本文介绍: 【代码】有向图查询所有环,非递归。
图:
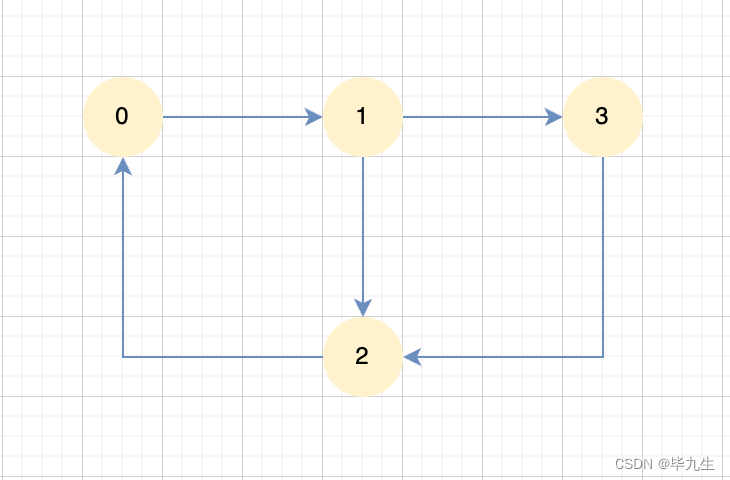
有向图查询所有环,非递归:
import java.util.*;
public class CycleTest {
private final int V; // 顶点数
private final List<List<Integer>> adjList; // 邻接表
public CycleTest(int vertices) {
this.V = vertices;
this.adjList = new ArrayList<>(vertices);
for (int i = 0; i < vertices; i++) {
adjList.add(new LinkedList<>());
}
}
// 添加有向边
public void addEdge(int src, int dest) {
adjList.get(src).add(dest);
}
// 查找所有环
public List<List<Integer>> findAllCycles() {
List<List<Integer>> cycles = new ArrayList<>();
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>();
Stack<Integer> pathStack = new Stack<>();
Stack<Integer> neighborPoint = new Stack<>();
Stack<Integer> levelStack = new Stack<>();
boolean[] visited = new boolean[V];
int level = 1;
for (int startVertex = 0; startVertex < V; startVertex++) {
if (visited[startVertex]) {
continue;
}
stack.push(startVertex);
pathStack.push(startVertex);
while (!stack.isEmpty() || !neighborPoint.isEmpty()) {
if (stack.isEmpty()) {
int l = levelStack.pop();
// 返回上一个邻接点搜索
Integer p = neighborPoint.pop();
stack.push(p);
while (pathStack.size() >= l) {
pathStack.pop();
}
pathStack.push(p);
level--;
}
int vertex = stack.pop();
List<Integer> neighbors = adjList.get(vertex);
for (int i = 0; i < neighbors.size(); i++) {
Integer neighbor = neighbors.get(i);
if (i == 0) {
if (!pathStack.contains(neighbor)) {
stack.push(neighbor);
pathStack.push(neighbor);
} else {
// 找到环
List<Integer> cycle = new ArrayList<>();
List<Integer> path = pathStack.stream().toList();
for(int j = path.size() - 1; j >= 0; j--) {
Integer p = path.get(j);
cycle.add(p);
visited[p] = true;
if (Objects.equals(p, neighbor)) {
break;
}
}
Collections.reverse(cycle);
cycles.add(cycle);
}
level++;
} else {
// 存储邻接点
neighborPoint.push(neighbor);
levelStack.push(level);
}
}
}
// 清除路径栈状态
pathStack.clear();
levelStack.clear();
level = 1;
}
return cycles;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
CycleTest graph = new CycleTest(4);
graph.addEdge(0, 1);
graph.addEdge(1, 2);
graph.addEdge(2, 0);
graph.addEdge(1, 3);
graph.addEdge(3, 2);
List<List<Integer>> cycles = graph.findAllCycles();
System.out.println("Cycles in the directed graph:");
for (List<Integer> cycle : cycles) {
System.out.println(cycle);
}
}
}
结果:

原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_39400984/article/details/135953682
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。
如若转载,请注明出处:http://www.7code.cn/show_64149.html
如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系代码007邮箱:suwngjj01@126.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
声明:本站所有文章,如无特殊说明或标注,均为本站原创发布。任何个人或组织,在未征得本站同意时,禁止复制、盗用、采集、发布本站内容到任何网站、书籍等各类媒体平台。如若本站内容侵犯了原著者的合法权益,可联系我们进行处理。




![[C#]IL指令](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/img_convert/913effb50dcaac79f9ee7413e2d4af77.png)
