本文介绍: 1.编译器提供的默认子类拷贝构造函数会调用父类拷贝构造函数。2.重写的子类拷贝构造函数默认不会调用父类的拷贝构造函数,而是调用父类默认构造函数。3.重写的子类拷贝构造函数时应当显式的告诉编译器去调用父类的拷贝构造函数去构造父类,从而避免调用子类拷贝构造函数去创建一个对象时,导致子类中包含父类的那部分数据丢失的情况发生。具体做法为:Child(const Child &other) : Parent(other);
一. 编译器提供的默认子类拷贝构造函数会调用父类拷贝构造函数。
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
class Parent {
public:
Parent(string home_address = "中国") : m_home_address(home_address) {
cout << "调用父类构造函数" << endl;
}
Parent(const Parent &other) {
m_home_address = other.m_home_address;
cout << "调用父类拷贝构造函数" << endl;
}
string get_home_address() {return m_home_address;}
private:
string m_home_address;
};
class Child : public Parent {
public:
Child(string home_address = "") : Parent(home_address) {
cout << "调用子类构造函数" << endl;
}
private:
};
int main(int argc, char *argv[]) {
Child c1("广州");
cout << "c1 home_address = " << c1.get_home_address() << endl << endl;
Child c2 = c1; // 调用了子类的默认拷贝构造函数
cout << "c2 home_address = " << c2.get_home_address() << endl;
return 0;
}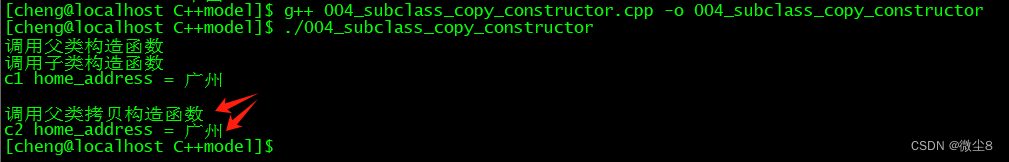
1. 创建一个对象 c1 时,先调用父类构造函数,后调用子类构造函数。
2. 创建 c2 对象时,执行了编译器提供的默认子类拷贝构造函数,具体构造顺序为:先调用父类拷贝构造函数,后调用编译器提供的默认子类拷贝构造函数。从而打印出 c2 home_address = 广州
二. 重写的子类拷贝构造函数默认不会调用父类的拷贝构造函数,而是调用父类默认构造函数。
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
class Parent {
public:
Parent(string home_address = "中国") : m_home_address(home_address) {
cout << "调用父类构造函数" << endl;
}
Parent(const Parent &other) {
m_home_address = other.m_home_address;
cout << "调用父类拷贝构造函数" << endl;
}
string get_home_address() {return m_home_address;}
private:
string m_home_address;
};
class Child : public Parent {
public:
Child(string home_address = "") : Parent(home_address) {
cout << "调用子类构造函数" << endl;
}
Child(const Child &other) {
cout << "调用子类拷贝构造函数" << endl;
}
private:
};
int main(int argc, char *argv[]) {
Child c1("广州");
cout << "c1 home_address = " << c1.get_home_address() << endl << endl;
Child c2 = c1; // 调用了子类的默认拷贝构造函数
cout << "c2 home_address = " << c2.get_home_address() << endl;
return 0;
}
创建 c2 对象时,执行了子类拷贝构造函数,具体构造顺序为:先调用父类默认构造函数,后调用子类拷贝构造函数。从而打印出 c2 home_address = 中国
三. 重写的子类拷贝构造函数时应当显式的告诉编译器去调用父类的拷贝构造函数去构造父类,从而避免调用子类拷贝构造函数去创建一个对象时,导致子类中包含父类的那部分数据丢失的情况发生。具体做法为:Child(const Child &other) : Parent(other);
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
class Parent {
public:
Parent(string home_address = "中国") : m_home_address(home_address) {
cout << "调用父类构造函数" << endl;
}
Parent(const Parent &other) {
m_home_address = other.m_home_address;
cout << "调用父类拷贝构造函数" << endl;
}
string get_home_address() {return m_home_address;}
private:
string m_home_address;
};
class Child : public Parent {
public:
Child(string home_address = "") : Parent(home_address) {
cout << "调用子类构造函数" << endl;
}
Child(const Child &other) : Parent(other) {
cout << "调用子类拷贝构造函数" << endl;
}
private:
};
int main(int argc, char *argv[]) {
Child c1("广州");
cout << "c1 home_address = " << c1.get_home_address() << endl << endl;
Child c2 = c1; // 调用了子类的默认拷贝构造函数
cout << "c2 home_address = " << c2.get_home_address() << endl;
return 0;
}
创建 c2 对象时,执行了子类拷贝构造函数,具体构造顺序为:先调用父类拷贝构造函数,后调用子类拷贝构造函数。从而打印出 c2 home_address = 广州
原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/d704791892/article/details/134709337
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。
如若转载,请注明出处:http://www.7code.cn/show_18291.html
如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系代码007邮箱:suwngjj01@126.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
声明:本站所有文章,如无特殊说明或标注,均为本站原创发布。任何个人或组织,在未征得本站同意时,禁止复制、盗用、采集、发布本站内容到任何网站、书籍等各类媒体平台。如若本站内容侵犯了原著者的合法权益,可联系我们进行处理。


![[Linux 进程控制(二)] 写时拷贝 – 进程终止](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/3dbeb6ece1be48c5ab271f177538e475.gif#pic_center)



