LangChain官网、LangChain官方文档 、langchain Github、langchain API文档、llm-universe
一、 部分提示模板
部分提示模板格式化(Partial prompt templates)是LangChain支持的一种提示模板使用方式。它允许用户仅格式化提示模板的部分必要变量,用户可以在之后传入剩余缺失的变量来进一步格式化该部分提示模板,最终完整地渲染出完整的提示。Partial prompt templates有以下应用场景:
-
分步骤构建提示。在某些场景下,提示可能需要通过多步构建,所以获取变量的时间或顺序可能不固定。部分格式化允许每一步只传递该步相关的变量,逐步完善提示模板。
-
复用提示模板。通过部分格式化,可以基于同一个提示模板,构建出适用于不同场景的定制化提示模板。不同的定制需求通过部分格式化来实现,使得提示模板更通用。
总体来说,部分提示模板格式化支持更加灵活和富有创造性的提示模板使用方式,使得提示功能的构建和使用更加高效。
1.1 使用字符串值进行部分格式化(Partial with strings)
Partial prompt templates的一个常见场景是获取模板变量的时间顺序不一致。假设提示模板需要两个变量foo和baz,在工作链中先获得了foo,后获得baz。通常做法是等到获取两个变量之后再在某个位置将它们传递给提示模板。现在你可以先使用 foo的 值部分格式化提示模板,然后使用该部分提示模板在后续步骤中传入baz的值。
- 部分格式化PromptTemplate示例
首先实例化一个PromptTemplate,然后调用它的partial方法进行部分格式化,得到一个部分格式化后的PromptTemplate对象(partial_prompt)。
from langchain.prompts import PromptTemplate
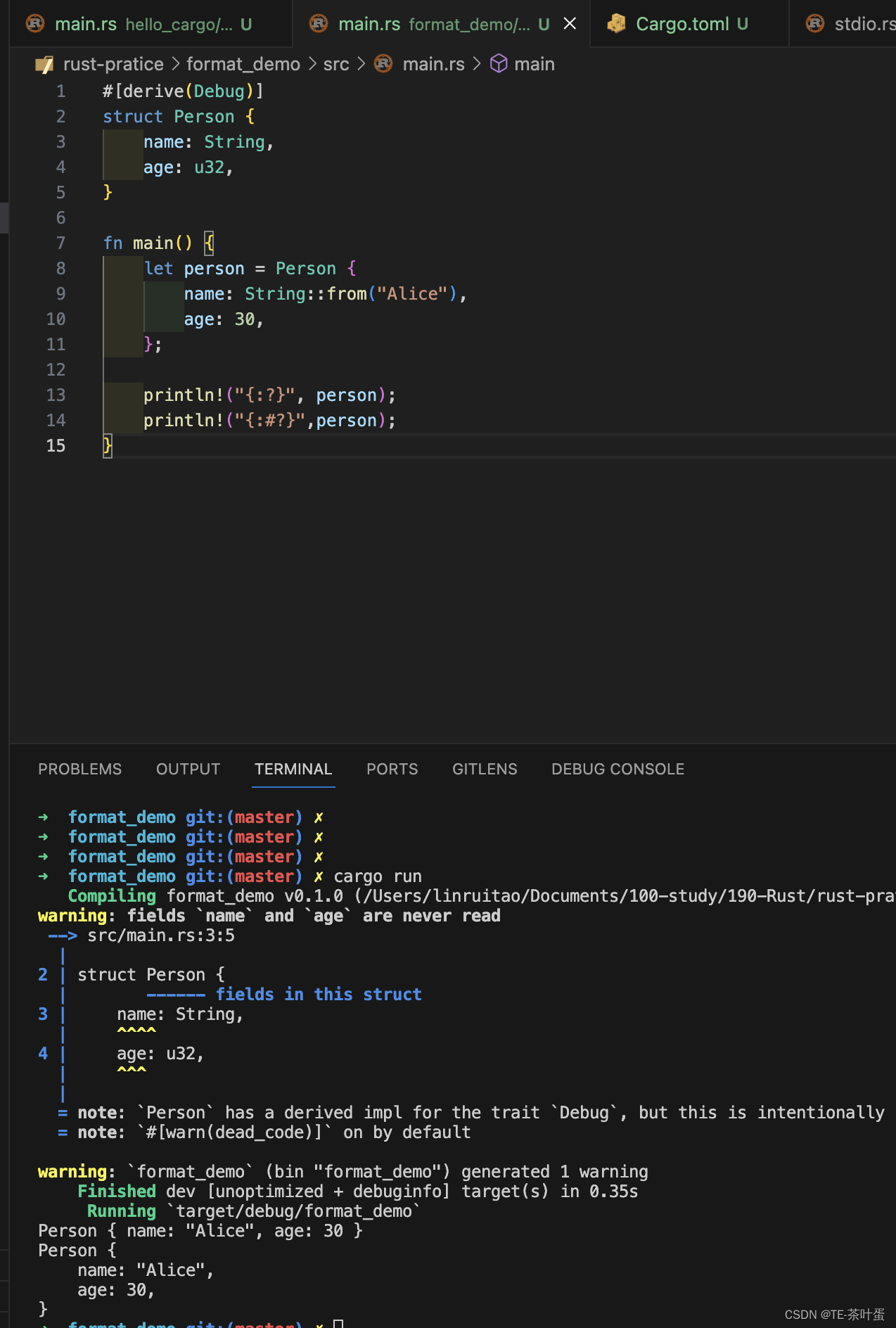
prompt = PromptTemplate(template="{foo}{bar}", input_variables=["foo", "bar"])
partial_prompt = prompt.partial(foo="foo");
print(partial_prompt.format(bar="baz"))
foobaz
prompt = PromptTemplate(template="{foo}{bar}", input_variables=["bar"], partial_variables={"foo": "foo"})
print(prompt.format(bar="baz"))
两段代码最终实现的效果是一样的,区别在于部分格式化的时机不同。第一种方式更加灵活,可以按需多次部分格式化
1.2 使用函数进行部分格式化(Partial with functions)
Partial prompt templates的另一种常见用法是使用函数进行部分格式化。当你有一个变量,希望总是通过某种常用的方式获取时,就可以这样做。
一个典型的例子就是获取日期或时间。假设你有一个提示模板,总是希望内含当前日期,你既不能在模板中硬编码日期,也不太方便每次和其他输入变量一起传递日期。这种情况下,使用函数部分格式化提示模板会非常方便,我们很容易写一个函数来返回当前日期和时间。
from datetime import datetime
def _get_datetime():
now = datetime.now()
return now.strftime("%m/%d/%Y, %H:%M:%S")
prompt = PromptTemplate(
template="Tell me a {adjective} joke about the day {date}",
input_variables=["adjective", "date"]
);
partial_prompt = prompt.partial(date=_get_datetime)
print(partial_prompt.format(adjective="funny"))
Tell me a funny joke about the day 02/27/2023, 22:15:16
你也可以可以使用部分变量初始化提示,这通常在此工作流程中更有意义。
prompt = PromptTemplate(
template="Tell me a {adjective} joke about the day {date}",
input_variables=["adjective"],
partial_variables={"date": _get_datetime}
);
print(prompt.format(adjective="funny"))
Tell me a funny joke about the day 02/27/2023, 22:15:16
使用
_get_datetime这种命名方式遵循了Python对私有函数的通用约定和规范,一般被定义在类或模块的内部,而不是外部接口,通常用于实现类或模块内部的某些逻辑,以起到辅助作用。
二、Prompt pipelining
prompt pipelining技术,旨在提供用户友好的界面,以便轻松组合不同部分的提示。该技术可以用于处理string prompts和chat prompts。
2.1 String prompt pipelining
使用String prompt 时,您可以直接使用提示或字符串来组合提示模板(列表中的第一个元素必须是提示)。
from langchain.prompts import PromptTemplate
prompt = (
PromptTemplate.from_template("Tell me a joke about {topic}")
+ ", make it funny"
+ "nnand in {language}"
)
prompt
PromptTemplate(input_variables=['language', 'topic'], output_parser=None, partial_variables={}, template='Tell me a joke about {topic}, make it funnynnand in {language}', template_format='f-string', validate_template=True)
prompt.format(topic="sports", language="spanish")
'Tell me a joke about sports, make it funnynnand in spanish'
from langchain.chains import LLMChain
from langchain.chat_models import ChatOpenAI
model = ChatOpenAI()
chain = LLMChain(llm=model, prompt=prompt)
chain.run(topic="sports", language="spanish")
'¿Por qué el futbolista llevaba un paraguas al partido?nnPorque pronosticaban lluvia de goles.'
2.2 Chat prompt pipelining
由于chat prompt由消息列表组成,一种便捷组合chat prompt的方式是,向chat prompt管道中添加new message。这种方法使得构建聊天对话变得更加直观和方便,开发者只需逐步添加新消息即可形成完整的对话提示。
通常我们会先用系统消息初始化基本 ChatPromptTemplate,然后逐个添加新的消息。如果没有需要格式化的变量,可以使用Message。而如果有需要格式化的变量,可以使用MessageTemplate。此外,还可以直接使用字符串,这会自动被推断为HumanMessagePromptTemplate。
from langchain.schema import AIMessage, HumanMessage, SystemMessage
prompt = SystemMessage(content="You are a nice pirate")
new_prompt = (
prompt + HumanMessage(content="hi") + AIMessage(content="what?") + "{input}"
)
在底层,这会创建 ChatPromptTemplate 类的一个实例,因此您可以像以前一样使用它
new_prompt.format_messages(input="i said hi")
[SystemMessage(content='You are a nice pirate', additional_kwargs={}),
HumanMessage(content='hi', additional_kwargs={}, example=False),
AIMessage(content='what?', additional_kwargs={}, example=False),
HumanMessage(content='i said hi', additional_kwargs={}, example=False)]
您也可以像以前一样在 LLMChain 中使用它。
from langchain.chains import LLMChain
from langchain.chat_models import ChatOpenAI
model = ChatOpenAI()
chain = LLMChain(llm=model, prompt=new_prompt)
chain.run("i said hi")
'Oh, hello! How can I assist you today?'
三、使用PipelinePrompt组合多个Pipeline prompts
通过 PipelinePrompt可以将多个提示组合在一起,当您想要重复使用部分提示时,这会很有用。 PipelinePrompt 由两个主要部分组成:
Final prompt: 返回的最终提示,比如以下示例中的full_prompt;Pipeline prompts:元组列表(string name,prompt template),比如示例中的input_prompts。每个提示模板将被格式化,然后作为具有相同名称的变量传递到未来的提示模板。
下面例子中,我们首先创建Final prompt:
from langchain.prompts.pipeline import PipelinePromptTemplate
from langchain.prompts.prompt import PromptTemplate
full_template = """{introduction}
{example}
{start}"""
full_prompt = PromptTemplate.from_template(full_template)
introduction_template = """You are impersonating {person}."""
introduction_prompt = PromptTemplate.from_template(introduction_template)
example_template = """Here's an example of an interaction:
Q: {example_q}
A: {example_a}"""
example_prompt = PromptTemplate.from_template(example_template)
start_template = """Now, do this for real!
Q: {input}
A:"""
start_prompt = PromptTemplate.from_template(start_template)
使用PipelinePromptTemplate组合所有提示模板:
input_prompts = [
("introduction", introduction_prompt),
("example", example_prompt),
("start", start_prompt)
]
pipeline_prompt = PipelinePromptTemplate(final_prompt=full_prompt, pipeline_prompts=input_prompts)
pipeline_prompt.input_variables
['example_a', 'person', 'example_q', 'input']
print(pipeline_prompt.format(
person="Elon Musk",
example_q="What's your favorite car?",
example_a="Tesla",
input="What's your favorite social media site?"
))
You are impersonating Elon Musk.
Here's an example of an interaction:
Q: What's your favorite car?
A: Tesla
Now, do this for real!
Q: What's your favorite social media site?
A:
四、prompts存储和加载
通常来说最好不要将prompts存储为 python 代码,而是存储为文件,这样便于prompts的管理、分享和版本控制。LangChain 提供了强大的 prompts 序列化功能来实现这一点。
-
LangChain支持JSON和YAML两种序列化格式。JSON和YAML格式在磁盘上是人类可读的,而且很很流行,通常用来存储prompts。对于其他资源,如示例(examples),可能支持不同的序列化方法。
-
LangChain支持单文件存储和多文件存储。你可以在一个文件中指定所有内容,或将不同组件存储在不同文件中并进行引用。有些情况下,将所有内容存储在一个文件中可能是最合理的,但对于其他情况,将某些资源(如长模板、大示例、可重复使用的组件)拆分开可能更可取。
4.1 PromptTemplate
首先我们可以用PromptTemplate的save方法将其进行存储:
from langchain.prompts import PromptTemplate
prompt = (
PromptTemplate.from_template("Tell me a joke about {topic}")
+ ", make it funny"
+ "nnand in {language}"
)
prompt.save("prompt.yaml")
cat prompt.yaml
_type: prompt
input_types: {}
input_variables:
- language
- topic
output_parser: null
partial_variables: {}
template: 'Tell me a joke about {topic}, make it funny
and in {language}'
template_format: f-string
validate_template: false
如果使用save方法存储ChatPromptTemplate,会报错ChatPromptTemplate,应该是此功能还未实现(截止0.0344版本)。
4.1.1 从 YAML 加载
在notebook中创建一个simple_prompt.yaml文件:
%%writefile simple_prompt.yaml
_type: prompt
input_variables:
- adjective
- content
template: Tell me a {adjective} joke about {content}.
cat simple_prompt.yaml
_type: prompt
input_variables:
- adjective
- content
template: Tell me a {adjective} joke about {content}.
prompt = load_prompt("simple_prompt.yaml")
print(prompt.format(adjective="funny", content="chickens"))
Tell me a funny joke about chickens.
4.1.2 从 JSON 加载
%%writefile simple_prompt.json
{
"_type": "prompt",
"input_variables": ["adjective", "content"],
"template": "Tell me a {adjective} joke about {content}."
}
prompt = load_prompt("simple_prompt.json")
print(prompt.format(adjective="funny", content="chickens"))
Tell me a funny joke about chickens.
4.1.3 多文件加载
下面演示将模板存储在单独的文件中,然后在配置中引用它的示例。
%%writefile simple_template.txt
Tell me a {adjective} joke about {content}.
%%writefile simple_prompt_with_template_file.json
{
"_type": "prompt",
"input_variables": ["adjective", "content"],
"template_path": "simple_template.txt"
}
prompt = load_prompt("simple_prompt_with_template_file.json")
print(prompt.format(adjective="funny", content="chickens"))
Tell me a funny joke about chickens.
4.2 FewShotPromptTemplate
4.2.1 单文件加载含示例的prompts
cat few_shot_prompt_examples_in.json
{
"_type": "few_shot",
"input_variables": ["adjective"],
"prefix": "Write antonyms for the following words.",
"example_prompt": {
"_type": "prompt",
"input_variables": ["input", "output"],
"template": "Input: {input}nOutput: {output}"
},
"examples": [
{"input": "happy", "output": "sad"},
{"input": "tall", "output": "short"}
],
"suffix": "Input: {adjective}nOutput:"
}
prompt = load_prompt("few_shot_prompt_examples_in.json")
print(prompt.format(adjective="funny"))
Write antonyms for the following words.
Input: happy
Output: sad
Input: tall
Output: short
Input: funny
Output:
4.2.2 多文件存储
首先使用YAML或JSON来存储具体的示例:
cat examples.json
[
{"input": "happy", "output": "sad"},
{"input": "tall", "output": "short"}
]
cat examples.yaml
- input: happy
output: sad
- input: tall
output: short
4.2.2.1 使用YAML 加载示例
cat few_shot_prompt.yaml
_type: few_shot
input_variables:
["adjective"]
prefix:
Write antonyms for the following words.
example_prompt:
_type: prompt
input_variables:
["input", "output"]
template:
"Input: {input}nOutput: {output}"
examples:
examples.json
suffix:
"Input: {adjective}nOutput:"
prompt = load_prompt("few_shot_prompt.yaml")
print(prompt.format(adjective="funny"))
Write antonyms for the following words.
Input: happy
Output: sad
Input: tall
Output: short
Input: funny
Output:
上面的few_shot_prompt.yaml中, examples:examples.json也可以改成 examples:examples.yaml,结果是一样的。
4.2.2.2 从 JSON 加载示例
cat few_shot_prompt.json
{
"_type": "few_shot",
"input_variables": ["adjective"],
"prefix": "Write antonyms for the following words.",
"example_prompt": {
"_type": "prompt",
"input_variables": ["input", "output"],
"template": "Input: {input}nOutput: {output}"
},
"examples": "examples.json",
"suffix": "Input: {adjective}nOutput:"
}
prompt = load_prompt("few_shot_prompt.json")
print(prompt.format(adjective="funny"))
Write antonyms for the following words.
Input: happy
Output: sad
Input: tall
Output: short
Input: funny
Output:
4.2.2.3 单文件加载
上面两个例子,只将examples单独写在JSON或者YAML文件中进行引用,你也可以将example_prompt(PromptTemplate )也单独放在一个文件中,等于是整个FewShotPromptTemplate分三个文件来存储。
新建example_prompt.json
cat example_prompt.json
{
"_type": "prompt",
"input_variables": ["input", "output"],
"template": "Input: {input}nOutput: {output}"
}
配置FewShotPromptTemplate:
cat few_shot_prompt_example_prompt.json
{
"_type": "few_shot",
"input_variables": ["adjective"],
"prefix": "Write antonyms for the following words.",
"example_prompt_path": "example_prompt.json",
"examples": "examples.json",
"suffix": "Input: {adjective}nOutput:"
}
prompt = load_prompt("few_shot_prompt_example_prompt.json")
print(prompt.format(adjective="funny")) # 结果是一样的
4.3 带有 OutputParser 的 PromptTemplate
下面演示从文件加载带有OutputParser的PromptTemplate:
cat prompt_with_output_parser.json
{
"input_variables": [
"question",
"student_answer"
],
"output_parser": {
"regex": "(.*?)\nScore: (.*)",
"output_keys": [
"answer",
"score"
],
"default_output_key": null,
"_type": "regex_parser"
},
"partial_variables": {},
"template": "Given the following question and student answer, provide a correct answer and score the student answer.nQuestion: {question}nStudent Answer: {student_answer}nCorrect Answer:",
"template_format": "f-string",
"validate_template": true,
"_type": "prompt"
}
prompt = load_prompt("prompt_with_output_parser.json")
prompt.output_parser.parse(
"George Washington was born in 1732 and died in 1799.nScore: 1/2"
)
{'answer': 'George Washington was born in 1732 and died in 1799.',
'score': '1/2'}
原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_56591814/article/details/134736463
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。
如若转载,请注明出处:http://www.7code.cn/show_24680.html
如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系代码007邮箱:suwngjj01@126.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!