Vue.js简介
| 什么是 Vue | 什么是 Vue? 考虑这个需求: 我们要把一个 json对象的数据,显示到一个元素上去。 如果不使用 Vue, 那么就会用到 JS 或者 JQuery,通过操作 HTML DOM 的方式,把数据显示上去。 如果使用Vue, 那么仅仅需要提供数据,以及数据要绑定到的元素的id,就行了,不需要显式地操作HTML DOM。 以下就用代码来表示这两种方式,通过比较,就知道Vue 是做什么的了。 |
|
JS 的 方式 2. 然后在js代码中准备一个json数据。
|
<div id=”div1″> </div> <script> //准备数据 var gareen = {“name“:”盖伦”,”hp“:616}; //获取 html dom var div1 = document.getElementById(“div1″); //显示数据 div1.innerHTML= gareen.name; </script> |
| js 方式有问题吗? 没问题。 不过敏锐的同学会意识到, html dom其实只是手段,我们真正想要的,就是数据,显示在元素上。 而vue.js 就是用来解决这个问题的。 下面请看vue.js 的做法。 |
|
|
VUE 的方式
<script src=”https://how2j.cn/study/vue.min.js“></script> |
1. 首先导入 vue.js 要用到的库: vue.min.js. 这里这个库我是放在网站上的,自己练习的同学,可以从右上角下载一个,方便自己本地用。
<script src=”http://how2j.cn/study/vue.min.js”></script> 4. 创建一个Vue对象。 这个Vue对象就把数据 gareen和 视图 div1 关联起来了 new Vue({ el: ‘#div1’, data: { } }) |
| vue 的更多用法 | 当然 vue.js 的内容不仅仅是这一点,接下来会逐渐把 vue.js 的做法都展开,其功能还是很强大的。 |
| 版本 | 本 Vue.js 系列教程用的版本是 :Vue.js v2.5.16 |
|
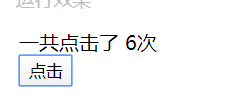
1. 在 js里为 Vue 对象的数据设置为 clickNumber } 2. 新建一个方法: count, 其作用是 clickNumber 自增1 methods:{ } } |
<script src=”https://how2j.cn/study/vue.min.js”></script> |
|
v-on 缩写为@ <button v-on:click=”count”>点击</button> 缩写之后: |
<script src=”https://how2j.cn/study/vue.min.js”></script> |
|
.stop .self .once |
|
|
冒泡这件事 事件修饰符 里面有几个都是关于冒泡的,那么什么是冒泡呢? 简单的说就是 父元素里有 子元素, 如果点击了 子元素, 那么click 事件不仅会发生在子元素上,也会发生在其父元素上,依次不停地向父元素冒泡,直到document元素。
|
<script src=”https://how2j.cn/study/vue.min.js”></script> <style type=”text/css“> * { margin: 0 auto; text–align:center; line–height: 40px; } div { width: 100px; cursor:pointer; } #grandFather { background: green; } #father { background: blue; } #me { background: red; }#son { background: gray; } </style> <div id=”content“> <div id=”grandFather” v-on:click=”doc“> grandFather <div id=”father” v-on:click=”doc“> father <div id=”me” v-on:click=”doc“> me <div id=”son” v-on:click=”doc“> son </div> </div> </div> </div> </div> <script> var content = new Vue({ el: “#content“, data: { id: ” }, methods: { doc: function () { this.id= event.currentTarget.id; alert(this.id) } } }) </script> |
|
在me上的click后面加一个 .stop, 那么冒泡到了这里就结束了,就不会冒到father上面去了。
|
<script src=”https://how2j.cn/study/vue.min.js”></script> <style type=”text/css“> * { margin: 0 auto; text–align:center; line–height: 40px; } div { width: 100px; cursor:pointer; } #grandFather { background: deeppink; } #father { background: pink; } #me { background: hotpink; }#son { background: #ff4225; } </style> <div id=”content“> <div id=”grandFather” v-on:click=”doc“> grandFather <div id=”father” v-on:click=”doc“> father <div id=”me” v-on:click.stop=”doc”> me <div id=”son” v-on:click=”doc”> son </div> </div> </div> </div> </div> <script> var content = new Vue({ el: “#content“, data: { id: ” }, methods: { doc: function () { this.id= event.currentTarget.id; alert(this.id) } } }) </script> |
|
在father 上增加一个.capture
|
<script src=”https://how2j.cn/study/vue.min.js”></script> <style type=”text/css“> * { margin: 0 auto; text–align:center; line–height: 40px; } div { width: 100px; cursor:pointer; } #grandFather { background: deeppink; } #father { background: pink; } #me { background: hotpink; }#son { background: #ff4225; } </style> <div id=”content“> <div id=”grandFather” v-on:click=”doc”> grandFather <div id=”father” v-on:click.capture=”doc”> father <div id=”me” v-on:click=”doc”> me <div id=”son” v-on:click=”doc”> son </div> </div> </div> </div> </div> <script> var content = new Vue({ el: “#content”, data: { id: ” }, methods: { doc: function () { this.id= event.currentTarget.id; alert(this.id) } } }) </script> |
|
修改father,增加 .self
|
<script src=”https://how2j.cn/study/vue.min.js”></script> <style type=”text/css“> * { margin: 0 auto; text–align:center; line-height: 40px; } div { width: 100px; cursor:pointer; } #grandFather { background: deeppink; } #father { background: pink; } #me { background: hotpink; }#son { background: #ff4225; } </style> <div id=”content”> <div id=”grandFather” v-on:click=”doc”> grandFather <div id=”father” v-on:click.self=”doc”> father <div id=”me” v-on:click=”doc”> me <div id=”son” v-on:click=”doc”> son </div> </div> </div> </div> </div> <script> var content = new Vue({ el: “#content”, data: { id: ” }, methods: { doc: function () { this.id= event.currentTarget.id; alert(this.id) } } }) </script> |
|
修改father,增加 .once
|
<script src=”https://how2j.cn/study/vue.min.js”></script> <style type=”text/css“> * { margin: 0 auto; text–align:center; line-height: 40px; } div { width: 100px; cursor:pointer; } #grandFather { background: deeppink; } #father { background: pink; } #me { background: hotpink; }#son { background: #ff4225; } </style> <div id=”content”> <div id=”grandFather” v-on:click=”doc”> grandFather <div id=”father” v-on:click.once=”doc”> father <div id=”me” v-on:click=”doc”> me <div id=”son” v-on:click=”doc”> son </div> </div> </div> </div> </div> <script> var content = new Vue({ el: “#content”, data: { id: ” }, methods: { doc: function () { this.id= event.currentTarget.id; alert(this.id) } } }) </script> |
|
通过在 click 后面添加 .prevent 可以阻止页面刷新。 @click.prevent 注: 只有超链和form这种会导致页面刷新的操作,.prevent 才有用。 普通的不导致页面刷新的按钮,加上这个没有任何变化。 |
<script src=”https://how2j.cn/study/vue.min.js”></script> <div id=”div1″> <a href=”http://12306.com” @click=”jump” >正常的链接 http://12306.com</a> <br> <a href=”http://12306.com” @click.prevent=”jump” >prevent jump()之后的链接 http://12306.com</a> <br> <a href=”http://12306.com” @click.prevent >纯prevent之后的链接 http://12306.com</a> <br> <br> <form @submit=”jump” action=”http://12306.com”> <button type=”submit“>正常的form</button> </form> <form @submit.prevent=”jump” action=”http://12306.com”> <button type=”submit“>prevent jump()之后的form</button> </form> <form @submit.prevent action=”http://12306.com”> <button type=”submit“>纯prevent之后的form</button> </form> </div> <script> new Vue({ el: ‘#div1’, data: { }, methods:{ jump:function(){ alert(“jump()函数被调用“); } } }) </script> |
Vue.js 条件语句
|
v-if 通过toggle函数切换show的值。 通过v-if 语句,当show 是true的时候,显示当前元素 <div v-if=”show“> 默认这一条是看得见的</div>
|
<script src=”https://how2j.cn/study/vue.min.js”></script> <div id=”div1″> <button v-on:click=”toggle”>切换隐藏显示</button> <div v-if=”show“> 默认这一条是看得见的</div> </div> <script> new Vue({ el: ‘#div1’, data: { show:true }, methods:{ toggle: function(){ this.show=!this.show; } } }) </script> |
|
v-else
|
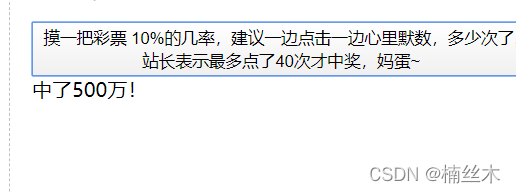
<script src=”https://how2j.cn/study/vue.min.js”></script> <div id=”div1″> <button v-on:click=”moyiba”> 摸一把彩票 10%的几率,建议一边点击一边心里默数,多少次了,站长表示最多点了40次才中奖,妈蛋~ </button> <div v-if=”show“> 中了500万!</div> <div v-else>谢谢惠顾!</div> </div> <script> new Vue({ el: ‘#div1’, data: { show:false }, methods:{ moyiba: function(){ this.show=Math.random()<0.1 } } }) </script> |
|
v-else-if
|
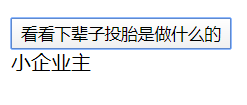
<script src=”https://how2j.cn/study/vue.min.js”></script> <div id=”div1″> <button v-on:click=”toutai“> 看看下辈子投胎是做什么的 </button> <div v-if=”number>98″> 神仙</div> <div v-else-if=”number>95″> 国家领导人</div> <div v-else-if=”number>90″> 大富商</div> <div v-else-if=”number>80″> 大企业主</div> <div v-else-if=”number>70″> 演艺明星</div> <div v-else-if=”number>60″> 小企业主</div> <div v-else-if=”number>50″> 普通公务员</div> <div v-else-if=”number>40″> 小个体户</div> <div v-else-if=”number>30″> 血汗工厂工人</div> <div v-else-if=”number>20″> 偏远山区农民</div> <div v-else> 流浪汉</div> </div> <script> new Vue({ el: ‘#div1’, data: { number:0 }, methods:{ toutai: function(){ this.number=Math.random()*100 } } }) </script> |
Vue.js 循环语句
|
{name:”盖伦”,hp:341}, {name:”提莫”,hp:225}, {name:”安妮”,hp:427}, {name:”死歌”,hp:893} ]; data: { } </tr> |
<script src=”https://how2j.cn/study/vue.min.js”></script> <style> table tr td{ border:1px solid gray; } table{ border–collapse:collapse; width:300px; } tr.firstLine{ background-color: lightGray; } </style> <div id=”div1″> <table align=”center” > <tr class=”firstLine”> <td>name</td> <td>hp</td> </tr> <tr v-for=”hero in heros”> <td>{{hero.name}}</td> <td>{{hero.hp}}</td> </tr> </table> </div> <script> var data = [ {name:”盖伦”,hp:341}, {name:”提莫”,hp:225}, {name:”安妮”,hp:427}, {name:”死歌”,hp:893} ]; new Vue({ el: ‘#div1’, data: { heros:data } }) </script> |
|
<tr v-for=”hero,index in heros“>
|
<script src=”https://how2j.cn/study/vue.min.js”></script> <style> table tr td{ border:1px solid gray; } table{ border–collapse:collapse; width:300px; } tr.firstLine{ background-color: lightGray; } </style> <div id=”div1″> <table align=”center” > <tr class=”firstLine”> <td>number</td> <td>name</td> <td>hp</td> </tr> <tr v-for=”hero,index in heros“> <td>{{index+1}}</td> <td>{{hero.name}}</td> <td>{{hero.hp}}</td> </tr> </table> </div> <script> var data = [ {name:”盖伦”,hp:341}, {name:”提莫”,hp:225}, {name:”安妮”,hp:427}, {name:”死歌”,hp:893} ]; new Vue({ el: ‘#div1’, data: { heros:data } }) </script> |
|
<div v-for=”i in 10″>
|
<script src=”https://how2j.cn/study/vue.min.js”></script> <div id=”div1″> <div v-for=”i in 10″> {{ i }} </div> </div> <script> new Vue({ el: ‘#div1’ }) </script> |
Vue.js 属性绑定 v-bind
|
<a v-bind:href=”page“>http://12306.com</a>
|
<script src=”https://how2j.cn/study/vue.min.js”></script> <div id=”div1″> <a v-bind:href=”page“>http://12306.com</a> </div> <script> new Vue({ el: ‘#div1’, data:{ page:’http://12306.com’ } }) </script> |
|
|
<script src=”https://how2j.cn/study/vue.min.js”></script> <div id=”div1″> <a :href=”page”>http://12306.com</a> </div> <script> new Vue({ el: ‘#div1’, data:{ page:’http://12306.com’ } }) </script> |
Vue.js 双向绑定 v-model
|
前面的例子,都是把 Vue对象上的数据显示在视图上,那么如何把视图上的数据放到Vue对象上去呢?
|
<script src=”https://how2j.cn/study/vue.min.js”></script> <div id=”div1″> hero name: <input v-model=”name” > <button @click=”doClick” >提交数据</button> </div> <script> new Vue({ el: ‘#div1’, data:{ name:”teemo“ }, methods:{ doClick:function(){ alert(this.name); } } }) </script> |
|
多种风格数据的绑定
|
<script src=”https://how2j.cn/study/vue.min.js”></script> <style> table tr td{ border:1px solid gray; padding:10px; } table{ border–collapse:collapse; width:800px; table-layout:fixed; } tr.firstLine{ background-color: lightGray; } </style> <div id=”div1″> <table align=”center” > <tr class=”firstLine”> <td>视图类型</td> <td>输入数据</td> <td>绑定到Vue上的数值</td> </tr> <tr> <td> 单行文本 </td> <td> <input v-model=”input” placeholder=”输入数据”> </td> <td> <p>{{ input }}</p> </td> </tr> <tr> <td> 多行文本 </td> <td> <textarea v-model=”textarea” placeholder=”输入数据”></textarea> </td> <td> <p>{{ textarea }}</p> </td> </tr> <tr> <td> 单个复选框 </td> <td> <input type=”checkbox” id=”checkbox” v-model=”checked“> </td> <td> <p>{{ checked }}</p> </td> </tr> <tr> <td> 多个复选框 </td> <td> <input type=”checkbox” id=”teemo” value=”teemo” v-model=”checkedes“> <label for=”teemo“>teemo</label> <input type=”checkbox” id=”gareen” value=”gareen” v-model=”checkedes“> <label for=”gareen”>gareen</label> <input type=”checkbox” id=”annie” value=”annie” v-model=”checkedes“> <label for=”annie”>annie</label> </td> <td> <p>{{ checkedes }}</p> </td> </tr> <tr> <td> 单选按钮 </td> <td> <input type=”radio” id=”one” value=”One” v-model=”radio“> <label for=”one”>One</label> <br> <input type=”radio” id=”two” value=”Two” v-model=”radio“> <label for=”two”>Two</label> </td> <td> <p>{{ radio }}</p> </td> </tr> <tr> <td> 单选选择框 </td> <td> <select v-model=”selected” size=”5″> <option disabled value=””>请选择</option> <option>AD</option> <option>AC</option> <option>ADC</option> </select> </td> <td> <p>{{ selected }}</p> </td> </tr> <tr> <td> 多选选择框 </td> <td> (通过ctrl或者shift进行多选)<br> <select v-model=”selecteds” multiple size=”5″> <option disabled value=””>请选择</option> <option>AD</option> <option>AC</option> <option>ADC</option> </select> </td> <td> <p>{{ selecteds }}</p> </td> </tr> <tr> <td> 单个复选框 </td> <td> 默认值是true或者false,也可以修改为自定义的值<br> <input type=”checkbox” id=”toggle” true–value=”yes” false–value=”no” v-model=”toggle”> </td> <td> <p>{{ toggle }}</p> </td> </tr> </table> </div> <script> new Vue({ el: ‘#div1’, data: { input:”, textarea:”, checked:”, checkedes:[], radio:”, selected:”, selecteds:[], toggle:”, } }) </script> |
|
修饰符 |
vue.js 还提供了一些修饰符方便用户操作,常见的有 .lazy .number .trim 接下来一一举例说明 |
|
修饰符 .lazy 对于输入元素,默认的行为方式是一旦有数据变化,马上进行绑定。
|
<script src=”https://how2j.cn/study/vue.min.js”></script> <style> table tr td{ border:1px solid gray; padding:10px; } table{ border–collapse:collapse; width:800px; table-layout:fixed; } tr.firstLine{ background-color: lightGray; } </style> <div id=”div1″> <table align=”center” > <tr class=”firstLine”> <td>视图类型</td> <td>输入数据</td> <td>绑定到Vue上的数值</td> </tr> <tr> <td> 单行文本1 </td> <td> <input v-model.lazy=”input1″ placeholder=”输入数据”> </td> <td> <p>{{ input1 }}</p> </td> </tr> <tr> <td> 单行文本2 </td> <td> <input v-model.lazy=”input2″ placeholder=”输入数据”> </td> <td> <p>{{ input2 }}</p> </td> </tr> </table> </div> <script> new Vue({ el: ‘#div1’, data: { input1:”, input2:” } }) </script> |
|
修饰符 .number 有时候,拿到了数据需要进行数学运算, 为了保证运算结果,必须先把类型转换为number类型,而v-model默认是string类型,所以就可以通过.number方式确保获取到的是数字类型了。
|
<script src=”https://how2j.cn/study/vue.min.js”></script> <style> table tr td{ border:1px solid gray; padding:10px; } table{ border-collapse:collapse; width:800px; table-layout:fixed; } tr.firstLine{ background-color: lightGray; } </style> <div id=”div1″> <table align=”center” > <tr class=”firstLine”> <td>视图类型</td> <td>输入数据</td> <td>绑定到Vue上的数值</td> <td>数值类型</td> </tr> <tr> <td> 单行文本1 </td> <td> <input v-model=”input1″ type=”number” placeholder=”输入数据”> </td> <td> <p>{{ input1 }}</p> </td> <td> <p>{{ typeof input1 }}</p> </td> </tr> <tr> <td> 单行文本2 </td> <td> <input v-model.number=”input2″ type=”number” placeholder=”输入数据”> </td> <td> <p>{{ input2 }}</p> </td> <td> <p>{{ typeof input2 }}</p> </td> </tr> </table> </div> <script> new Vue({ el: ‘#div1’, data: { input1:”, input2:” } }) </script> |
|
修饰符 .trim
|
<script src=”https://how2j.cn/study/vue.min.js”></script> <style> table tr td{ border:1px solid gray; padding:10px; } table{ border-collapse:collapse; width:800px; table-layout:fixed; } tr.firstLine{ background-color: lightGray; } </style> <div id=”div1″> <table align=”center” > <tr class=”firstLine”> <td>视图类型</td> <td>输入数据</td> <td>绑定到Vue上的数值</td> </tr> <tr> <td> 单行文本 </td> <td> <input v-model.trim=”input” placeholder=”输入数据”> </td> <td> <p>”{{ input }}”</p> </td> </tr> </table> </div> <script> new Vue({ el: ‘#div1’, data: { input:” } }) </script> |
Vue.js 计算属性
|
先看不用computed
|
<script src=”https://how2j.cn/study/vue.min.js”></script> |
|
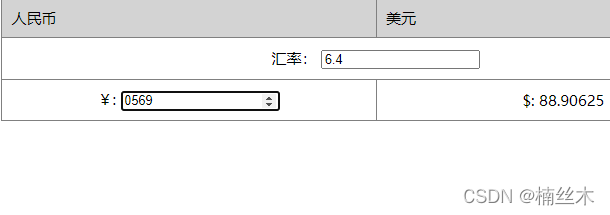
{{ rmb/exchange }} 所以可以把运算过程,都放在computed里去,只用显示运算结果就好了。 {{ dollar }} |
<script src=”https://how2j.cn/study/vue.min.js”></script> <style> table tr td{ border:1px solid gray; padding:10px; } table{ border-collapse:collapse; width:800px; table-layout:fixed; } tr.firstLine{ background-color: lightGray; } </style> <div id=”div1″> <table align=”center” > <tr class=”firstLine”> <td>人民币</td> <td>美元</td> </tr> <tr> <td align=”center” colspan=”2″> 汇率: <input type=”number” v-model.number=”exchange” /> </td> </tr> <tr> <td align=”center”> ¥: <input type=”number” v-model.number = “rmb” /> </td> <td align=”center”> $: {{ dollar }} </td> </tr> </table> </div> <script> new Vue({ el: ‘#div1’, data: { exchange:6.4, rmb:0 }, computed:{ dollar:function() { return this.rmb / this.exchange; } } }) </script> |
|
运行效果
|
<script src=”https://how2j.cn/study/vue.min.js”></script> <style> table tr td{ border:1px solid gray; padding:10px; } table{ border-collapse:collapse; width:800px; table-layout:fixed; } tr.firstLine{ background-color: lightGray; } </style> <div id=”div1″> <table align=”center” > <tr class=”firstLine”> <td>人民币</td> <td>美元</td> </tr> <tr> <td align=”center” colspan=”2″> 汇率: <input type=”number” v-model.number=”exchange” /> </td> </tr> <tr> <td align=”center”> ¥: <input type=”number” v-model.number = “rmb” /> </td> <td align=”center”> $: {{ getDollar() }} </td> </tr> </table> </div> <script> new Vue({ el: ‘#div1’, data: { exchange:6.4, rmb:0 }, methods:{ getDollar:function() { return this.rmb / this.exchange; } } }) </script> |
| computed 是有缓存的,只要rmb没有变化,dollar 会直接返回以前计算出来的值,而不会再次计算。 这样如果是复杂计算,就会节约不少时间。 而methods每次都会调用 |
Vue.js 监听属性
|
vue可以通过watch来监听属性值的变化。
|
<script src=”https://how2j.cn/study/vue.min.js”></script> <style> table tr td{ border:1px solid gray; padding:10px; } table{ border-collapse:collapse; width:800px; table-layout:fixed; } tr.firstLine{ background-color: lightGray; } </style> <div id=”div1″> <table align=”center” > <tr class=”firstLine”> <td>人民币</td> <td>美元</td> </tr> <tr> <td align=”center” colspan=”2″> 汇率: <input type=”number” v-model.number=”exchange” /> </td> </tr> <tr> <td align=”center”> ¥: <input type=”number” v-model.number = “rmb” /> </td> <td align=”center”> $: <input type=”number” v-model.number = “dollar” /> </td> </tr> </table> </div> <script> new Vue({ el: ‘#div1’, data: { exchange:6.4, rmb:0, dollar:0 }, watch:{ rmb:function(val) { this.rmb = val; this.dollar = this.rmb / this.exchange; }, dollar:function(val) { this.dollar = val; this.rmb = this.dollar * this.exchange; }, } }) </script> |
Vue.js 过滤器
|
一个过滤器 filters:{ if (!value) return ” //如果为空,则返回空字符串 return value.charAt(0).toUpperCase() + value.substring(1) } } {{ data|capitalize }} |
|
|
多个过滤器 |
<script src=”https://how2j.cn/study/vue.min.js”></script> |
|
全局过滤器 在上面的例子里可以看到,过滤器是定义在Vue对象里的。 但是有时候,很多不同的页面都会用到相同的过滤器,如果每个Vue对象里都重复开发相同的过滤器,不仅开发量增加,维护负担也增加了。 Vue.filter(‘capitalize’, function (value) { if (!value) return ” value = value.toString() return value.charAt(0).toUpperCase() + value.slice(1) }) Vue.filter(‘capitalizeLastLetter’, function (value) { if (!value) return ” //如果为空,则返回空字符串 value = value.toString() return value.substring(0,value.length-1)+ value.charAt(value.length-1).toUpperCase() }) |
<script src=”https://how2j.cn/study/vue.min.js”></script> |
Vue.js 组件
|
组件是什么 如效果所示,每个产品展示,就是一个模板。 只用做一个模板,然后照着这个模板,传递不同的参数就可以看到不同的产品展示了。 |
 |
|
接下来就由浅入深地展开组件的学习。 先看最简单的局部组件。 ‘product‘:{ template:'<div class=”product” >MAXFEEL休闲男士手包真皮手拿包大容量信封包手抓包夹包软韩版潮</div>’ } 然后在视图里,通过如下方式就可以调用了 如果想重复使用,则多写几次就行了 |
<script src=”https://how2j.cn/study/vue.min.js”></script> |
|
和vue.js 里的过滤器一样,有的组件会在不同页面使用,这个时候就可以考虑用全局组件。 template: ‘<div class=”product” >MAXFEEL休闲男士手包真皮手拿包大容量信封包手抓包夹包软韩版潮</div>’ }) 写法其实跟局部差不多,只是提出来了。 这样到处都可以用了。 |
<script src=”https://how2j.cn/study/vue.min.js”></script> |
|
像前面的例子,产品名称都是固定的,这样肯定不行,所以就要能够传递参数给组件。 Vue.component(‘product’, { props:[‘name’], template: ‘<div class=”product” >{{name}}</div>’ }) 调用的时候,就当作是一个自定义属性传进去就可以了 <product name=”MAXFEEL休闲男士手包真皮手拿包大容量信封包手抓包夹包软韩版潮”></product> <product name=”宾度 男士手包真皮大容量手拿包牛皮个性潮男包手抓包软皮信封包”></product> <product name=”唯美诺新款男士手包男包真皮大容量小羊皮手拿包信封包软皮夹包潮”></product> |
<script src=”https://how2j.cn/study/vue.min.js”></script> |
|
所谓的动态参数,就是指组件内的参数可以和组件外的值关联起来 <product v-bind:name=”outName”></product> |
<script src=”https://how2j.cn/study/vue.min.js”></script> <style> div.product{ float:left; border:1px solid lightGray; width:200px; margin:10px; cursor: pointer; } </style> <div id=”div1″> 组件外的值:<input v-model=”outName” ><br> <product v-bind:name=”outName”></product> </div> <script> Vue.component(‘product’, { props:[‘name’], template: ‘<div class=”product” >{{name}}</div>’ }) new Vue({ el: ‘#div1’, data:{ outName:’产品名称‘ } }) </script> |
|
自定义事件 增加自定义事件和在一个Vue对象上增加 methods 是一样的做法 methods:{ this.sale++ } } 然后在组件里: v-on:click=”increaseSale” |
<script src=”https://how2j.cn/study/vue.min.js”></script> |
| 遍历 json 数组 | |
| 最开始效果步骤里的代码 | <script src=”https://how2j.cn/study/vue.min.js”></script> <style> div.product{ float:left; border:1px solid lightGray; width:200px; margin:10px; cursor: pointer; } div.product:hover{ border:1px solid #c40000; } div.price{ color:#c40000; font–weight:bold; font–size:1.2em; margin:10px; } div.productName{ color:gray; font–size:0.8em; margin:10px; } div.sale{ float:left; width:100px; border:1px solid lightgray; border-width:1px 0px 0px 0px; color:gray; font-size:0.8em; padding-left:10px; } div.review{ overflow:hidden; border:1px solid lightgray; border-width:1px 0px 0px 1px; color:gray; font-size:0.8em; padding-left:10px; } </style> <div id=”tempalate” style=”display:none“> <div class=”product” v-on:click=”increaseSales“> <div class=”price”> ¥ {{product.price}} </div> <div class=”productName”> {{product.name}} </div> <div class=”sale”> 月成交 {{product.sale}} 笔</div> <div class=”review“> 评价 {{product.review}} </div> </div> </div> <div id=”div1″> <product v-for=”item in products” v-bind:product=”item“></product> </div> <script> var tempalateDiv=document.getElementById(“tempalate”).innerHTML; var templateObject = { props: [‘product’], template: tempalateDiv, methods: { increaseSales: function () { this.product.sale = parseInt(this.product.sale); this.product.sale += 1 this.$emit(‘increment‘) } } } Vue.component(‘product’, templateObject) new Vue({ el: ‘#div1’, data:{ products:[ {“name”:”MAXFEEL休闲男士手包真皮手拿包大容量信封包手抓包夹包软韩版潮”,”price”:”889″,”sale”:”18″,”review”:”5″}, {“name”:”宾度 男士手包真皮大容量手拿包牛皮个性潮男包手抓包软皮信封包”,”price”:”322″,”sale”:”35″,”review”:”12″}, {“name”:”唯美诺新款男士手包男包真皮大容量小羊皮手拿包信封包软皮夹包潮”,”price”:”523″,”sale”:”29″,”review”:”3″}, ] } }) </script> |
Vue.js 自定义指令
|
像 v-if, v-bind, v-on 等等前面学习的指令,都是 vus.js 自带的指令,那么除了这些指令,开发者还可以开发自定义的指令,比如 v-xart 来做一些效果。 Vue.directive(‘xart’, function (el) { el.innerHTML = el.innerHTML + ‘ ( x-art ) ‘ el.style.color = ‘pink’ }) |
<script src=”https://how2j.cn/study/vue.min.js”></script> |
|
带参数的自定义指令 上面例子是不带参数的,现在带上参数 Vue.directive(‘xart’, function (el,binding) { el.innerHTML = el.innerHTML + ‘( ‘ + binding.value.text + ‘ )’ el.style.color = binding.value.color }) 视图上用就传递个json 对象进去 <div v-xart=”{color:’red‘,text:’best learning video‘}”> 好好学习,天天向上 </div> 当然也可以传递个简单的 |
<script src=”https://how2j.cn/study/vue.min.js”></script> |
|
钩子函数 钩子函数是什么意思? 又叫做回调函数,或者事件响应函数。 指的是,一个指令在创建过程中,经历不同生命周期的时候,vue.js 框架调用的函数。 以bind为例,可以传递主要是用到binding里的属性 |
<script src=”https://how2j.cn/study/vue.min.js”></script> |
Vue.js 路由
|
vue.js 里的路由概念 vue.js 里的路由相当于就是局部刷新。 |
 |
|
vue-router.min.js vue-router.min.js <script src=”http://how2j.cn/study/vue-router.min.js”></script> |
|
|
路由代码讲解
|
<script src=”https://how2j.cn/study/vue.min.js”></script> <script src=”https://how2j.cn/study/vue-router.min.js”></script> <head> <style> a{ text-decoration: none; } a.router–link–active{ /* color:blue; */ background-color: lightGray; } div.menu{ border:1px solid gray; float:left; } div.menu a{ display:block; } div.workingRoom{ margin-left:100px; } div#app{ width:500px; padding:10px; margin:10px auto; } </style> </head> <div id=”app“> <div class=”menu“> <!– router–link 相当于就是超链 to 相当于就是 href –> <router–link to=”/user“>用户管理</router–link> <router-link to=”/product”>产品管理</router-link> <router-link to=”/order”>订单管理</router-link> </div> <div class=”workingRoom“> <!– 点击上面的/user,那么/user 对应的内容就会显示在router-view 这里 –> <router-view></router-view> </div> </div> <script> /* * 申明三个模板( html 片段 ) */ var user = { template: ‘<p>用户管理页面的内容</p>’ }; var second = { template: ‘<p>产品管理页面的内容</p>’ }; var order = { template: ‘<p>订单管理页面的内容</p>’ }; /* * 定义路由 */ var routes = [ { path: ‘/’, redirect: ‘/user’}, // 这个表示会默认渲染 /user,没有这个就是空白 { path: ‘/user’, component: user }, { path: ‘/product’, component: second }, { path: ‘/order’, component: order } ]; /* * 创建VueRouter实例 */ var router = new VueRouter({ routes:routes }); /* * 给vue对象绑定路由 */ new Vue({ el:”#app”, router }) </script> |
Vue.js fetch.js
|
fetch.js 本来要开始讲解 Vue.js 里如何使用 Ajax了。 一般说来 Vue 不会直接使用原生的 Ajax 而是使用 ajax 框架。 而 fetch.js 就是眼下比较流行的一种 ajax 框架 |
|||
|
json 数据很简单,然后我把他放在:http://how2j.cn/study/json.txt 方便调用 代码比较复制代码
|
|||
| 通过fetch 获取数据 | <script src=”https://how2j.cn/study/fetch.min.js”></script> <div id=”hero”> </div> <script> var url = “http://how2j.cn/study/json.txt“ fetch(url).then(function(response) { response.json().then(function (jsonObject) { var jsonString = JSON.stringify(jsonObject) document.getElementById(“hero”).innerHTML = “通过fetch获取到的json数据:”+ jsonString; }) }).catch(function(err){ console.log(“Fetch错误:”+err); }) </script> |
||
Vue.js axios.js
| axios.js | 本来要开始讲解 Vue.js 里如何使用 Ajax了。 一般说来 Vue 不会直接使用原生的 Ajax 而是使用 ajax 框架。 而 axios.js 就是眼下比较流行的一种 ajax 框架 |
| 准备json数据 |
json 数据很简单,然后我把他放在:http://how2j.cn/study/json.txt 方便调用 {“name”:”gareen”,”hp”:”355″} |
| <script src=”https://how2j.cn/study/axios.min.js”></script> <div id=”hero”> </div> <script> var url = “http://how2j.cn/study/json.txt“ axios.get(url).then(function(response) { var jsonObject = response.data; var jsonString = JSON.stringify(jsonObject) document.getElementById(“hero”).innerHTML = “通过 axios 获取到的json数据:”+ jsonString; }) </script> |
Vue.js Ajax
|
Ajax Vue.js 并没有限制使用哪种方式进行 ajax 访问,所以可以使用如下方式 |
那么到底用哪种方式呢?
1. 原生一般不在项目中直接用 |
|
首先准备 json 数组 json 数据很简单,然后我把它放在:http://how2j.cn/study/jsons.txt 方便调用 |
[ |
|
fetch..js 方式 fetch 的调用就是前面 fetch 教程里讲解的。
|
<script src=”https://how2j.cn/study/vue.min.js”></script> <script src=”https://how2j.cn/study/fetch.min.js”></script> <head> <style> table tr td{ border:1px solid gray; } table{ border-collapse:collapse; width:300px; } tr.firstLine{ background-color: lightGray; } </style> </head> <div id=”div1″> <table align=”center” > <tr class=”firstLine”> <td>name</td> <td>hp</td> </tr> <tr v-for=”hero in heros“> <td>{{hero.name}}</td> <td>{{hero.hp}}</td> </tr> </table> </div> <script> var url = “http://how2j.cn/study/jsons.txt“; new Vue({ el:’#div1′, data:{ heros:[] }, mounted:function(){ //mounted 表示这个 Vue 对象加载成功了 self=this fetch(url).then(function(response) { response.json().then(function (jsonObject) { self.heros = jsonObject }) }).catch(function(err){ console.log(“Fetch错误:”+err); }) } }) </script> |
|
axios.js 方式 axios 的调用就是前面 axios 教程里讲解的。 mounted:function(){ //mounted 表示这个 Vue 对象加载成功了 mounted:function(){ //mounted 表示这个 Vue 对象加载成功了
|
<script src=”https://how2j.cn/study/vue.min.js”></script> <script src=”https://how2j.cn/study/axios.min.js”></script> <head> <style> table tr td{ border:1px solid gray; } table{ border-collapse:collapse; width:300px; } tr.firstLine{ background-color: lightGray; } </style> </head> <div id=”div1″> <table align=”center” > <tr class=”firstLine”> <td>name</td> <td>hp</td> </tr> <tr v-for=”hero in heros“> <td>{{hero.name}}</td> <td>{{hero.hp}}</td> </tr> </table> </div> <script> var url = “http://how2j.cn/study/jsons.txt“; new Vue({ el:’#div1′, data:{ heros:[] }, mounted:function(){ //mounted 表示这个 Vue 对象加载成功了 var self = this axios.get(url).then(function(response) { self.heros= response.data; //此时还是字符串 self.heros = eval(“(“+self.heros+”)”); //字符串转换为数组对象 }) } }) </script> |
Vue.js Vue-cli
Vue.js crud
| Crud | CRUD 这个东西还是绕不过去的,毕竟业务上太常见了。 接下来会用 VUE.js 做一套 CRUD。 不过这个 CRUD,是仅仅前端的,并没有和服务端交互。 需要看 VUE.js 和服务端交互的CRUD教程,请点击: VUE.JS + RESTFUL + PAGEHELPER + THYMELEAF + SPRINGBOOT 前后端分离 CRUD 教程 |
|
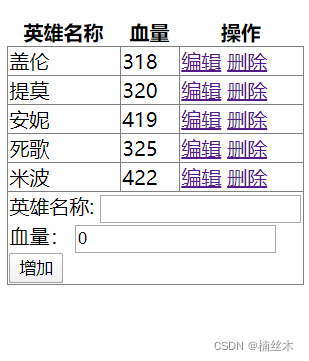
效果 |
 |
| 接下来,就按照查询,增加,删除,编辑和更新,由浅入深地把这个 CRUD 一点点做出来。 | |
|
|
<html> div#app{ |
|
增加
接着就是增加功能 <td colspan=”3″> 英雄名称: <input type=”text” v-model=”hero4Add.name” /> <br> 血量: <input type=”number” v-model=”hero4Add.hp” /> <br> <button type=”button” v-on:click=”add”>增加</button> </td> 输入组件都和 hero4Add 对象通过 v-model 进行了双向绑定。 2. maxId var maxId = 5; //计算最大值 for (var i=0;i<data.heros.length;i++){ if (data.heros[i].id > maxId) maxId= this.heros[i].id; } 准备了 maxId,作为自增长键,初始值取当前数据的最大id. 3. add函数 methods: { add: function (event) { //获取最大id maxId++; //赋予新id this.hero4Add.id = maxId; if(this.hero4Add.name.length==0) this.hero4Add.name = “Hero#”+this.hero4Add.id; //把对象加入到数组 this.heros.push(this.hero4Add); //让 hero4Add 指向新的对象 this.hero4Add = { id: 0, name: ”, hp: ‘0’} } } |
<html> <head> <script src=”https://how2j.cn/study/js/jquery/2.0.0/jquery.min.js”></script> <script src=”https://how2j.cn/study/vue.min.js”></script> <style type=”text/css“> td{ border:1px solid gray; } table{ border-collapse:collapse; } div#app{ margin:20px auto; width:400px; padding:20px; } </style> </head> <body> <div id=”app”> <table id=”heroListTable” > <thead> <tr> <th>英雄名称</th> <th>血量</th> </tr> </thead> <tbody> <tr v-for=”hero in heros “> <td>{{hero.name}}</td> <td>{{hero.hp}}</td> </tr> <tr> <td colspan=”3″> 英雄名称: <input type=”text” v-model=”hero4Add.name” /> <br> 血量: <input type=”number” v-model=”hero4Add.hp” /> <br> <button type=”button” v-on:click=”add”>增加</button> </td> </tr> </tbody> </table> </div> <script type=”text/javascript“> //Model var data = { heros: [ { id: 1, name: ‘盖伦’, hp: 318}, { id: 2, name: ‘提莫’, hp: 320}, { id: 3, name: ‘安妮’, hp: 419}, { id: 4, name: ‘死歌’, hp: 325}, { id: 5, name: ‘米波’, hp: 422}, ], hero4Add: { id: 0, name: ”, hp: ‘0’}, hero4Update: { id: 0, name: ”, hp: ‘0’} }; //用于记录最大id值 var maxId = 5; //计算最大值 for (var i=0;i<data.heros.length;i++){ if (data.heros[i].id > maxId) maxId= this.heros[i].id; } //ViewModel var vue = new Vue({ el: ‘#app’, data: data, methods: { add: function (event) { //获取最大id maxId++; //赋予新id this.hero4Add.id = maxId; if(this.hero4Add.name.length==0) this.hero4Add.name = “Hero#”+this.hero4Add.id; //把对象加入到数组 this.heros.push(this.hero4Add); //让 hero4Add 指向新的对象 this.hero4Add = { id: 0, name: ”, hp: ‘0’} } } }); </script> </body> </html> |
|
删除
1. 增加删除的链接 <td> <a href=”#nowhere” @click=”deleteHero(hero.id)”>删除</a> </td> 2. 增加 deleteHero 函数,逻辑很简单,就是遍历所有的hero对象,如果id相同,就删掉。 deleteHero: function (id) { for (var i=0;i<this.heros.length;i++){ if (this.heros[i].id == id) { this.heros.splice(i, 1); } } } |
<html> <head> <script src=”https://how2j.cn/study/js/jquery/2.0.0/jquery.min.js”></script> <script src=”https://how2j.cn/study/vue.min.js”></script> <style type=”text/css“> td{ border:1px solid gray; } table{ border-collapse:collapse; } div#app{ margin:20px auto; width:400px; padding:20px; } </style> </head> <body> <div id=”app”> <table id=”heroListTable” > <thead> <tr> <th>英雄名称</th> <th>血量</th> <th>操作</th> </tr> </thead> <tbody> <tr v-for=”hero in heros “> <td>{{hero.name}}</td> <td>{{hero.hp}}</td> <td> <a href=”#nowhere” @click=”deleteHero(hero.id)”>删除</a> </td> </tr> <tr> <td colspan=”3″> 英雄名称: <input type=”text” v-model=”hero4Add.name” /> <br> 血量: <input type=”number” v-model=”hero4Add.hp” /> <br> <button type=”button” v-on:click=”add”>增加</button> </td> </tr> </tbody> </table> </div> <script type=”text/javascript“> //Model var data = { heros: [ { id: 1, name: ‘盖伦’, hp: 318}, { id: 2, name: ‘提莫’, hp: 320}, { id: 3, name: ‘安妮’, hp: 419}, { id: 4, name: ‘死歌’, hp: 325}, { id: 5, name: ‘米波’, hp: 422}, ], hero4Add: { id: 0, name: ”, hp: ‘0’}, hero4Update: { id: 0, name: ”, hp: ‘0’} }; //用于记录最大id值 var maxId = 5; //计算最大值 for (var i=0;i<data.heros.length;i++){ if (data.heros[i].id > maxId) maxId= this.heros[i].id; } //ViewModel var vue = new Vue({ el: ‘#app’, data: data, methods: { add: function (event) { //获取最大id maxId++; //赋予新id this.hero4Add.id = maxId; if(this.hero4Add.name.length==0) this.hero4Add.name = “Hero#”+this.hero4Add.id; //把对象加入到数组 this.heros.push(this.hero4Add); //让 hero4Add 指向新的对象 this.hero4Add = { id: 0, name: ”, hp: ‘0’} }, deleteHero: function (id) { console.log(“id”+id); for (var i=0;i<this.heros.length;i++){ if (this.heros[i].id == id) { this.heros.splice(i, 1); break; } } } } }); </script> </body> </html> |
|
1. 增加链接 <a href=”#nowhere” @click=”edit(hero)”>编辑</a> <div id=”div4Update“> 英雄名称: <input type=”text” v-model=”hero4Update.name” /> <br> 血量: <input type=”number” v-model=”hero4Update.hp” /> <input type=”hidden” v-model=”hero4Update.id” /> <br> <button type=”button” v-on:click=”update”>修改</button> <button type=”button” v-on:click=”cancel”>取消</button> </div> 3. 增加相关函数 edit: function (hero) { $(“#heroListTable”).hide(); this.hero4Update = hero; }, update:function(){ //因为v-model,已经同步修改了,所以只需要进行恢复显示就行了 $(“#heroListTable”).show(); }, cancel:function(){ //其实就是恢复显示 $(“#heroListTable”).show(); } |
<html> <head> <script src=”https://how2j.cn/study/js/jquery/2.0.0/jquery.min.js”></script> <script src=”https://how2j.cn/study/vue.min.js”></script> <style type=”text/css“> td{ border:1px solid gray; } table{ border-collapse:collapse; } div#app{ margin:20px auto; width:400px; padding:20px; } </style> </head> <body> <div id=”app”> <table id=”heroListTable” > <thead> <tr> <th>英雄名称</th> <th>血量</th> <th>操作</th> </tr> </thead> <tbody> <tr v-for=”hero in heros “> <td>{{hero.name}}</td> <td>{{hero.hp}}</td> <td> <a href=”#nowhere” @click=”edit(hero)”>编辑</a> <a href=”#nowhere” @click=”deleteHero(hero.id)”>删除</a> </td> </tr> <tr> <td colspan=”3″> 英雄名称: <input type=”text” v-model=”hero4Add.name” /> <br> 血量: <input type=”number” v-model=”hero4Add.hp” /> <br> <button type=”button” v-on:click=”add”>增加</button> </td> </tr> </tbody> </table> <div id=”div4Update”> 英雄名称: <input type=”text” v-model=”hero4Update.name” /> <br> 血量: <input type=”number” v-model=”hero4Update.hp” /> <input type=”hidden” v-model=”hero4Update.id” /> <br> <button type=”button” v-on:click=”update”>修改</button> <button type=”button” v-on:click=”cancel”>取消</button> </div> </div> <script type=”text/javascript“> //修改区域隐藏起来先 $(“#div4Update”).hide(); //Model var data = { heros: [ { id: 1, name: ‘盖伦’, hp: 318}, { id: 2, name: ‘提莫’, hp: 320}, { id: 3, name: ‘安妮’, hp: 419}, { id: 4, name: ‘死歌’, hp: 325}, { id: 5, name: ‘米波’, hp: 422}, ], hero4Add: { id: 0, name: ”, hp: ‘0’}, hero4Update: { id: 0, name: ”, hp: ‘0’} }; //用于记录最大id值 var maxId = 5; //计算最大值 for (var i=0;i<data.heros.length;i++){ if (data.heros[i].id > maxId) maxId= this.heros[i].id; } //ViewModel var vue = new Vue({ el: ‘#app’, data: data, methods: { add: function (event) { //获取最大id maxId++; //赋予新id this.hero4Add.id = maxId; if(this.hero4Add.name.length==0) this.hero4Add.name = “Hero#”+this.hero4Add.id; //把对象加入到数组 this.heros.push(this.hero4Add); //让 hero4Add 指向新的对象 this.hero4Add = { id: 0, name: ”, hp: ‘0’} }, deleteHero: function (id) { console.log(“id”+id); for (var i=0;i<this.heros.length;i++){ if (this.heros[i].id == id) { this.heros.splice(i, 1); break; } } }, edit: function (hero) { $(“#heroListTable”).hide(); $(“#div4Update”).show(); this.hero4Update = hero; }, update:function(){ //因为v-model,已经同步修改了,所以只需要进行恢复显示就行了 $(“#heroListTable”).show(); $(“#div4Update”).hide(); }, cancel:function(){ //其实就是恢复显示 $(“#heroListTable”).show(); $(“#div4Update”).hide(); } } }); </script> <div style=”height:300px”></div> </body> </html> |
1
1
1
原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/m0_58495313/article/details/122510614
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。
如若转载,请注明出处:http://www.7code.cn/show_45712.html
如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系代码007邮箱:suwngjj01@126.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
























 <script src=”https://how2j.cn/study/vue.min.js”></script>
<script src=”https://how2j.cn/study/vue.min.js”></script>