python实现鼠标实时坐标监测
一、说明
tkinter:用于创建GUI界面。pyperclip:用于复制文本到剪贴板。pynput.mouse:用于监听鼠标事件,包括移动和点击。threading:用于创建多线程,以便在后台执行鼠标事件监听和标签更新的任务。time:用于控制线程休眠,以定时更新标签文本。
二、代码
# coding=gbk # 指定文件编码为GBK
import tkinter as tk # 导入tkinter库,用于创建GUI界面
import pyperclip # 导入pyperclip库,用于复制文本到剪贴板
from pynput import mouse # 导入pynput库的mouse模块,用于监听鼠标事件
import threading # 导入threading库,用于创建多线程
import time # 导入time库,用于线程休眠
# 创建一个MouseCoordinateApp类,用于处理鼠标坐标显示和复制
class MouseCoordinateApp:
def __init__(self):
self.root = tk.Tk() # 创建一个Tkinter窗口
self.root.title("鼠标坐标实时展示") # 设置窗口标题
self.root.geometry("350x80") # 设置窗口大小
self.root.resizable(False, False) # 禁止窗口大小调整
self.label = tk.Label(self.root, text="单机截取坐标:X: - , Y: -n实时坐标:X: - , Y: -") # 创建一个标签控件
self.label.pack() # 将标签控件添加到窗口
copy_button = tk.Button(self.root, text="复制坐标", command=self.copy_coordinates) # 创建一个按钮控件
copy_button.pack() # 将按钮控件添加到窗口
self.root.attributes("-topmost", True) # 设置窗口置顶
self.extracted_coordinates = (0, 0) # 初始化截取坐标
self.current_coordinates = (0, 0) # 初始化实时坐标
self.last_extracted_coordinates = (0, 0) # 初始化上一次截取的坐标
self.update_interval = 0.1 # 更新标签的时间间隔
threading.Thread(target=self.start_mouse_listener, daemon=True).start() # 创建并启动鼠标事件监听的线程
threading.Thread(target=self.update_label_thread, daemon=True).start() # 创建并启动标签更新的线程
def copy_coordinates(self):
x, y = self.last_extracted_coordinates # 获取上一次截取的坐标
coordinates = f"X: {x}, Y: {y}" # 格式化坐标文本
pyperclip.copy(coordinates) # 复制坐标文本到剪贴板
self.label.config(text=f"已复制坐标:{coordinates}") # 更新标签文本
def start_mouse_listener(self):
with mouse.Listener(on_move=self.on_move, on_click=self.on_click) as listener:
listener.join() # 启动鼠标事件监听
def on_move(self, x, y):
self.current_coordinates = (x, y) # 更新实时坐标
def on_click(self, x, y, button, pressed):
if pressed:
self.last_extracted_coordinates = self.extracted_coordinates # 更新上一次截取的坐标
self.extracted_coordinates = (x, y) # 如果鼠标被按下,更新截取坐标
def update_label_thread(self):
while True:
time.sleep(self.update_interval) # 线程休眠一段时间
self.update_label() # 更新标签文本
def update_label(self):
extracted_x, extracted_y = self.extracted_coordinates # 获取截取坐标
current_x, current_y = self.current_coordinates # 获取实时坐标
self.label.config(text=f"截取坐标:X: {extracted_x}, Y: {extracted_y}n实时坐标:X: {current_x}, Y: {current_y}")
def run(self):
self.root.mainloop() # 启动主程序的主循环
if __name__ == "__main__":
app = MouseCoordinateApp() # 创建MouseCoordinateApp实例
app.run() # 启动应用程序的主循环
三、效果
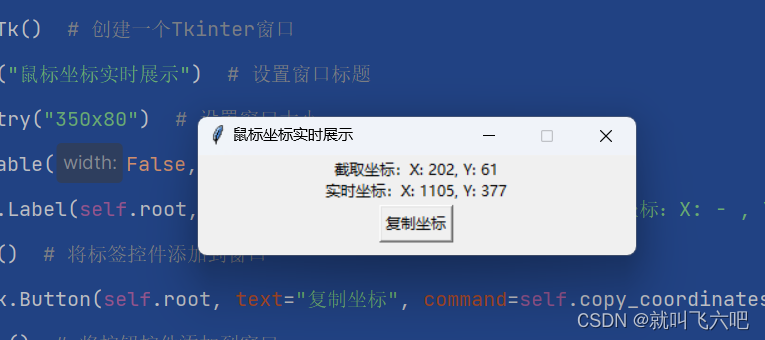
原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_52236586/article/details/134560410
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。
如若转载,请注明出处:http://www.7code.cn/show_2145.html
如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系代码007邮箱:suwngjj01@126.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
声明:本站所有文章,如无特殊说明或标注,均为本站原创发布。任何个人或组织,在未征得本站同意时,禁止复制、盗用、采集、发布本站内容到任何网站、书籍等各类媒体平台。如若本站内容侵犯了原著者的合法权益,可联系我们进行处理。