本文介绍: pandas中DataFrame表连接操作,及merge与join的区别。ValueError: columns overlap but no suffix specified: Index([‘dishes_id‘], dtype=’object‘) 错误解释
前言:
为了方便维护,一般公司的数据在数据库内都是分表存储的,比如用一个表存储所有用户的基本信息,一个表存储用户的消费情况。
所以,在日常的数据处理中,经常需要将两张表拼接起来使用,这样的操作对应到SQL中是join,在Pandas中则是用merge来实现。
上面的引入部分说到merge是用来拼接两张表的,那么拼接时自然就需要将用户信息一一对应地进行拼接。
所以进行拼接的两张表需要有一个共同的识别用户的键(key),也就是on参数所指定的列。
总结来说,整个merge的过程就是将信息一一对应匹配的过程,下面介绍merge的四种类型,分别为’inner‘、’left‘、’right‘和’outer‘。
表的连接方式可参考以下文档: https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/102274476
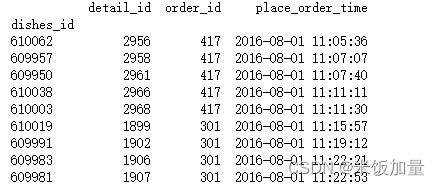
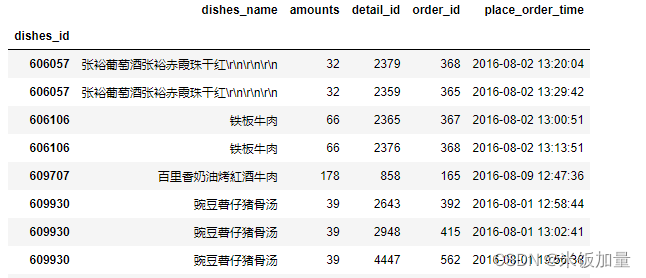
创建两个DataFrame

声明:本站所有文章,如无特殊说明或标注,均为本站原创发布。任何个人或组织,在未征得本站同意时,禁止复制、盗用、采集、发布本站内容到任何网站、书籍等各类媒体平台。如若本站内容侵犯了原著者的合法权益,可联系我们进行处理。