display属性
dispaly属性的作用
在CSS中display属性表示“显示框类型“,即不同的盒模型。简单来说,可以把块级盒子转成内联盒子,也可以把内联盒子转换为块级盒子。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
.box1{
display: block;
background-color: skyblue;
}
.box2{
display: inline;
background-color: pink;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="box1">块元素</div>
<div class="box1">块元素</div>
<span class="box2">行内元素</span >
<span class="box2">行内元素</span >
</body>
</html>
展示效果如下:

可以看到,div具备了内联盒子的特性,而span则具备了块级盒子的特性。(块级元素和行内元素的区别)但是display远比这个复杂的多,其中弹性布局、网格布局等都是跟display有着紧密关系。
display的分类
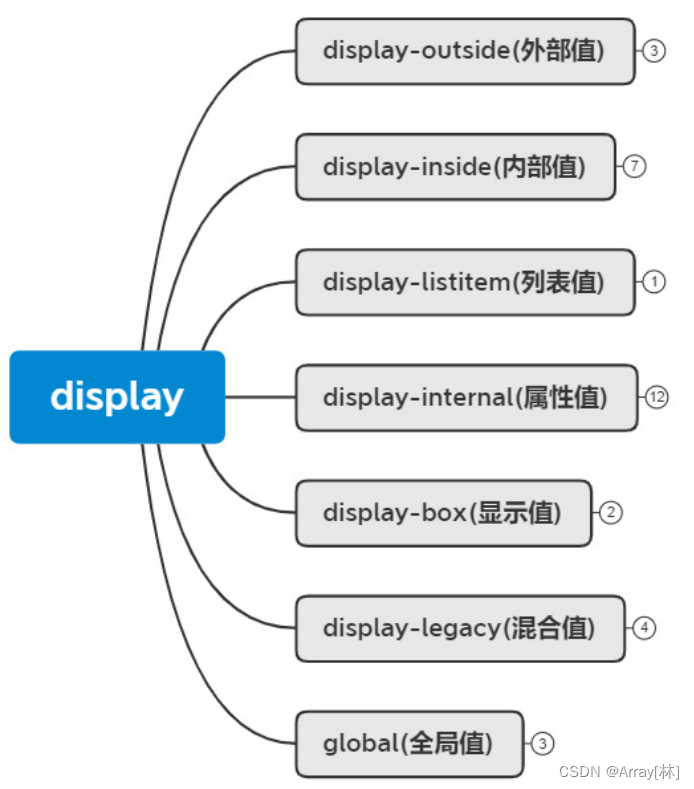
display–outside(外部值)
外部值就是定义自身元素的外部表现,而不影响其内的子元素。

block:将元素表示为块级元素
inline:将元素表示为内联盒子
run–in:实际是块元素和行内元素的混合,可以使某些元素成为下一个块级框元素的行内部分。实验性质的属性,浏览器兼容不好
display–inside(内部值)
和外部值相反,内部值就死定义子元素布局的。像flex,grid这些都会影响到子元素的布局形式。
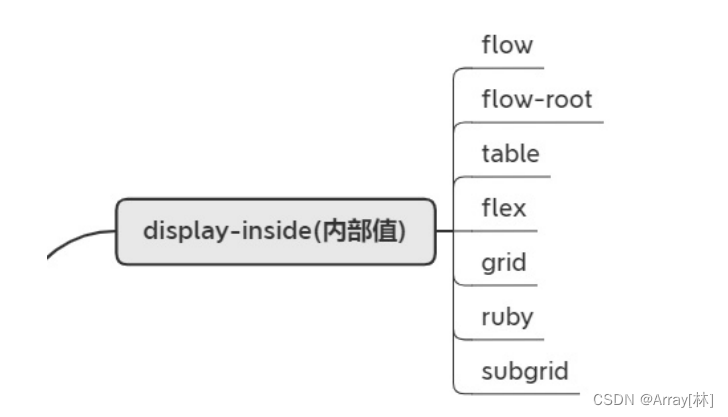
flow–root:一个BFC的块级盒子(注:BFC后面小节会讲解)
table:带有内部表格布局的块级盒子。
flex:带有内部弹性布局的块级盒子
grid:带有内部网格布局的块级盒子
flex布局和grid网格布局都是强大的布局属性,在当下的网页布局中,大多数是采用这两种布局。常用的flex布局就不多说了,下面是grid布局的基本使用:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
.grid{
box-shadow: 0 0 1px #f6f;
width: 300px;
height: 300px;
background-color: aqua;
display: grid;
grid-template-columns:repeat(3,100px);
grid-template-rows:repeat(3,100px);
}
.grid div{
line-height: 100px;
text-align: center;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="grid">
<div>1</div>
<div>2</div>
<div>3</div>
<div>4</div>
<div>5</div>
<div>6</div>
<div>7</div>
<div>8</div>
<div>9</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
展现效果:main元素被划分成了五个小方块,其中grid-template–columns是定义列宽;grid-template–rows是定义行宽的。

以下是flex布局的常用的使用方法:
使用flex实现上下左右居中:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
.main {
width: 300px;
height: 200px;
background: skyblue;
display: flex;
align-items: center;
justify-content: center;
}
.box{
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: pink;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="main">
<div class="box"></div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
使用flex实现两列或三列布局:
两列布局:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
.main {
height: 100vh;
background: skyblue;
display: flex;
}
.box1 {
width: 200px;
background: pink;
}
.box2 {
width: 100px;
background: tan;
flex-grow: 1;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="main">
<div class="box1"></div>
<div class="box2"></div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
.main {
height: 100vh;
background: skyblue;
display: flex;
}
.box1 {
width: 200px;
background: pink;
}
.box2 {
width: 100px;
background: red;
flex-grow: 1;
}
.box3 {
width: 100px;
background: purple;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="main">
<div class="box1"></div>
<div class="box2"></div>
<div class="box3"></div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
展现效果:

display-listitem(列表值)不常用

list–item–属性就是生成一个容纳内容和单独列表行内元素盒的块级盒子,目的是为了用div去代替
display-internal(属性值)不常用
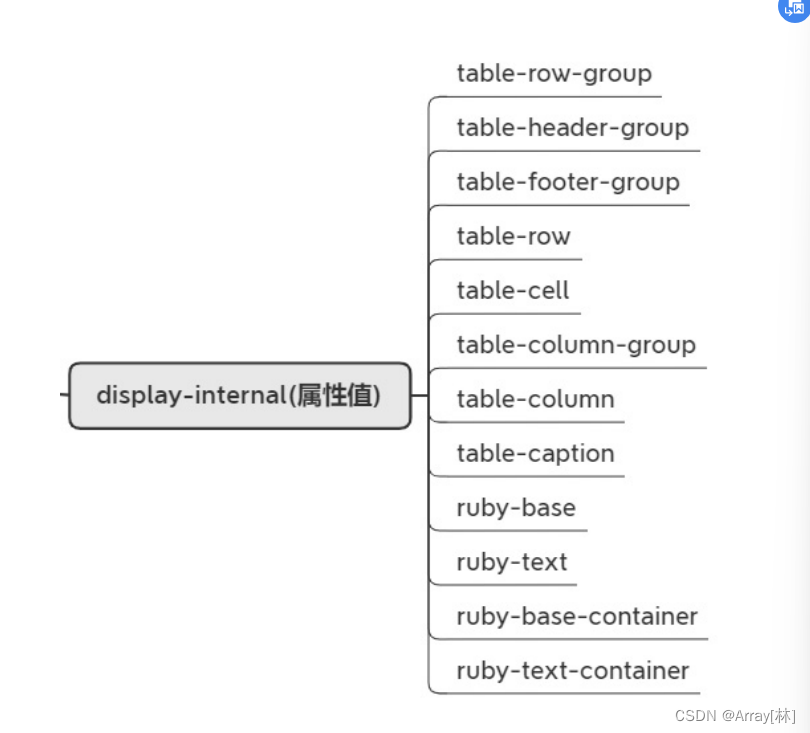
一些和table布局,ruby搭配一起控制页面布局的属性值。
display-box(显示值)

contents:只影响其内容的样式生效,比如:字体带大小,文本颜色等;但像背景色、边框是不会生效的。设置了display: contents的元素本身不会被渲染,但是其子元素能够正常被渲染。
none:从盒子树中移除,包括其所有后代元素。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
.content{
width: 500px;
height: 500px;
display: contents;
background-color: aqua;
}
.content div{
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: blue;
font-size: 20px;
text-align: center;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="content">
<div>1</div>
<div>2</div>
<div>3</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
展现效果如下:

可以看出,对父元素content设置的样式完全不生效,相当于将content元素变成了一个仅供包裹的”无用”元素。
display-legacy(混合值)
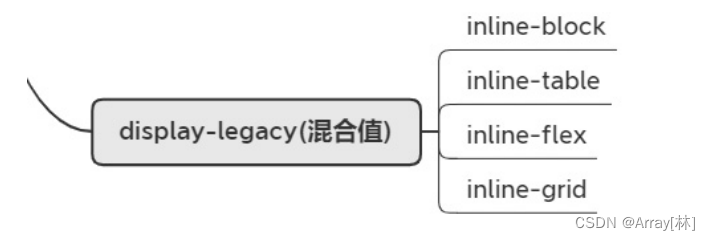
inline-block:对外表现成内联盒子,对内表现成块级盒子
inline–table:对外表现成内联盒子,对子元素表现成表格盒子
inline–flex:对外表现成内联盒子,对子元素表现成弹性盒子
inline-grid:对外表现成内联盒子,对子元素表现成网格盒子
global(全局值)
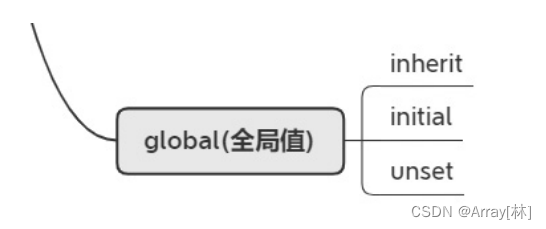
inherit:继承父元素的display属性
initial:不管父元素怎么设定,恢复到浏览器最初始时的display属性
unset:unset混合了inherit和intial。如果父元素设置值了,就用父元素的设定,如果父元素没设置值,就用浏览器的缺省设定。
原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/m0_50785976/article/details/127583687
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。
如若转载,请注明出处:http://www.7code.cn/show_34518.html
如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系代码007邮箱:suwngjj01@126.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!