1.CSS简介
CSS(Cascading Style Sheets)层叠样式表,是用来为结构化文档(HTML、XML等应用)添加样式,比如字体、颜色、大小、间距的计算机语言。CSS目前已经发展到了CSS3.0了。
2.CSS导入方式
1.行内样式:直接在标签元素中编写style属性,在其中编写样式即可:
<p style="color: paleturquoise">你好,这是CSS</p>2.内部样式:在头部head标签中,我们写上<style>标签,然后就可以在其中写入CSS样式了:
<style>
p{
color: paleturquoise;
font-size: 20px;
}
</style>3.外部样式:外部样式就是新建一个.css文件,在其中编写css样式然后引入html文件之中,引入方式有两种:
连接式:
<link type="text/css" rel="stylesheet" href="first.css">
导入式:
<style>
@import url("first.css");
</style>3.选择器
3.1. 基本选择器
/*标签选择器*/
h1{
color: pink;
background-color: #eeeeee;
font-family: 楷体;
}
p{
color: pink;
background-color: #eeeeee;
font-family: 楷体;
}2.类选择器:可以选择class一致的标签,在class名前面加上一个小点 .className {xxx样式}
/*类选择器*/
.font1{
color: pink;
background-color: #eeeeee;
font-family: 楷体;
}
.font2{
color: pink;
background-color: #eeeeee;
font-family: 楷体;
}3.Id选择器:这是全局唯一的样式,指定某个id,设置样式,在id名字前加上井号,如:#idName{xxx样式}
/*Id选择器*/
#demo1{
color: pink;
background-color: #eeeeee;
font-family: 楷体;
}
#demo2{
color: pink;
background-color: #eeeeee;
font-family: 楷体;
}优先级对比:
3.2.层次选择器:
/*后代选择器*/
body p{
background-color: pink;
}
2.子选择器:只选择一代
/*后代选择器*/
body>p{
background-color: pink;
}
3. 同辈选择器:选择相邻的兄弟选择器
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<style>
.d1+.d2{
background-color: #aaaaaa;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="d1">你好</div>
<div class="d2">hello</div>
</body>
</html>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<style>
.d1~div{
background-color: #aaaaaa;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="d1">你好</div>
<div class="d2">hello</div>
<div class="d3">oook</div>
</body>
</html>
3.3. 结构伪类选择器

(上图引用至:CSS结构伪类选择器-CSDN博客)
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<!--避免使用,class,id选择器-->
<style>
/*ul的第一个子元素*/
ul li:first-child{
background: firebrick;
}
/*ul的最后一个子元素*/
ul li:last-child{
background: darkcyan;
}
/*选中p1:定位到父元素,选择当前的第一个元素
选择当前p元素的父级元素,选中父级元素的第一个子元素为p的
按顺序
*/
p:nth-child(2){
background: salmon;
}
/*选中父元素下的p元素的第二个,按类型*/
p:nth-of-type(1){
background: gold;
}
p:nth-child(3){
background-color: whitesmoke;
}
a:hover{
background: violet;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<!--<h1>h1</h1>-->
<p>p1</p>
<p>p2</p>
<p>p3</p>
<ul>
<li>li1</li>
<li>li2</li>
<li>li3</li>
</ul>
<a href="">链接标签</a>
</body>
</html>
4.CSS样式
css能够设计出多种多样的样式,现在我们详细的介绍这些样式。
4.1. 背景:
- background-color 背景颜色。
- background-image 背景图片。
- background-repeat 背景图像是否重复。
- background-attachment 背景图像是否固定或者随着页面的其余部分滚动。
- background-position 设置背景图像的起始位置。
- background 属性简写,包含上面的几种写法。
.div1 {
width: 600px;
height: 208px;
background-image: url("../20231115/button.png");
background-repeat: no-repeat;
background-size: cover;
}4.2. 文本
| 属性 | 描述 |
| color | 设置文字颜色 |
| direction | 文本方向 |
| letter-spacing | 字符间距 |
| line-height | 行高 |
| text–align | 对齐方式 |
| text-decoration | 设置划线的位置 |
| text-indent | 缩进 |
| text-shadow | 设置文本阴影 |
| text–transform | 控制元素中的字母 |
| vertical-align | 垂直对齐 |
| white-space | 设置元素中空白的处理方式 |
| word-spacing | 设置字间距 |
写个代码试一试:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<style>
p{
color: rebeccapurple;
direction: initial;
letter-spacing: 10px;
line-height: 20px;
text-decoration: line-through;
text-shadow: darkolivegreen;
word-spacing: 50px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<p>hello world</p>
</body>
</html>4.3. 字体
| 属性 | 描述 |
| font-family | 文本的字体系列 |
| font-size | 字体大小 |
| font- style | 字体样式 |
| font-variant | 以小型大型显示文本 |
| font-weight | 字体粗细 |
4.4. 链接
4.5. 显示状态
CSS中可以使用display和visibility来设置元素的显示与隐藏
visibility:hidden:可以隐藏某个元素,但隐藏的元素仍需占用与未隐藏之前一样的空间。也就是说,该元素虽然被隐藏了,但仍然会影响布局。
display:none:可以隐藏某个元素,且隐藏的元素不会占用任何空间。也就是说,该元素不但被隐藏了,而且该元素原本占用的空间也会从页面布局中消失。
display中的inline和block分别会把元素设置为内联元素和块元素。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<style>
.hidden {
visibility: hidden;
}
.none {
display: none;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<p>hello world</p>
<p class="none">hello world</p>
<p>hello world</p>
<p class="hidden">hello world</p>
<p>hello world</p>
</body>
</html>
4.6. 定位 Position
CSS定位Position拥有五个值:static、relative、fixed、absolute、sticky
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>定位</title>
</head>
<style>
.sta{ /*静态定位---默认 静态定位的元素不会受到 top, bottom, left, right影响。*/
position: static;
border: 2px solid red;
}
.fix{ /*固定位置 元素的位置相对于浏览器窗口是固定位置。即使窗口是滚动的它也不会移动:*/
position: fixed;
top: 30px;
left: 50px;
}
.rel{ /* 相对定位 相对定位元素的定位是相对其正常位置*/
position: relative;
left: -30px;
}
.abs{ /* 绝对定位的元素的位置相对于最近的已定位父元素,如果元素没有已定位的父元素,那么它的位置相对于<html>: */
position: absolute;
left: 100px;
top: 100px;
z-index: -1;
}
.sti{ /* 粘性定位 元素定位表现为在跨越特定阈值前为相对定位,之后为固定定位。*/
position: -webkit-sticky;
width: 300px;
height: 50px;
background-color: whitesmoke;
position: sticky;
top: 0;
}
</style>
<body>
<p class="sta">静态定位</p>
<p class="rel">相对定位</p>
<p class="fix">页面固定位置</p>
<p class="abs">绝对位置</p>
<div class="sti"></div>
<p>666666666666666666666666</p>
<p>777777777777777777777777</p>
<p>777777777777777777777777</p>
<p>777777777777777777777777</p>
<p>777777777777777777777777</p>
<p>777777777777777777777777</p>
<p>777777777777777777777777</p>
<p>777777777777777777777777</p>
<p>777777777777777777777777</p>
<p>777777777777777777777777</p>
<p>777777777777777777777777</p>
<p>777777777777777777777777</p>
<p>777777777777777777777777</p>
<p>777777777777777777777777</p>
<p>777777777777777777777777</p>
<p>777777777777777777777777</p>
<p>777777777777777777777777</p>
<p>777777777777777777777777</p>
<p>777777777777777777777777</p>
<p>777777777777777777777777</p>
<p>777777777777777777777777</p>
<p>777777777777777777777777</p>
<p>777777777777777777777777</p>
<p>777777777777777777777777</p>
<p>777777777777777777777777</p>
<p>777777777777777777777777</p>
<p>777777777777777777777777</p>
<p>777777777777777777777777</p>
<p>777777777777777777777777</p>
<p>777777777777777777777777</p>
<p>777777777777777777777777</p>
<p>777777777777777777777777</p>
<p>777777777777777777777777</p>
<p>777777777777777777777777</p>
</body>
</html>4.7.布局–Overflow
| 值 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| visible | 默认值。内容不会被修剪,会呈现在元素框之外。 |
| hidden | 内容会被修剪,并且其余内容是不可见的。 |
| scroll | 内容会被修剪,但是浏览器会显示滚动条以便查看其余的内容。 |
| auto | 如果内容被修剪,则浏览器会显示滚动条以便查看其余的内容。 |
| inherit | 规定应该从父元素继承 overflow 属性的值。 |
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<style>
.all{
display: flex;
flex-direction: row;
}
#visible {
background: #4CAF50;
color: black;
padding: 15px;
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
overflow: visible;
border: 1px solid #ccc;
}
#hidden{
background: #4CAF50;
color: black;
padding: 15px;
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
overflow: hidden;
border: 1px solid #ccc;
}
#scroll {
background: #4CAF50;
color: black;
padding: 15px;
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
overflow: scroll;
border: 1px solid #ccc;
}
#auto {
background: #4CAF50;
color: black;
padding: 15px;
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
overflow: auto;
border: 1px solid #ccc;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="all">
<div id="visible">
<p>第一种: visible</p>
<p>visible</p>
<p>visible</p>
<p>visible</p>
<p>visible</p>
<p>visible</p>
<p>visible</p>
<p>visible</p>
<p>visible</p>
<p>visible</p>
</div>
<div id="hidden">
<p>第二种: hidden</p>
<p>hidden</p>
<p>hidden</p>
<p>hidden</p>
<p>hidden</p>
<p>hidden</p>
<p>hidden</p>
<p>hidden</p>
<p>hidden</p>
</div>
<div id="scroll">
<p>第三种:scroll</p>
<p>scroll</p>
<p>scroll</p>
<p>scroll</p>
<p>scroll</p>
<p>scroll</p>
<p>scroll</p>
<p>scroll</p>
<p>scroll</p>
</div>
<div id="auto">
<p>第四种:auto</p>
<p>auto</p>
<p>auto</p>
<p>auto</p>
<p>auto</p>
<p>auto</p>
<p>auto</p>
<p>auto</p>
<p>auto</p>
</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
如图所示,会溢出来。
4.8. 浮动 — Float
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<style>
.image{
float: left;
width: 300px;
height: 300px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h2>图片库</h2>
<p>调整串口试一试</p>
<div>
<img src="dog.jpg" class="image">
<img src="dog.jpg" class="image">
<img src="dog.jpg" class="image">
<img src="dog.jpg" class="image">
<img src="dog.jpg" class="image">
<img src="dog.jpg" class="image">
<img src="dog.jpg" class="image">
<img src="dog.jpg" class="image">
<img src="dog.jpg" class="image">
<img src="dog.jpg" class="image">
</div>
</body>
</html>
4.9. 居中方式
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>居中方式</title>
<style>
*{
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
}
h4{
margin: 10px 0 10px 0;
}
.all{
width: auto;
height: 100vh;
background-color: whitesmoke;
display: flex;
flex-direction: row;
justify-content: space-around;
}
.shuiping, .chuizhi, .shuipingcuizhi{
height: 100%;
width: 30%;
}
.content{
width: 300px;
height: 100px;
background-color: salmon;
border: 1px solid black;
}
.item{
background-color: #4CAF50;
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
}
/* ===============1===============*/
/* 使用 margin:auto 实现居中 */
.margin-center{
margin: auto;
}
/* ===============2=============== */
.content2{
text-align: center;
/* 这里的text-align:center子元素会继承该属性 */
/* 我们的目的是将元素居中而不是文本居中 */
}
.block-center{
display: inline-block;
}
/* ================3================ */
.content3{
position: relative;
}
.absolute-center{
position: absolute;
left: 50%;
transform: translateX(-50%);
}
/* ==================4=================== */
.content4{
display: flex;
justify-content: center;
}
/* ======================垂直居中=======================*/
.Ccontent{
width: 300px;
height: 100px;
background-color: olive;
border: 1px solid black;
}
.item2{
width: 300px;
height: 30px;
background-color: gold;
}
/* ========== 1 =========*/
.Ccontent1{
display: table-cell;
vertical-align: middle;
}
/* =============2=================*/
.Ccontent2{
line-height: 100px;
}
.vertical-center{
display: inline-block;
vertical-align: middle;
}
/* ==========3===================*/
.Ccontent3{
display: flex;
align-items: center;
}
/* =========4================= */
.Ccontent4{
position: relative;
}
.abs-center{
position: absolute;
top: 50%;
transform: translateY(-50%);
}
/* ==============================水平垂直居中====================*/
.SCcontent{
background-color: paleturquoise;
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
}
.item3{
background-color: lightgoldenrodyellow;
width: 50px;
height: 50px;
}
/* ===================1 =================*/
.SCcontent1{
position: relative;
}
.abso-center{
position: absolute;
top: 50%;
left: 50%;
transform: translate(-50% , -50%);
}
/* ====================2==================*/
.SCcontent2{
display: flex;
justify-content: center;
align-items: center;
}
/*================ 3 ========================*/
.SCcontent3{
text-align: center;
line-height: 100px;
}
.SCitem3{
display: inline-block;
vertical-align: middle;
}
/* ===================== 4 =========================*/
.SCcontent4{
display: table-cell;
text-align: center;
vertical-align: middle;
}
.SCitem4{
display: inline-block;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="all">
<div class="shuiping">
<h3>水平居中方式:</h3>
<h4>第一种方式: margin:auto</h4>
<div class="content">
<div class="margin-center item"></div>
</div>
<h4>第二种方式: 使用inline-block 和 text-align实现 </h4>
<div class="content content2">
<div class="item block-center"></div>
</div>
<h4>第三种方式: 使用绝对定位 实现 </h4>
<div class="content content3">
<div class="item absolute-center"></div>
</div>
<h4>第四种方式: 使用flex布局 实现 </h4>
<div class="content content4">
<div class="item"></div>
</div>
</div>
<div class="chuizhi">
<h3>垂直居中方式:</h3>
<h4>第一种方式:使用display:table-cell来实现</h4>
<div class="Ccontent Ccontent1">
<div class="item2"></div>
</div>
<h4>第二种方式:使用line-height、 inline-block 来实现</h4>
<div class="Ccontent Ccontent2">
<div class="item2 vertical-center"></div>
</div>
<h4>第三种方式:使用flex布局 来实现</h4>
<div class="Ccontent Ccontent3">
<div class="item2"></div>
</div>
<h4>第四种方式:使用 绝对定位 来实现</h4>
<div class="Ccontent Ccontent4">
<div class="item2 abs-center"></div>
</div>
</div>
<div class="shuipingcuizhi">
<h3>水平 + 垂直居中方式:</h3>
<h4>第一种方式:使用absolute绝对定位 来实现</h4>
<div class="SCcontent SCcontent1 ">
<div class="item3 abso-center"></div>
</div>
<h4>第二种方式:使用flex布局来实现</h4>
<div class="SCcontent SCcontent2 ">
<div class="item3"></div>
</div>
<h4>第三种方式:用inline-block.text-align和vertical-align来实现</h4>
<div class="SCcontent SCcontent3 ">
<div class="item3 SCitem3"></div>
</div>
<h4>第四种方式:table-cell+display: inline-block来实现</h4>
<div class="SCcontent SCcontent4 ">
<div class="item3 SCitem4"></div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
4.10.提示框
实现一个提示框,练练手
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<style>
.main{
position: relative;
display: inline-block;
}
.main:hover .jian{
visibility: visible;
}
.jian{
color: white;
text-align: center;
visibility: hidden;
top: -5px;
left: 120%;
padding-top: 5px;
background-color: black;
border-radius: 6px;
width: 200px;
height: 30px;
position: absolute;
}
.jian::after{
position: absolute;
content: "";
top: 50%;
right: 100%;
transform: translateY(-50%);
z-index: 1;
border-width: 5px;
border-style: solid;
border-color: transparent black transparent transparent;
}
</style>
<body>
<h1>提示框</h1>
<div class="main">
显示我
<div class="jian">
提示框成功了
</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
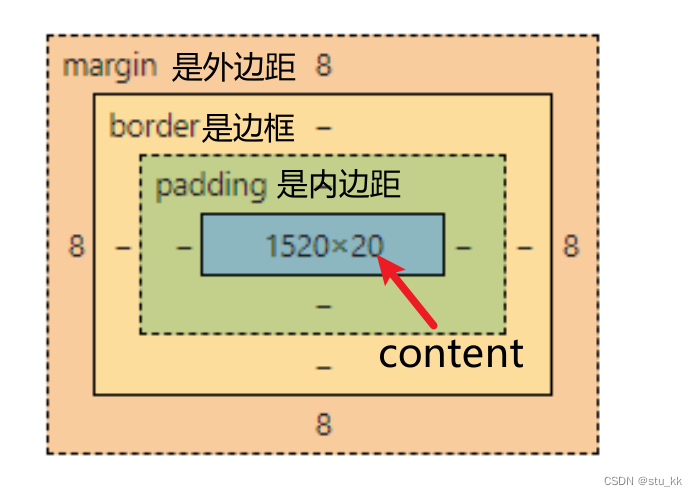
5. 盒子模型 Box Model
我们可以把每一个标签元素看成一个盒子,盒子中包括了边距、边框、填充和实际内容,盒子模型允许在盒子周围的空间放置其他元素。
6. CSS3
CSS3是CSS的技术新版本,拥有很多新的特性,下面是新的特性介绍:
6.1. CSS3边框
由三个新的边框属性:border-radius、box-shadow、border-image
border-radius:圆角
使用border-radius:10px 就可以轻易实现圆角了,值越大圆角的弧度越大。
border-image:边界图片
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>css3边框</title>
<style>
.css3-border{
/*width: 400px;*/
/*height: 400px;*/
/*background-color: #4CAF50;*/
/*border-radius: 100px;*/
border: 15px solid transparent;
border-image: url(border.png) 30 30 stretch;
/*box-shadow: 10px 10px 30px #4CAF50;*/
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="css3-border" >
你好
</div>
</body>
</html>6.2. 渐变
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<style>
.jianBian1{
width: 300px;
height: 100px;
/*上到下*/
background-image: linear-gradient(to bottom, black , pink);
}
.jianBian2{
width: 300px;
height: 100px;
/*从右到左*/
background-image: linear-gradient(to left, orange , blue);
}
.jianBian3{
width: 300px;
height: 100px;
/*对角线*/
background-image: linear-gradient(to bottom right, blanchedalmond , purple);
}
.jianBian4{
width: 300px;
height: 100px;
/* 使用角度 */
background-image: linear-gradient(-30deg, lawngreen , palegoldenrod);
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="jianBian1">
</div>
<div class="jianBian2">
</div>
<div class="jianBian3">
</div>
<div class="jianBian4">
</div>
</body>
</html>6.3. 文本效果
1.文本阴影:text-shadow
2. 文本溢出属性:text-overflow
3. text-outline
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>文本效果</title>
<style>
p{
width: 200px;
overflow: hidden;
white-space: nowrap;
text-shadow: 10px 10px 5px red;
}
.ellipsis{
/*添加省略号*/
text-overflow: ellipsis;
}
.clip{
/*直接断开*/
text-overflow: clip;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<p class="ellipsis"> 你好,如果超出的话会怎么样呢??? </p>
<p class="clip"> 你好,如果超出的话会怎么样呢??? </p>
</body>
</html>6.4. 过渡
CSS3 过渡是元素从一种样式逐渐改变为另一种的效果。
要实现这一点,必须规定两项内容:
使用transition: 变化的属性 时间
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>过渡</title>
<style>
.transition{
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: #4CAF50;
transition: background-color 2s, width 2s, height 2s, transform 2s;
}
.transition:hover{
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background-color: purple;
transform: rotate(90deg);
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="transition">
哥们你好
</div>
</body>
</html>6.5.动画
要创建 CSS3 动画,你需要了解 @keyframes 规则。
@keyframes 规则内指定一个 CSS 样式和动画将逐步从目前的样式更改为新的样式。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<style>
.animation{
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: red;
position: relative;
/*动画名称*/
animation-name: move;
/*动画运行时间*/
animation-duration: 5s;
/*速度曲线*/
animation-timing-function: linear;
/*动画何时开始*/
animation-delay: 2s;
/*动画运行次数*/
animation-iteration-count: infinite;
/*动画再下一个周期是否逆向运行*/
animation-direction: alternate;
/*规定是否运行*/
animation-play-state: running;
}
/*设置动画*/
@keyframes move {
0% {background-color: red; left: 0px; top: 0px;}
25% {background-color: yellow; left: 200px; top: 0px;}
50% {background-color: blue; left: 200px; top: 200px;}
75% {background-color: green; left: 0px; top: 200px;}
100% {background-color: red; left: 0px; top: 0px;}
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="animation">
</div>
</body>
</html>6.6. CSS3图片
CSS3对图片样式有了新的属性:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<style>
.yuan{
/* 圆形图片 */
width: 100px;
border: solid black;
border-radius: 50%;
}
/*如果你需要自由缩放图片,且图片放大的尺寸不大于其原始的最大值,则可使用以下代码:*/
.xiangYing{
max-width: 100%;
height: auto;
}
/* 卡片式图片*/
div.polaroid{
width: 200px;
background-color: white;
box-shadow: 0 4px 8px 0 gray, 0 10px 20px 0 lightgray;
margin-bottom: 25px;
}
img.dog:hover{
opacity: 0.7;
}
div.container{
text-align: center;
padding: 5px 10px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<a href="../20231118/dog.jpg">
<img src="../20231118/dog.jpg" class="yuan" />
</a>
<h1>响应式图片</h1>
<img src="../20231118/border.png" class="xiangYing">
<h1>这是响应式卡片</h1>
<div class="polaroid">
<img src="../20231118/dog.jpg" alt="Norway" class="dog" style="width:100%;">
<div class="container">
<p>The Troll's tongue in Hardanger, Norway</p>
</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
7. 总结
通过对CSS的学习,我们可以使得html页面变得更加好看了,接下来我们就要开始学习JavaScript来操控页面元素了。
原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/m0_54409739/article/details/134421676
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。
如若转载,请注明出处:http://www.7code.cn/show_4805.html
如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系代码007邮箱:suwngjj01@126.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!