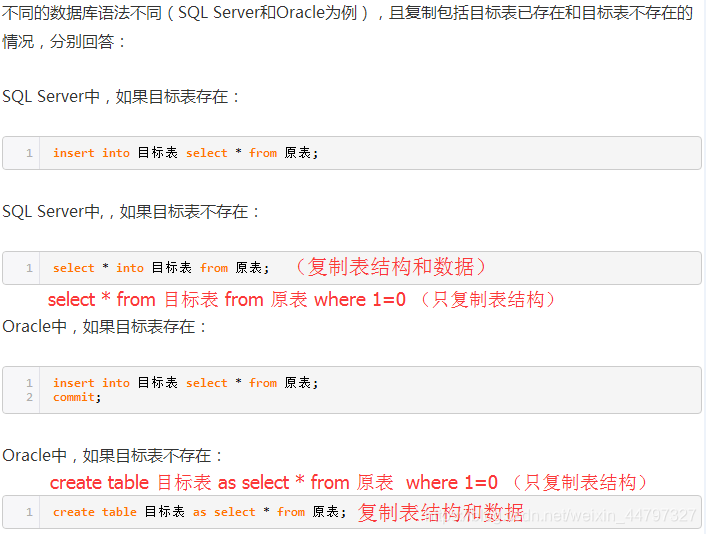
5、数据复制
-
表数据复制
-
复制表结构
create table table1 select * from table2 where 1>1;
-
复制表结构和数据
create table table1 select * from table2;
-
复制指定字段
create table table1 as select id, name from table2 where 1>1;
6、数据库复制命令
一.入门部分
1. 创建表空间
create tablespace schooltbs datafile ‘D:oracledatasourceschooltbs.dbf’ size 10M autoextend on;
2. 删除表空间
drop tablespace schooltbs[including contents and datafiles];
3. 查询表空间基本信息
select *||tablespace_name from DBA_TABLESPACES;
4. 创建用户
create user lihua
identified by lihua
default tablespace schooltbs
temporary tablespace temp;
5. 更改用户
alter user lihua
identified by 123
default tablespace users;
6. 锁定用户
alter user lihua account lock|unlock;
7. 删除用户
drop user lihua cascade;--删除用户模式
8. oracle数据库中的角色
connect,dba,select_catalog_role,delete_catalog_role,execute_catalog_role,exp_full_database,imp_full_database,resource
9. 授予连接服务器的角色
grant connect to lihua;
10. 授予使用表空间的角色
grant resource to lihua with grant option;--该用户也有授权的权限
11. 授予操作表的权限
grant select,insert on user_tbl to scott;--当前用户
grant delete,update on lihua.user_tbl to scott;--系统管理员
二.SQL查询和SQL函数
1.SQl支持的命令:
数据定义语言(DDL):create,alter,drop
数据操纵语言(DML):insert,delete,update,select
数据控制语言(DCL):grant,revoke
事务控制语言(TCL):commit,savepoint,rollback
2.Oracle数据类型
字符,数值,日期,RAW,LOB
字符型
char:1-2000字节的定长字符
varchar2:1-4000字节的变长字符
long:2GB的变长字符
注意:一个表中最多可有一列为long型
Long列不能定义唯一约束或主键约束
long列上不能创建索引
过程或存储过程不能接受long类型的参数。
数值型
number:最高精度38位
日期时间型
date:精确到ss
timestamp:秒值精确到小数点后6位
函数
sysdate,systimestamp返回系统当前日期,时间和时区。
更改时间的显示
alter session set nls_date_language=’american’;
alter session set nls_date_format=’yyyy-mm-dd’;
Oracle中的伪列
像一个表列,但没有存储在表中
伪列可以查询,但不能插入、更新和修改它们的值
常用的伪列:rowid和rownum
rowid:表中行的存储地址,可唯一标示数据库中的某一行,可以使用该列快速定位表中的行。
rownum:查询返回结果集中的行的序号,可以使用它来限制查询返回的行数。
3.数据定义语言
用于操作表的命令
create table
alter table
truncate table
drop table
修改表的命令
alter table stu_table rename to stu_tbl;--修改表名
alter table stu_tbl rename column stu_sex to sex;--修改列名
alter table stu_tbl add (stu_age number);--添加新列
alter table stu_tbl drop(sex);--删除列
alter table stu_tbl modify(stu_sex varchar2(2));--更改列的数据类型
alter table stu_tbl add constraint pk_stu_tbl primary key(id);--添加约束
4.数据操纵语言
select,update,delete,insert
利用现有的表创建表
create table stu_tbl_log as select id,stu_name,stu_age from stu_tbl;--
选择无重复的行
select distinct stu_name from stu_tbl;--
插入来自其他表中的记录
insert into stu_tbl_log select id,stu_name,stu_age from stu_tbl;
5.数据控制语言
grant,revoke
6.事务控制语言
commit,savepoint,rollback
7.SQL操作符
算术操作符:L+-*/
比较操作符:L=,!=,<>,>,<,>=,<=,between-and,in,like,is null等
逻辑操作符:Land,or,not
集合操作符:Lunion,union all,intersect,minus
连接操作符:L||
示例中stu_tbl_log中的数据如下:
ID STU_NAME STU_AGE
---------- -------------------- ----------
1000 李华 20
1001 accp 20
1003 nimda 3
stu_tbl中的数据如下:
ID STU_NAME ST STU_AGE
---------- -------------------- -- ----------
1000 李华 男 20
1001 accp 男 20
1002 admin 男 30
示例:
select (3+2)/2 from dual;--算术操作符,结果:2.5
select * from stu_tbl where stu_age>=20;--比较操作符
select * from stu_tbl where stu_name like '%a%';--比较操作符:like
select * from stu_tbl where stu_name like 'a___';--比较操作符:like
select * from stu_tbl where stu_age in(20,30);--比较操作符:in
select * from stu_tbl where stu_age between 20 and 30;--比较操作符:between
select stu_name from stu_tbl union all
select stu_name from stu_tbl_log;--集合操作符:union all,测试结果具体如下:
STU_NAME
-----------
李华
accp
admin
李华
accp
nimda
已选择6行。
select stu_name from stu_tbl union
select stu_name from stu_tbl_log;--集合操作符:union,测试结果具体如下:
STU_NAME
---------
accp
admin
nimda
李华
select stu_name from stu_tbl intersect
select stu_name from stu_tbl_log;--集合操作符:intersect,测试结具体如下:
STU_NAME
----------
accp
李华
select stu_name from stu_tbl minus
select stu_name from stu_tbl_log;--集合操作符:minus,测试结果如下:
STU_NAME
----------
Admin
从中可以看出:
minus是获取第一张表独有的数据
intersect是获取两张表中都有的数据
union是整合两张表的数据,都有的只显示一次
union all是纯粹的两张表数据整合
select id,stu_name||' '||stu_sex as name_sex,stu_age
from stu_tbl;--连接操作符||,测试结果具体如下:
ID NAME_SEX STU_AGE
---------- ----------------------- ----------
1000 李华 男 20
1001 accp 男 20
1002 admin 男 30
8.SQL函数
单行函数:从表中查询的每一行只返回一个值,可出现在select子句,where子句中
日期函数
数字函数
字符函数
转换函数:ToChar(),ToDate(),ToNumber()
其他函数:
Nvl(exp1,exp2):表达式一为null时,返回表达式二
Nvl2(exp1,exp2,exp3):表达式一为null时返回表达式三,否则返回表达式二
Nullif(exp1,exp2):两表达式相等时,返回null,否则返回表达式一
分组函数:基于一组行来返回
Avg,Min,Max,Sum,Count
Group by,having
分析函数
Row_number,rank,dense_rank
示例:
select u.user_name,sum(oi.order_num*oi.order_price) as total,row_number() over (order by sum(oi.order_num*oi.order_price) desc) as sort from order_item_tbl
oi,user_tbl u,order_tbl o where oi.order_id = o.id and o.user_id = u.id group by u.user_name;
三.锁和数据库对象
1.锁:数据库用来控制共享资源并发访问的机制。
锁的类型:行级锁,表级锁
行级锁:对正在被修改的行进行锁定。行级锁也被称之为排他锁。
在使用下列语句时,Oracle会自动应用行级锁:
insert,update,delete,select…… for update
select……for update允许用户一次锁定多条记录进行更新。
使用commit or rollback释放锁。
表级锁:
lock table user_tbl in mode mode;
表级锁类型:
行共享 row share
行排他 row exclusive
共享 share
共享行排他 share row exclusive
排他 exclusive
死锁:两个或两个以上的事务相互等待对方释放资源,从而形成死锁
2.数据库对象
oracle数据库对象又称模式对象
数据库对象是逻辑结构的集合,最基本的数据库对象是表
数据库对象:
表,序列,视图,索引
序列
用于生成唯一,连续序号的对象。
创建语法:
create sequence user_id_seq
start with 1000
increment by 1
maxvalue 2000
minvalue 1000
nocycle
cache 1000;--指定内存中预先分配的序号
访问序列:
select user_id_seq.currval from dual;
select user_id-seq.nextval from dual;
更改删除序列:
alter sequence user_id_seq maxvalue 10000;--不能修改其start with 值
drop sequence user_id_seq;
在Hibernate中访问序列:
<generator class="sequence">
<param name="sequence">
user_id_seq
</param>
</generator>
视图
以经过定制的方式显示来自一个或多个表的数据
创建视图:
create or replace view
user_tbl_view (vid,vname,vage)
as select id,user_name,age from user_tbl
[with check option]|[with read only];
创建带有错误的视图:
create force view user_tbl_force_view as
select * from user_table;--此时user_table可以不存在
创建外联接视图:
create view user_stu_view as
select u.id,u.user_name,u.password,s.ddress
from user_tbl u,stu_tbl s
where u.s_id(+)=s.id;--哪一方带有(+),哪一方就是次要的
删除视图:
drop user_stu_view;
索引
用于提高SQL语句执行的性能
索引类型:
唯一索引,位图索引,组合索引,基于函数的索引,反向键索引
创建标准索引:
create index user_id_index on user_tbl(id) tablespace schooltbs;
重建索引:
alter index user_id_index rebuild;
删除索引:
drop index user_id_index;
创建唯一索引:
create unique index user_id_index on user_tbl(id);
创建组合索引:
create index name_pass_index on user_tbl(user_name,password);
创建反向键索引:
create index user_id_index on user_tbl(id) reverse;
原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_44797327/article/details/134563310
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。
如若转载,请注明出处:http://www.7code.cn/show_3652.html
如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系代码007邮箱:suwngjj01@126.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!