Runtime源码解析–alloc
前言
- 从这篇文章开始,我们进行
OC底层研究。主要研究方向包括了:对象和类的具体实现,属性、方法、协议等是如何存储的,方法是如何调用,类和category是如何加载,weak是如何实现的等等一些问题 - 本系列博客所用的是818.2版本的
objc4源码(目前最新版)
alloc
@interface Test : NSObject
@end
@implementation Test
@end
- (void)viewDidLoad {
[super viewDidLoad];
Test *test = [Test alloc];
}
通过汇编查看调用流程
- 首先通过
Debug->Debug Workflow->Always Show Disassembly,打开汇编 - 然后在
Test *test1 = [Test alloc];添加断点。


1. objc_alloc方法
id
objc_alloc(Class cls)
{
return callAlloc(cls, true/*checkNil*/, false/*allocWithZone*/);
}
2. callAlloc方法
static ALWAYS_INLINE id
callAlloc(Class cls, bool checkNil, bool allocWithZone=false)
{
#if __OBJC2__ // 判断是否是否objc2.0版本,目前所采用都是2.0版本
if (slowpath(checkNil && !cls)) return nil;
if (fastpath(!cls->ISA()->hasCustomAWZ())) {
return _objc_rootAllocWithZone(cls, nil);
}
#endif
// No shortcuts available.
if (allocWithZone) {
return ((id(*)(id, SEL, struct _NSZone *))objc_msgSend)(cls, @selector(allocWithZone:), nil);
}
return ((id(*)(id, SEL))objc_msgSend)(cls, @selector(alloc));
}
#define fastpath(x) (__builtin_expect(bool(x), 1)) // fastpath(x):x很可能为真
#define slowpath(x) (__builtin_expect(bool(x), 0)) // slowpath(x):x很可能为假,为真的概率很小
首次进入
- 会接着进入
alloc方法
+ (id)alloc {
return _objc_rootAlloc(self);
}
id
_objc_rootAlloc(Class cls)
{
return callAlloc(cls, false/*checkNil*/, true/*allocWithZone*/);
}
非首次进入
LLVM优化
- 这里为什么会走两次
callAlloc方法?为什么alloc方法需要先调用objc_alloc然后再调用alloc。 - 这里是苹果在LLVM中做了操作,会给
alloc方法,添加一个hook方法objc_alloc。让每第一次走到alloc方法,都先走到object_alloc方法。只有走过这个方法后,再去调用真正的alloc方法。 - 苹果在
objc_alloc方法做一些额外操作,比如ARC相关,类型转换等,方便苹果做一些监控,以及优化。
3. _objc_rootAllocWithZone方法
NEVER_INLINE
id
_objc_rootAllocWithZone(Class cls, malloc_zone_t *zone __unused)
{
// allocWithZone under __OBJC2__ ignores the zone parameter
return _class_createInstanceFromZone(cls, 0, nil,
OBJECT_CONSTRUCT_CALL_BADALLOC);
}
4. _class_createInstanceFromZone方法
static ALWAYS_INLINE id
_class_createInstanceFromZone(Class cls, size_t extraBytes, void *zone,
int construct_flags = OBJECT_CONSTRUCT_NONE,
bool cxxConstruct = true,
size_t *outAllocatedSize = nil)
{
ASSERT(cls->isRealized());
// Read class's info bits all at once for performance
bool hasCxxCtor = cxxConstruct && cls->hasCxxCtor();
bool hasCxxDtor = cls->hasCxxDtor();
bool fast = cls->canAllocNonpointer();
size_t size;
// 1. 计算需要初始化的大小
size = cls->instanceSize(extraBytes);
if (outAllocatedSize) *outAllocatedSize = size;
// 2. 开辟对应大小的内存空间
id obj;
if (zone) {
obj = (id)malloc_zone_calloc((malloc_zone_t *)zone, 1, size);
} else {
obj = (id)calloc(1, size);
}
if (slowpath(!obj)) {
if (construct_flags & OBJECT_CONSTRUCT_CALL_BADALLOC) {
return _objc_callBadAllocHandler(cls);
}
return nil;
}
// 3. 把开辟的内存和类关联起来
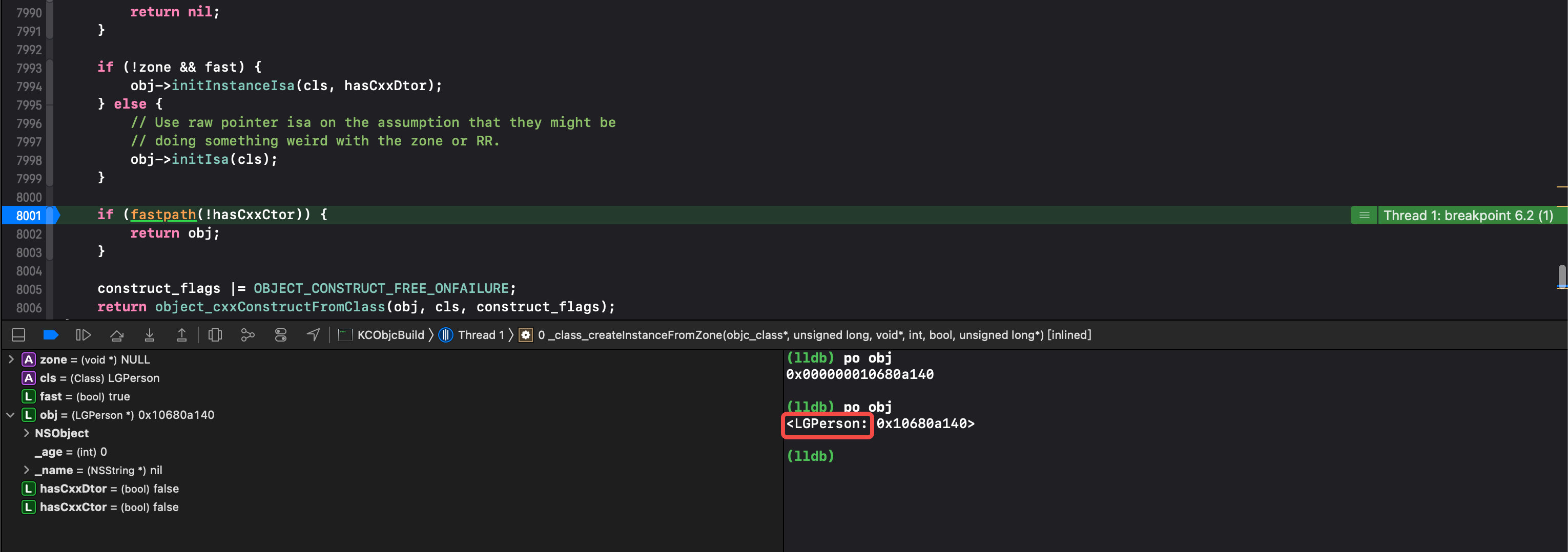
if (!zone && fast) {
obj->initInstanceIsa(cls, hasCxxDtor);
} else {
// Use raw pointer isa on the assumption that they might be
// doing something weird with the zone or RR.
obj->initIsa(cls);
}
if (fastpath(!hasCxxCtor)) {
return obj;
}
construct_flags |= OBJECT_CONSTRUCT_FREE_ONFAILURE;
return object_cxxConstructFromClass(obj, cls, construct_flags);
}
instanceSize:计算内存大小
inline size_t instanceSize(size_t extraBytes) const {
// 是否通过缓存,快速计算大小
if (fastpath(cache.hasFastInstanceSize(extraBytes))) {
return cache.fastInstanceSize(extraBytes);
}
// 没有缓存,计算大小
size_t size = alignedInstanceSize() + extraBytes;
// CF requires all objects be at least 16 bytes.
if (size < 16) size = 16;
return size;
}
fastInstanceSize
size_t fastInstanceSize(size_t extra) const
{
ASSERT(hasFastInstanceSize(extra));
if (__builtin_constant_p(extra) && extra == 0) {
return _flags & FAST_CACHE_ALLOC_MASK16;
} else {
size_t size = _flags & FAST_CACHE_ALLOC_MASK;
// remove the FAST_CACHE_ALLOC_DELTA16 that was added
// by setFastInstanceSize
// 删除由setFastInstanceSize添加的FAST_CACHE_ALLOC_DELTA16 8个字节
// 进行16字节对齐
return align16(size + extra - FAST_CACHE_ALLOC_DELTA16);
}
}
- 这里的
size是通过_flags & FAST_CACHE_ALLOC_MASK计算得到的。这里需要我们了解类的具体结构,这里可以简单理解为一个类中成员变量的大小 - 通过16字节,进行内存对齐。如果这里不了解内存对齐知识,请看内存对齐
static inline size_t align16(size_t x) {
return (x + size_t(15)) & ~size_t(15);
}
alignedInstanceSize
// Class's ivar size rounded up to a pointer-size boundary.
uint32_t alignedInstanceSize() const {
return word_align(unalignedInstanceSize());
}
// May be unaligned depending on class's ivars.
// 可以根据类的成员变量进行对齐。
uint32_t unalignedInstanceSize() const {
ASSERT(isRealized());
return data()->ro()->instanceSize;
}
#define WORD_MASK 7UL
static inline uint32_t word_align(uint32_t x) {
return (x + WORD_MASK) & ~WORD_MASK;
}
malloc/calloc:开辟内存
-
calloc具体底层实现,可阅读iOS中calloc和malloc源码分析
initInstanceIsa/initIsa:内存和类关联
inline void
objc_object::initInstanceIsa(Class cls, bool hasCxxDtor)
{
ASSERT(!cls->instancesRequireRawIsa());
ASSERT(hasCxxDtor == cls->hasCxxDtor());
initIsa(cls, true, hasCxxDtor);
}
总结
init
- (id)init {
return _objc_rootInit(self);
}
id
_objc_rootInit(id obj)
{
// In practice, it will be hard to rely on this function.
// Many classes do not properly chain -init calls.
return obj;
}
new
+ (id)new {
return [callAlloc(self, false/*checkNil*/) init];
}
- 直接调用了
callAlloc函数,并且调用init函数。所以可以得出new等价[alloc init] - 一般不建议使用
new。原因是有时候会重写init方法,类似于initWithXXX。使用new方法,无法调用到自定义的初始化方法
原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_42376419/article/details/128226510
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。
如若转载,请注明出处:http://www.7code.cn/show_23988.html
如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系代码007邮箱:suwngjj01@126.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
声明:本站所有文章,如无特殊说明或标注,均为本站原创发布。任何个人或组织,在未征得本站同意时,禁止复制、盗用、采集、发布本站内容到任何网站、书籍等各类媒体平台。如若本站内容侵犯了原著者的合法权益,可联系我们进行处理。