流程控制语句是用来控制程序中各 语句执行顺序 的语句,可以把语句组合成能 完成一定功能 的小逻辑模块。程序设计中规定的 三种 流程结构,即:
1.顺序结构。 程序从上到下逐行地执行,中间没有任何判断和跳转。
2.分支结构。 根据条件,选择性地执行某段代码。有 if…else 和 switch-case 两种分支语句。
3.循环结构。 根据循环条件,重复性的执行某段代码。有 for、while、do-while 三种循环语句。补充:JDK5.0 提供了 foreach 循环,方便的遍历集合、数组元素。
生活中、工业生产中流程控制举例:
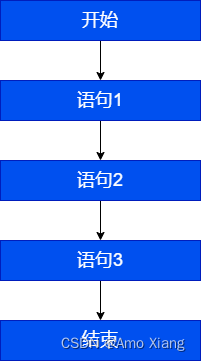
一、顺序结构
顺序结构就是程序 从上到下逐行 地执行。表达式语句都是顺序执行的。并且上一行对某个变量的修改对下一行会产生影响。
public class StatementTest{
public static void main(String[] args){
int x = 1;
int y = 2;
System.out.println("x = " + x);
System.out.println("y = " + y);
//对x、y的值进行修改
x++;
y = 2 * x + y;
x = x * 10;
System.out.println("x = " + x);
System.out.println("y = " + y);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int num1 = 12;
int num2 = num1 + 2;
}
错误形式:
public static void main(String[] args) {
int num2 = num1 + 2;
int num1 = 12;
}
二、分支语句
2.1 if-else条件判断结构
2.1.1 基本语法
结构1:单分支条件判断:if,语法格式如下:
if(条件表达式){
语句块;
}
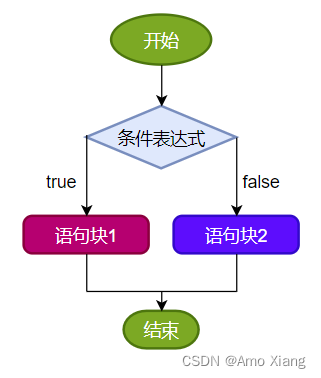
说明: 条件表达式必须是布尔表达式(关系表达式或逻辑表达式)或布尔变量。执行流程:
if(条件表达式) {
语句块1;
}else {
语句块2;
}
执行流程:
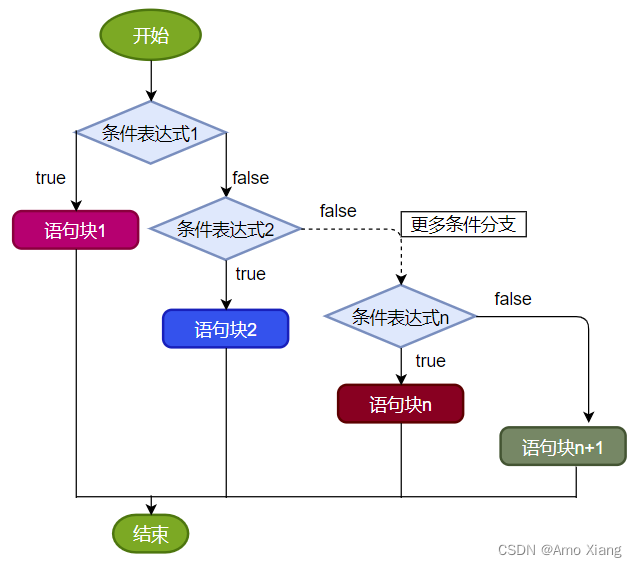
结构3:多分支条件判断:if…else if…else,语法格式如下:
if (条件表达式1) {
语句块1;
} else if (条件表达式2) {
语句块2;
}
...
}else if (条件表达式n) {
语句块n;
} else {
语句块n+1;
}
说明:一旦条件表达式为 true,则进入执行相应的语句块。执行完对应的语句块之后,就跳出当前结构。执行流程:
- 首先判断关系表达式1看其结果是 true 还是 false
- 如果是 true 就执行语句块1,然后结束当前多分支
- 如果是 false 就继续判断关系表达式2看其结果是 true 还是 false
- 如果是 true 就执行语句块2,然后结束当前多分支
- 如果是 false 就继续判断关系表达式…看其结果是 true 还是 false
- 如果没有任何关系表达式为 true,就执行语句块 n+1,然后结束当前多分支。
2.1.2 应用举例
案例1: 成年人心率的正常范围是每分钟60-100次。体检时,如果心率不在此范围内,则提示需要做进一步的检查。
public class IfElseTest1 {
public static void main(String[] args){
int heartBeats = 89;
if(heartBeats < 60 || heartBeats > 100){
System.out.println("你需要做进一步的检查");
}
System.out.println("体检结束");
}
}
public class IfElseTest2 {
public static void main(String[] args){
int a = 10;
if(a % 2 == 0) {
System.out.println(a + "是偶数");
} else{
System.out.println(a + "是奇数");
}
}
}
案例3:
/*岳小鹏参加Java考试,他和父亲岳不群达成承诺:
如果:
成绩为100分时,奖励一辆跑车;
成绩为(80,99]时,奖励一辆山地自行车;
当成绩为[60,80]时,奖励环球影城一日游;
其它时,胖揍一顿。
说明:默认成绩是在[0,100]范围内*/
public class IfElseTest3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int score = 67;//岳小鹏的期末成绩
//写法一:默认成绩范围为[0,100]
if(score == 100){
System.out.println("奖励一辆跑车");
}else if(score > 80 && score <= 99){ //错误的写法:}else if(80 < score <= 99){
System.out.println("奖励一辆山地自行车");
}else if(score >= 60 && score <= 80){
System.out.println("奖励环球影城玩一日游");
}
//else{
// System.out.println("胖揍一顿");
//}
//写法二:
// 默认成绩范围为[0,100]
if(score == 100){
System.out.println("奖励一辆跑车");
}else if(score > 80){
System.out.println("奖励一辆山地自行车");
}else if(score >= 60){
System.out.println("奖励环球影城玩一日游");
}else{
System.out.println("胖揍一顿");
}
}
}
程序解析:

 当条件表达式之间是
当条件表达式之间是 互斥 关系时(即彼此没有交集),条件判断语句及执行语句间顺序无所谓。当条件表达式之间是 包含 关系时,小上大下/子上父下,否则范围小的条件表达式将不可能被执行。
2.1.3 if…else嵌套
在 if 的语句块中,或者是在 else 语句块中,又包含了另外一个条件判断(可以是单分支、双分支、多分支),就构成了 嵌套结构。执行的特点:
- 如果是嵌套在 if 语句块中的,只有当外部的 if 条件满足,才会去判断内部的条件
- 如果是嵌套在 else 语句块中的,只有当外部的 if 条件不满足,进入 else 后,才会去判断内部的条件
案例4: 由键盘输入三个整数分别存入变量 num1、num2、num3,对它们进行排序(使用 if-else if-else),并且从小到大输出。
class IfElseTest4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//声明num1,num2,num3三个变量并赋值
int num1 = 23,num2 = 32,num3 = 12;
if(num1 >= num2){
if(num3 >= num1)
System.out.println(num2 + "-" + num1 + "-" + num3);
else if(num3 <= num2)
System.out.println(num3 + "-" + num2 + "-" + num1);
else
System.out.println(num2 + "-" + num3 + "-" + num1);
}else{ //num1 < num2
if(num3 >= num2){
System.out.println(num1 + "-" + num2 + "-" + num3);
}else if(num3 <= num1){
System.out.println(num3 + "-" + num1 + "-" + num2);
}else{
System.out.println(num1 + "-" + num3 + "-" + num2);
}
}
}
}
2.1.4 其它说明
语句块只有一条执行语句时,一对 {} 可以省略,但建议保留。当 if-else 结构是 多选一 时,最后的 else是可选的,根据需要可以省略。
2.1.5 练习
练习1:
//1)对下列代码,若有输出,指出输出结果。
int x = 4;
int y = 1;
if (x > 2) {
if (y > 2)
System.out.println(x + y);
System.out.println("atguigu");
} else
System.out.println("x is " + x);
练习2:
boolean b = true;
//如果写成if(b=false)能编译通过吗?如果能,结果是?
if(b == false) //建议:if(!b)
System.out.println("a");
else if(b)
System.out.println("b");
else if(!b)
System.out.println("c");
else
System.out.println("d");
练习3: 定义两个整数,分别为 small 和 big,如果第一个整数 small 大于第二个整数 big,就交换。输出显示 small 和 big 变量的值。
public class IfElseExer3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int small = 10;
int big = 9;
if (small > big) {
int temp = small;
small = big;
big = temp;
}
System.out.println("small=" + small + ",big=" + big);
}
}
练习4: 小明参加期末 Java 考试,通过考试成绩,判断其 Java 等级,成绩范围 [0,100]
/*90-100 优秀
80-89 好
70-79 良
60-69 及格
60以下 不及格*/
import java.util.Scanner;
//写法一:
public class IfElseExer4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.print("小明的期末Java成绩是:[0,100]");
int score = 89;
if (score < 0 || score > 100) {
System.out.println("你的成绩是错误的");
} else if (score >= 90 && score <= 100) {
System.out.println("你的成绩属于优秀");
} else if (score >= 80 && score < 90) {
System.out.println("你的成绩属于好");
} else if (score >= 70 && score < 80) {
System.out.println("你的成绩属于良");
} else if (score >= 60 && score < 70) {
System.out.println("你的成绩属于及格");
} else {
System.out.println("你的成绩属于不及格");
}
}
}
写法二:
import java.util.Scanner;
public class IfElseExer4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.print("小明的期末Java成绩是:[0,100]");
int score = 89;
if (score < 0 || score > 100) {
System.out.println("你的成绩是错误的");
} else if (score >= 90) {
System.out.println("你的成绩属于优秀");
} else if (score >= 80) {
System.out.println("你的成绩属于好");
} else if (score >= 70) {
System.out.println("你的成绩属于良");
} else if (score >= 60) {
System.out.println("你的成绩属于及格");
} else {
System.out.println("你的成绩属于不及格");
}
}
}
练习5: 编写程序,声明2个int型变量并赋值。判断两数之和,如果大于等于50,打印 hello world!
public class IfElseExer5 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int num1 = 12, num2 = 32;
if (num1 + num2 >= 50) {
System.out.println("hello world!");
}
}
}
练习6: 编写程序,声明2个double型变量并赋值。判断第一个数大于10.0,且第2个数小于20.0,打印两数之和。否则,打印两数的乘积。
public class IfElseExer6 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
double d1 = 21.2,d2 = 12.3;
if(d1 > 10.0 && d2 < 20.0){
System.out.println("两数之和为:" + (d1 + d2));
}else{
System.out.println("两数乘积为:" + (d1 * d2));
}
}
}
练习7:判断水的温度。
/*如果大于95℃,则打印“开水”;
如果大于70℃且小于等于95℃,则打印“热水”;
如果大于40℃且小于等于70℃,则打印“温水”;
如果小于等于40℃,则打印“凉水”。*/
public class IfElseExer7 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int waterTemperature = 85;
if(waterTemperature > 95){
System.out.println("开水");
}else if(waterTemperature > 70 && waterTemperature <= 95){
System.out.println("热水");
}else if(waterTemperature > 40 && waterTemperature <= 70){
System.out.println("温水");
}else{
System.out.println("凉水");
}
}
}
2.2 switch-case选择结构
2.2.1 基本语法
语法格式:
switch(表达式){
case 常量值1:
语句块1;
//break;
case 常量值2:
语句块2;
//break;
// ...
[default:
语句块n+1;
break;
]
}
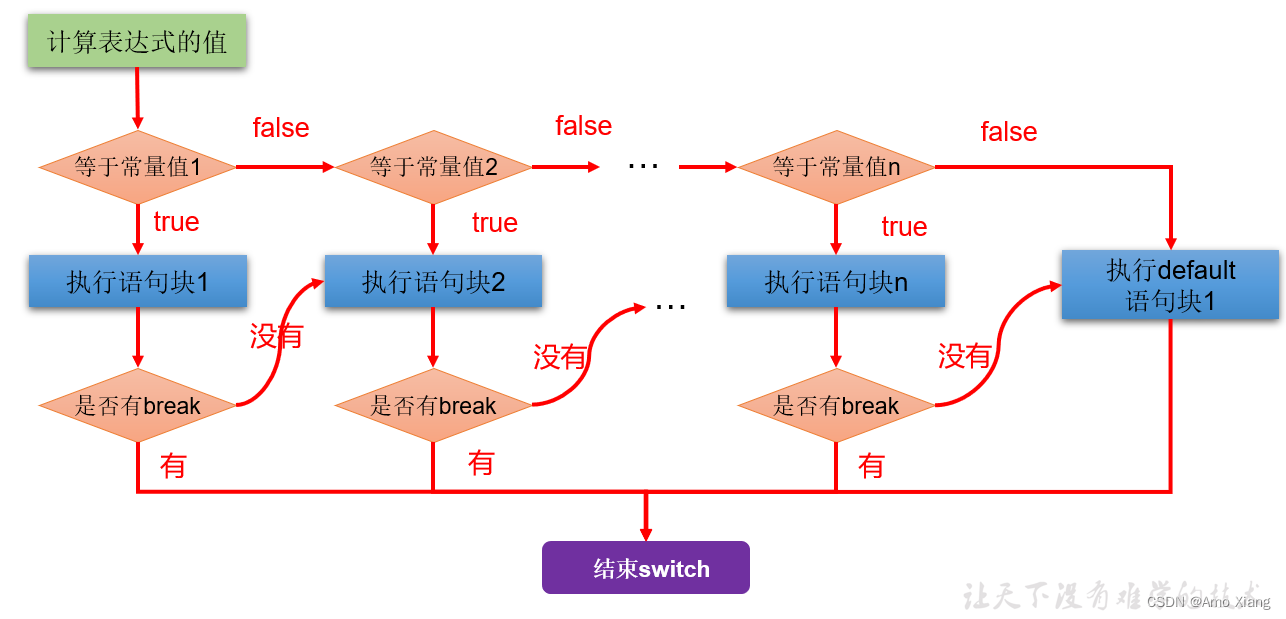
执行流程图:
执行过程:
使用注意点:
- switch(表达式)中表达式的值必须是下述几种类型之一:byte,short,char,int,枚举 (jdk 5.0),String (jdk 7.0);
- case子句中的值必须是常量,不能是变量名或不确定的表达式值或范围;
- 同一个 switch 语句,所有 case 子句中的常量值互不相同;
- break 语句用来在执行完一个 case 分支后使程序跳出 switch 语句块;
- 如果没有 break,程序会顺序执行到 switch 结尾;
- default 子句是可选的。同时,位置也是灵活的。当没有匹配的 case 时,执行 default 语句。
2.2.2 应用举例
案例1:
public class SwitchCaseTest1 {
public static void main(String args[]) {
int num = 1;
switch(num){
case 0:
System.out.println("zero");
break;
case 1:
System.out.println("one");
break;
case 2:
System.out.println("two");
break;
case 3:
System.out.println("three");
break;
default:
System.out.println("other");
//break;
}
}
}
案例2:
public class SwitchCaseTest2 {
public static void main(String args[]) {
String season = "summer";
switch (season) {
case "spring":
System.out.println("春暖花开");
break;
case "summer":
System.out.println("夏日炎炎");
break;
case "autumn":
System.out.println("秋高气爽");
break;
case "winter":
System.out.println("冬雪皑皑");
break;
default:
System.out.println("季节输入有误");
break;
}
}
}
错误举例:
int key = 10;
switch(key){
case key > 0 :
System.out.println("正数");
break;
case key < 0:
System.out.println("负数");
break;
default:
System.out.println("零");
break;
}
案例3: 使用 switch-case 实现:对学生成绩大于60分的,输出 合格。 低于60分的,输出 不合格。
class SwitchCaseTest3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int score = 67;
/*
写法1:极不推荐
switch(score){
case 0:
System.out.println("不及格");
break;
case 1:
System.out.println("不及格");
break;
//...
case 60:
System.out.println("及格");
break;
//...略...
}
*/
//写法2:
switch(score / 10){
case 0:
case 1:
case 2:
case 3:
case 4:
case 5:
System.out.println("不及格");
break;
case 6:
case 7:
case 8:
case 9:
case 10:
System.out.println("及格");
break;
default:
System.out.println("输入的成绩有误");
break;
}
//写法3:
switch(score / 60){
case 0:
System.out.println("不及格");
break;
case 1:
System.out.println("及格");
break;
default:
System.out.println("输入的成绩有误");
break;
}
}
}
2.2.3 利用case的穿透性
在 switch 语句中,如果 case 的后面不写 break,将出现穿透现象,也就是一旦匹配成功,不会在判断下一个 case 的值,直接向后运行,直到遇到 break 或者整个 switch 语句结束,执行终止。
案例4: 编写程序:从键盘上输入2023年的 month 和 day,要求通过程序输出输入的日期为2023年的第几天。
import java.util.Scanner;
class SwitchCaseTest4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入2023年的month:");
int month = scan.nextInt();
System.out.println("请输入2023年的day:");
int day = scan.nextInt();
//这里就不针对month和day进行合法性的判断了,以后可以使用正则表达式进行校验。
int sumDays = 0;//记录总天数
//写法1 :不推荐(存在冗余的数据)
/*
switch(month){
case 1:
sumDays = day;
break;
case 2:
sumDays = 31 + day;
break;
case 3:
sumDays = 31 + 28 + day;
break;
//....
case 12:
//sumDays = 31 + 28 + ... + 30 + day;
break;
}
*/
//写法2:推荐
switch(month){
case 12:
sumDays += 30;//这个30是代表11月份的满月天数
case 11:
sumDays += 31;//这个31是代表10月份的满月天数
case 10:
sumDays += 30;//这个30是代表9月份的满月天数
case 9:
sumDays += 31;//这个31是代表8月份的满月天数
case 8:
sumDays += 31;//这个31是代表7月份的满月天数
case 7:
sumDays += 30;//这个30是代表6月份的满月天数
case 6:
sumDays += 31;//这个31是代表5月份的满月天数
case 5:
sumDays += 30;//这个30是代表4月份的满月天数
case 4:
sumDays += 31;//这个31是代表3月份的满月天数
case 3:
sumDays += 28;//这个28是代表2月份的满月天数
case 2:
sumDays += 31;//这个31是代表1月份的满月天数
case 1:
sumDays += day;//这个day是代表当月的第几天
}
System.out.println(month + "月" + day + "日是2023年的第" + sumDays + "天");
//关闭资源
scan.close();
}
}
拓展:
/*从键盘分别输入年、月、日,判断这一天是当年的第几天
注:判断一年是否是闰年的标准:
1)可以被4整除,但不可被100整除
或
2)可以被400整除
例如:1900,2200等能被4整除,但同时能被100整除,但不能被400整除,不是闰年*/
import java.util.Scanner;
public class SwitchCaseTest04 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("请输入year:");
int year = scanner.nextInt();
System.out.print("请输入month:");
int month = scanner.nextInt();
System.out.print("请输入day:");
int day = scanner.nextInt();
//判断这一天是当年的第几天==>从1月1日开始,累加到xx月xx日这一天
//(1)[1,month-1]个月满月天数
//(2)单独考虑2月份是否是29天(依据是看year是否是闰年)
//(3)第month个月的day天
//声明一个变量days,用来存储总天数
int sumDays = 0;
//累加[1,month-1]个月满月天数
switch (month) {
case 12:
//累加的1-11月
sumDays += 30;//这个30是代表11月份的满月天数
//这里没有break,继续往下走
case 11:
//累加的1-10月
sumDays += 31;//这个31是代表10月的满月天数
//这里没有break,继续往下走
case 10:
sumDays += 30;//9月
case 9:
sumDays += 31;//8月
case 8:
sumDays += 31;//7月
case 7:
sumDays += 30;//6月
case 6:
sumDays += 31;//5月
case 5:
sumDays += 30;//4月
case 4:
sumDays += 31;//3月
case 3:
sumDays += 28;//2月
//在这里考虑是否可能是29天
if (year % 4 == 0 && year % 100 != 0 || year % 400 == 0) {
sumDays++;//多加1天
}
case 2:
sumDays += 31;//1月
case 1:
sumDays += day;//第month月的day天
}
//输出结果
System.out.println(year + "年" + month + "月" + day + "日是这一年的第" + sumDays + "天");
scanner.close();
}
}
案例5: 根据指定的月份输出对应季节
import java.util.Scanner;
/*
* 需求:指定一个月份,输出该月份对应的季节。一年有四季:
* 3,4,5 春季
* 6,7,8 夏季
* 9,10,11 秋季
* 12,1,2 冬季
*/
public class SwitchCaseTest5 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("请输入月份:");
int month = input.nextInt();
/*
switch(month) {
case 1:
System.out.println("冬季");
break;
case 2:
System.out.println("冬季");
break;
case 3:
System.out.println("春季");
break;
case 4:
System.out.println("春季");
break;
case 5:
System.out.println("春季");
break;
case 6:
System.out.println("夏季");
break;
case 7:
System.out.println("夏季");
break;
case 8:
System.out.println("夏季");
break;
case 9:
System.out.println("秋季");
break;
case 10:
System.out.println("秋季");
break;
case 11:
System.out.println("秋季");
break;
case 12:
System.out.println("冬季");
break;
default:
System.out.println("你输入的月份有误");
break;
}
*/
// 改进版
switch(month) {
case 1:
case 2:
case 12:
System.out.println("冬季");
break;
case 3:
case 4:
case 5:
System.out.println("春季");
break;
case 6:
case 7:
case 8:
System.out.println("夏季");
break;
case 9:
case 10:
case 11:
System.out.println("秋季");
break;
default:
System.out.println("你输入的月份有误");
break;
}
input.close();
}
}
常见错误实现:
switch(month){
case 3|4|5://3|4|5 用了位运算符,11 | 100 | 101结果是 111是7
System.out.println("春季");
break;
case 6|7|8://6|7|8用了位运算符,110 | 111 | 1000结果是1111是15
System.out.println("夏季");
break;
case 9|10|11://9|10|11用了位运算符,1001 | 1010 | 1011结果是1011是11
System.out.println("秋季");
break;
case 12|1|2://12|1|2 用了位运算符,1100 | 1 | 10 结果是1111,是15
System.out.println("冬季");
break;
default:
System.out.println("输入有误");
}
if ((month == 1) || (month == 2) || (month == 12)) {
System.out.println("冬季");
} else if ((month == 3) || (month == 4) || (month == 5)) {
System.out.println("春季");
} else if ((month == 6) || (month == 7) || (month == 8)) {
System.out.println("夏季");
} else if ((month == 9) || (month == 10) || (month == 11)) {
System.out.println("秋季");
} else {
System.out.println("你输入的月份有误");
}
2.2.4 if-else语句与switch-case语句比较
结论:凡是使用 switch-case 的结构都可以转换为 if-else 结构。反之,不成立。
开发经验:如果既可以使用 switch-case,又可以使用 if-else,建议使用 switch-case。因为效率稍高。细节对比:
- if-else 语句优势
- switch语句优势
- 当条件是判断某个变量或表达式是否等于某个固定的常量值时,使用 if 和 switch 都可以,习惯上使用 switch 更多。因为
效率稍高。当条件是区间范围的判断时,只能使用 if 语句。 - 使用 switch 可以利用
穿透性,同时执行多个分支,而 if…else 没有穿透性。
- 当条件是判断某个变量或表达式是否等于某个固定的常量值时,使用 if 和 switch 都可以,习惯上使用 switch 更多。因为
案例:只能使用 if-else。 从键盘输入一个整数,判断是正数、负数、还是零。
import java.util.Scanner;
public class IfOrSwitchDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("请输入整数:");
int num = input.nextInt();
if (num > 0) {
System.out.println(num + "是正整数");
} else if (num < 0) {
System.out.println(num + "是负整数");
} else {
System.out.println(num + "是零");
}
input.close();
}
}
2.2.5 练习
练习1: 从键盘输入星期的整数值,输出星期的英文单词
import java.util.Scanner;
public class SwitchCaseExer1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//定义指定的星期
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("请输入星期值:");
int weekday = input.nextInt();
//switch语句实现选择
switch(weekday) {
case 1:
System.out.println("Monday");
break;
case 2:
System.out.println("Tuesday");
break;
case 3:
System.out.println("Wednesday");
break;
case 4:
System.out.println("Thursday");
break;
case 5:
System.out.println("Friday");
break;
case 6:
System.out.println("Saturday");
break;
case 7:
System.out.println("Sunday");
break;
default:
System.out.println("你输入的星期值有误!");
break;
}
input.close();
}
}
练习2:
/*使用switch把小写类型的char型转为大写。只转换a, b, c, d, e. 其它的输出 other*/
public class SwitchCaseExer2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
char word = 'c';
switch (word) {
case 'a':
System.out.println("A");
break;
case 'b':
System.out.println("B");
break;
case 'c':
System.out.println("C");
break;
case 'd':
System.out.println("D");
break;
case 'e':
System.out.println("E");
break;
default :
System.out.println("other");
}
}
}
练习3:
/*编写程序:从键盘上读入一个学生成绩,存放在变量score中,根据score的值输出其对应的成绩等级:
score>=90 等级: A
70<=score<90 等级: B
60<=score<70 等级: C
score<60 等级: D
方式一:使用if-else
方式二:使用switch-case: score / 10: 0 - 10*/
public class SwitchCaseExer3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入学生成绩:");
int score = scan.nextInt();
char grade;//记录学生等级
//方式1:
// if(score >= 90){
// grade = 'A';
// }else if(score >= 70 && score < 90){
// grade = 'B';
// }else if(score >= 60 && score < 70){
// grade = 'C';
// }else{
// grade = 'D';
// }
//方式2:
switch(score / 10){
case 10:
case 9:
grade = 'A';
break;
case 8:
case 7:
grade = 'B';
break;
case 6:
grade = 'C';
break;
default :
grade = 'D';
}
System.out.println("学生成绩为" + score + ",对应的等级为" + grade);
scan.close();
}
}
练习4:
/*编写一个程序,为一个给定的年份找出其对应的中国生肖。中国的生肖基于12年一个周期,每年用一个动物代表:rat、ox、tiger、rabbit、dragon、snake、horse、sheep、monkey、rooster、dog、pig。
提示:2022年:虎 2022 % 12 == 6 */
public class SwitchCaseExer4 {
public static void main(String[] args){
//从键盘输入一个年份
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("请输入年份:");
int year = input.nextInt();
input.close();
//判断
switch(year % 12){
case 0:
System.out.println(year + "是猴年");
break;
case 1:
System.out.println(year + "是鸡年");
break;
case 2:
System.out.println(year + "是狗年");
break;
case 3:
System.out.println(year + "是猪年");
break;
case 4:
System.out.println(year + "是鼠年");
break;
case 5:
System.out.println(year + "是牛年");
break;
case 6:
System.out.println(year + "是虎年");
break;
case 7:
System.out.println(year + "是兔年");
break;
case 8:
System.out.println(year + "是龙年");
break;
case 9:
System.out.println(year + "是蛇年");
break;
case 10:
System.out.println(year + "是马年");
break;
case 11:
System.out.println(year + "是羊年");
break;
default:
System.out.println(year + "输入错误");
}
}
}
练习5:押宝游戏
/*随机产生3个1-6的整数,如果三个数相等,那么称为“豹子”,如果三个数之和大于9,称为“大”,如果三个数之和小于等于9,称为“小”,用户从键盘输入押的是“豹子”、“大”、“小”,并判断是否猜对了
提示:随机数 Math.random()产生 [0,1)范围内的小数
如何获取[a,b]范围内的随机整数呢?(int)(Math.random() * (b - a + 1)) + a*/
```java
import java.util.Scanner;
public class SwitchCaseExer5 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1、随机产生3个1-6的整数
int a = (int)(Math.random()*6 + 1);
int b = (int)(Math.random()*6 + 1);
int c = (int)(Math.random()*6 + 1);
//2、押宝
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("请押宝(豹子、大、小):");
String ya = input.next();
input.close();
//3、判断结果
boolean result = false;
//switch支持String类型
switch (ya){
case "豹子": result = a == b && b == c; break;
case "大": result = a + b + c > 9; break;
case "小": result = a + b + c <= 9; break;
default:System.out.println("输入有误!");
}
System.out.println("a,b,c分别是:" + a +"," + b +"," + c );
System.out.println(result ? "猜中了" : "猜错了");
}
}
练习6:
使用switch语句改写下列if语句:
int a = 3;
int x = 100;
if(a==1)
x+=5;
else if(a==2)
x+=10;
else if(a==3)
x+=16;
else
x+=34;
int a = 3;
int x = 100;
switch(a){
case 1:
x += 5;
break;
case 2:
x += 10;
break;
case 3:
x += 16;
break;
default :
x += 34;
}
至此今天的学习就到此结束了,笔者在这里声明,笔者写文章只是为了学习交流,以及让更多学习Java语言的读者少走一些弯路,节省时间,并不用做其他用途,如有侵权,联系博主删除即可。感谢您阅读本篇博文,希望本文能成为您编程路上的领航者。祝您阅读愉快!

好书不厌读百回,熟读课思子自知。而我想要成为全场最靓的仔,就必须坚持通过学习来获取更多知识,用知识改变命运,用博客见证成长,用行动证明我在努力。
如果我的博客对你有帮助、如果你喜欢我的博客内容,请点赞、评论、收藏一键三连哦!听说点赞的人运气不会太差,每一天都会元气满满呦!如果实在要白嫖的话,那祝你开心每一天,欢迎常来我博客看看。
编码不易,大家的支持就是我坚持下去的动力。点赞后不要忘了关注我哦!
原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/xw1680/article/details/134306860
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。
如若转载,请注明出处:http://www.7code.cn/show_1337.html
如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系代码007邮箱:suwngjj01@126.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!