二叉搜索树
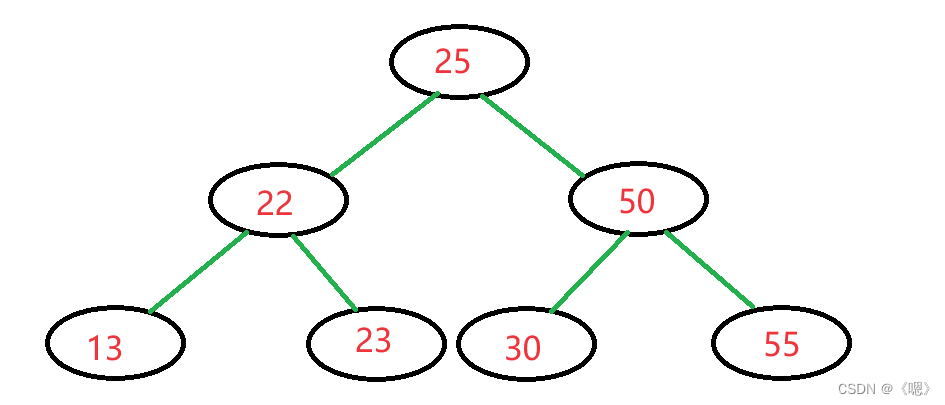
二叉搜索树的插入
public class BinarySearchTree {
//描述节点的内部类
public static class TreeNode {
public int key;
public TreeNode left;
public TreeNode right;
TreeNode(int key) {
this.key = key;
}
}
//搜索树的根节点
public TreeNode root;
}添加一个插入元素的方法,注:二叉搜索树的插入只会出现在null节点处,也就是插入的新节点都会成为搜索书的叶子节点 。
public class BinarySearchTree {
public static class TreeNode {
public int key;
public TreeNode left;
public TreeNode right;
TreeNode(int key) {
this.key = key;
}
}
public TreeNode root;
/**
* 插入一个元素
*/
public boolean insert(int key) {
TreeNode tmp = new TreeNode(key);
//树如果为空就直接令其成为根节点
if (this.root == null) {
this.root = tmp;
//插入成功返回true
return true;
}
TreeNode parent = this.root;
TreeNode p1 = this.root;
//寻找新元素的插入位置
while (p1 != null) {
parent = p1;
if (p1.key > key) {
p1 = p1.left;
}else {
p1 = p1.right;
}
}
//插入新元素
if (parent.key > key) {
parent.left = tmp;
}else {
parent.right = tmp;
}
//插入成功返回true
return true;
}
}二叉搜索树的查找
在二叉搜索树中查找一个元素分为两步:
//查找key是否存在
public TreeNode search(int key) {
//判断树是否为空,为空就直接返回null
if (this.root == null){
return null;
}
TreeNode tmp = this.root;
while (tmp != null) {
if (tmp.key > key) {
tmp = tmp.left;
}else if (tmp.key < key) {
tmp = tmp.right;
}else {
//找到该元素后将其作为返回值返回
return tmp;
}
}
//当出循环之后代表没找到该元素返回null
return null;
}二叉搜索树的删除
二叉搜索树的删除相比于插入和查找还是比较复杂的,因为要保证删除待删除结点之后,树依旧是一颗二叉搜索树。
分两种情况:
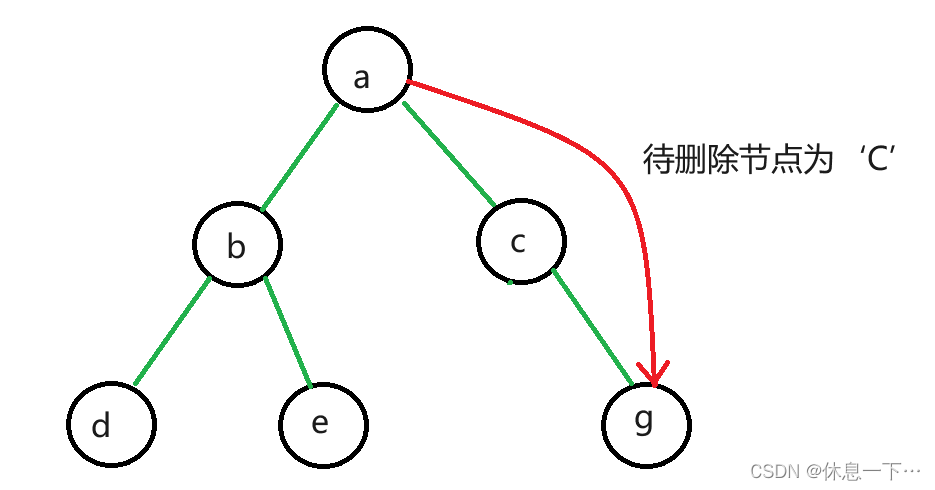
//删除key的值
public boolean remove(int key) {
if (this.root == null) {
return false;
}
TreeNode tmp = this.root;
TreeNode privat = tmp;
//寻找待删除节点
while (tmp != null) {
if (tmp.key > key) {
privat = tmp;
tmp = tmp.left;
}else if (tmp.key < key) {
privat = tmp;
tmp = tmp.right;
}else {
break;
}
}
if (tmp == null) {
return false;
}
//判断待删除节点是否只有一颗子树
if (tmp.left == null || tmp.right == null) {
判断该子树为左右哪颗子树
if (tmp.left == null) {
if (tmp == this.root) {
this.root = tmp.right;
}else {
if (privat.left == tmp) {
privat.left = tmp.right;
}else {
privat.right = tmp.right;
}
}
}else {
if (tmp == this.root) {
this.root = tmp.left;
}else {
if (privat.left == tmp) {
privat.left = tmp.left;
}else {
privat.right = tmp.left;
}
}
}
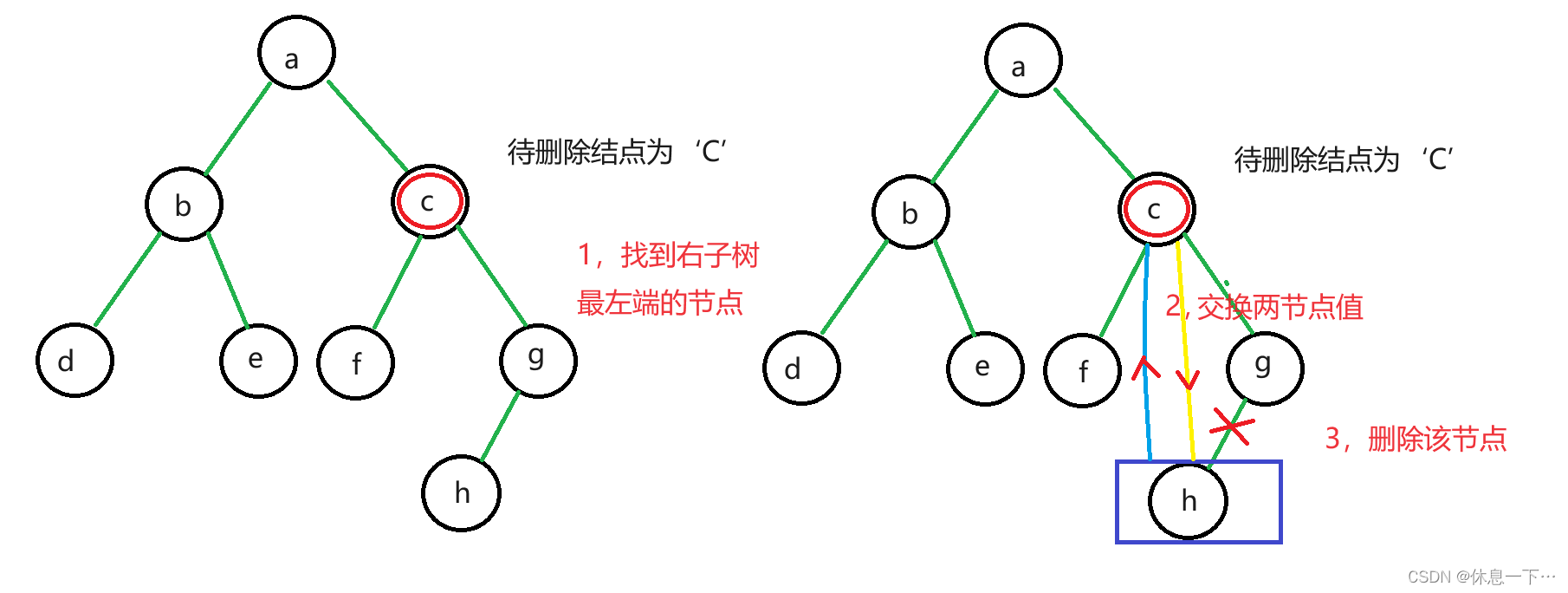
}else {
//待删除节点有两棵子树时
//寻找右子树的最左端的节点
TreeNode a = tmp.right;
while(a.left != null) {
privat = a;
a = a.left;
}
//将右子树的最左端的节点的值赋值给待删除节点
tmp.key = a.key;
//删除右子树的最左端的节点
if (privat.left == a) {
privat.left = a.right;
}else {
privat.right = a.right;
}
}
return true;
}性能分析:
最好情况下:当前二叉搜索树为一颗完全二叉树,查找效率为树的高度,即O()。
最坏情况下:当前二叉搜索树为一颗单分支的树,查找效率为O(N)。
哈希表
在顺序结构和平衡树中,顺序查找时间复杂度为O(N),平衡树中为树的高度,即O()。
而哈希表是一种插入/删除/查找时间复杂度都是O(1)的数据结构,它的查询之所以也可以如此之快的的原因就是它在查找时不需要经过任何比较,直接一次从表中得到要搜索的元素。
实现这种数据结构的方法就是通过某种函数使元素的存储位置与它的关键码之间能够建立一一对应的映射关系,在查找时通过该函数就可以很快找到该元素。而这种数据结构被称作哈希表或散列表,这种函数被称为哈希(散列)函数。
哈希函数的设计有以下要求:
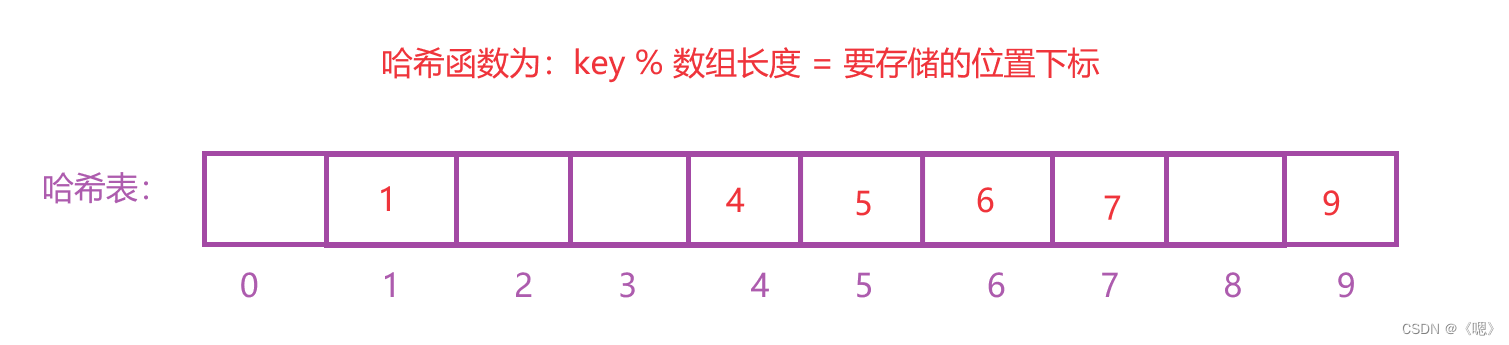
存入的时候将每个元素都带入哈希函数计算出下标然后插入,查找时也是同理。
但是此时又出现了一个新问题如果此时要插入元素15 就会发现没地方可以放了,而这也是哈希表中经常会发生的问题,被称为:哈希冲突或哈希碰撞。
哈希冲突
- 采用更优的哈希函数,哈希函数设计的越精妙,产生哈希冲突的可能性就越低,但是无法避免哈希冲突;
- 减小负载因子(负载因子 = 填入表中的元素个数 / 表的大小 JDK中负载因子被设置成里0.75)也就是增大哈希表的存储地址。
闭散列
闭散列也叫开放定址法,当发生哈希冲突时,如果哈希表未被装满,说明在哈希表中必然还有空位置,那么可以把key存放到冲突位置中的“下一个” 空位置中去。
常见的闭散列有两种:
线性探测法
线性探测:从发生冲突的位置开始,依次向后探测,直到寻找到下一个空位置为止。
例如在前面的例子中插入元素14:
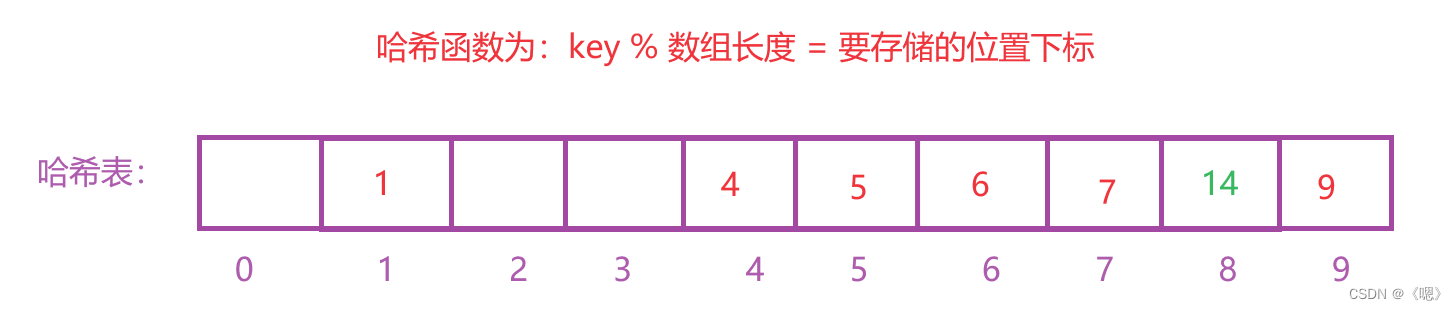
因为下标为4的地方已经有值了,所以就看下一个位置即下标为5的地方,此处因为也有值所以继续向后寻找直到出现空位。
线性探测的缺陷:产生冲突的数据会堆积在一起,这与其找下一个空位置的方式关系,因为找空位置的方式就是挨着往后逐个去找。
二次探测法
二次探测法的本质与线性探测法相同,它们的区别是当发生哈希冲突时找下一个空位置的方法不同。
二次探测法找空位置的方法为: % m 其中:i = 1,2,3…, H0是通过散列函数对元素的关键码 key 进行计算得到的位置其中m是表的大小。
例如在前面的例子中插入元素14:

虽然插入位置和线性探测法相同但是原理不同:
- 先计算得到插入位置H0 = 4,因为4下标处已有值所以带入利用
% m 公式代入i=1;
- 计算得到的新下标为5,但5下标处也有值所以带入i = 2;
- 计算得到新下标为8,插入;
但是闭散列还有一个问题:如果此时删除元素4那么就找不到元素14了。
开散列
开散列法又叫链地址法(开链法),首先对关键码集合用散列函数计算散列地址,具有相同地址的关键码归于同一子集合,每一个子集合称为一个桶,各个桶中的元素通过一个单链表链接起来,各链表的头结点存储在哈希表中。
比如采用开散列的方式存储集合{1,7,6,4,5,9,14}
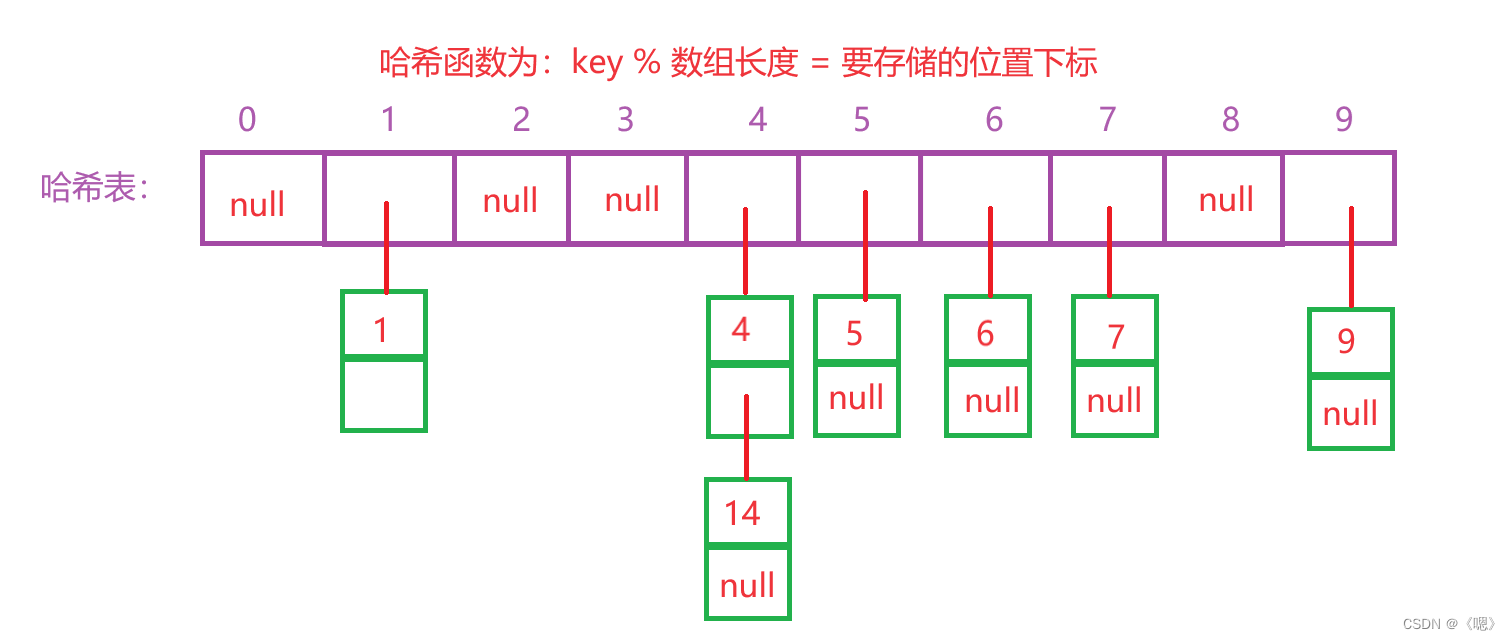
而开散列最重要的是控制负载因子,因为当负载因子过大就无法使哈希表的速度达到O(1)。JAVA中的哈希表就是采用的开散列的方式,在JDK中负载因子为0.75。
开散列代码实现:
散列函数和上面的例子相同
class MyHash{
//哈希表中存储元素的节点
static class node{
public int data;
public node next;
public node(int data) {
this.data = data;
}
}
//哈希表,默认大小为10
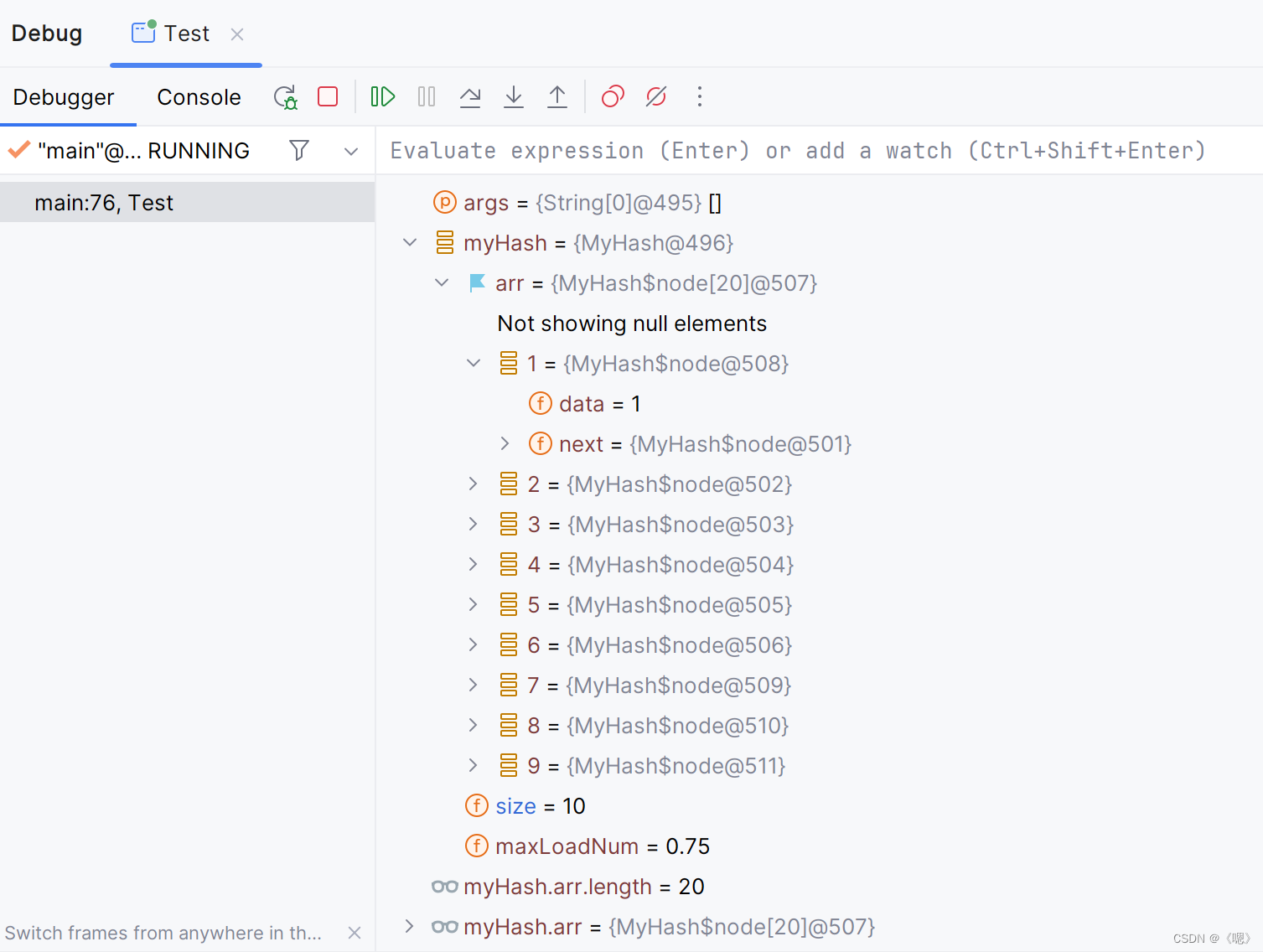
node[] arr = new node[10];
//数组中的元素个数
int size = 0;
//最大负载因子,默认为0.75
double maxLoadNum = 0.75;
}插入元素
加入插入元素的方法,注:开散列最重要的是控制负载因子,因为当负载因子过大就无法使哈希表的速度达到O(1)所以插入元素之后必须进行负载因子的判断:
public void insert(int data) {
//先利用散列函数计算出插入位置
int index = data % this.arr.length;
//创建节点
node tmp = new node(data);
if (this.arr[index] == null) {
this.arr[index] = tmp;
}else {
//头插法
tmp.next = this.arr[index];
this.arr[index] = tmp;
}
this.size++;
//计算负载因子是否过大,如果过大就必须进行扩容,然后将所有元素重新哈希
if (((double)this.size / this.arr.length) >= this.maxLoadNum) {
this.size = 0;
node[] arr1 = new node[this.arr.length * 2];
for (int i = 0; i < this.arr.length; i++) {
while (this.arr[i] != null) {
int index1 = this.arr[i].data % arr1.length;
node tmp1 = this.arr[i];
//在原表中删除该节点
this.arr[i] = this.arr[i].next;
tmp1.next = null;
//将节点插入新表中
if (arr1[index1] == null) {
arr1[index1] = tmp1;
}else {
//头插法
tmp1.next = arr1[index1];
arr1[index1] = tmp1;
}
this.size++;
}
}
//用新表替换原表
this.arr = arr1;
}
} 
删除元素
public void remove (int data) {
//先利用散列函数计算出插入位置
int index = data % this.arr.length;
node p = this.arr[index];
if (p == null) {
return;
}
if (p.data == data) {
this.arr[index] = p.next;
}else {
while (p.next != null){
if (p.next.data == data) {
p.next = p.next.next;
break;
}
p = p.next;
}
}
}查找元素
//找到该元素返回该元素的值,没找到返回-1
public int check(int data) {
//先利用散列函数计算出插入位置
int index = data % this.arr.length;
node p = this.arr[index];
if (p == null) {
return -1;
}
while (p != null){
if (p.data == data) {
return p.data;
}
p = p.next;
}
return -1;
}原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/2302_76339343/article/details/133500003
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。
如若转载,请注明出处:http://www.7code.cn/show_8703.html
如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系代码007邮箱:suwngjj01@126.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!