为什么尝试使用Tencent Cloud VectorDB替换Milvus向量库?
亮点:Tencent Cloud VectorDB支持Embedding,免去自己搭建模型的负担(搭建一个生产环境的模型实在耗费精力和体力)。
腾讯云向量数据库是什么?
腾讯云向量数据库是一款全托管的自研企业级分布式数据库服务,专用于存储、检索、分析多维向量数据。该数据库支持多种索引类型和相似度计算方法,单索引支持10亿级向量规模,可支持百万级 QPS 及毫秒级查询延迟。腾讯云向量数据库不仅能为大模型提供外部知识库,提高大模型回答的准确性,还可广泛应用于推荐系统、NLP 服务、计算机视觉、智能客服等 AI 领域。
Milvus是什么?
Milvus是在2019年创建的,其唯一目标是存储、索引和管理由深度神经网络和其他机器学习(ML)模型生成的大规模嵌入向量。作为一个专门设计用于处理输入向量查询的数据库,它能够处理万亿级别的向量索引。与现有的关系型数据库主要处理遵循预定义模式的结构化数据不同,Milvus从底层设计用于处理从非结构化数据转换而来的嵌入向量。
项目展示
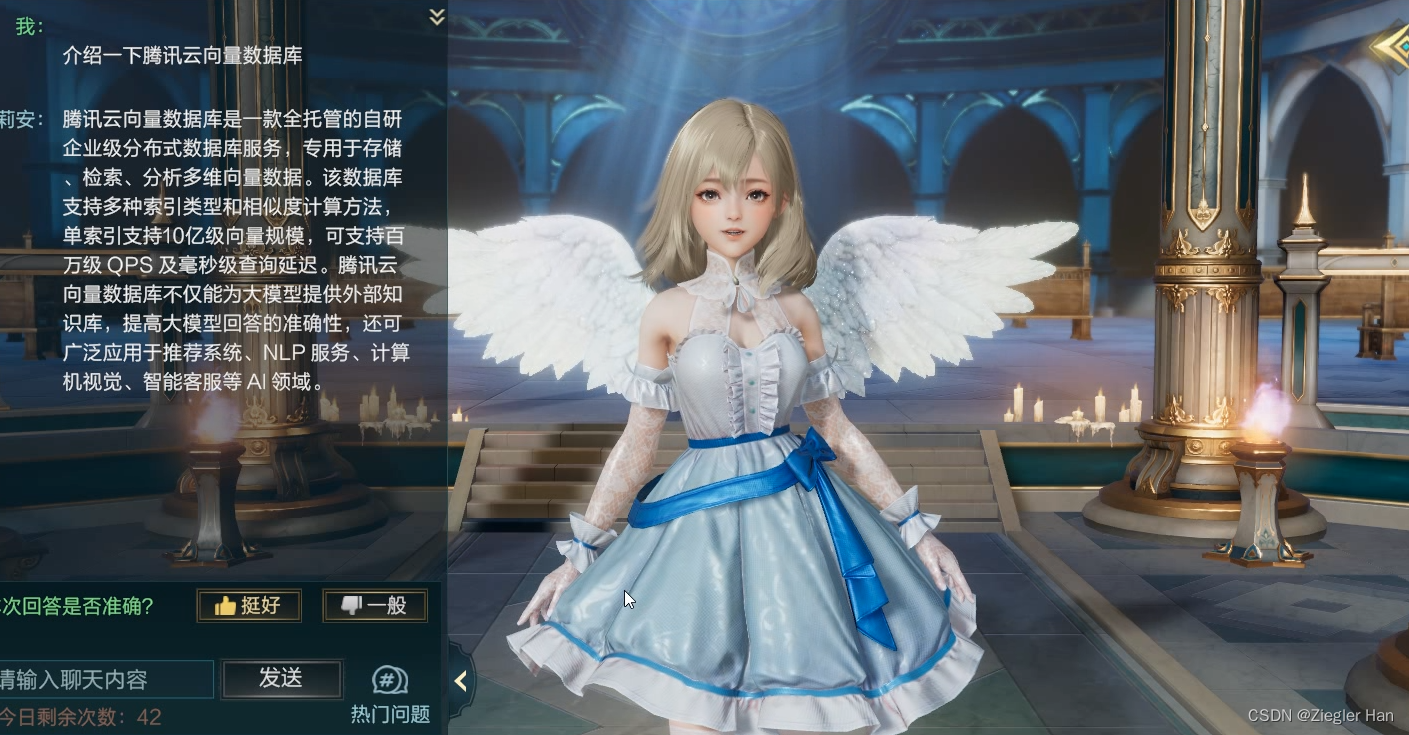
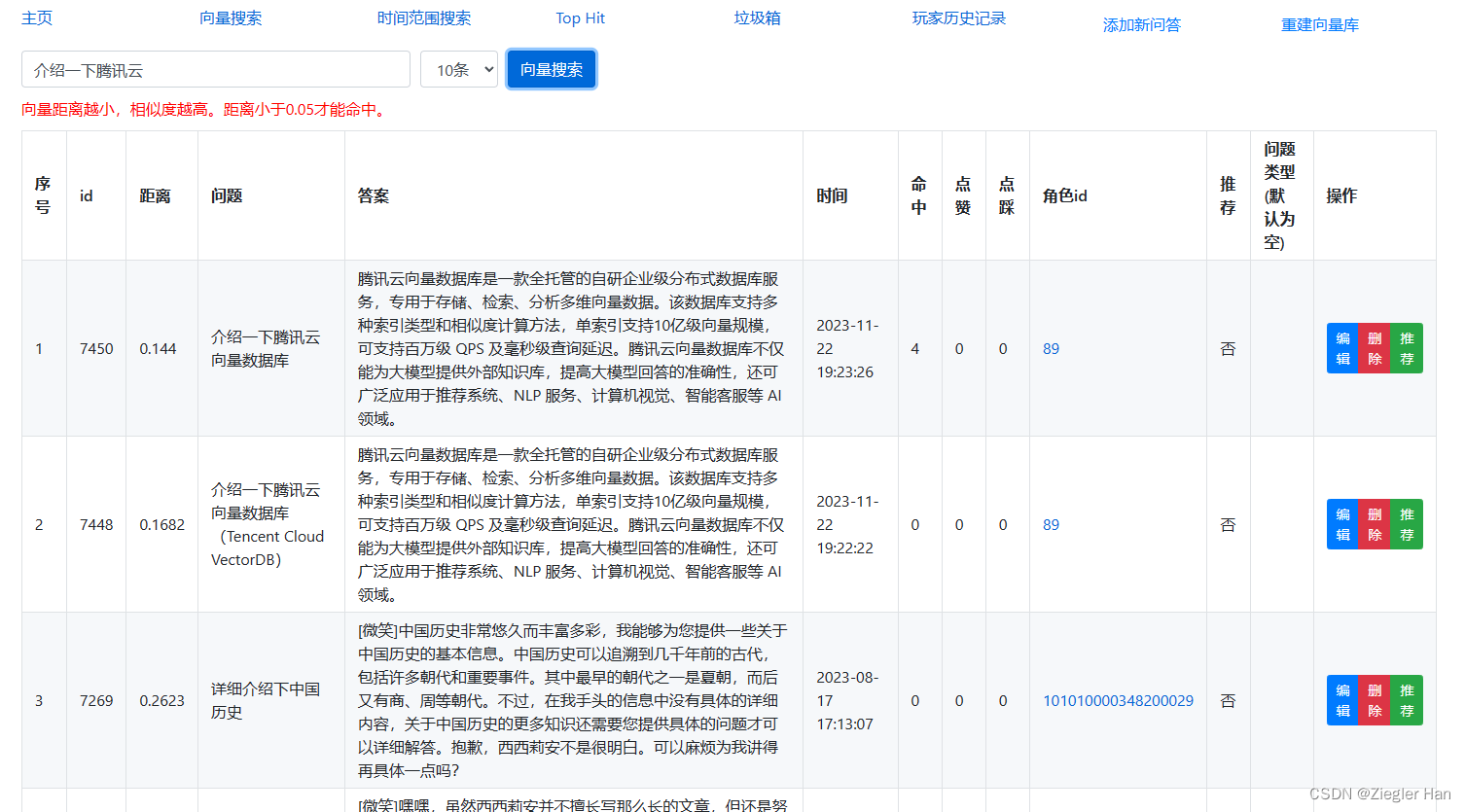
项目介绍游戏内部接入ChatGPT的智能NPC,可以与她进行语音交流。可以回答与游戏相关的问题(这个专业问题是为了编写这个文章,专门添加到问答缓存库中的,游戏内会拒绝回答此类问题)。为了加快ChatGPT的回复速度和降低ChatGPT的费用,增加问答缓存机制。这里运用向量数据库的相似文本相似度高的特性,通过向量搜索,匹配相似度大于一定值,例如:0.95。搜索到相似问题,直接返回答案,不在进行ChatGPT访问。
其次,存在缓存,针对相似问题,还可以给予特定回复答案。例如上面示例,当提问“介绍一下腾讯向量数据库”,直接回复“腾讯云向量数据库是一款全托管的自研企业级分布式数据库服务,专用于存储、检索、分析多维向量数据。该数据库支持多种索引类型和相似度计算方法,单索引支持10亿级向量规模,可支持百万级 QPS 及毫秒级查询延迟。腾讯云向量数据库不仅能为大模型提供外部知识库,提高大模型回答的准确性,还可广泛应用于推荐系统、NLP 服务、计算机视觉、智能客服等 AI 领域。”
为什么使用向量数据库?
重点:速度
向量相似度匹配是很长的数组,例如:bge-large-zh模型文本转向量,生成的是768维的float数组。拿问题文本转换为的768维向量与缓存的所有问题的向量进行相似性计算,然后获取最相似的几条数据,这个运算量非常大,速度非常慢。
测试代码:
与300个768维向量进行相似比对,获取最相似的一条数据,耗时几秒钟。按照这个速度,如果与几千上万条数据进行这么计算,简直无法忍受。
这时就必须使用向量数据库了,向量数据库可以支持毫秒级检索上百万行数据。本人曾使用Milvus数据库,分别插入1000行数数据和插入10万行数据,然后进行搜索对比,都在几十毫秒返回结果,数据量的增多,对检索速度几乎没有任何影响。
本项目哪里需要使用向量数据库?
使用腾讯云向量数库(Tencent Cloud VectorDB)的优点?
- 支持Embedding:腾讯云向量数据库(Tencent Cloud VectorDB)提供将非结构化数据转换为向量数据的能力,目前已支持文本 Embedding 模型,能够覆盖多种主流语言的向量转换,包括但不限于中文、英文。对于小型项目这是一个非常大的优势。可以降低自己搭建embedding模型或者使用第三方embedding模型的成本。
- FilterIndex的field_type支持数据类型简单:只有String和Uint64,使用起来非常省心。而Milvus数据支持10几种类型,对于初学者不友好,还要研究具体如何使用。
指定 Filter 字段的数据类型。取值如下:
String:字符型。若 name 为 id,则该参数固定为 FieldType.String。
Uint64:指无符号整数,该参数可设置为 FieldType.Uint64。
研究Tencent Cloud VectorDB,测试并封装代码库my_tc_vector_db.py
if __name__ == '__main__':
# 初始化
myTcVectorDB = MyTcVectorDB("http://****************.tencentclb.com:30000", "root",
"2epSOV3HK6tiyALo6UqE3mGV**************")
# 删除数据库
myTcVectorDB.drop_collection("db-qa", "question_768")
myTcVectorDB.drop_database("db-qa")
# 创建数据库
myTcVectorDB.create_database("db-qa")
# 创建索引和embedding,并创建集合
index = Index(
FilterIndex(name='id', field_type=FieldType.String, index_type=IndexType.PRIMARY_KEY),
FilterIndex(name='question', field_type=FieldType.String, index_type=IndexType.FILTER),
VectorIndex(name='vector', dimension=768, index_type=IndexType.HNSW,
metric_type=MetricType.COSINE, params=HNSWParams(m=16, efconstruction=200))
)
embedding = Embedding(vector_field='vector', field='text', model=EmbeddingModel.BGE_BASE_ZH)
collection = myTcVectorDB.create_collection("db-qa", "question_768", index, embedding)
# 批量插入
myTcVectorDB.upsert("db-qa", "question_768", [Document(id='0001', text='罗贯中', question='罗贯中'),
Document(id='0002', text='吴承恩', question='吴承恩'),
Document(id='0003', text='曹雪芹', question='曹雪芹'),
Document(id='0004', text='郭富城', question='郭富城')])
# 单条插入
myTcVectorDB.upsert_one("db-qa", "question_768", id='0005', text='周杰伦', question='周杰伦')
myTcVectorDB.upsert_one("db-qa", "question_768", id='0006', text='林俊杰', question='林俊杰')
# 删除0003
myTcVectorDB.delete_by_id("db-qa", "question_768", "0003")
# 文本搜索(无需向量转换)
text = myTcVectorDB.search_by_text("db-qa", "question_768", "郭富城")
# 打印结果
print_object(text)
# 仅打印id
if len(text[0]) > 0:
for i in text[0]:
print(i['id'])
-
重新创建数据库db-qa
-
指定索引和embedding,并创建集合question_768:这里指定id为主键、question为FilterIndex标量索引,vector为VectorIndex向量索引(注意官方文档说明:指定向量索引字段名,固定为 vector。)因为使用中文检索,Embedding使用BGE_BASE_ZH。

MyTcVectorDB库代码
import json
import tcvectordb
from tcvectordb.model.collection import Embedding
from tcvectordb.model.document import Document, SearchParams
from tcvectordb.model.enum import ReadConsistency, MetricType, FieldType, IndexType, EmbeddingModel
from tcvectordb.model.index import Index, FilterIndex, VectorIndex, HNSWParams
class MyTcVectorDB:
def __init__(self, url: str, username: str, key: str, timeout: int = 30):
self._client = tcvectordb.VectorDBClient(url=url, username=username, key=key,
read_consistency=ReadConsistency.EVENTUAL_CONSISTENCY, timeout=timeout)
def create_database(self, database_name: str):
"""
Create a database
:param database_name: database name
:return: database
"""
return self._client.create_database(database_name=database_name)
def drop_database(self, database_name: str):
"""
Drop a database
:param database_name: database name
:return: result
"""
return self._client.drop_database(database_name=database_name)
def create_collection(self, db_name: str, collection_name: str, index: Index, ebd: Embedding):
db = self._client.database(db_name)
# 第二步,创建 Collection
coll = db.create_collection(
name=collection_name,
shard=1,
replicas=0,
description='this is a collection of question embedding',
index=index,
embedding=ebd
)
return coll
def drop_collection(self, db_name: str, collection_name: str):
"""
Drop a collection
:param db_name: db name
:param collection_name: collection name
:return: result
"""
db = self._client.database(db_name)
return db.drop_collection(collection_name)
def upsert_one(self, db_name: str, collection_name: str, **kwargs):
"""
Upsert one document to collection
:param db_name : db name
:param collection_name: collection name
:param document: Document
:return: result
"""
db = self._client.database(db_name)
coll = db.collection(collection_name)
res = coll.upsert(documents=[Document(**kwargs)])
return res
def upsert(self, db_name: str, collection_name: str, documents):
"""
Upsert documents to collection
:param db_name : db name
:param collection_name: collection name
:param documents: list of Document
:return: result
"""
db = self._client.database(db_name)
coll = db.collection(collection_name)
res = coll.upsert(documents=documents)
return res
def search_by_text(self, db_name: str, collection_name: str, text: str, limit: int = 10):
"""
Search documents by text
:param db_name : db name
:param collection_name: collection name
:param text: text
:return: result
"""
db = self._client.database(db_name)
coll = db.collection(collection_name)
# searchByText 返回类型为 Dict,接口查询过程中 embedding 可能会出现截断,如发生截断将会返回响应 warn 信息,如需确认是否截断可以
# 使用 "warning" 作为 key 从 Dict 结果中获取警告信息,查询结果可以通过 "documents" 作为 key 从 Dict 结果中获取
res = coll.searchByText(embeddingItems=[text],
params=SearchParams(ef=200),
limit=limit)
return res.get('documents')
def delete_by_id(self, db_name: str, collection_name: str, document_id):
"""
Delete document by id
:param db_name : db name
:param collection_name: collection name
:param document_id: document id
:return: result
"""
db = self._client.database(db_name)
coll = db.collection(collection_name)
res = coll.delete(document_ids=[document_id])
return res
def print_object(obj):
"""
Print object
"""
for elem in obj:
# ensure_ascii=False 保证中文不乱码
if hasattr(elem, '__dict__'):
print(json.dumps(vars(elem), indent=4, ensure_ascii=False))
else:
print(json.dumps(elem, indent=4, ensure_ascii=False))
开始动手使用Tencent Cloud VectorDB在项目中替换Milvus
1、创建问题库db-qa和集合question_768
# 初始化
myTcVectorDB = MyTcVectorDB("http://****tencentclb.com:30000", "root",
"2epSOV3HK6tiyALo6UqE3mGVMbpP*******")
# 创建数据库
myTcVectorDB.create_database("db-qa")
# 创建索引和embedding,并创建集合
index = Index(
FilterIndex(name='id', field_type=FieldType.String, index_type=IndexType.PRIMARY_KEY),
FilterIndex(name='question', field_type=FieldType.String, index_type=IndexType.FILTER),
VectorIndex(name='vector', dimension=768, index_type=IndexType.HNSW,
metric_type=MetricType.COSINE, params=HNSWParams(m=16, efconstruction=200))
)
embedding = Embedding(vector_field='vector', field='text', model=EmbeddingModel.BGE_BASE_ZH)
collection = myTcVectorDB.create_collection("db-qa", "question_768", index, embedding)
2、游戏端和后台文本向量搜索,用MyTcVectorDB替换Milvus
两处代码基本一致。这里去掉文本转向量的步骤,因为TcVectorDB支持Embedding
# 获取问题转换后的向量
# success, vector = get_vector_from_text(question)
# if not success:
# return {"code": -1, "id": 0, "answer": "向量计算失败"}
# results = questionCollection.search(vector, limit)
results = myVectorDB.search_by_text("db-qa", "question_768", question, limit)
...
上面代码需要注意一点,腾讯向量数据的search结果与milvus的搜索结果是不一样的,需要做一下适配。
3、重建向量数据库
问答缓存的数据保存在mysql数据库,向量数据库主要作用是向量搜索。如果更换向量库,只需要重建向量库即可。下面代码:
def rebuild_vector():
# 查找所有的数据
select_all = qaTable.select_all_qa()
# 遍历所有的数据
for qa in select_all:
insertId = qa[0]
question = qa[1]
timestamp = int(time.time())
print(question)
# 计算向量
# 更新向量
# success, vector = get_vector_from_text(question)
# if not success:
# # 向量计算失败,question
# logging.error("向量计算失败,insertId:%s, question:%s", insertId, question)
# continue
# # 删除原有的向量
# questionCollection.delete_question(insertId)
# # 插入新的向量
# questionCollection.insert_question(insertId, vector, question, timestamp)
myVectorDB.delete_by_id("db-qa", "question_768", str(insertId))
myVectorDB.upsert_one("db-qa", "question_768", id=str(insertId), text=question, question=question)
return "重建向量库成功"
4、修改后台展示,看下修改后的效果图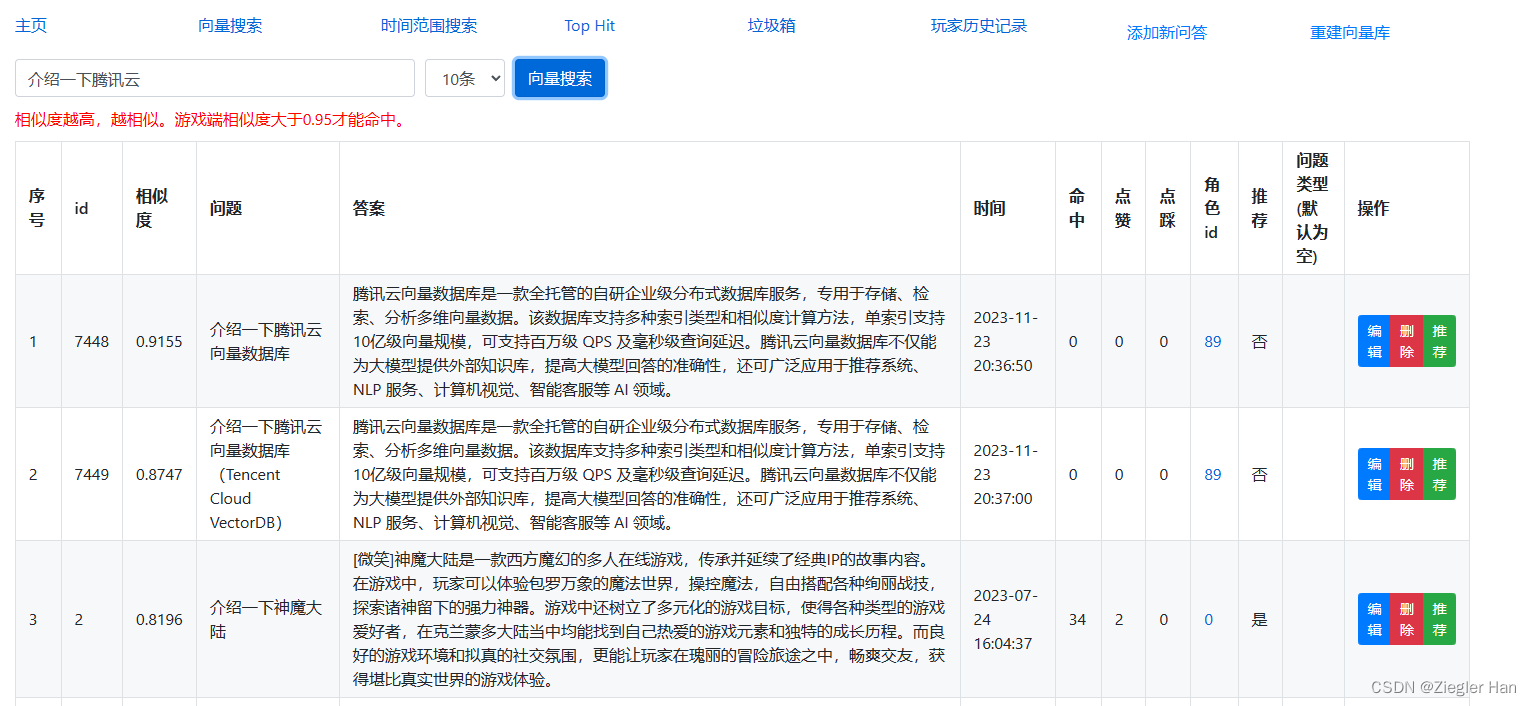
- 使用的文本转向量的模型是:BGE_BASE_ZH
- 向量索引是:VectorIndex(name=‘vector’, dimension=768, index_type=IndexType.HNSW, metric_type=MetricType.COSINE, params=HNSWParams(m=16, efconstruction=200))
- 搜索文本返回结果代表的是相似度,保存在score中。
总结:
- 使用腾讯向量数据库要比使用Milvus更加简单易用,无需自己部署服务器。
- 腾讯云向量库支持主流Embedding,直接支持文本向量搜索,避免自己部署Embedding模型,并避免调用文本转向量的过程。对于开发者来说非常便利。
如果是个人,或者小型项目开发,非常值得使用腾讯云数据库。如果是大型项目,不缺钱的话也非常推荐使用腾讯云数据库,稳定、高效且安全。
原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_40677588/article/details/134469818
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。
如若转载,请注明出处:http://www.7code.cn/show_16155.html
如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系代码007邮箱:suwngjj01@126.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!