Hertz介绍
Hertz是字节跳动研发的企业级微服务HTTP框架,具有高易用性、易扩展、低时延等特点。是基于自研网络库Netpoll开发的内部框架Hertz。Hertz框架整体上满足:
1.极致性能优化的问题性
2.面对未来不可控需求的扩展能力,Hertz采用了4层分层设计(应用层、路由层、协议层、传输层),保证各个层级功能内聚,同时通过层级之间的接口达到灵活扩展的目标。整体框架如下图:
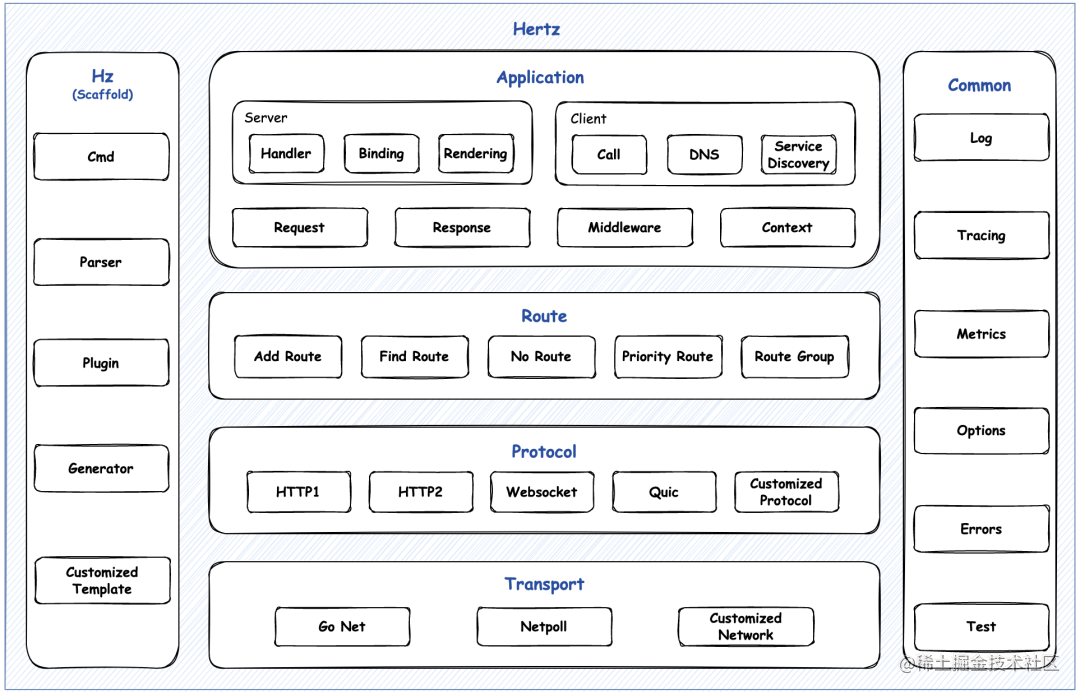
应用层
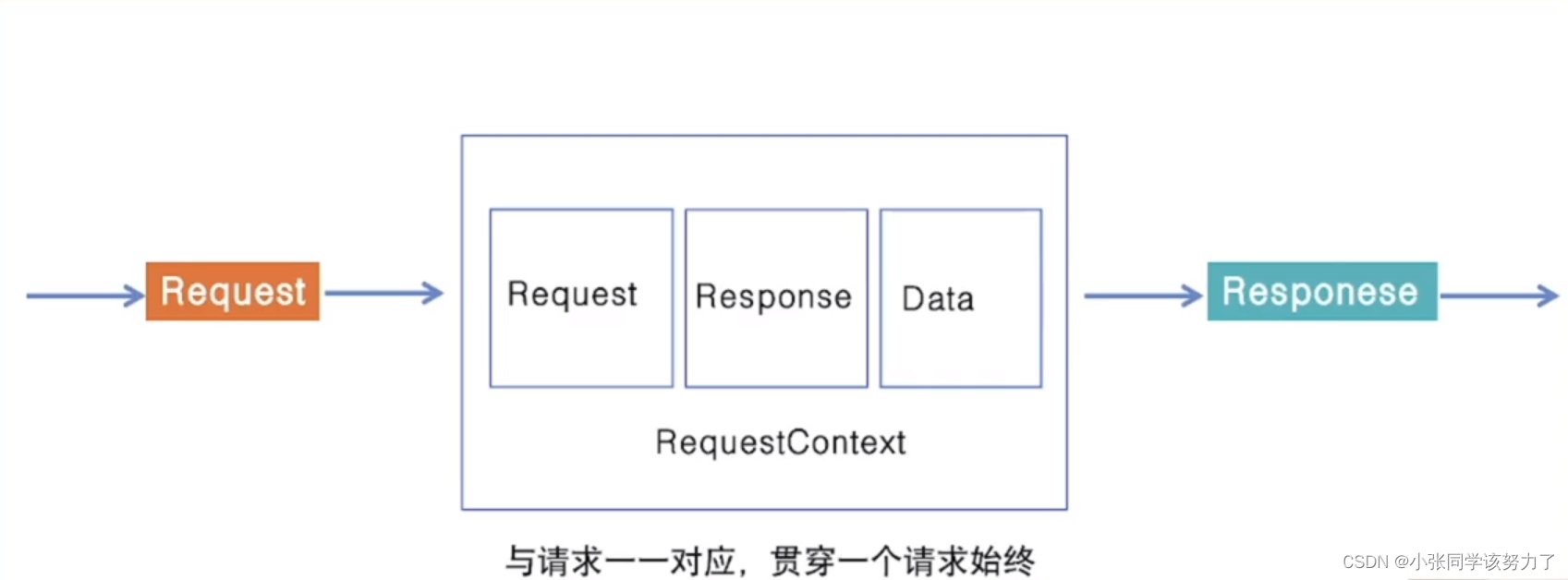
主要包括与用户直接交互的易用的API,主要包括Server、Client和一些其他通用抽象。Hertz框架最具特点的是处理函数(HandlerFunc)多了一个context上下文,这是在大量的实践过程中发现的,业务方通常需要一个标准的上下文在RPC Client或者日志、Tracing等组件间传递,但由于请求上下文(RequestContext)生命周期局限于一次HTTP请求之内而以上提到的场景往往存在异步的传递和处理, 导致如果直接传递请求上下文,会导致出现一些数据不一致的问题。因此最终增加了一个标准的上下文入参,从根本上解决各种因为上下文生命周期不一致的异常问题,处理函数的格式为:
type HandlerFunc func(c context.Context,ctx *app.RequestContext)
路由层
Hertz在设计路由时,给了用户极高的自由度去注册路由,支持的路由有:支持静态路由、参数路由的注册;支持按优先级匹配,支持路由回溯,支持尾斜线重定向。例如:
1.优先级匹配,如/a/b和/:c/b,同时满足时,优先匹配/a/b
2.路由回溯,如注册/a/b和/:c/d,当匹配/a/d时仍然能够匹配上/:c/d
3.支持尾斜线重定向,如注册/a/b,当匹配/a/b/时重定向到/a/b上
协议层
协议层负责不同协议的实现和扩展。Hertz支持协议的扩展,用户只需要实现下面的接口便可以按照自己的需求在引擎上扩展协议,同时也支持通过ALPN协议协商的方式注册。Hertz首批只开源了 HTTP1 实现,未来会陆续开源 HTTP2、QUIC 等实现。协议层扩展提供的灵活性甚至可以超越 HTTP 协议的范畴,用户完全可以按需注册任意符合自身需求的协议层实现,并且加入到Hertz的引擎中来,同时,也能够无缝享受到传输层带来的极致性能。
传输层
传输层负责底层的网络库的抽象和实现
Hertz支持底层网络库的扩展。Hertz原生完美匹配Netpoll,在时延方面有很多深度的优化,Netpoll对TLS能力的支持有待完善,为此Hertz底层同时支持基于Golang标准网络库的实现适配,同时支持网络库的一键切换,用户可根据自己的需求选择合适的网络库进行替换。如果用户有更加高效的网络库或其他网络库需求,也完全可以根据需求自行扩展。
BIO:
go func(){
for{
conn,_:=listener.Accept()
go func(){
conn.Read(request)
handle...
conn.Write(response)
}
}
}
NIO:
go func(){
for{
readableConns,_:=Monitor(conns) //监听器,有足够的数据之后再去唤醒
for conn:=range readableConns{
go func(){
conn.Read(request)
handle...
conn.Write(response)
}
}
}
}
go net是“BIO”,需要用户来管理buffer.
go net存下全部Header,减少系统调用次数,能够复用内存,能够多次读
type Conn interface{
Read(b []byte)(n int,err error)
Write(b []byte)(n int,err error)
...
}
type Reader interface{
Peek(n int)([]byte,error)
Discard(n int)(discarded int,err error)
Release()error
Size()int
Read(b []byte)(l int,err error)
...
}
type Writer interface{
Write(p []byte)
Size()int
Flush()error
...
}
go net的优点:1.流式友好 2.小包性能高(连接上绑定一块内存,一旦超过就涉及buffer的申请和回收)
netpoll是“NIO”,网络库管理buffer
netpoll存下全部Header,拷贝出完整的Body
netpoll with nocopy peek
分配足够大的buffer
限制最大buffer size
type Conn interface{
net.Conn
Reader
Writer
}
type Reader interface{
Peek(n int)([]byte,error)
...
}
type Writer interface{
Malloc(n int)(buf []byte,err error)
Flush()error
...
}
netpoll的优点:1.中大包性能高(底层进行buffer的管理) 2.时延低
netpoll在Header解析的优化:
针对协议相关的Headers快速解析:
1.通过Header key首字母快速筛除掉完全不可能的key
2.解析对应value到独立字段
3.使用byte slice管理对应header存储,方便复用
优点:
1.核心字段快速解析
2.使用byte slice存储
3.额外存储到成员变量中
缺点:
1.普通header性能较低
2.没有map结构
Header key规范化:aaa-bbb–>Aaa-Bbb
优点:
超高的转换效率,比net.http提高40倍
缺点:
额外的内存开销,变更困难
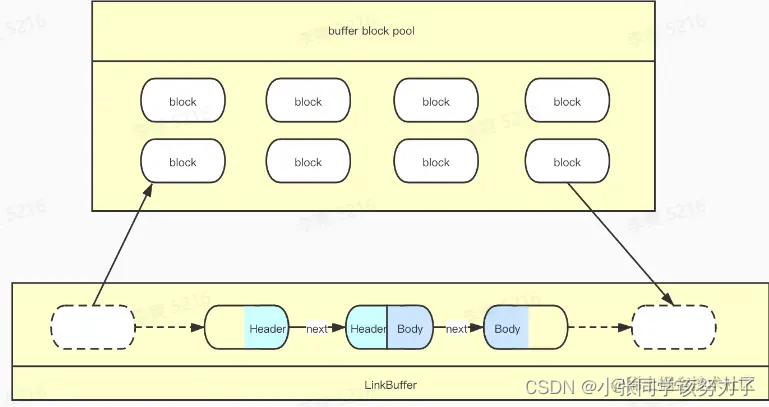
热点资源池化:
请求来的时候,request从请求池当中拿一个RequestContext
优点:
1.减少了内存分配
2.提高了内存复用
3.降低了GC压力
4.性能提升
缺点:
1.额外的Reset逻辑
2.请求内有效
3.问题定位难度增加
HZ脚手架
用户可以提供一个IDL,利用命令行工具Hz,一键生成项目脚手架。Hz也支持基于IDL的更新能力,能够基于IDL变动智能地更新项目代码。Hz支持Thrift和Protobuf两种IDL定义。
Hertz的使用
一个简单的案例:利用Hertz监听8080端口并编写/ping的get处理函数
package main
import (
"context"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/server"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/common/utils"
"net/http"
)
func main() {
h := server.Default(server.WithHostPorts("127.0.0.1:8080"))
h.GET("/ping", func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
ctx.JSON(http.StatusOK, utils.H{"ping": "pong"})
})
h.Spin()
}
Hertz和gin一样,提供了分组路由的功能
v1 := h.Group("/v1")
{
v1.GET("/login", func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
})
}
v2 := h.Group("/v2")
{
v2.GET("/login", func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
})
}
Hertz路由的匹配优先级:静态路由>命名路由>通配路由
h.GET("/herz/:version", func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
})
h.GET("/herz/*action", func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
})
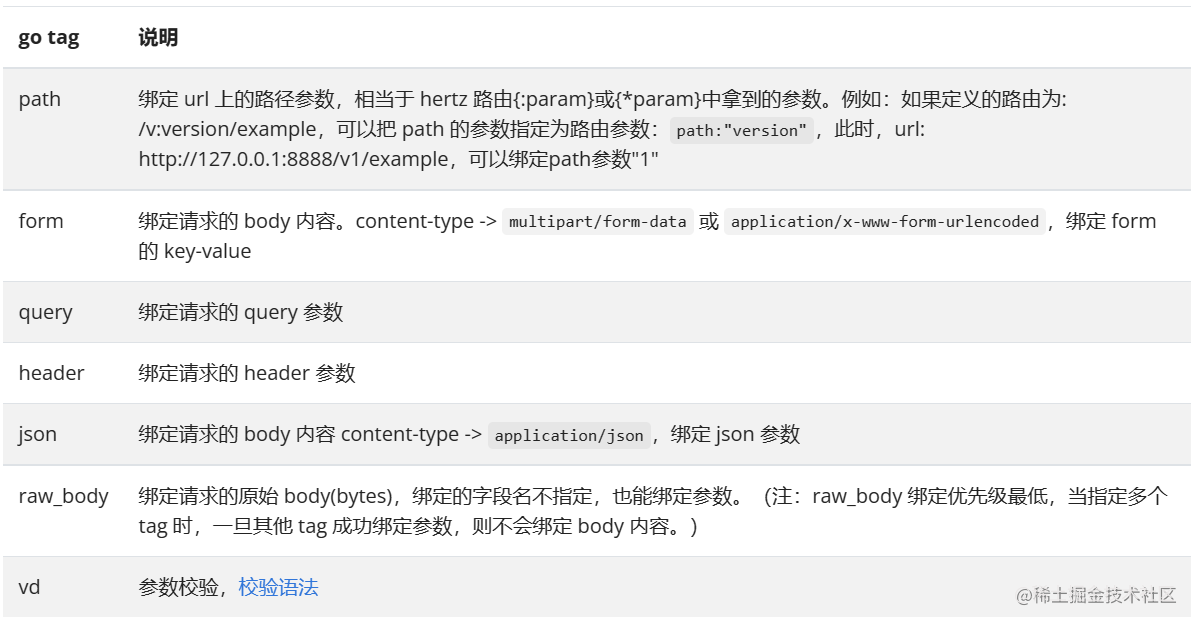
参数绑定:Bind、Validate、BindAndValidate用于参数绑定和校验
type InfoRequest struct {
Name string `vd:"($!='Alice'||(Age)$==18) && regexp('w')"`
Age int `vd:"$>0"`
Email string `vd:"email($)"`
Phone1 string `vd:"phone($)"`
OtherPhones []string `vd:"range($, phone(#v,'CN'))"`
*InfoRequest `vd:"?"`
Info1 *InfoRequest `vd:"?"`
Info2 *InfoRequest `vd:"-"`
}
import "github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/server/binding"
func init() {
binding.MustRegValidateFunc("test", func(args ...interface{}) error {
if len(args) != 1 {
return fmt.Errorf("the args must be one")
}
s, _ := args[0].(string)
if s == "123" {
return fmt.Errorf("the args can not be 123")
}
return nil
})
}
参数绑定优先级:
path > form > query > cookie > header > json > raw_body
type Args struct {
Query string `query:"query"vd:"$!='Hertz'"`
QuerySlice []string `query:"queryslice"`
Path string `path:"path"`
Header string `header:"header"`
Form string `form:"form"`
Json string `json:"json"`
}
func main(){
h := server.Default(server.WithHostPorts("127.0.0.1:8080"))
h.POST("v:path/bind", func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
var arg Args
err := ctx.BindAndValidate(&arg)
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
})
}
中间件
func MyMiddleware() app.HandlerFunc {
return func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
fmt.Println("pre-handle")
ctx.Next(c)
fmt.Println("post-handle")
}
}
func main() {
h := server.Default(server.WithHostPorts("127.0.0.1:8080"))
h.Use(MyMiddleware())
}
HTTP Client
package main
import (
"context"
"fmt"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/client"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/protocol"
)
func main() {
c, err := client.NewClient()
if err != nil {
return
}
status, body, _ := c.Get(context.Background(), nil, "http://baidu.com")
fmt.Printf("status:%v body:%v", status, string(body))
var postArgs protocol.Args
postArgs.Set("arg", "a")
status, body, _ = c.Post(context.Background(), nil, "http://baidu.com", &postArgs)
fmt.Printf("status:%v body:%v", status, string(body))
}
Hertz代码生成工具
go install github.com/cloudwego/hertz/cmd/hz@latest
#hz生成用例代码
hz new -module example
编写IDL
namespace go hello.example
struct HelloReq{
1:string Name (api.query="name");
}
struct HelloResp{
1:string RespBody;
}
service HelloService{
HelloResp HelloMethod(1:HelloReq request)(api.get="/hello")
}
hz new -module mod_name -idl idl/hello.thrift
生成的主要代码:
biz/handler/hello/example/hello_service.go
// Code generated by hertz generator.
package example
import (
"context"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/protocol/consts"
example "hertz-demo/biz/model/hello/example"
)
// HelloMethod .
// @router /hello [GET]
func HelloMethod(ctx context.Context, c *app.RequestContext) {
var err error
var req example.HelloReq
err = c.BindAndValidate(&req)
if err != nil {
c.String(consts.StatusBadRequest, err.Error())
return
}
resp := new(example.HelloResp)
c.JSON(consts.StatusOK, resp)
}
biz/router/hello/example/hello.go
// Code generated by hertz generator. DO NOT EDIT.
package Example
import (
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/server"
example "hertz-demo/biz/handler/hello/example"
)
/*
This file will register all the routes of the services in the master idl.
And it will update automatically when you use the "update" command for the idl.
So don't modify the contents of the file, or your code will be deleted when it is updated.
*/
// Register register routes based on the IDL 'api.${HTTP Method}' annotation.
func Register(r *server.Hertz) {
root := r.Group("/", rootMw()...)
root.GET("/hello", append(_hellomethodMw(), example.HelloMethod)...)
}
Hertz的一些基本函数
func main() {
h := server.Default()
h.GET("/user/:name", func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
fpath := ctx.FullPath()
println(fpath)
})
//请求 http://localhost:8888/user/zyj 会打印/user/:name
h.NoRoute(func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
println(ctx.FullPath())
})
//任何不符合匹配规则的uri请求都会返回空
h.GET("/user/:name", func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
name := ctx.Param("name")
println(name)
})
//Param获取Param参数
h.GET("/user", func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
name := ctx.Query("name")
println(name)
})
//获取的是Query参数,即?后面的参数
//DefaultQuery获取不到Query参数给一个默认值
h.Use(cors.New(cors.Config{ //跨域中间件
AllowAllOrigins: true, //允许所有origin的请求
AllowMethods: []string{"GET", "PUT", "POST", "DELETE"}, //允许的方法
AllowHeaders: []string{"Origin"}, //允许的头部
ExposeHeaders: []string{"Content-Length"}, //暴漏的头部信息
AllowCredentials: true, //允许携带证书
AllowWildcard: true, //允许使用通配符匹配
AllowOriginFunc: func(origin string) bool { //自定义处理源的函数
return origin == "https://github.com"
},
MaxAge: 12 * time.Hour, //请求缓存的最长时间
}))
register(h)
h.Spin()
}
h.GET("/header", func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
ctx.Request.Header.Add("hertz1", "value1")
ctx.Request.Header.SetContentTypeBytes([]byte("application/x-www-form-urlencoded")) //设置内容类型
ctx.Request.Header.Add("Content-Type", "application/json;charset=utf-8")
hertz := ctx.Request.Header.GetAll("hertz1")
println(hertz)
contentType2 := ctx.Request.Header.ContentType()
fmt.Println(contentType2)
})
h.POST("/form_data", func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
data := ctx.PostForm("data")
fmt.Println(data)
})
//多文件
h.POST("/multifile", func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
form, err := ctx.MultipartForm()
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
name := form.Value["name"][0]
file := form.File["file"][0]
fmt.Println(name)
fmt.Println(file.Filename)
})
//单文件
h.POST("/user", func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
file, err := ctx.FormFile("file")
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
fmt.Println(file.Filename)
})
session存储
store := cookie.NewStore([]byte("secret"))
h.Use(sessions.New("mysession", store))
h.GET("/incr", func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
session := sessions.Default(ctx)
var count int
v := session.Get("count")
if v != nil {
count = v.(int)
count++
}
session.Set("count", count)
_ = session.Save()
ctx.JSON(200, utils.H{"count": count})
})
h.Use(gzip.Gzip(
gzip.DefaultCompression,
gzip.WithExcludedExtensions([]string{".pdf", ".mp4"}), //pdf和mp4不压缩
))
原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_43716830/article/details/128744034
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。
如若转载,请注明出处:http://www.7code.cn/show_21132.html
如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系代码007邮箱:suwngjj01@126.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!