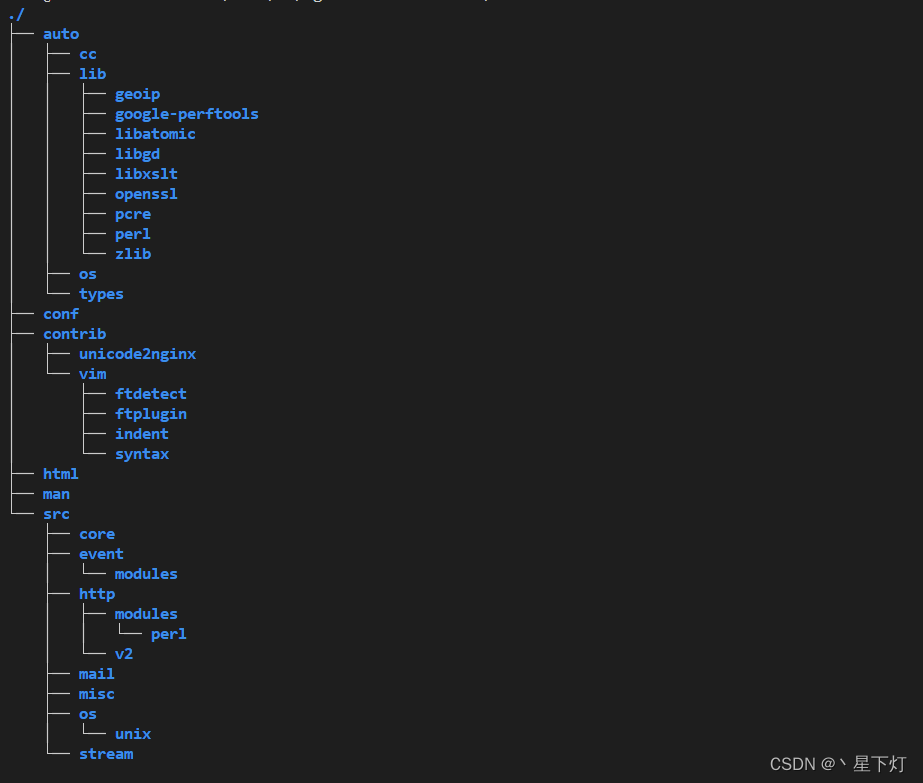
Nginx的源码目录结构
nginx的源码目录与nginx的模块化以及功能的划分是紧密结合,这也使得我们可以很方便地找到相关功能的代码。我们先来看一下nginx源码的目录结构。
主要目录详情如下:
- auto:自动检测系统环境以及编译相关的脚本。
- conf:存放默认配置文件,在make install后,会拷贝到安装目录中去。
- contrib:存放一些实用工具,如geo配置生成工具(geo2nginx.pl)。
- html:存放默认的网页文件,在make install后,会拷贝到安装目录中去。
- man:nginx的man手册。
- src:存放nginx的源代码。
Nginx中configure的原理
Nginx的编译流程从configure开始:configure脚本将根据我们输入的选项、系统环境参与来生成所需的文件(包含源文件与Makefile文件)。configure会调用一系列auto脚本来实现编译环境的初始化
auto脚本
auto脚本由一系列脚本组成,他们有一些是实现一些通用功能由其它脚本来调用(如have),有一些则是完成一些特定的功能(如option)。
. auto/options
. auto/init
. auto/sources
这是configure源码开始执行的前三行,依次交由auto目录下面的option、init、sources来处理。
-
auto/options:主是处理用户输入的configure选项,并由选项生成一些全局变量的值,这些值在其它文件中会用到。该文件也会输出configure的帮助信息
##1. 设置选项对应的shell变量以及他们的初始值 help=no NGX_PREFIX= NGX_SBIN_PATH= NGX_CONF_PREFIX= NGX_CONF_PATH= NGX_ERROR_LOG_PATH= NGX_PID_PATH= NGX_LOCK_PATH= NGX_USER= NGX_GROUP= ... ## 2, 处理每一个选项值,并设置到对应的全局变量中 for option do opt="$opt `echo $option | sed -e "s/(--[^=]*=)(.* .*)/1'2'/"`" # 得到此选项的value部分 case "$option" in -*=*) value=`echo "$option" | sed -e 's/[-_a-zA-Z0-9]*=//'` ;; *) value="" ;; esac # 根据option内容进行匹配,并设置相应的选项 case "$option" in --help) help=yes ;; --prefix=) NGX_PREFIX="!" ;; --prefix=*) NGX_PREFIX="$value" ;; --sbin-path=*) NGX_SBIN_PATH="$value" ;; --conf-path=*) NGX_CONF_PATH="$value" ;; --error-log-path=*) NGX_ERROR_LOG_PATH="$value";; --pid-path=*) NGX_PID_PATH="$value" ;; --lock-path=*) NGX_LOCK_PATH="$value" ;; --user=*) NGX_USER="$value" ;; --group=*) NGX_GROUP="$value" ;; ... *) # 没有找到的对应选项 echo "$0: error: invalid option "$option"" exit 1 ;; esac done ## 3. 对选项进行处理 # 如果有--help,则输出帮助信息 if [ $help = yes ]; then cat << END --help print this message --prefix=PATH set installation prefix --sbin-path=PATH set nginx binary pathname --conf-path=PATH set nginx.conf pathname --error-log-path=PATH set error log pathname --pid-path=PATH set nginx.pid pathname --lock-path=PATH set nginx.lock pathname --user=USER set non-privileged user for worker processes --group=GROUP set non-privileged group for worker processes END exit 1 fi # 默认文件路径 NGX_CONF_PATH=${NGX_CONF_PATH:-conf/nginx.conf} NGX_CONF_PREFIX=`dirname $NGX_CONF_PATH` NGX_PID_PATH=${NGX_PID_PATH:-logs/nginx.pid} NGX_LOCK_PATH=${NGX_LOCK_PATH:-logs/nginx.lock} ... -
auto/init:该文件的目录在于初始化一些临时文件的路径,检查echo的兼容性,并创建Makefile。
# Copyright (C) Igor Sysoev # Copyright (C) Nginx, Inc. NGX_MAKEFILE=$NGX_OBJS/Makefile NGX_MODULES_C=$NGX_OBJS/ngx_modules.c NGX_AUTO_HEADERS_H=$NGX_OBJS/ngx_auto_headers.h NGX_AUTO_CONFIG_H=$NGX_OBJS/ngx_auto_config.h NGX_AUTOTEST=$NGX_OBJS/autotest NGX_AUTOCONF_ERR=$NGX_OBJS/autoconf.err # STUBs NGX_ERR=$NGX_OBJS/autoconf.err MAKEFILE=$NGX_OBJS/Makefile NGX_PCH= NGX_USE_PCH= # check the echo's "-n" option and "c" capability if echo "testc" | grep c >/dev/null; then if echo -n test | grep n >/dev/null; then ngx_n= ngx_c= else ngx_n=-n ngx_c= fi else ngx_n= ngx_c='c' fi # create Makefile cat << END > Makefile default: build clean: rm -rf Makefile $NGX_OBJS .PHONY: default clean END -
auto/sources:它的主要作用是定义不同功能或系统所需要文件的变量。根据功能,分为CORE、REGEX、EVENT、UNIX、FREEBSD、HTTP等。
每一个功能将会由四个变量组成,”_MODULES”表示此功能相关的模块,最终会输出到ngx_modules.c文件中,即动态生成需要编译到nginx中的模块;
“INCS”表示此功能依赖的源码目录,查找头文件的时候会用到,在编译选项中,会出现在”-I”中;
“DEPS”显示指明在Makefile中需要依赖的文件名,即编译时,需要检查这些文件的更新时间;
“SRCS”表示需要此功能编译需要的源文件。
以auto/sources中的core为例:CORE_MODULES="ngx_core_module ngx_errlog_module ngx_conf_module" CORE_INCS="src/core" CORE_DEPS="src/core/nginx.h src/core/ngx_config.h ···" CORE_SRCS="src/core/nginx.c src/core/ngx_log.c ···" -
auto/have:这个工具的作用是,将$have变量的值,宏定义为1,并输出到auto_config文件中。通常我们通过这个工具来控制是否打开某个特性。这个工具在使用前,需要先定义宏的名称 ,即$have变量。
# Copyright (C) Igor Sysoev # Copyright (C) Nginx, Inc. cat << END >> $NGX_AUTO_CONFIG_H #ifndef $have #define $have 1 #endif END
再看configure文件:
# NGX_DEBUG是在auto/options文件中处理的,如果有--with-debug选项,则其值是YES
if [ $NGX_DEBUG = YES ]; then
have=NGX_DEBUG . auto/have
fi
可以看出,configure通过have定义NGX_DEBUG :通过宏定义,输出到config头文件中,然后在程序中可以判断这个宏是否有定义,来实现不同的逻辑。(实际上这段代码表示的就是是否启用debug调试nginx源码)
继续configure:
# 编译器选项
. auto/cc/conf
# 头文件支持宏定义
if [ "$NGX_PLATFORM" != win32 ]; then
. auto/headers
fi
# 操作系统相关的配置的检测
. auto/os/conf
# unix体系下的通用配置检测
if [ "$NGX_PLATFORM" != win32 ]; then
. auto/unix
fi
依次调用auto中其它几个文件,来进行环境的检测,包括编译器、操作系统相关。
-
auto/feature:nginx的configure会自动检测不同平台的特性,靠的就是auto/feature的实现。此工具的核心思想是,输出一小段代表性c程序,然后设置好编译选项,再进行编译连接运行,再对结果进行分析。
- 例如:
如果想检测某个库是否存在,就在小段c程序里面调用库里面的某个函数,再进行编译链接,如果出错,则表示库的环境不正常,如果编译成功,且运行正常,则库的环境检测正常。我们在写nginx第三方模块时,也常使用此工具来进行环境的检测,所以,此工具的作用贯穿整个configure过程。
auto/unix里面利用auto/feature实现检测当前操作系统是否支持poll函数调用:ngx_feature="poll()" ngx_feature_name= ngx_feature_run=no ngx_feature_incs="#include <poll.h>" ngx_feature_path= ngx_feature_libs= ngx_feature_test="int n; struct pollfd pl; pl.fd = 0; pl.events = 0; pl.revents = 0; n = poll(&pl, 1, 0); if (n == -1) return 1" . auto/feature if [ $ngx_found = no ]; then # 如果没有找到poll,就设置变量的值 EVENT_POLL=NONE fi在调用auto/feature之前,需要先设置几个输入参数变量的值,然后结果会存在$ngx_found变量里面, 并输出宏定义以表示支持此特性。
$ngx_feature 特性名称 $ngx_feature_name 特性的宏定义名称,如果特性测试成功,则会定义该宏定义 $ngx_feature_path 编译时要查找头文件目录 $ngx_feature_test 要执行的测试代码 $ngx_feature_incs 在代码中要include的头文件 $ngx_feature_libs 编译时需要link的库文件选项 $ngx_feature_run 编译成功后,对二进制文件需要做的动作,可以是yes value bug 其它 $ngx_found 如果找到,并测试成功,其值为yes,否则其值为no
再来看auto/feature的代码:
# 初始化输出结果为no ngx_found=no # 将特性名称小写转换成大写 if test -n "$ngx_feature_name"; then ngx_have_feature=`echo $ngx_feature_name | tr abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ` fi # 将所有include目录转换成编译选项 if test -n "$ngx_feature_path"; then for ngx_temp in $ngx_feature_path; do ngx_feature_inc_path="$ngx_feature_inc_path -I $ngx_temp" done fi # 生成临时的小段c程序代码。 # $ngx_feature_incs变量是程序需要include的头文件 # $ngx_feature_test是测试代码 cat << END > $NGX_AUTOTEST.c #include <sys/types.h> $NGX_INCLUDE_UNISTD_H $ngx_feature_incs int main(void) { $ngx_feature_test; return 0; } END # 编译命令 # 编译之后的目标文件是 $NGX_AUTOTEST,后面会判断这个文件是否存在来判断是否编译成功 ngx_test="$CC $CC_TEST_FLAGS $CC_AUX_FLAGS $ngx_feature_inc_path -o $NGX_AUTOTEST $NGX_AUTOTEST.c $NGX_TEST_LD_OPT $ngx_feature_libs" ngx_feature_inc_path= # 执行编译过程 # 编译成功后,会生成$NGX_AUTOTEST命名的文件 eval "/bin/sh -c "$ngx_test" >> $NGX_AUTOCONF_ERR 2>&1" # 如果文件存在,则编译成功 if [ -x $NGX_AUTOTEST ]; then case "$ngx_feature_run" in # 需要运行来判断是否支持特性 # 测试程序能否正常执行(即程序退出后的状态码是否是0),如果正常退出,则特性测试成功,设置ngx_found为 yes) # 如果程序正常退出,退出码为0,则程序执行成功,我们可以在测试代码里面手动返回非0来表示程序出错 # /bin/sh is used to intercept "Killed" or "Abort trap" messages if /bin/sh -c $NGX_AUTOTEST >> $NGX_AUTOCONF_ERR 2>&1; then echo " found" ngx_found=yes # 添加宏定义,宏的值为1 if test -n "$ngx_feature_name"; then have=$ngx_have_feature . auto/have fi else echo " found but is not working" fi ;; # 需要运行程序来判断是否支持特性,如果支持,将程序标准输出的结果作为宏的值 value) # /bin/sh is used to intercept "Killed" or "Abort trap" messages if /bin/sh -c $NGX_AUTOTEST >> $NGX_AUTOCONF_ERR 2>&1; then echo " found" ngx_found=yes # 与yes不一样的是,value会将程序从标准输出里面打印出来的值,设置为ngx_feature_name宏变量的值 # 在此种情况下,程序需要设置ngx_feature_name变量名 cat << END >> $NGX_AUTO_CONFIG_H #ifndef $ngx_feature_name #define $ngx_feature_name `$NGX_AUTOTEST` #endif END else echo " found but is not working" fi ;; # 与yes正好相反 bug) # /bin/sh is used to intercept "Killed" or "Abort trap" messages if /bin/sh -c $NGX_AUTOTEST >> $NGX_AUTOCONF_ERR 2>&1; then echo " not found" else echo " found" ngx_found=yes if test -n "$ngx_feature_name"; then have=$ngx_have_feature . auto/have fi fi ;; # 不需要运行程序,最后定义宏变量 *) echo " found" ngx_found=yes if test -n "$ngx_feature_name"; then have=$ngx_have_feature . auto/have fi ;; esac else # 编译失败 echo " not found" # 编译失败,会保存信息到日志文件中 echo "----------" >> $NGX_AUTOCONF_ERR # 保留编译文件的内容 cat $NGX_AUTOTEST.c >> $NGX_AUTOCONF_ERR echo "----------" >> $NGX_AUTOCONF_ERR # 保留编译文件的选项 echo $ngx_test >> $NGX_AUTOCONF_ERR echo "----------" >> $NGX_AUTOCONF_ERR fi # 最后删除生成的临时文件 rm -rf $NGX_AUTOTEST* - 例如:
-
auto/cc/conf:这一步主要是检测编译器,并设置编译器相关的选项。它先调用auto/cc/name来得到编译器的名称,然后根据编译器选择执行不同的编译器相关的文件如gcc执行auto/cc/gcc来设置编译器相关的一些选项。
-
auto/include:这个工具用来检测是头文件是否支持。需要检测的头文件放在$ngx_include里面,如果支持,则$ngx_found变量的值为yes,并且会产生NGX_HAVE_{ngx_include}的宏定义。
-
auto/headers:生成头文件的宏定义。生成的定义放在objs/ngx_auto_headers.h里面。
ngx_include="unistd.h"; . auto/include ngx_include="inttypes.h"; . auto/include ngx_include="limits.h"; . auto/include ngx_include="sys/filio.h"; . auto/include ngx_include="sys/param.h"; . auto/include ngx_include="sys/mount.h"; . auto/include ngx_include="sys/statvfs.h"; . auto/include ngx_include="crypt.h"; . auto/include -
auto/os/conf:针对不同的操作系统平台特性的检测,并针对不同的操作系统,设置不同的CORE_INCS、CORE_DEPS、CORE_SRCS变量。nginx跨平台的支持就是在这个地方体现出来的。
继续configure:
# 生成模块列表
. auto/modules
# 配置库的依赖
. auto/lib/conf
-
auto/modules:该脚本根据不同的条件,输出不同的模块列表,最后输出的模块列表的文件在objs/ngx_modules.c(生成的ngx_modules.c代码如下)
#include <ngx_config.h> #include <ngx_core.h> extern ngx_module_t ngx_core_module; extern ngx_module_t ngx_errlog_module; extern ngx_module_t ngx_conf_module; extern ngx_module_t ngx_emp_server_module; ... ngx_module_t *ngx_modules[] = { &ngx_core_module, &ngx_errlog_module, &ngx_conf_module, &ngx_emp_server_module, ... NULL };这个文件会决定所有模块的顺序,这会直接影响到最后的功能。这个文件会加载我们的第三方模块,这也是我们值得关注的地方。
来看一下auto/modules中的部分内容:if test -n "$DYNAMIC_ADDONS"; then echo configuring additional dynamic modules for ngx_addon_dir in $DYNAMIC_ADDONS do echo "adding module in $ngx_addon_dir" ngx_module_type= ngx_module_name= ngx_module_incs= ngx_module_deps= ngx_module_srcs= ngx_module_libs= ngx_module_order= ngx_module_link=DYNAMIC if test -f $ngx_addon_dir/config; then . $ngx_addon_dir/config # 执行第三方模块的配置 echo " + $ngx_addon_name was configured" else echo "$0: error: no $ngx_addon_dir/config was found" exit 1 fi done fi这段代码实现了nginx很强大的扩展性。
加载第三方模块,$ngx_addon_dir变量是在configure执行时,命令行从代码中,我们可以看到,它就是针对每一个第三方模块执行其目录下的config文件参数–add-module加入的,它是一个目录列表,每一个目录,表示一个第三方模块。
于是我们可以在config文件里面执行我们自己的检测逻辑,比如检测库依赖,添加编译选项等。 -
auto/lib/conf:该文件会针对nginx编译所需要的基础库的检测,比如rewrite模块需要的PCRE库的检测支持。
configure接下来定义一些宏常量,主要是是文件路径方面的:
case ".$NGX_PREFIX" in
.)
NGX_PREFIX=${NGX_PREFIX:-/usr/local/nginx}
have=NGX_PREFIX value=""$NGX_PREFIX/"" . auto/define
;;
.!)
NGX_PREFIX=
;;
*)
have=NGX_PREFIX value=""$NGX_PREFIX/"" . auto/define
;;
esac
if [ ".$NGX_CONF_PREFIX" != "." ]; then
have=NGX_CONF_PREFIX value=""$NGX_CONF_PREFIX/"" . auto/define
fi
have=NGX_SBIN_PATH value=""$NGX_SBIN_PATH"" . auto/define
have=NGX_CONF_PATH value=""$NGX_CONF_PATH"" . auto/define
have=NGX_PID_PATH value=""$NGX_PID_PATH"" . auto/define
have=NGX_LOCK_PATH value=""$NGX_LOCK_PATH"" . auto/define
have=NGX_ERROR_LOG_PATH value=""$NGX_ERROR_LOG_PATH"" . auto/define
if [ ".$NGX_ERROR_LOG_PATH" = "." ]; then
have=NGX_ERROR_LOG_STDERR . auto/have
fi
have=NGX_HTTP_LOG_PATH value=""$NGX_HTTP_LOG_PATH"" . auto/define
have=NGX_HTTP_CLIENT_TEMP_PATH value=""$NGX_HTTP_CLIENT_TEMP_PATH""
. auto/define
have=NGX_HTTP_PROXY_TEMP_PATH value=""$NGX_HTTP_PROXY_TEMP_PATH""
. auto/define
have=NGX_HTTP_FASTCGI_TEMP_PATH value=""$NGX_HTTP_FASTCGI_TEMP_PATH""
. auto/define
have=NGX_HTTP_UWSGI_TEMP_PATH value=""$NGX_HTTP_UWSGI_TEMP_PATH""
. auto/define
have=NGX_HTTP_SCGI_TEMP_PATH value=""$NGX_HTTP_SCGI_TEMP_PATH""
. auto/define
# 生成objs/makefile文件
. auto/make
# 生成关于库的编译选项到makefile文件
. auto/lib/make
# 生成与安装相关的makefile文件内容,并生成最外层的makefile文件
. auto/install
# STUB
. auto/stubs
have=NGX_USER value=""$NGX_USER"" . auto/define
have=NGX_GROUP value=""$NGX_GROUP"" . auto/define
if [ ".$NGX_BUILD" != "." ]; then
have=NGX_BUILD value=""$NGX_BUILD"" . auto/define
fi
# 编译的最后阶段,汇总信息
. auto/summary
模块编译顺序
nginx模块的顺序很重要,会直接影响到程序的功能。而且,nginx和部分模块,也有着自己特定的顺序要求,比如ngx_http_write_filter_module模块一定要在filter模块的最后一步执行。想查看模块的执行顺序,可以在objs/ngx_modules.c这个文件中找到,这个文件在configure之后生成。
ngx_module_t *ngx_modules[] = {
// 全局core模块
&ngx_core_module,
&ngx_errlog_module,
&ngx_conf_module,
&ngx_emp_server_module,
&ngx_emp_server_core_module,
// event模块
&ngx_events_module,
&ngx_event_core_module,
&ngx_kqueue_module,
// 正则模块
&ngx_regex_module,
// http模块
&ngx_http_module,
&ngx_http_core_module,
&ngx_http_log_module
&ngx_http_upstream_module,
// http handler模块
&ngx_http_static_module,
&ngx_http_autoindex_module,
&ngx_http_index_module,
&ngx_http_auth_basic_module,
&ngx_http_access_module,
&ngx_http_limit_conn_module,
&ngx_http_limit_req_module,
&ngx_http_geo_module,
&ngx_http_map_module,
&ngx_http_split_clients_module,
&ngx_http_referer_module,
&ngx_http_rewrite_module,
&ngx_http_proxy_module,
&ngx_http_fastcgi_module,
&ngx_http_uwsgi_module,
&ngx_http_scgi_module,
&ngx_http_memcached_module,
&ngx_http_empty_gif_module,
&ngx_http_browser_module,
&ngx_http_upstream_ip_hash_module,
&ngx_http_upstream_keepalive_module,
//此处是第三方handler模块
// http filter模块
&ngx_http_write_filter_module,
&ngx_http_header_filter_module,
&ngx_http_chunked_filter_module,
&ngx_http_range_header_filter_module,
&ngx_http_gzip_filter_module,
&ngx_http_postpone_filter_module,
&ngx_http_ssi_filter_module,
&ngx_http_charset_filter_module,
&ngx_http_userid_filter_module,
&ngx_http_headers_filter_module,
// 第三方filter模块
&ngx_http_copy_filter_module,
&ngx_http_range_body_filter_module,
&ngx_http_not_modified_filter_module,
NULL
}
http handler模块与http filter模块的顺序很重要,我们主要关注一下这两类模块。
-
http handler模块:
对于content phase之前的handler,同一个阶段的handler,模块是顺序执行的。
比如上面的示例代码中,ngx_http_auth_basic_module与ngx_http_access_module这两个模块都是在access phase阶段,由于ngx_http_auth_basic_module在前面,所以会先执行。
由于content phase只会有一个执行,所以不存在顺序问题。另外,我们加载的第三方handler模块永远是在最后执行。 -
http filter模块:
filter模块会将所有的filter handler排成一个倒序链,所以在最前面的最后执行。
上面的例子中,ngx_http_write_filter_module最后执行,ngx_http_not_modified_filter_module最先执行。
结束!
原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/Stars____/article/details/129874565
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。
如若转载,请注明出处:http://www.7code.cn/show_16119.html
如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系代码007邮箱:suwngjj01@126.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!