背景
现项目中涉及红色、金色主题,同时需要适配红色暗黑、金色暗黑,本地需要手动维护4套色值,并且切换主题时需要重新销毁创建页面,维护跟用户体验都不是很友好。
设计思路来源
通过调研,发现换肤的实现原理比较符合适用当前项目的使用场景,开源项目 Android-Skin-Loader
通过查看源码换肤实现原理其实为 通过下载或者加载本地资源包,这里的资源包其实就是一个只有资源文件的项目通过编译打包生成的.apk文件,点击切换时,通过提前手动绑定view和要改变的资源类型 将资源Resource替换成资源包的Resource资源进行设置替换,从而达到换肤的效果。
由此整理出方案需要自行实现的点
- 获取需要支持主题切换的view和要改变的属性类型
- 资源包不通过.apk的形式存在而是跟正常的资源文件存放的于项目中,可以在XML布局里直接使用
- 定义需要支持适配的具体属性 android:textColor|android:background|android:src
- 自定义属性配置 是否需要支持切换 以及 是否只区分暗黑不区分红色主题、金色主题
- 处理debug开发的日志以及异常处理情况
- 支持除textColor 和 background、src,能支持属性扩展
- 支持动态创建view动态切换主题
具体实现
前提了解下LayoutInflater原理
LayoutInflatersetFactory(LayoutInflater.Factoryfactory)和setFactory2(LayoutInflater.Factory2 factory)两个方法可以让你去自定义布局的填充(有点类似于过滤器,我们在填充这个View之前可以手动绑定view和要改变的资源类型),Factory2 是在API 11才添加的。
通过阅读源码可以发现,我们在进入setContentView(R.layout.activity_main)可以看到
@Override
public void setContentView(@LayoutRes int layoutResID) {
getDelegate().setContentView(layoutResID);
}
这里的getDelegate()获取到的是AppCompatDelegateImpl,我们可以看到
@RestrictTo(LIBRARY)
class AppCompatDelegateImpl extends AppCompatDelegate
implements MenuBuilder.Callback, LayoutInflater.Factory2 {
实现了LayoutInflater.Factory2接口,在看 获取到的是AppCompatDelegateImpl的
@Override
public void setContentView(int resId) {
ensureSubDecor();
ViewGroup contentParent = mSubDecor.findViewById(android.R.id.content);
contentParent.removeAllViews();
LayoutInflater.from(mContext).inflate(resId, contentParent);
mAppCompatWindowCallback.getWrapped().onContentChanged();
}
LayoutInflater.from(mContext)获取最终获取的是ontext.getSystemService(Context.LAYOUT_INFLATER_SERVICE)
/**
* Obtains the LayoutInflater from the given context.
*/
public static LayoutInflater from(Context context) {
LayoutInflater LayoutInflater =
(LayoutInflater) context.getSystemService(Context.LAYOUT_INFLATER_SERVICE);
if (LayoutInflater == null) {
throw new AssertionError("LayoutInflater not found.");
}
return LayoutInflater;
}
继续往里看会找到
public View inflate(XmlPullParser parser, @Nullable ViewGroup root, boolean attachToRoot) {
synchronized (mConstructorArgs) {
Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_VIEW, "inflate");
final Context inflaterContext = mContext;
final AttributeSet attrs = Xml.asAttributeSet(parser);
Context lastContext = (Context) mConstructorArgs[0];
mConstructorArgs[0] = inflaterContext;
View result = root;
try {
advanceToRootNode(parser);
final String name = parser.getName();
if (DEBUG) {
System.out.println("**************************");
System.out.println("Creating root view: "
+ name);
System.out.println("**************************");
}
if (TAG_MERGE.equals(name)) {
if (root == null || !attachToRoot) {
throw new InflateException("<merge /> can be used only with a valid "
+ "ViewGroup root and attachToRoot=true");
}
rInflate(parser, root, inflaterContext, attrs, false);
} else {
// Temp is the root view that was found in the xml
final View temp = createViewFromTag(root, name, inflaterContext, attrs);
ViewGroup.LayoutParams params = null;
if (root != null) {
if (DEBUG) {
System.out.println("Creating params from root: " +
root);
}
// Create layout params that match root, if supplied
params = root.generateLayoutParams(attrs);
if (!attachToRoot) {
// Set the layout params for temp if we are not
// attaching. (If we are, we use addView, below)
temp.setLayoutParams(params);
}
}
if (DEBUG) {
System.out.println("-----> start inflating children");
}
// Inflate all children under temp against its context.
rInflateChildren(parser, temp, attrs, true);
if (DEBUG) {
System.out.println("-----> done inflating children");
}
// We are supposed to attach all the views we found (int temp)
// to root. Do that now.
if (root != null && attachToRoot) {
root.addView(temp, params);
}
// Decide whether to return the root that was passed in or the
// top view found in xml.
if (root == null || !attachToRoot) {
result = temp;
}
}
} catch (XmlPullParserException e) {
final InflateException ie = new InflateException(e.getMessage(), e);
ie.setStackTrace(EMPTY_STACK_TRACE);
throw ie;
} catch (Exception e) {
final InflateException ie = new InflateException(
getParserStateDescription(inflaterContext, attrs)
+ ": " + e.getMessage(), e);
ie.setStackTrace(EMPTY_STACK_TRACE);
throw ie;
} finally {
// Don't retain static reference on context.
mConstructorArgs[0] = lastContext;
mConstructorArgs[1] = null;
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_VIEW);
}
return result;
}
}
可以看到如果不是merge标签会通过createViewFromTag(root,name,inflaterContext, attrs)创建view,找到方法
@UnsupportedAppUsage
View createViewFromTag(View parent, String name, Context context, AttributeSet attrs,
boolean ignoreThemeAttr) {
if (name.equals("view")) {
name = attrs.getAttributeValue(null, "class");
}
// Apply a theme wrapper, if allowed and one is specified.
if (!ignoreThemeAttr) {
final TypedArray ta = context.obtainStyledAttributes(attrs, ATTRS_THEME);
final int themeResId = ta.getResourceId(0, 0);
if (themeResId != 0) {
context = new ContextThemeWrapper(context, themeResId);
}
ta.recycle();
}
try {
View view = tryCreateView(parent, name, context, attrs);
if (view == null) {
final Object lastContext = mConstructorArgs[0];
mConstructorArgs[0] = context;
try {
if (-1 == name.indexOf('.')) {
view = onCreateView(context, parent, name, attrs);
} else {
view = createView(context, name, null, attrs);
}
} finally {
mConstructorArgs[0] = lastContext;
}
}
return view;
} catch (InflateException e) {
throw e;
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
final InflateException ie = new InflateException(
getParserStateDescription(context, attrs)
+ ": Error inflating class " + name, e);
ie.setStackTrace(EMPTY_STACK_TRACE);
throw ie;
} catch (Exception e) {
final InflateException ie = new InflateException(
getParserStateDescription(context, attrs)
+ ": Error inflating class " + name, e);
ie.setStackTrace(EMPTY_STACK_TRACE);
throw ie;
}
}
最终我们在tryCreateView(@Nullable View parent, @NonNull String name,@NonNull Context context,@NonNull AttributeSet attrs)里看到
@UnsupportedAppUsage(trackingBug = 122360734)
@Nullable
public final View tryCreateView(@Nullable View parent, @NonNull String name,
@NonNull Context context,
@NonNull AttributeSet attrs) {
if (name.equals(TAG_1995)) {
// Let's party like it's 1995!
return new BlinkLayout(context, attrs);
}
View view;
if (mFactory2 != null) {
view = mFactory2.onCreateView(parent, name, context, attrs);
} else if (mFactory != null) {
view = mFactory.onCreateView(name, context, attrs);
} else {
view = null;
}
if (view == null && mPrivateFactory != null) {
view = mPrivateFactory.onCreateView(parent, name, context, attrs);
}
return view;
}
最终是调用的LayoutInflater的setFactory2()方法创建View,当我们不手动调用设置Factory2,我们还记得前面说的AppCompatDelegateImpl实现了LayoutInflater.Factory2接口重写了createView()方法并设置了
@Override
public void installViewFactory() {
LayoutInflater layoutInflater = LayoutInflater.from(mContext);
if (layoutInflater.getFactory() == null) {
LayoutInflaterCompat.setFactory2(layoutInflater, this);
} else {
if (!(layoutInflater.getFactory2() instanceof AppCompatDelegateImpl)) {
Log.i(TAG, "The Activity's LayoutInflater already has a Factory installed"
+ " so we can not install AppCompat's");
}
}
}
@Override
public View createView(View parent, final String name, @NonNull Context context,
@NonNull AttributeSet attrs) {
if (mAppCompatViewInflater == null) {
TypedArray a = mContext.obtainStyledAttributes(R.styleable.AppCompatTheme);
String viewInflaterClassName =
a.getString(R.styleable.AppCompatTheme_viewInflaterClass);
if ((viewInflaterClassName == null)
|| AppCompatViewInflater.class.getName().equals(viewInflaterClassName)) {
// Either default class name or set explicitly to null. In both cases
// create the base inflater (no reflection)
mAppCompatViewInflater = new AppCompatViewInflater();
} else {
try {
Class<?> viewInflaterClass = Class.forName(viewInflaterClassName);
mAppCompatViewInflater =
(AppCompatViewInflater) viewInflaterClass.getDeclaredConstructor()
.newInstance();
} catch (Throwable t) {
Log.i(TAG, "Failed to instantiate custom view inflater "
+ viewInflaterClassName + ". Falling back to default.", t);
mAppCompatViewInflater = new AppCompatViewInflater();
}
}
}
发现具体是通过AppCompatViewInflater的createView()去创建的View具体
final View createView(View parent, final String name, @NonNull Context context,
@NonNull AttributeSet attrs, boolean inheritContext,
boolean readAndroidTheme, boolean readAppTheme, boolean wrapContext) {
final Context originalContext = context;
// We can emulate Lollipop's android:theme attribute propagating down the view hierarchy
// by using the parent's context
if (inheritContext && parent != null) {
context = parent.getContext();
}
if (readAndroidTheme || readAppTheme) {
// We then apply the theme on the context, if specified
context = themifyContext(context, attrs, readAndroidTheme, readAppTheme);
}
if (wrapContext) {
context = TintContextWrapper.wrap(context);
}
View view = null;
// We need to 'inject' our tint aware Views in place of the standard framework versions
switch (name) {
case "TextView":
view = createTextView(context, attrs);
verifyNotNull(view, name);
break;
case "ImageView":
view = createImageView(context, attrs);
verifyNotNull(view, name);
break;
case "Button":
view = createButton(context, attrs);
verifyNotNull(view, name);
break;
case "EditText":
view = createEditText(context, attrs);
verifyNotNull(view, name);
break;
case "Spinner":
view = createSpinner(context, attrs);
verifyNotNull(view, name);
break;
case "ImageButton":
view = createImageButton(context, attrs);
verifyNotNull(view, name);
break;
case "CheckBox":
view = createCheckBox(context, attrs);
verifyNotNull(view, name);
break;
case "RadioButton":
view = createRadioButton(context, attrs);
verifyNotNull(view, name);
break;
case "CheckedTextView":
view = createCheckedTextView(context, attrs);
verifyNotNull(view, name);
break;
case "AutoCompleteTextView":
view = createAutoCompleteTextView(context, attrs);
verifyNotNull(view, name);
break;
case "MultiAutoCompleteTextView":
view = createMultiAutoCompleteTextView(context, attrs);
verifyNotNull(view, name);
break;
case "RatingBar":
view = createRatingBar(context, attrs);
verifyNotNull(view, name);
break;
case "SeekBar":
view = createSeekBar(context, attrs);
verifyNotNull(view, name);
break;
case "ToggleButton":
view = createToggleButton(context, attrs);
verifyNotNull(view, name);
break;
default:
// The fallback that allows extending class to take over view inflation
// for other tags. Note that we don't check that the result is not-null.
// That allows the custom inflater path to fall back on the default one
// later in this method.
view = createView(context, name, attrs);
}
if (view == null && originalContext != context) {
// If the original context does not equal our themed context, then we need to manually
// inflate it using the name so that android:theme takes effect.
view = createViewFromTag(context, name, attrs);
}
if (view != null) {
// If we have created a view, check its android:onClick
checkOnClickListener(view, attrs);
}
return view;
}
通过上面的了解我们可以大概知道可以通过自定义一个ThemeInflaterFactory implements LayoutInflater.Factory2用来解析XML布局创建View(相当于hook主系统创建view的过程)。这里我们可以合理的保存下来需要适配主题的view以及属性
ThemeInflaterFactory的功能 具体逻辑可以查看代码
- 维护一个mThemeItemMap集合,用来保存需要适配的view 以及属性,并对外提供添加跟清除方法
- ThemeItem对象包含一个View,以及需要修改的属性扩展BaseAttr,具体实现当前有BackgroundAttr、ImageViewSrcAttr、TextColorAttr
- 对外提供applyTheme方法,遍历集合mThemeItemMap,修改属性值
@Override
public View onCreateView(View parent, String name, Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
boolean isThemeEnable = attrs.getAttributeBooleanValue(ThemeConfig.NAMESPACE, ThemeConfig.ATTR_THEME_ENABLE, false);
//调用系统创建基本控件
AppCompatDelegate delegate = mAppCompatActivity.getDelegate();
View view = delegate.createView(parent, name, context, attrs);
if (isThemeEnable || ThemeConfig.isGlobalSkinApply()) { //控件支持切换模式 或者开启类全局支持开关
if (view == null) {
view = ViewCreate.createViewFromTag(context, name, attrs);
}
if (view == null) {
return null;
}
parseSkinAttr(context, attrs, view);
}
return view;
}
private void parseSkinAttr(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, View view) {
List<BaseAttr> viewAttrs = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < attrs.getAttributeCount(); i++) {
String attrName = attrs.getAttributeName(i);
String attrValue = attrs.getAttributeValue(i);
if ("style".equals(attrName)) { //mxl布局引入style
int[] skinAttrs = new int[]{android.R.attr.textColor, android.R.attr.background};
TypedArray a = context.getTheme().obtainStyledAttributes(attrs, skinAttrs, 0, 0);
int textColorId = a.getResourceId(0, -1);
int backgroundId = a.getResourceId(1, -1);
if (textColorId != -1) {
String entryName = context.getResources().getResourceEntryName(textColorId);
String typeName = context.getResources().getResourceTypeName(textColorId);
BaseAttr skinAttr = AttrFactory.get("textColor", textColorId, entryName, typeName);
if (skinAttr != null) {
viewAttrs.add(skinAttr);
}
}
if (backgroundId != -1) {
String entryName = context.getResources().getResourceEntryName(backgroundId);
String typeName = context.getResources().getResourceTypeName(backgroundId);
BaseAttr skinAttr = AttrFactory.get("background", backgroundId, entryName, typeName);
if (skinAttr != null) {
viewAttrs.add(skinAttr);
}
}
a.recycle();
continue;
}
if (AttrFactory.isSupportedAttr(attrName) && attrValue.startsWith("@")) {
try {
int id = Integer.parseInt(attrValue.substring(1));
if (id == 0) {
continue;
}
boolean isOnlyDark = attrs.getAttributeBooleanValue(ThemeConfig.NAMESPACE, ThemeConfig.ATTR_THEME_ONLY_DARK, false);
String entryName = context.getResources().getResourceEntryName(id);
String typeName = context.getResources().getResourceTypeName(id);
BaseAttr mSkinAttr = AttrFactory.get(attrName, id, entryName, typeName, isOnlyDark);
if (mSkinAttr != null) {
viewAttrs.add(mSkinAttr);
}
} catch (NumberFormatException e) {
}
}
}
if (!viewAttrs.isEmpty()) {
ThemeItem skinItem = new ThemeItem();
skinItem.view = view;
skinItem.attrs = viewAttrs;
mThemeItemMap.put(skinItem.view, skinItem);
if (!AppThemeManager.getInstance().isNormalTheme() || AppThemeManager.getInstance().isInNightTheme()) {
skinItem.changeTheme();
}
}
}
view 支持主题切换或者全局支持开关打开,保存对应的view以及属性AttrFactory获取的BaseAttr的实现类到ThemeItem里,保存于mThemeItemMap集合里
/**
* 运用主题
*/
public void applyTheme() {
if (mThemeItemMap.isEmpty()) {
return;
}
for (View view : mThemeItemMap.keySet()) {
if (view == null) {
continue;
}
mThemeItemMap.get(view).changeTheme();
}
}
对外提供方法修改主题
AppThemeManager的功能
- 维护一个主题切换监听集合ListmThemeObservers,在baseActivity实现IThemeUpdate接口,并调用AppThemeManager的addObserver(IThemeUpdate observer)添加监听,对应onDestory移除监听,
- 点击切换主题时调用notifyThemeUpdate()方法遍历集合通知各个页面调用ThemeInflaterFactory对外提供applyTheme方法修改对应的属性资源值
ThemeResourceUtil的功能
- 通过编译后的资源在R文件的id,获取到资源名称,在根据当前主题拼接资源名称,再获取R文件对应拼接后到资源id返回供BaseAttr的 applyTheme(view)设置切换后的资源达到切换主题的功能
- ThemeConfig 配置信息,包括是否开启全局view支持主题切换开关debug模式开关状态栏适配开关本地主题记录sp等
具体使用
1.在Application初始化AppThemeManager以及配置ThemeConfig
public class DarkApplication extends Application {
@Override
public void onCreate() {
super.onCreate();
AppThemeManager.getInstance().init(this);
ThemeConfig.setCanChangeStatusColor(true);
ThemeConfig.enableGlobalThemeApply();
ThemeConfig.setDebug(true);
}
}
2.BaseActivity实现IThemeUpdate, IDynamicNewView 接口
public class BaseActivity extends AppCompatActivity implements IThemeUpdate, IDynamicNewView {
/**
* 自定义 InflaterFactory
*/
private ThemeInflaterFactory mThemeInflaterFactory;
@Override
protected void onCreate(@Nullable Bundle savedInstanceState) {
mThemeInflaterFactory = new ThemeInflaterFactory(this);
LayoutInflaterCompat.setFactory2(getLayoutInflater(), mThemeInflaterFactory);
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
AppThemeManager.getInstance().addObserver(this);
changeStatusColor();
}
public void changeStatusColor() {
if (!ThemeConfig.isCanChangeStatusColor()) {
return;
}
if (Build.VERSION.SDK_INT >= Build.VERSION_CODES.LOLLIPOP) {
int color = ThemeResourceUtil.getColorPrimaryDark();
if (color != -1) {
Window window = getWindow();
window.addFlags(WindowManager.LayoutParams.FLAG_DRAWS_SYSTEM_BAR_BACKGROUNDS);
window.setStatusBarColor(ThemeResourceUtil.getColorPrimaryDark());
}
}
}
public ThemeInflaterFactory getInflaterFactory() {
return mThemeInflaterFactory;
}
@Override
public void dynamicAddView(View view, List<DynamicAttr> pDAttrs) {
mThemeInflaterFactory.dynamicAddThemeEnableView(this, view, pDAttrs);
}
@Override
public void dynamicAddView(View view, String attrName, int attrValueResId, boolean isOnlyDark) {
mThemeInflaterFactory.dynamicAddThemeEnableView(this, view, attrName, attrValueResId, isOnlyDark);
}
@Override
public void onThemeUpdate() {
mThemeInflaterFactory.applyTheme();
changeStatusColor();
}
@Override
protected void onDestroy() {
super.onDestroy();
AppThemeManager.getInstance().removeObserver(this);
mThemeInflaterFactory.clean();
}
}
注意 setFactory2()一定要在 super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)之前调用即setContentView之前设置Factory2
3.在需要切换主题的根布局上添加 xmlns:theme=“http://schemas.android.com/android/theme” ,然后在需要切换主题的View上加上 theme:enable=“true” ,注意theme:onlyDark=“true” 的使用场景是红色主题 和金色主题都使用的同一资源,不需要区分,只区分暗黑资源。不写默认为false
4.资源文件下创建对应资源区分colors.xml、colors-night.xml、colors_gold.xml、colors_gold_night.xml 或者mipmap_img.png、mipmap_img_night.png、mipmap_img_gold.png、mipmap_img_gold_night.png
具体获取的方法看参考ThemeResourceUtil
主题属性扩展
默认支持 textColor 和 background、src的主题切换。如果你还需要对其他属性进行主题切换,需要去自定义了
比如 TabLayout它下面会有一个指示器,当我们换主题的时候也希望这个指示器的颜色也跟着更改。
- 第一步
public class TabLayoutIndicatorAttr extends BaseAttr {
@Override
public void applyTheme(View view) {
if (view instanceof TabLayout) {
TabLayout tl = (TabLayout) view;
if (RES_TYPE_NAME_COLOR.equals(attrValueTypeName)) {
int color = ThemeResourceUtil.getColor(attrValueRefId);
tl.setSelectedTabIndicatorColor(color);
}
}
}
}
- 第二步
方法中加入ThemeConfig.addSupportAttr(“tabLayoutIndicator”, new TabLayoutIndicatorAttr()); - 最后我们就可以正常使用了,
dynamicAddView(tablayout, “tabLayoutIndicator”, R.color.colorPrimaryDark);
注意事项
- 主题切换默认只支持android的常用控件,支持库的控件和自定义控件需要动态添加(如:
dynamicAddView(toolbar, “background”, R.color.colorPrimaryDark);),在布局文件中使用theme:enable=“true”是无效的 - 默认不支持状态栏颜色的更改,如果需要主题切换的同时也要更改状态栏颜色,在Application中配置
ThemeConfig.setCanChangeStatusColor(true);,状态栏的颜色值来源于colorPrimaryDark
3.有主题切换需求 View 所使用的资源一定要是引用值,如:@color/red,而不是 #ff0000
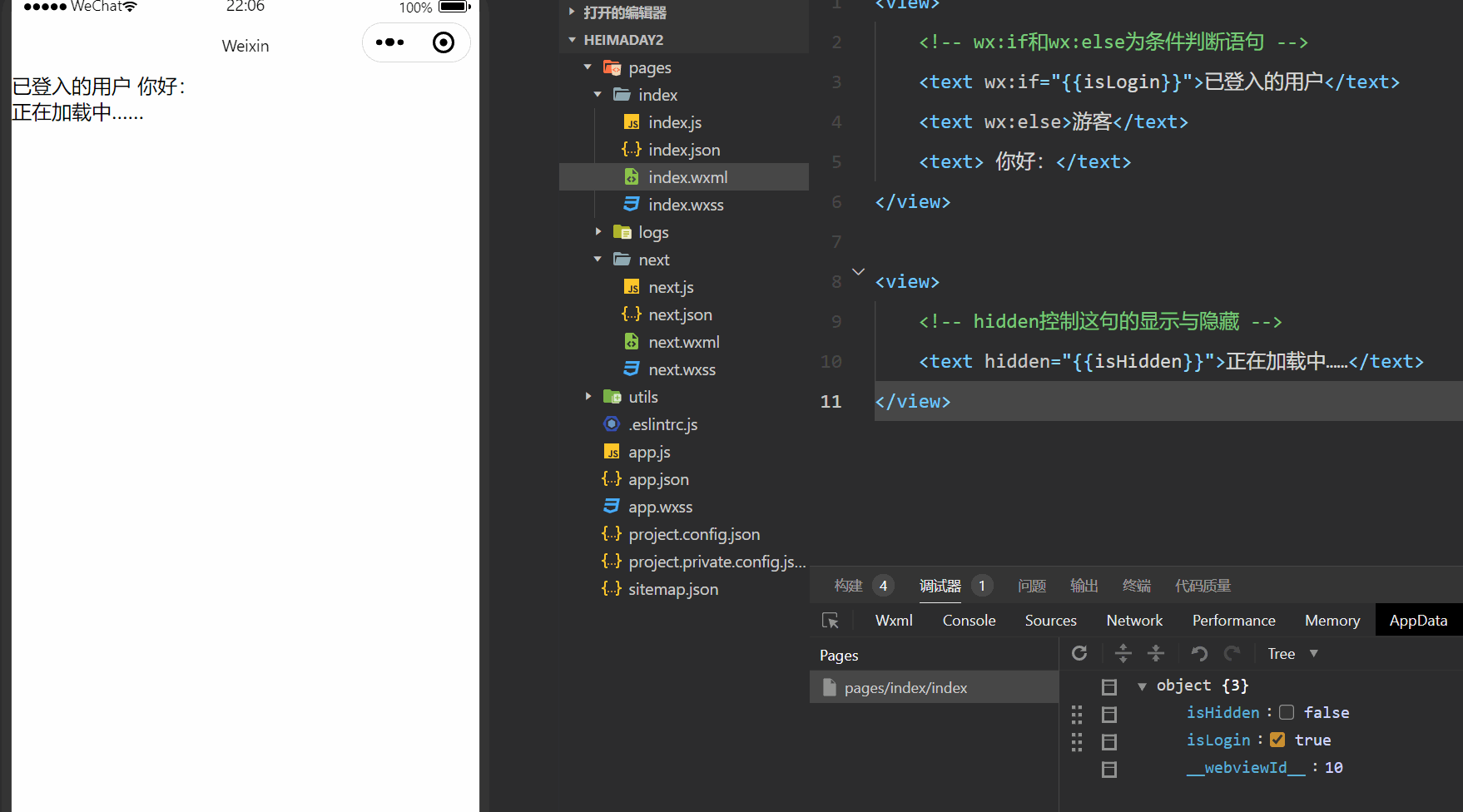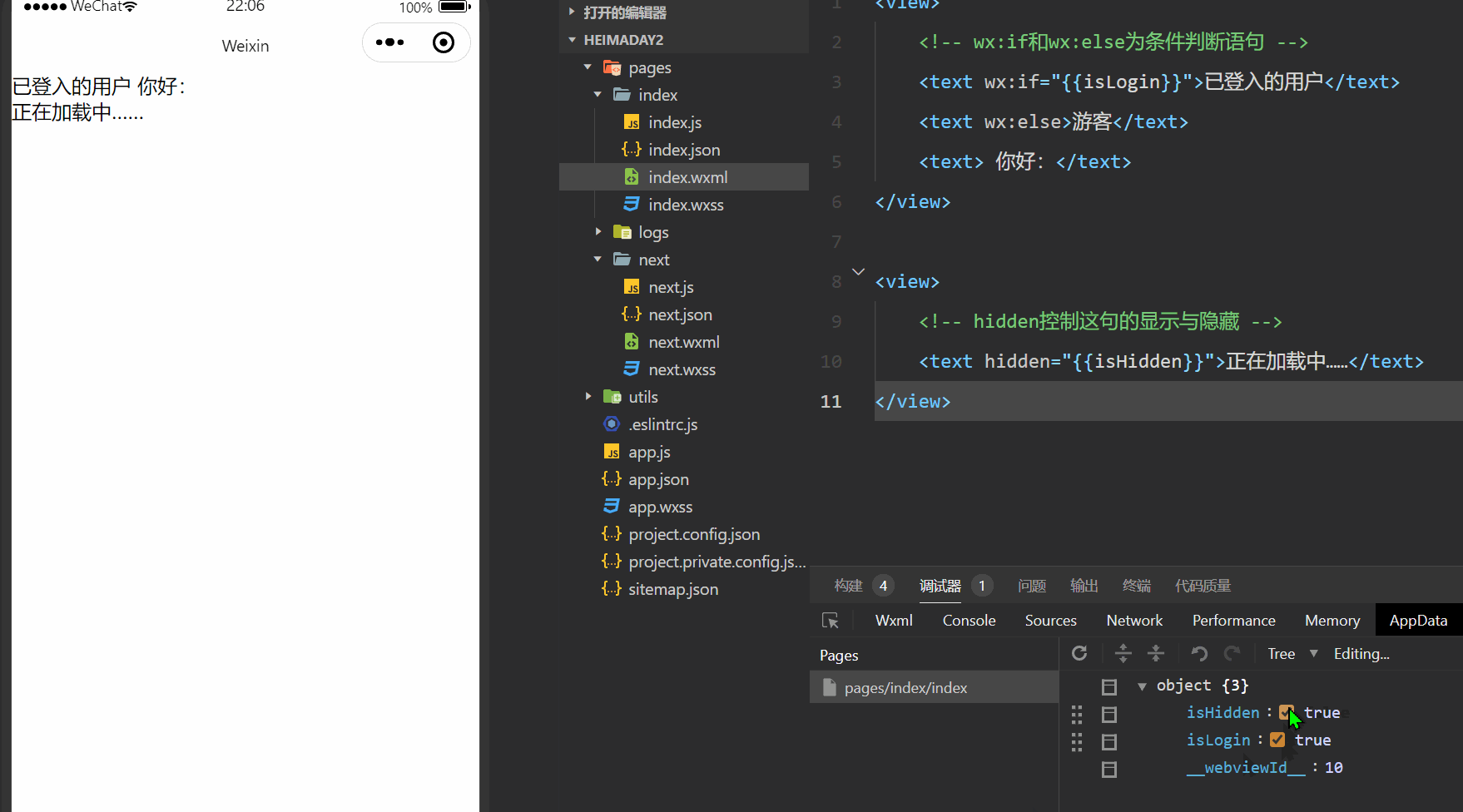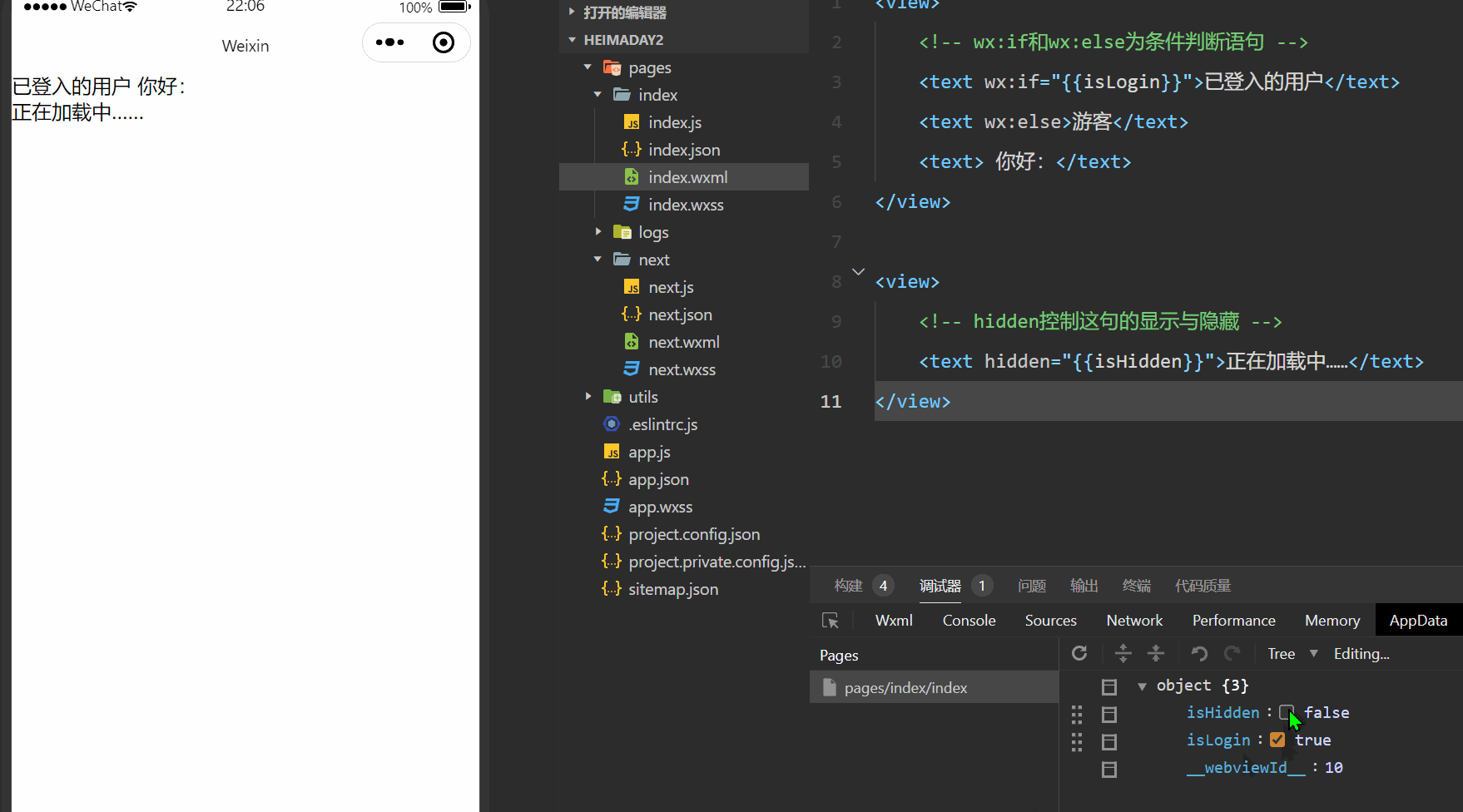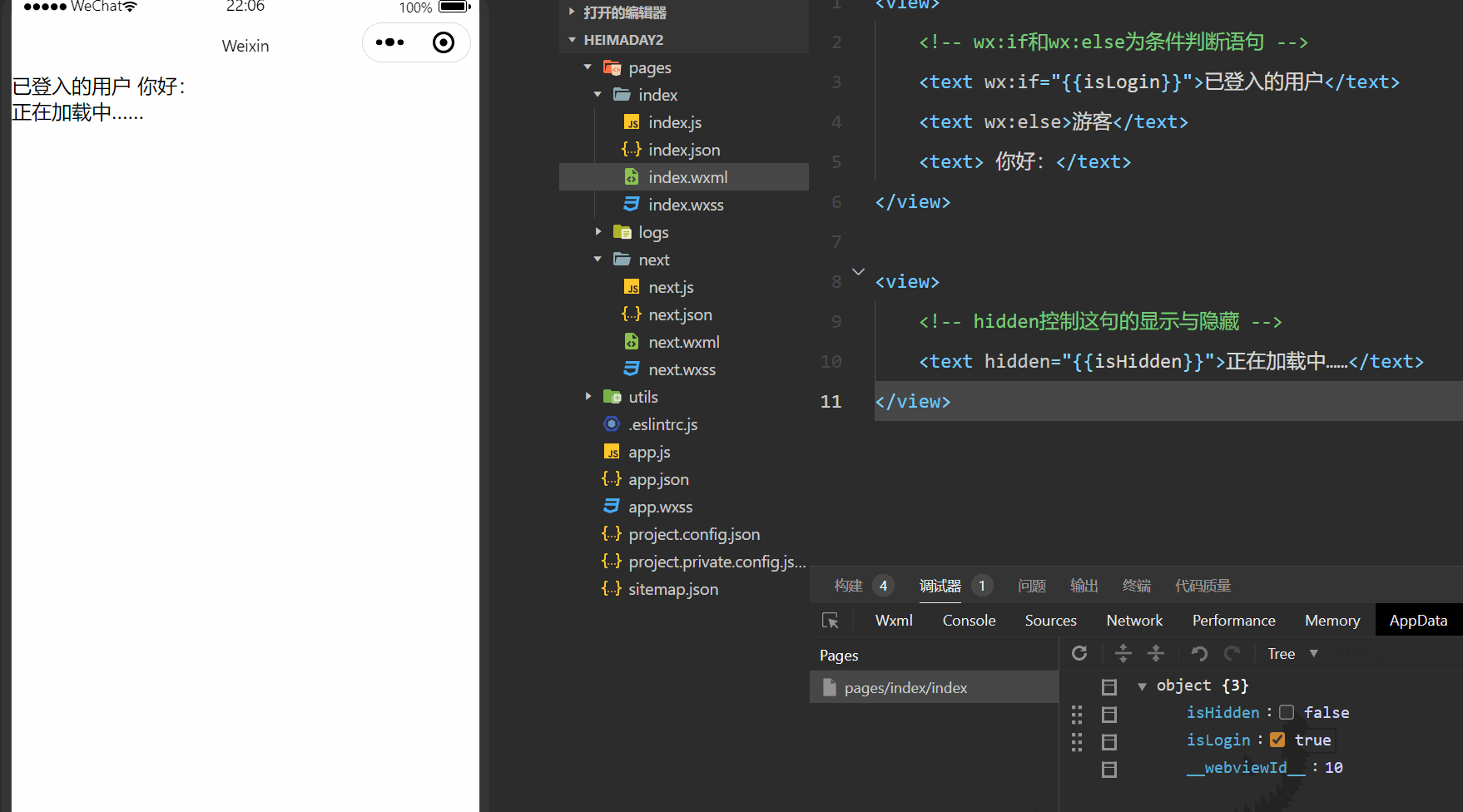
demo效果截图
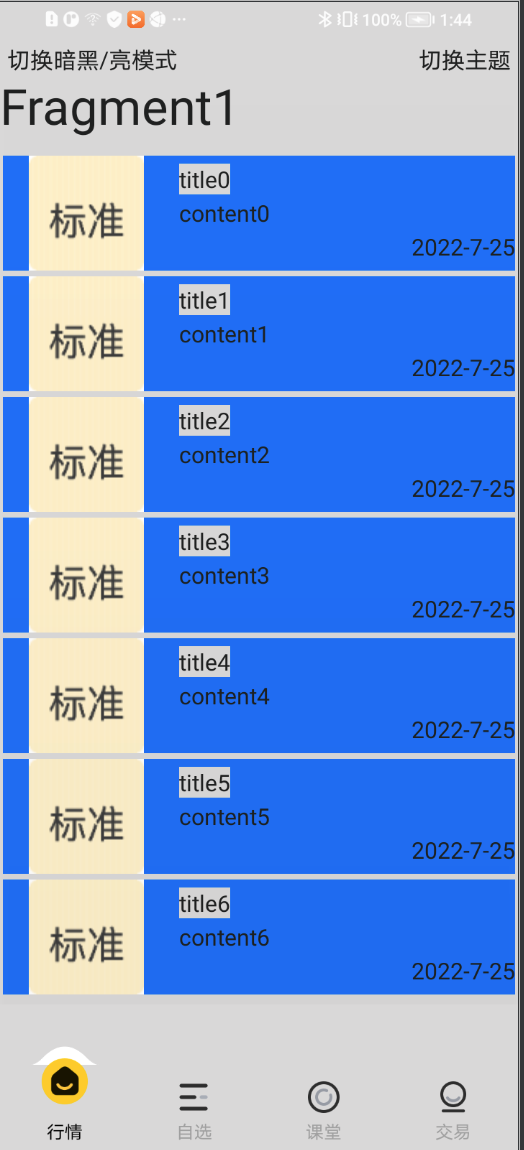
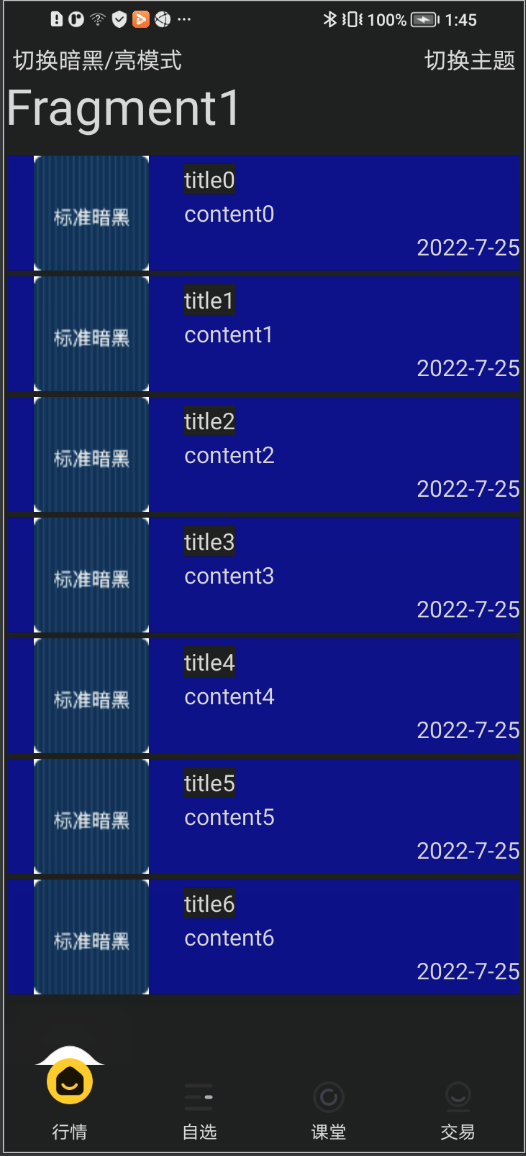

原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_36276974/article/details/126014555
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。
如若转载,请注明出处:http://www.7code.cn/show_15885.html
如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系代码007邮箱:suwngjj01@126.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!