一、需求分析
1、项目背景
由于选课时间集中, 在同一时间进入系统抢占有限的资源, 导致系统服务响应速度明显下降, 严重时甚至会造成服务器崩溃。这种问题在目前实行学分制的国内高校中普遍存在。当系统软件不具备高并发性时,就无法顺畅承接超大流量,当请求过多,系统就会直接崩溃。
2、项目目标
本小组致力于针对原有选课系统的缺点,利用高并发技术的方法论以及设计原则,结合业务本身进行架构设计,以应对系统面临的流量冲击。从网络、架构、数据库等多方面进行系统优化,从而降低系统的响应时间,提高系统吞吐量,为学生提供一个高可用的选课系统,以达到系统能够在高并发下平稳处理大流量且自身依然运行良好的目的,让学生不再受系统崩溃所困扰。
二、系统功能分析
1、多角色划分
- **普通用户(学生):**登录注销、查看全校课程、查看方案内课程以及推荐班选课,选课退课、查看选课退课日志、查看课表
- **普通管理员:**学院、系、专业、班级管理,学生管理、课程管理、通知管理、选课轮次管理、课程紧急设置
- **超级管理员:**进行系统设置,查看系统日志,对普通管理员用户进行设置
2、模块功能详述
- 选课模块
- **登录注销:**学生可以通过学号和密码登入系统,登录后会保持一天的登入状态,登录凭证过期后再进行操作则会重新跳转至登录页面。也可以通过注销功能退出当前用户的登录
- **查看全校课程:**学生进入选课系统后可以查看与搜索全校开设的课程班。可以通过是否必修、是否通识课、课程学分等条件进行课程筛选,也可以进行课程搜索。同时会根据学生已选课程显示课程是否出现时间冲突
- **查看方案内课程:**学生可以查看自己所在班级的方案内课程,以及当前学期的推荐班选课。学生同样可以通过各种条件进行筛选和搜索,方便查找目的课程
- **选课退课:**学生可以对显示的课程进行选课,该操作会判断学生学分是否足够、课程是否冲突、是否已完成先修课程的学习以及课程容量充足等一系列条件。对于通识课程,如果当前处于第一轮次选课,则会允许选择人数超过课程容量,后台会在之后筛选
- **选课日志查询:**学生可以查看当前学期自己已经选择的课程,会分为通识选修课以及其他课程。同时也可以查看当前学期的退选日志,推选日志包括自己退选和系统退选
- 管理模块
三、系统架构
1、技术选型
2、系统分析
选课系统的特点
1.业务特点:在选课开始之前,流量一直是很平稳的状态;当选课刚刚开始时,系统流量呈直线突增;在选课活动开始一段时间或结束之后,流量又会急速下落。
2.技术特点:
– 瞬时并发量高。因为课程容量限制的特性,决定了一旦开始“抢课”,热门的课程就会出现流量洪峰。
– 并发读写。读比写要多,属于多读写少的场景。课程查询页访问大,但是真正选课成功的不多,即查询的流量要远大于扣减容量的流量。
3、架构设计
系统基于Spring、SpringMVC、Mybatis框架,采用MVC开发模式,将系统分为模型层、视图层、控制层三层。模型层Model主要负责处理业务逻辑以及数据库的交互,视图层View主要负责显示数据和提交数据,控制层Controller主要是用作辅助捕获请求并控制请求转发。
- SpringMVC:作为View层的实现者,接收用户的请求。SpringMVC的Controller作为整个应用的控制器,完成用户请求的转发及用户的响应。
- MyBatis:作为Model层的实现者,主要负责对数据库的增删改查。
- Spring:作为依赖注入和控制反转的框架,主要用于控制Bean的注入和管理Bean的生命周期。
同时从业务逻辑上来看,系统按照三层架构进行软件包的归类,分为控制层Controller、业务层Service和持久层Dao,让架构更加清晰。
- Controller层负责具体业务模块流程的控制,在此层面要调用Service层的接口来控制业务流程,控制的配置也同样是在Spring的配置文件里面进行,针对具体的业务流程,会有不同的控制器,我们具体的设计过程中可以将流程进行抽象归纳,设计出可以重复利用的子单元流程模块,这样不仅可以使程序结构变得清晰,和大大减少了代码量。
- Service层主要设计业务模块的逻辑应用设计。首先设计接口,再设计其实现类。接着再在Spring的配置文件中配置其实现的关联。这样我们就可以在应用中调用Service接口来进行业务处理。Service层的业务实现,具体要调用到已定义的DAO层接口。封装Service层的业务逻辑有利于通用的业务逻辑的独立性和重复利用性,程序显得非常简洁。
- DAO层的设计首先是设计DAO的接口。然后在Spring的配置文件中定义此接口的实现类。然后就可以在模块中调用此接口来进行数据业务的处理,而不用关心此接口的具体实现类是哪个类,显示结构非常清晰。DAO层的数据源配置,以及有关数据库连接的参数都是在Spring的配置文件中进行配置。
problem-provider
|--annotation # 自定义注解
|--aop # 切面类 —— SpringAOP的应用
|--common # 通用类
| |--config # 配置类
| |--constant # 常量类
| |--enums # 枚举类
| |--util # 工具类
|--controller # 控制层 —— Controller层的体现
|--dto # 数据传输对象
|--entity # 实体类 —— MyBatis中实体类的定义
|--event # 事件 —— 观察者设计模式
|--filter # 过滤器 —— SpringMVC实现请求的拦截过滤
|--handle # 处理器
|--listener # 监听器
|--mapper # 持久层 —— dao层的体现
|--service # 业务层 —— 接口设计思想体现
| |--impl # 实现类 —— Service层的体现
同时本系统通过SpringBoot对SSM进行整合,约定大于配置,避免了定义大量配置文件的繁琐,也一定程度的解决版本依赖冲突等问题。只需要在资源目录下配置application.yml文件配置数据库,redis,rabbitmq等服务的连接信息以及mapper文件即可。
4、系统演变
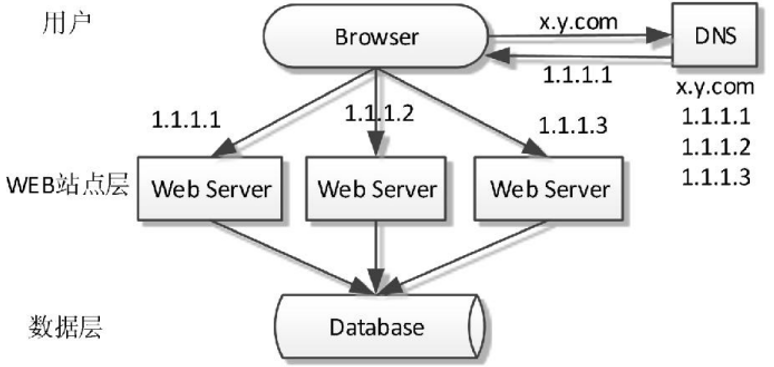
水平扩展有多种方式,由于DNS不会感知到具体WEB站点的可用性,当某个WEB站点服务故障(如网络中断、系统崩溃等),用户对这个站点的访问将失败,故不通过DNS进行水平扩展。
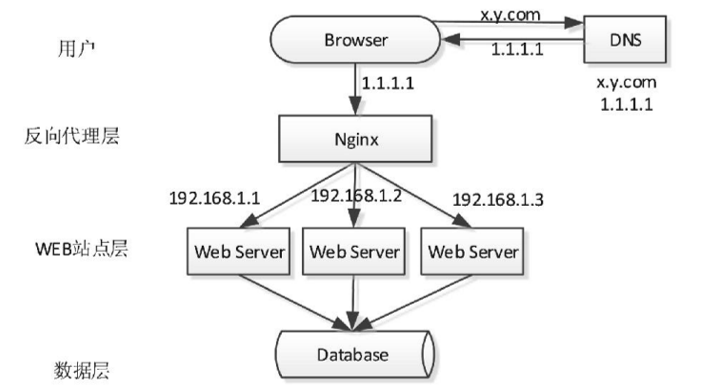
考虑到Nginx是一个高性能的 HTTP 和反向代理服务器,反向代理可以实现隐藏服务器的内部结构,集成防火墙来防御外界DDOS攻击,通过负载均衡分配流量到不同服务器上等功能。此外Nginx支持对故障 WEB 站点的探测感知,能够把流量引导到非故障的WEB站点,同时也没有DNS 负载均衡模式下暴露过多IP、扩容非实时等问题。
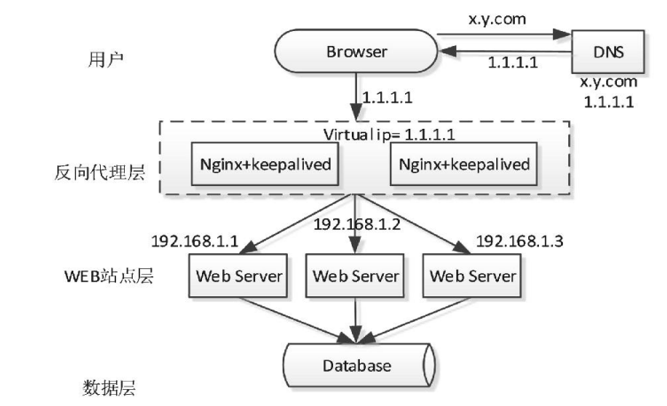
为避免反向代理层的单点故障风险,采用两台 Nginx 组成一个集群,分别部署 Keepalived,设置成相同的虚 IP,实现 Nginx 负载均衡服务的高可用。当一台 Nginx 挂了, Keepalived 能够探测到并将流量自动迁移到另一台 Nginx 上。该方案解决了反向代理层的高可用问题,但是 Nginx 集群的资源利用率下降到 50%(一主一备)。对于院校选课活动,每秒的HTTP请求峰值一般在 10 万以下,该架构的 WEB 站点响应能力应能满足要求,最多再适当提高 Nginx 服务器的配置应能解决问题。故系统最终决定采用基于Nginx集群反向代理的方式对WEB站点层进行水平扩展。
四、数据库设计
1、概念结构设计
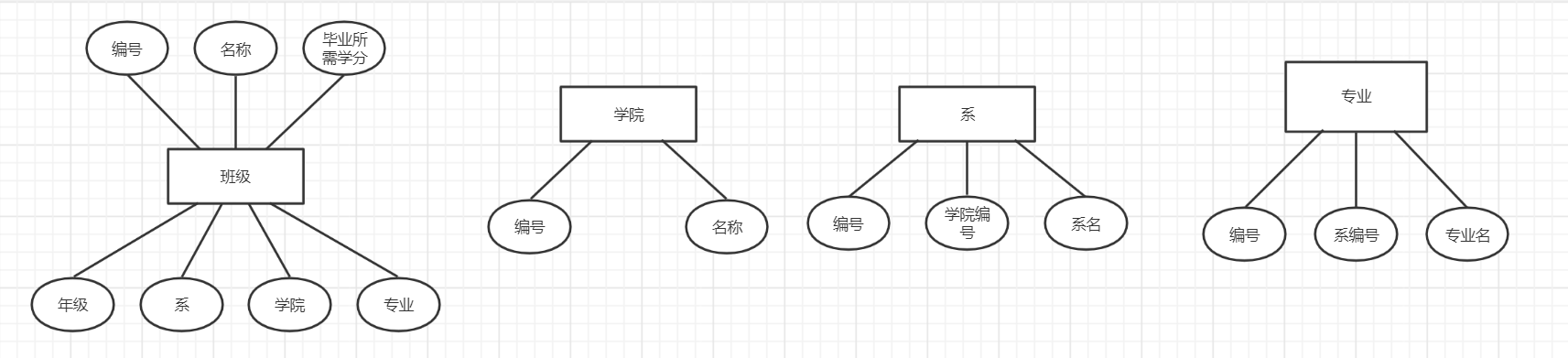
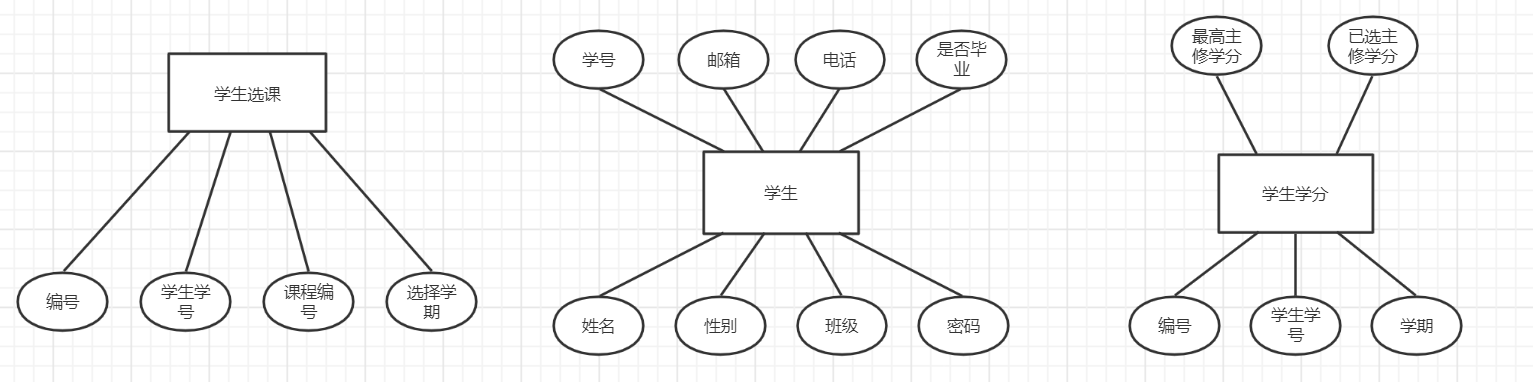
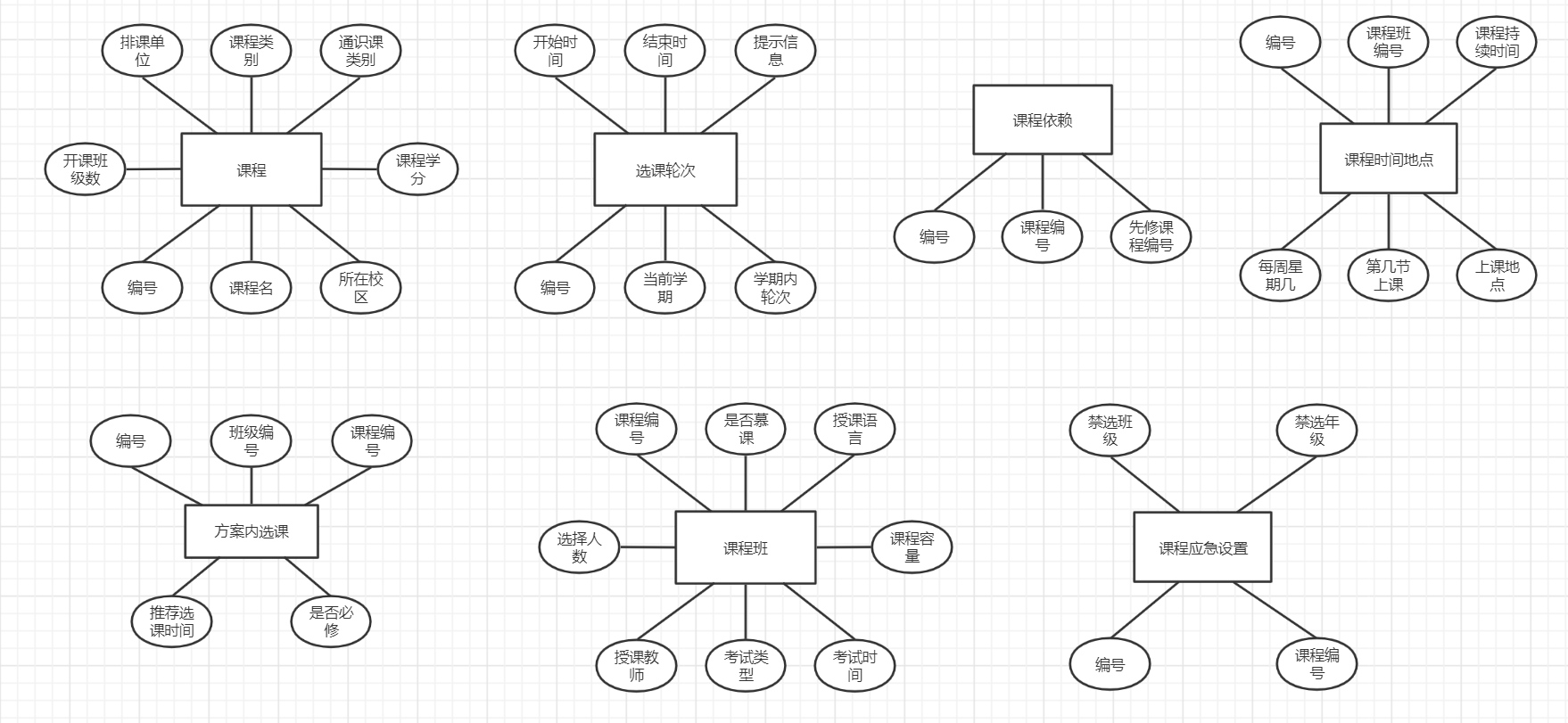
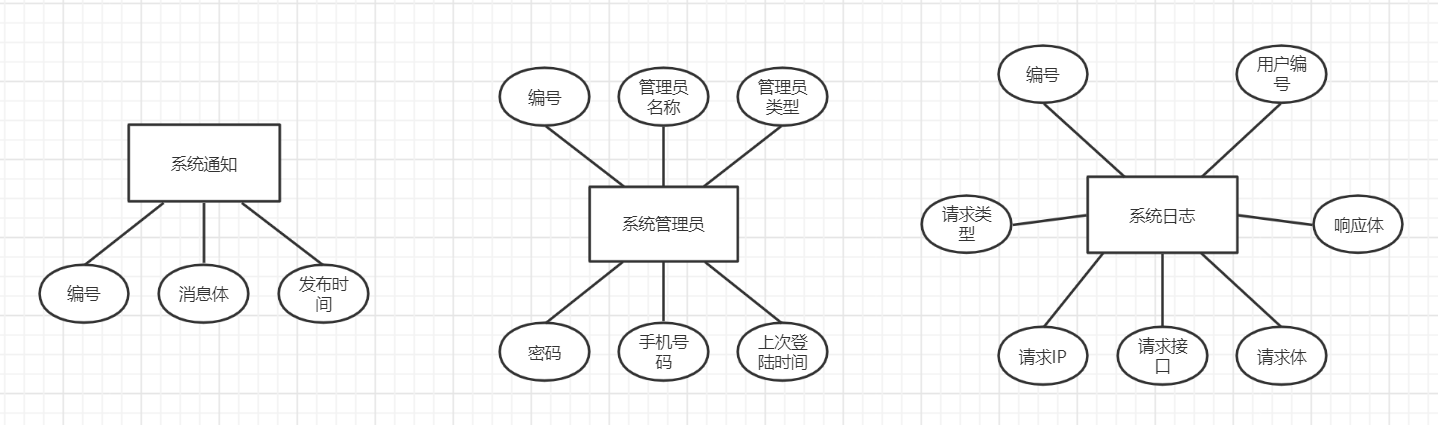
实体联系图
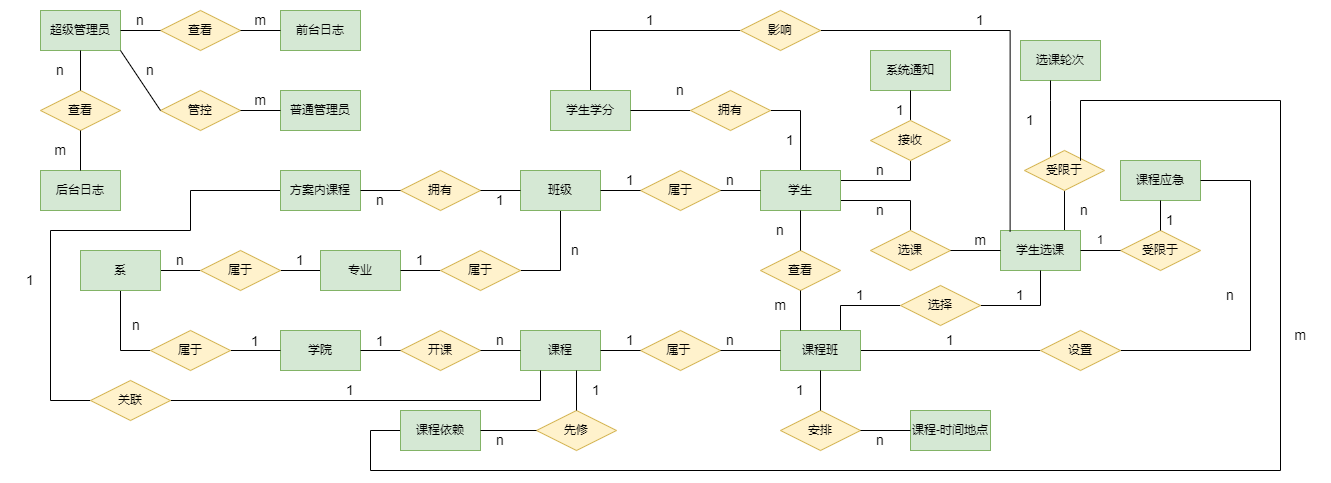
2、逻辑结构设计
- 班级(班级编号,班级所在学院名,班级所在系名,班级所在专业名,班级对应年份,班级序号,班级名称,毕业所需学分)
- 学院 (学院编号,学院名称)
- 系(系编号,学院编号,系名)
- 专业(专业编号,系编号,专业名称)
- 学生(学生学号,班级编号,姓名,性别,邮箱,电话号码,密码,状态)
- 学生选课(选课记录号,学生学号,课程班编号,选择学期,课程学分)
- 学生学分(学分记录号,学生学号,学期,最高主修学分,已选主修学分)
- 方案内选课(方案内选课记录号,班级编号,课程编号,推荐选课时间,是否必修)
- 选课轮次(选课轮次记录号,轮次所在学期,学期内轮次序号,开始时间,结束时间,提示信息)
- 课程(课程编号,课程名,所在校区,排课单位,课程类别,通识课类型,课程学分,开课班级数量)
- 课程班(课程班编号,课程编号,是否慕课,授课语言,选择人数,课程容量,授课教师,考试类型,考试时间)
- 课程时间地点( 课程时间地点记录号,课程班编号,授课持续时间,每周星期几上课,第几节课上课,上课地点)
- 课程依赖(课程依赖记录号,课程编号,先修课程编号)
- 课程应急设置( 课程应急设置记录号,课程编号,禁选班级编号,禁选年级)
- 系统管理员(管理员编号,管理员名称,类型,密码,手机号码,上次登录时间)
- 系统通知(通知编号,接收对象编号,消息体)
- 系统日志(日志编号,学生学号/管理员编号,请求类型,请求IP,请求接口,请求体,响应体,请求时间)
实体间关系分析
3、物理结构设计
字段规定:
- 小数类型使用decimal、禁止使用float和double类型,时间采用date_time类型
- 绝大多数表必备三个字段:id、create_time以及update_time,部分表的数据采用逻辑删除
SQL语句:
安全性问题:
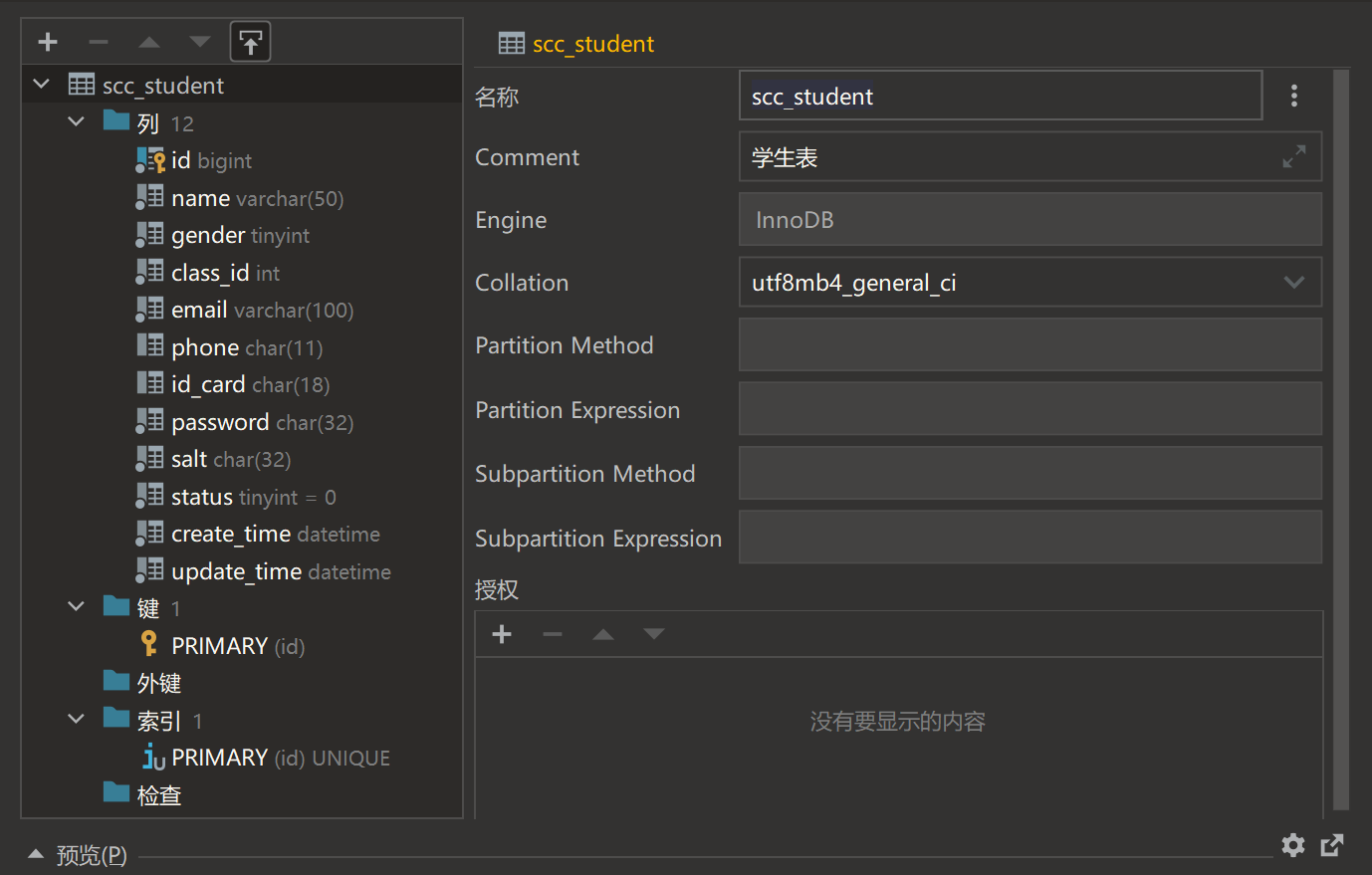
使用DataGrip数据库设计工具,根据上述实体属性以及联系进行数据库以及表的创建。
以下为学生表创建示例:
create table scc_choose_round
(
id int not null
primary key,
semester int null,
round_no tinyint null,
start_time datetime null,
end_time datetime null,
tips varchar(255) null,
create_time datetime null,
update_time datetime null
)
comment '选课轮次表';
create table scc_class
(
id int not null
primary key,
college_name varchar(20) null,
department_name varchar(20) null,
subject_name varchar(20) null,
year smallint null,
class_no tinyint null,
class_name varchar(20) null,
graduation_credits smallint null,
create_time datetime null,
update_time datetime null
)
comment '班级表';
create table scc_class_course
(
id bigint not null
primary key,
class_id int null,
course_id int null,
commended_time int null,
is_must tinyint null,
is_deleted tinyint default 0 null,
create_time datetime null,
update_time datetime null
)
comment '方案内课程表';
create table scc_college
(
id smallint not null
primary key,
college_name varchar(20) null
)
comment '学院表';
create table scc_course
(
id char(10) not null
primary key,
course_name varchar(30) null,
campus varchar(20) null,
college varchar(20) null,
type varchar(20) null,
general_type varchar(20) null,
credit decimal(10, 1) null,
class_num tinyint null,
create_time datetime null,
update_time datetime null
)
comment '课程表';
create table scc_course_class
(
id bigint not null
primary key,
course_id char(10) null,
is_mooc tinyint null,
language varchar(20) null,
choosing_num int null,
capacity int null,
teacher varchar(100) null,
exam_type varchar(20) null,
exam_time varchar(50) null,
is_deleted tinyint default 0 null,
create_time datetime null,
update_time datetime null
)
comment '课程班表';
create table scc_course_dependence
(
id bigint not null
primary key,
course_id int null,
pre_course_id int null,
is_deleted tinyint default 0 null,
create_time datetime null,
update_time datetime null
)
comment '课程依赖表';
create table scc_course_emergency
(
id bigint not null
primary key,
course_id char(10) null,
only_to_class int null,
only_to_grade int null,
is_deleted tinyint default 0 null,
create_time datetime null,
update_time datetime null
)
comment '课程紧急设置表';
create table scc_course_timeplace
(
id bigint not null
primary key,
course_class_id bigint null,
duration_time varchar(20) null,
week_day tinyint null,
day_no varchar(20) null,
place varchar(50) null,
is_deleted tinyint default 0 null,
create_time datetime null,
update_time datetime null
)
comment '课程时间地点表';
create table scc_department
(
id smallint not null
primary key,
college_id smallint null,
department_name varchar(20) null
)
comment '系表';
create table scc_student
(
id bigint not null
primary key,
name varchar(50) null,
gender tinyint null,
class_id int null,
email varchar(100) null,
phone char(11) null,
id_card char(18) null,
password char(32) null,
salt char(32) null,
status tinyint default 0 null,
create_time datetime null,
update_time datetime null
)
comment '学生表';
create table scc_student_course
(
id bigint not null
primary key,
student_id int null,
course_class_id bigint null,
semester int null,
credits decimal null,
is_deleted tinyint default 0 null,
create_time datetime null,
update_time datetime null
)
comment '学生选课表';
create table scc_student_credits
(
id bigint not null
primary key,
student_id bigint null,
semester int null,
max_subject_credit decimal(10, 1) null,
choose_subject_credit decimal(10, 1) null,
create_time datetime null,
update_time datetime null
)
comment '学生学分表';
create table scc_subject
(
id smallint not null
primary key,
department_id smallint null,
subject_name varchar(20) null
)
comment '专业表';
create table scc_sys_backend_log
(
id bigint not null
primary key,
type tinyint null,
request_ip varchar(255) null,
manager_id int null,
request_api varchar(255) null,
request_body text null,
response_body text null,
create_time datetime null
)
comment '后台日志表';
create table scc_sys_frontend_log
(
id bigint not null
primary key,
type tinyint null,
request_ip varchar(255) null,
student_id int null,
request_api varchar(255) null,
request_body text null,
response_body text null,
create_time datetime null
)
comment '前台日志表';
create table scc_sys_manager
(
id int not null
primary key,
manager_name varchar(20) null,
type smallint null,
password char(32) null,
salt char(32) null,
mobile_phone varchar(20) null,
last_login datetime null,
is_deleted tinyint default 0 null,
create_time datetime null,
update_time datetime null
)
comment '系统管理员表';
create table scc_sys_notice
(
id bigint not null
primary key,
student_id bigint null,
message varchar(255) null,
status smallint default 0 null,
create_time datetime null,
update_time datetime null
)
comment '系统通知表';
五、系统优化
经过前面的设计,WEB 站点层的高性能、高可用都得到了一定的保证,但此时数据库IO操作很可能成为了瓶颈。 数据层同样需要进行改进,数据层库架构优化的目的同样是实现高性能、高可用。
优化方案:
1、缓存
**问题:**当请求的QPS达到一定的水平后,系统将面临性能降低(并发越大查询速率越低)以及并发下降(当请求数超过正常单机数据库所能抗住的QPS时,数据库将会卡顿甚至宕机)。
使用缓存方案可以提高访问性能、降低网络拥堵,减轻服务负载等。缓存读写性能高,且预热快。将要被请求的数据放入缓存中,请求将先在缓存中获取数据(单级缓存可承载的并发量可能是MySQL的几十倍)。
引入缓存数据库Redis设计合适的缓存淘汰策略,将热点数据存入Redis方便后续读取。
Todo:引入Redis集群,解决数据一致性问题,预防缓存雪崩与缓存穿透问题,以搭建高可用的Redis集群。
2、池化技术
如果每次请求都需要新建连接,即TCP需要经历“三次握手”,这个过程很费时间。另外一旦建立连接则还需要关闭连接,即TCP需要经历“四次挥手”,又需要时间开销。
问题:
可以用数据库连接池来优化数据库的连接,这就是连接池技术。即预先分配一批并将他们放入一个缓存区中循环使用,形成池化效应。
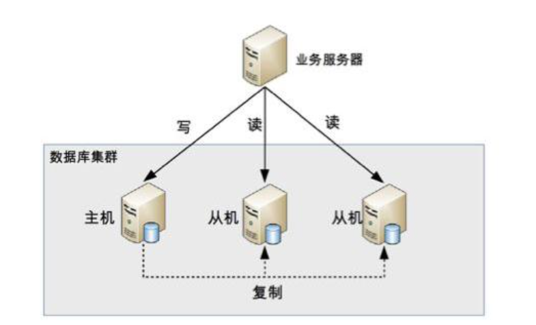
3、读写分离
**问题:**由于选课系统中每个人的目标课程不同,所以缓存命中率就没有那么高,会有很大的流量被转发到MySQL数据库中,MySQL的压力也随之增大,单台MySQL实例将面临无法满足当前的业务需求。
优化方案:引入读写分离
针对于选课这种并发量大的读请求,最直接的便是搭建多台MySQL实例分摊读请求。将读流量分摊到各个从库中,而主库负责写流量,通过Binlog实现数据同步。
4、后续优化
解决数据一致性问题
做好幂等性设计(所谓幂等性即指用户对于同一个操作发起一次请求或多次请求,得到的结果都是一样的,主要用在重复请求上)。由于并发量大的问题,考虑采用乐观锁而非悲观锁以得到更好的并发访问性能。
优化方案:引入池化技术
可以用数据库连接池来优化数据库的连接,这就是连接池技术。即预先分配一批并将他们放入一个缓存区中循环使用,形成池化效应。
项目开源地址:
https://gitee.com/Ken-Chy129/
https://github.com/Ken-Chy129/
原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_25046827/article/details/128259774
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。
如若转载,请注明出处:http://www.7code.cn/show_20022.html
如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系代码007邮箱:suwngjj01@126.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!