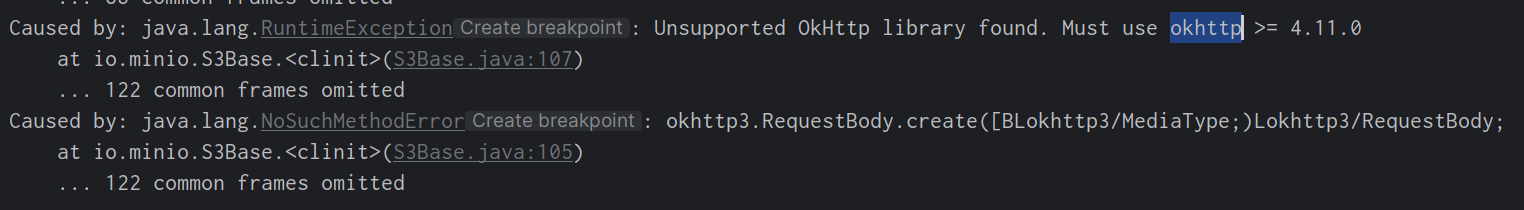
1.RealCall.enqueue
final class RealCall implements Call {
@Override
public void enqueue(Callback responseCallback) {
synchronized (this) {
if (executed) throw new IllegalStateException("Already Executed");
executed = true;
}
transmitter.callStart();
//创建AsyncCall,调用Dispatcher的enqueue
client.dispatcher().enqueue(new AsyncCall(responseCallback));
}
}2.Dispatcher.enqueue
public final class Dispatcher {
private final Deque<AsyncCall> readyAsyncCalls = new ArrayDeque<>();
void enqueue(AsyncCall call) {
synchronized (this) {
readyAsyncCalls.add(call); //将call添加到readyAsyncCalls
}
promoteAndExecute(); //调用执行的方法
}
}
3.Dispatcher.promoteAndExecute
public final class Dispatcher {
private boolean promoteAndExecute() {
assert (!Thread.holdsLock(this));
List<AsyncCall> executableCalls = new ArrayList<>();
boolean isRunning;
synchronized (this) {
//遍历readyAsyncCalls
for (Iterator<AsyncCall> i = readyAsyncCalls.iterator(); i.hasNext(); ) {
AsyncCall asyncCall = i.next();
//如果正在执行的call超过了最大数目64,则不执行
if (runningAsyncCalls.size() >= maxRequests) break; // Max capacity.
// Host max capacity.
//超过了一个主机的最大请求数5
if (asyncCall.callsPerHost().get() >= maxRequestsPerHost) continue;
//从readyAsyncCalls remove
i.remove();
asyncCall.callsPerHost().incrementAndGet();
//添加到executableCalls
executableCalls.add(asyncCall);
//添加到runningAsyncCalls
runningAsyncCalls.add(asyncCall);
}
isRunning = runningCallsCount() > 0;
}
for (int i = 0, size = executableCalls.size(); i < size; i++) {
AsyncCall asyncCall = executableCalls.get(i);
//执行
asyncCall.executeOn(executorService());
}
return isRunning;
}
}4.AsyncCall执行
AsyncCall其实是一个Runnable,所以最终执行的是AsyncCall的execute
整个execute()都是在线程里执行的,所以onResponse和onFailure也是在线程触发的
final class RealCall implements Call {
@Override
protected void execute() {
try {
Response response = getResponseWithInterceptorChain();
//触发callback,返回response
responseCallback.onResponse(RealCall.this, response);
} catch (Throwable t) {
responseCallback.onFailure(RealCall.this, canceledException);
} finally {
client.dispatcher().finished(this);//从runningAsyncCalls移除
}
}
}5.总结
将AsyncCall添加到executableCalls
将AsyncCall添加到runningAsyncCalls
遍历executableCalls,执行里面的每一个AsyncCall
原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/lostfish123/article/details/134686298
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。
如若转载,请注明出处:http://www.7code.cn/show_40492.html
如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系代码007邮箱:suwngjj01@126.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
声明:本站所有文章,如无特殊说明或标注,均为本站原创发布。任何个人或组织,在未征得本站同意时,禁止复制、盗用、采集、发布本站内容到任何网站、书籍等各类媒体平台。如若本站内容侵犯了原著者的合法权益,可联系我们进行处理。