1.1、redis(Remote Dictionary Server)
一、整合redis
1、介绍
1.1、redis(Remote Dictionary Server)
- Redis是一种基于内存的键值存储系统,它将数据存储在内存中,因此读写速度非常快。
- Redis支持多种数据结构,如字符串、哈希、列表、集合、有序集合等,这使得Redis适用于各种应用场景,如缓存、消息队列、计数器等。
- Redis具有高可用性和可扩展性,支持主从复制和分片,以实现数据的备份和负载均衡。
- Redis的持久化方式有RDB(快照)和AOF(日志追加),可以将数据持久化到磁盘,保证数据的安全性。
1.2、MySQL
- MySQL是一种关系型数据库管理系统,使用标准的SQL语言进行数据操作。
- MySQL将数据存储在磁盘上,因此相对于Redis来说,读写速度较慢。
- MySQL支持事务处理和复杂的查询,适用于需要处理结构化数据的应用,如网站、电子商务等。
- MySQL具有较高的稳定性和成熟度,支持ACID特性(原子性、一致性、隔离性、持久性),可以保证数据的完整性和一致性。
1.3、区别
2、整合
2.1、配置
<redis.version>2.9.0</redis.version> <redis.spring.version>1.7.1.RELEASE</redis.spring.version> <dependency> <groupId>redis.clients</groupId> <artifactId>jedis</artifactId> <version>${redis.version}</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.data</groupId> <artifactId>spring-data-redis</artifactId> <version>${redis.spring.version}</version> </dependency>
2.2、文件配置
编写一个配置文件redis.properties,在我们的resources包里面。
redis.hostName:对应的IP地址
redis.port:对应的端口号
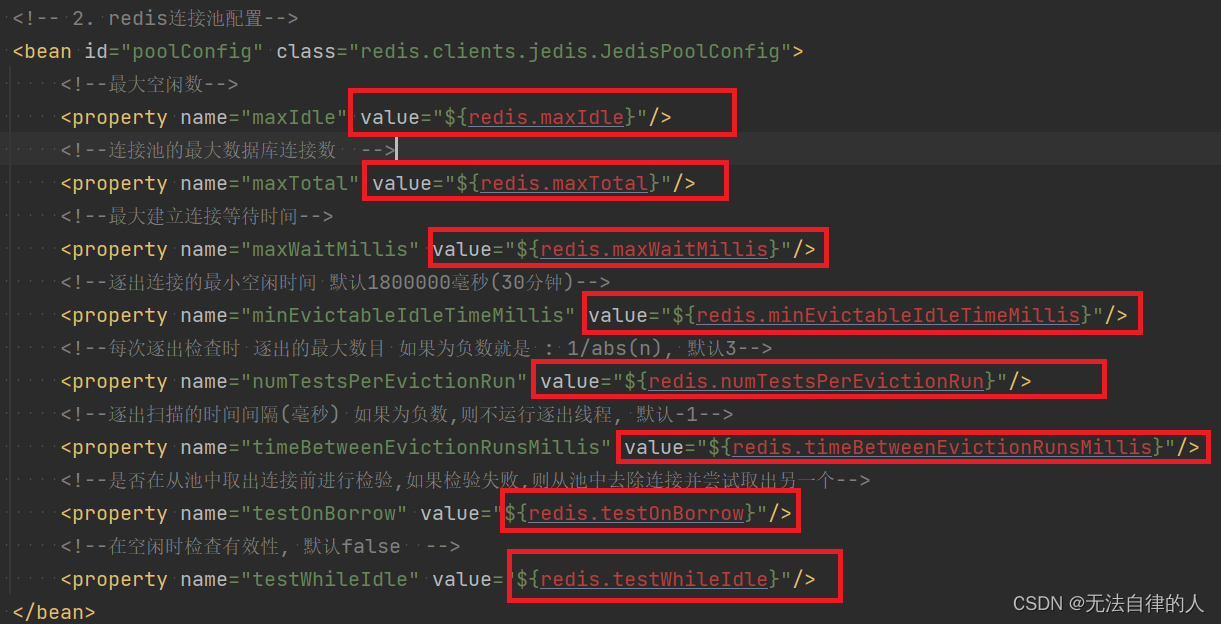
redis.password:对应的redis连接的密码redis.hostName=localhsot redis.port=6379 redis.password=123456 redis.timeout=10000 redis.maxIdle=300 redis.maxTotal=1000 redis.maxWaitMillis=1000 redis.minEvictableIdleTimeMillis=300000 redis.numTestsPerEvictionRun=1024 redis.timeBetweenEvictionRunsMillis=30000 redis.testOnBorrow=true redis.testWhileIdle=true redis.expiration=3600
- 添加注册
- redis的连接池配置:对应的value值是redis.properties里面的配置
- redis的的连接工厂:这里就用到了连接池的配置redis。
- 配置序列化:里面有string、json、hash的序列化器
- 配置key的生成
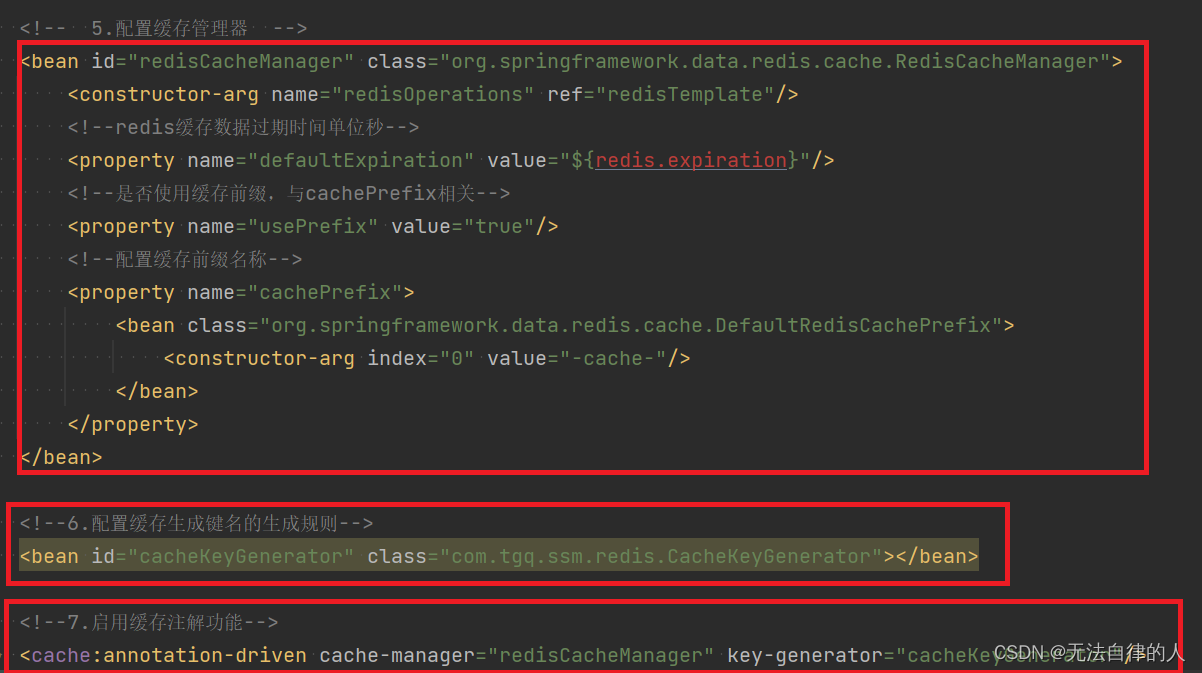
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xmlns:cache="http://www.springframework.org/schema/cache" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/cache http://www.springframework.org/schema/cache/spring-cache.xsd"> <!-- 1. 引入properties配置文件 --> <!--<context:property-placeholder location="classpath:redis.properties" />--> <!-- 2. redis连接池配置--> <bean id="poolConfig" class="redis.clients.jedis.JedisPoolConfig"> <!--最大空闲数--> <property name="maxIdle" value="${redis.maxIdle}"/> <!--连接池的最大数据库连接数 --> <property name="maxTotal" value="${redis.maxTotal}"/> <!--最大建立连接等待时间--> <property name="maxWaitMillis" value="${redis.maxWaitMillis}"/> <!--逐出连接的最小空闲时间 默认1800000毫秒(30分钟)--> <property name="minEvictableIdleTimeMillis" value="${redis.minEvictableIdleTimeMillis}"/> <!--每次逐出检查时 逐出的最大数目 如果为负数就是 : 1/abs(n), 默认3--> <property name="numTestsPerEvictionRun" value="${redis.numTestsPerEvictionRun}"/> <!--逐出扫描的时间间隔(毫秒) 如果为负数,则不运行逐出线程, 默认-1--> <property name="timeBetweenEvictionRunsMillis" value="${redis.timeBetweenEvictionRunsMillis}"/> <!--是否在从池中取出连接前进行检验,如果检验失败,则从池中去除连接并尝试取出另一个--> <property name="testOnBorrow" value="${redis.testOnBorrow}"/> <!--在空闲时检查有效性, 默认false --> <property name="testWhileIdle" value="${redis.testWhileIdle}"/> </bean> <!-- 3. redis连接工厂 --> <bean id="connectionFactory" class="org.springframework.data.redis.connection.jedis.JedisConnectionFactory" destroy-method="destroy"> <property name="poolConfig" ref="poolConfig"/> <!--IP地址 --> <property name="hostName" value="${redis.hostName}"/> <!--端口号 --> <property name="port" value="${redis.port}"/> <!--如果Redis设置有密码 --> <property name="password" value="${redis.password}"/> <!--客户端超时时间单位是毫秒 --> <property name="timeout" value="${redis.timeout}"/> </bean> <!-- 4. redis操作模板,使用该对象可以操作redis hibernate课程中hibernatetemplete,相当于session,专门操作数据库。 --> <bean id="redisTemplate" class="org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate"> <property name="connectionFactory" ref="connectionFactory"/> <!--如果不配置Serializer,那么存储的时候缺省使用String,如果用User类型存储,那么会提示错误User can't cast to String!! --> <property name="keySerializer"> <bean class="org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.StringRedisSerializer"/> </property> <property name="valueSerializer"> <bean class="org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.GenericJackson2JsonRedisSerializer"/> </property> <property name="hashKeySerializer"> <bean class="org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.StringRedisSerializer"/> </property> <property name="hashValueSerializer"> <bean class="org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.GenericJackson2JsonRedisSerializer"/> </property> <!--开启事务 --> <property name="enableTransactionSupport" value="true"/> </bean> <!-- 5.配置缓存管理器 --> <bean id="redisCacheManager" class="org.springframework.data.redis.cache.RedisCacheManager"> <constructor-arg name="redisOperations" ref="redisTemplate"/> <!--redis缓存数据过期时间单位秒--> <property name="defaultExpiration" value="${redis.expiration}"/> <!--是否使用缓存前缀,与cachePrefix相关--> <property name="usePrefix" value="true"/> <!--配置缓存前缀名称--> <property name="cachePrefix"> <bean class="org.springframework.data.redis.cache.DefaultRedisCachePrefix"> <constructor-arg index="0" value="-cache-"/> </bean> </property> </bean> <!--6.配置缓存生成键名的生成规则--> <bean id="cacheKeyGenerator" class="com.tgq.ssm.redis.CacheKeyGenerator"></bean> <!--7.启用缓存注解功能--> <cache:annotation-driven cache-manager="redisCacheManager" key-generator="cacheKeyGenerator"/> </beans>
redis.properties与jdbc.properties在与Spring做整合时会发生冲突;所以引入配置文件的地方要放到applicationContext.xml中
applicationContext.xml配置如下
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx" xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd"> <!--1. 引入外部多文件方式 --> <bean id="propertyConfigurer" class="org.springframework.beans.factory.config.PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer"> <property name="systemPropertiesModeName" value="SYSTEM_PROPERTIES_MODE_OVERRIDE" /> <property name="ignoreResourceNotFound" value="true" /> <property name="locations"> <list> <value>classpath:jdbc.properties</value> <value>classpath:redis.properties</value> </list> </property> </bean> <!-- 随着后续学习,框架会越学越多,不能将所有的框架配置,放到同一个配制间,否者不便于管理 --> <import resource="applicationContext-mybatis.xml"></import> <import resource="spring-redis.xml"></import> <import resource="applicationContext-shiro.xml"></import> </beans>
2.3、key的生成规则方法
spring-redis.xml的最后的配置就说明了键的配置规则。
package com.tgq.ssm.redis;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.cache.interceptor.KeyGenerator;
import org.springframework.util.ClassUtils;
import java.lang.reflect.Array;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
@Slf4j
public class CacheKeyGenerator implements KeyGenerator {
// custom cache key
public static final int NO_PARAM_KEY = 0;
public static final int NULL_PARAM_KEY = 53;
@Override
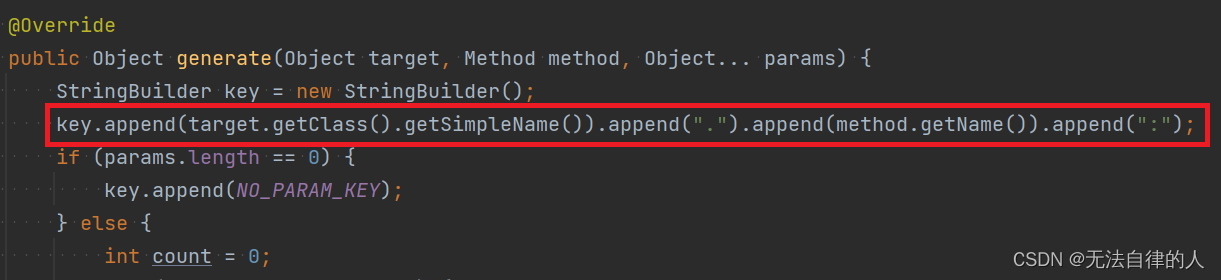
public Object generate(Object target, Method method, Object... params) {
StringBuilder key = new StringBuilder();
key.append(target.getClass().getSimpleName()).append(".").append(method.getName()).append(":");
if (params.length == 0) {
key.append(NO_PARAM_KEY);
} else {
int count = 0;
for (Object param : params) {
if (0 != count) {//参数之间用,进行分隔
key.append(',');
}
if (param == null) {
key.append(NULL_PARAM_KEY);
} else if (ClassUtils.isPrimitiveArray(param.getClass())) {
int length = Array.getLength(param);
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
key.append(Array.get(param, i));
key.append(',');
}
} else if (ClassUtils.isPrimitiveOrWrapper(param.getClass()) || param instanceof String) {
key.append(param);
} else {//Java一定要重写hashCode和eqauls
key.append(param.hashCode());
}
count++;
}
}
String finalKey = key.toString();
// IEDA要安装lombok插件
log.debug("using cache key={}", finalKey);
return finalKey;
}
}
2.4、注意
二、redis注解式缓存
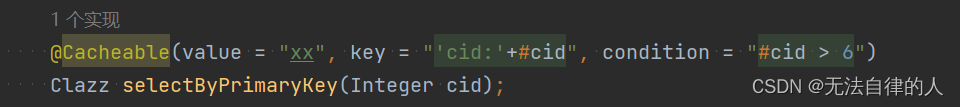
1、@Cacheable注解
配置在方法或类上,作用:本方法执行后,先去缓存看有没有数据,如果没有,从数据库中查找出来,给缓存中存一份,返回结果,
下次本方法执行,在缓存未过期情况下,先在缓存中查找,有的话直接返回,没有的话从数据库查找。value:缓存位置的一段名称,不能为空。
key:缓存的key,默认为空,表示使用方法的参数类型及参数值作为key,支持SpEL。
condition:触发条件,满足条件就加入缓存,默认为空,表示全部都加入缓存,支持SpEL 。
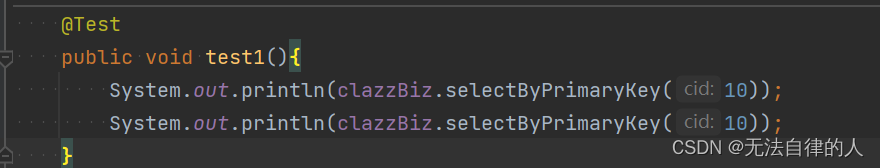
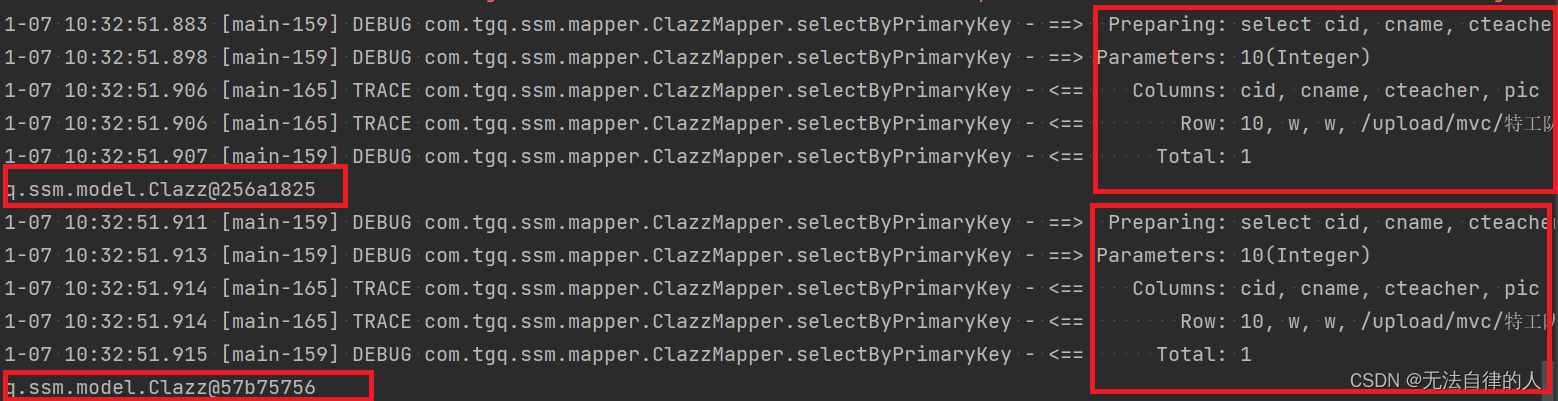
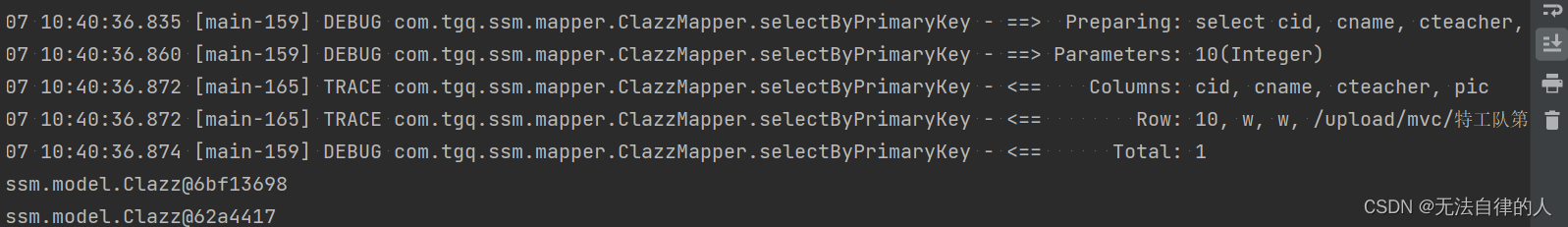
但我们调用查询的方法而没有用@Cacheable注解的时候我们可以看到我们查询出来的结果是两个,而且查询了数据库两次。
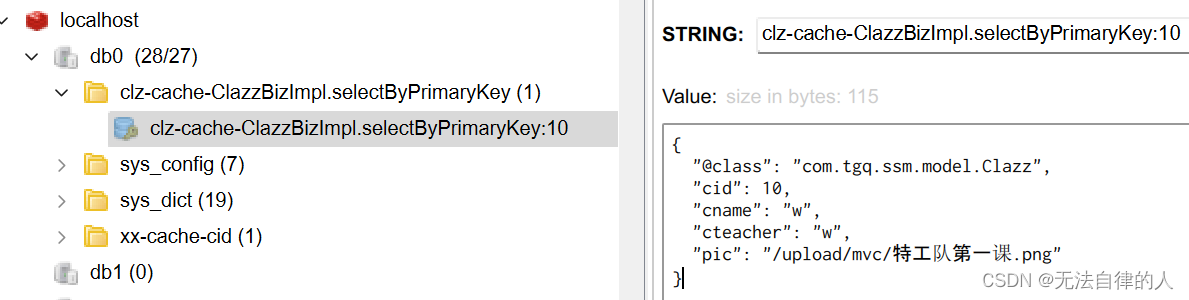
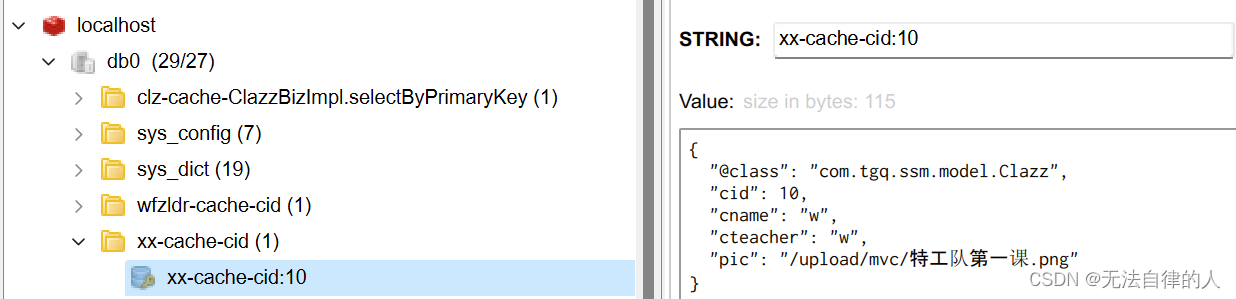
当我们用到@Cacheable注解的时候我们只查询了数据库一次,如果再次查询就不会出现sql语句,而且已经缓存到了redis里面。
- 改变原有的key生成规则
改变原有的规则之后我们再次运行,我们的redis的键就不一样了。
condition:当某个值大于或者小于某个值才进行缓存。
2、@CachePut注解
类似于更新操作,即每次不管缓存中有没有结果,都从数据库查找结果,并将结果更新到缓存,并返回结果。
value:缓存的名称,在 spring 配置文件中定义,必须指定至少一个。
key:缓存的 key,可以为空,如果指定要按照 SpEL 表达式编写,如果不指定,则缺省按照方法的所有参数进行组合。
condition:缓存的条件,可以为空,使用 SpEL 编写,返回 true 或者 false,只有为 true 才进行缓存。
当我们使用它测试出来的结果则是:只存不取
@Cacheable注解表示方法的返回值可以被缓存,下次访问相同的方法时,会直接从缓存中获取结果,而不会再执行方法内部的逻辑。该注解标记在方法上,指定了缓存的名称(也可以使用默认的缓存名称),也可以通过参数指定缓存的Key。如果缓存中已有相应的Key存在,则会直接返回缓存中的值;若缓存中不存在对应的Key,则会执行方法,并将方法的返回值添加到缓存中。
@CachePut注解表示无条件地执行方法内部的逻辑,并将方法的返回值添加到缓存中。该注解也标记在方法上,通常用于更新缓存的操作。它与@Cacheable注解的不同之处在于,每次调用带有@CachePut注解的方法时,都会执行方法内部的逻辑,并将结果添加到缓存中,覆盖原有的缓存值。
@CachePut注解常用于需要更新缓存中数据的场景,可以保证每次调用方法时都会执行方法内部的逻辑,并更新缓存的结果。Cacheable:会在redis中存储数据,同时也会读取数据。
3、@CacheEvict注解
value:缓存位置的一段名称,不能为空
key:缓存的key,默认为空,表示使用方法的参数类型及参数值作为key,支持SpEL
condition:触发条件,满足条件就加入缓存,默认为空,表示全部都加入缓存,支持SpEL
allEntries:true表示清除value中的全部缓存,默认为false
4、应用场景
Redis注解式缓存是一种通过使用注解来简化缓存操作的方法,它可以方便地在方法调用前后自动进行缓存的读取和写入。以下是Redis注解式缓存的常见应用场景:
-
方法结果缓存:对于一些计算成本较高的方法,可以使用注解将其结果缓存起来,避免重复计算。当下次调用相同的方法时,可以直接从缓存中获取结果,提高性能并减轻服务器负载。
-
数据查询缓存:对于频繁读取的数据查询操作,可以使用注解将查询结果缓存起来。这样可以避免反复查询数据库,提高系统的响应速度。
-
限流和熔断:通过使用注解实现限流,可以控制对某些资源或接口的并发请求量,避免系统过载。同时,可以设置特定的缓存时间,当资源或接口不可用时,返回缓存中的数据,实现熔断降级。
-
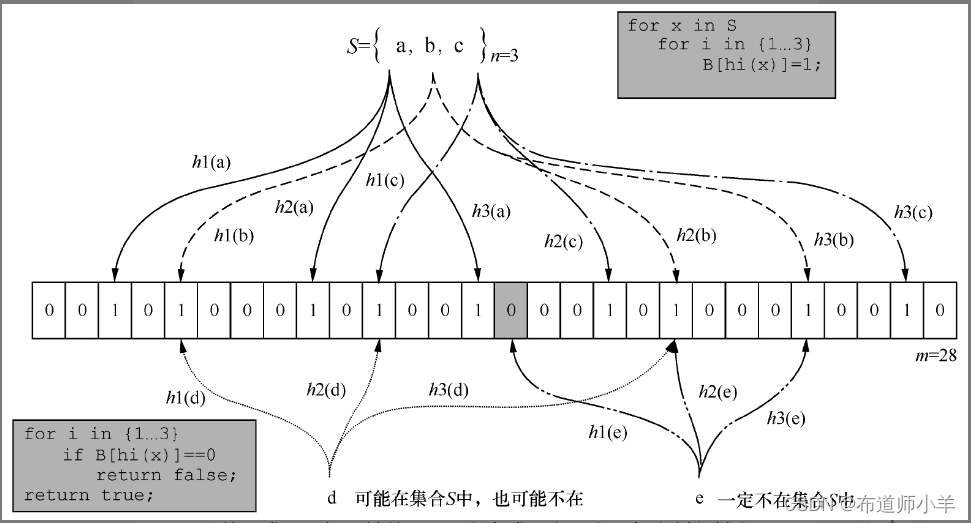
防止缓存穿透:通过使用注解和布隆过滤器等技术,可以在查询之前拦截请求,并且判断缓存中是否存在对应的数据。如果不存在,则直接返回空值,避免对数据库的无效查询。
三、redis击穿穿透雪崩
redis的简单的作用:能够极大的减轻MySQL的访问压力。
大部分的解决方案需要根据具体的场景和需求选择合适的解决方案。同时,合理的缓存策略、数据预热和监控是缓解这些问题的关键,以确保系统的稳定性和可靠性。
1、击穿(Cache Miss)
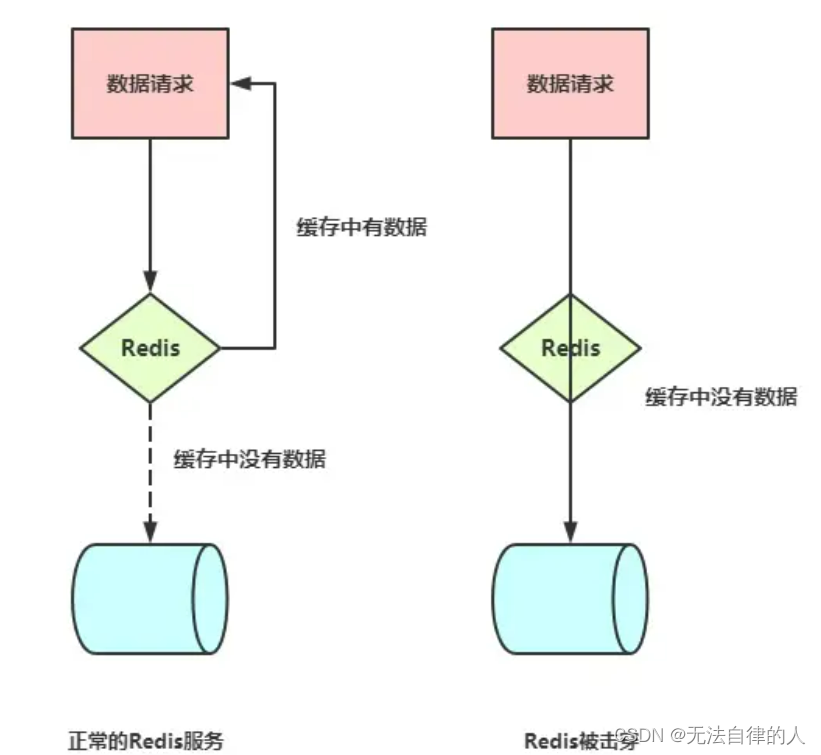
缓存击穿就是在处于集中式高并发访问的情况下,当某个热点 key 在失效的瞬间,大量的请求在缓存中获取不到。瞬间击穿了缓存,所有请求直接打到数据库,就像是在一道屏障上击穿了一个洞。
2、穿透(Cache Penetration)
3、雪崩(Cache Avalanche)
原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_74383330/article/details/134248681
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。
如若转载,请注明出处:http://www.7code.cn/show_25110.html
如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系代码007邮箱:suwngjj01@126.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!