1、多表查询概览
1.1、分类
- 等值接连:where条件中,表字段与表字段直接使用等于符号(”=“)进行判断
- 非等值连接:where条件中,表字段与表字段使用非”=”符号,如:<=(小于等于)、>=(大于等于)、between and等等。
- 内连接:合并具有同一列的两个以上的表的行,结果集中不包含一个表与另一个表不匹配的行
- 外连接:合并具有同一列的两个以上的表的行,结果集中包含一个表与另一个表匹配的行之外,还包含了左表 或 右表不匹配的行
1.2、外连接的分类
- 左外连接(left outer join,可缩写为left join):两个表连接过程中,除了返回满足条件的行以外,还会返回左表中不满足条件的行,这种连接称为左连接
- 右外连接(right outer join,可缩写为right join):两个表连接过程中,除了返回满足条件的行以外,还会返回右表中不满足条件的行,这种连接称为右连接
- 全连接(full outer join,可缩写为full join):又称为”满外连接”,两个表连接过程中,返回两表直接的所有数据,这种连接称为全连接
1.3、常用的SQL语法标准
2、内外联接案例
2.1、初始化表
create table if not exists taobao.student
(
id int auto_increment primary key,
name varchar(50) null,
classid int null,
age int null
)
comment '学生表';
INSERT INTO student (id, name, classid, age) VALUES (1, '张三', 1, 18);
INSERT INTO student (id, name, classid, age) VALUES (2, '李四', 1, 18);
INSERT INTO student (id, name, classid, age) VALUES (3, '王五', 2, 17);
INSERT INTO student (id, name, classid, age) VALUES (4, '老六', 2, 18);
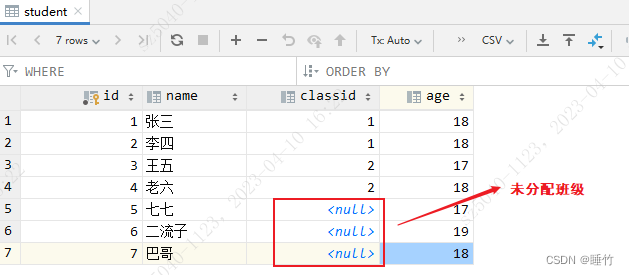
INSERT INTO student (id, name, classid, age) VALUES (5, '七七', null, 17);
INSERT INTO student (id, name, classid, age) VALUES (6, '二流子', null, 19);
INSERT INTO student (id, name, classid, age) VALUES (7, '巴哥', null, 18);create table if not exists taobao.classinfo
(
classid int auto_increment primary key,
name varchar(100) null
)
comment '班级表';
INSERT INTO classinfo (name) VALUES ('高一1班');
INSERT INTO classinfo (name) VALUES ('高一2班');
INSERT INTO classinfo (name) VALUES ('高一3班');2.2、内连接
<1>SQL92内连接写法:
select
t1.id -- 学生ID
,t1.name -- 学生姓名
,t1.age -- 学生年龄
,t2.name -- 班级名称
from student t1,classinfo t2
where t1.classid=t2.classid<2>SQL99内连接写法:
select
t1.id -- 学生ID
,t1.name -- 学生姓名
,t1.age -- 学生年龄
,t2.name -- 班级名称
from student t1
join classinfo t2
on t1.classid=t2.classid结果:
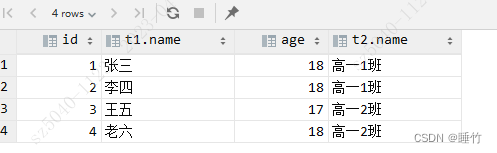
2.3、外连接案例
【注意:多表查询时,当查询一个表所有数据,该查询语句一定是外连接】
<1>SQL92外连接写法:
注意:
select t1.id -- 学生ID ,t1.name -- 学生姓名 ,t1.age -- 学生年龄 ,t2.name -- 班级名称 from student t1,classinfo t2 where t1.classid=t2.classid(+)
<2>SQL99外连接写法:
左连接写法:
select
t1.id -- 学生ID
,t1.name -- 学生姓名
,t1.age -- 学生年龄
,t2.name -- 班级名称
from student t1
left join classinfo t2 --注意:left join是缩写,也可以写为:left outer join
on t1.classid=t2.classid右连接写法:
select
t2.id -- 学生ID
,t2.name -- 学生姓名
,t2.age -- 学生年龄
,t1.name -- 班级名称
from classinfo t1
right join student t2
on t1.classid=t2.classid结果:

2.4、全连接案例
需求:查询学生表中的所有信息,并关联班级表信息及显示未关联的班级表信息
SQL99全连接写法(Oracle):
关键字:full join … on … 或者 full outer join … on …
select
t1.id -- 学生ID
,t1.name -- 学生姓名
,t1.age -- 学生年龄
,t2.name -- 班级名称
from student t1
full join classinfo t2
on t1.classid=t2.classidMySQL实现全连接,需要使用关键字“union“或者”union all”
2.5、union和union all
-
union:对两个查询的结果集,进行合并操作,会对重复的数据进行去重,同时进行默认规则(主键升序)的排序(因此效率比较低)。
-
union all:对两个查询的结果集,进行合并操作,不对数据进行去重,也不进行排序,直接把两个结果进行合并(效率高)。
例如:我们把学生表查询两次,并使用union或union all进行合并
select * from student
union -- 会进行去重操作
select * from student结果:
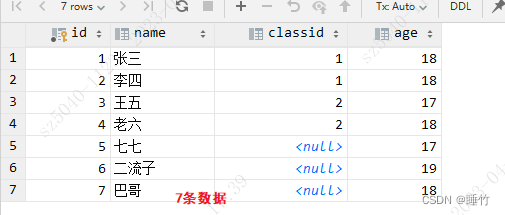
select * from student
union all -- 不去重
select * from student结果:

注意:
2.6、实现MySQL全连接
需求:查询学生表中的所有信息,并关联班级表信息及显示未关联的班级表信息
select
t1.id -- 学生ID
,t1.name -- 学生姓名
,t1.age -- 学生年龄
,t2.name -- 班级名称
from student t1
left join classinfo t2 -- 注意:left join是缩写,也可以写为:left outer join
on t1.classid=t2.classid
union all
select
null -- null:这里设置为null,只是为了与上一个select的结果行字段(数量)进行匹配,以下2个null作用一样
,null
,null
,t1.name
from classinfo t1
where t1.classid not in (
select
distinct classid -- distinct表示去重
from student t2 where t2.classid is not null
)结果:

2.7、内外连接面试基础
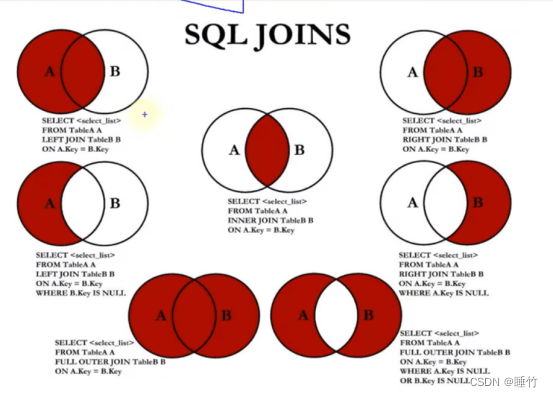
上述图对应7种多表查询,是面试及实际开发中,必会的操作,这里就不多言了
- A:看作是学生表
- B:看作是班级表
注意:当关联表的数量超过3个时,禁止使用join,因为一个join相当于一个for,性能会很差
2.8、SQL99多表查询新特性
<1>natural join
如:上面的内连接SQL为:
select
t1.id -- 学生ID
,t1.name -- 学生姓名
,t1.age -- 学生年龄
,t2.name -- 班级名称
from student t1
join classinfo t2
on t1.classid=t2.classid使用natural join进行改造,如下:
select
t1.id -- 学生ID
,t1.name -- 学生姓名
,t1.age -- 学生年龄
,t2.name -- 班级名称
from student t1
natural join classinfo t2 --自然连接结果:

查询到了0条数据,这是因为:
- natural join 关联多张表时,会自动根据表中相同的字段名称去匹配
- 上述student表中classid(班级编号)、name(学生姓名)与classinfo表中的 classid(班级编号)、name(班级名称)是一样的字段,而班级名称不可能与学生姓名相等,所以查询不到数据
也就是上述的自然连接,转义为内连接的SQL为:
select
t1.id -- 学生ID
,t1.name -- 学生姓名
,t1.age -- 学生年龄
,t2.name -- 班级名称
from student t1
join classinfo t2
on t1.classid=t2.classid
and t1.name = t2.name -- 这个条件也被自然连接附带上了因此,使用natural join的前提条件就是:
综上:在实际开发中,我们应当避免使用natural join,造成表与表之间的耦合较高
<2>using
-
等值条件的一种优化写法
语法:
- using(多表关联的字段名称)
前提:
如:上面的内连接SQL为:
select
t1.id -- 学生ID
,t1.name -- 学生姓名
,t1.age -- 学生年龄
,t2.name -- 班级名称
from student t1
join classinfo t2
on t1.classid=t2.classid使用using:
select
t1.id -- 学生ID
,t1.name -- 学生姓名
,t1.age -- 学生年龄
,t2.name -- 班级名称
from student t1
join classinfo t2
using(classid)结果:

原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_42675423/article/details/130067465
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。
如若转载,请注明出处:http://www.7code.cn/show_16337.html
如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系代码007邮箱:suwngjj01@126.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!