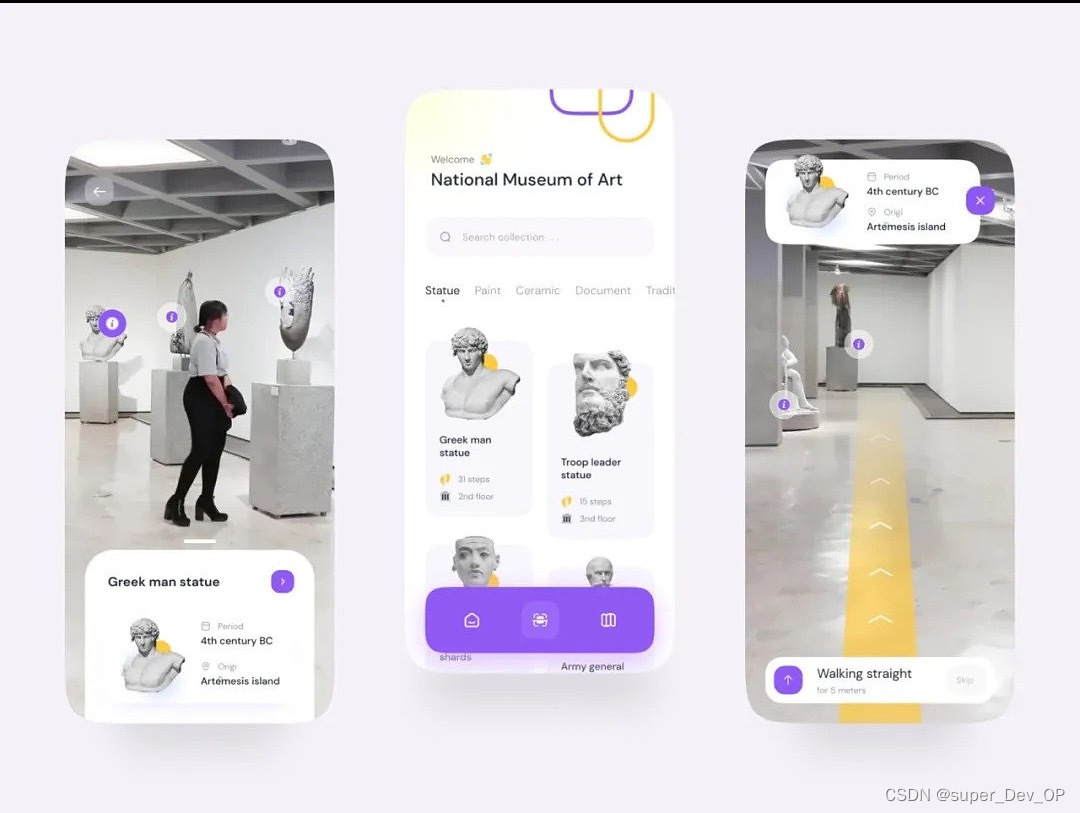
真正理解区块链底层原理的方法就是写一个底层,UTXO模型区块链的开发难度还是比较简单的,等开发完后再去尝试一下基于account模型的。
什么是区块链以及UTXO模型和account模型等问题我就不在这里写了,网上的资料有很多,跟着写之前可以先去了解一下区块链的基础知识。
开发环境:goland+go1.20
该项目github地址:lighteningchain
mirror地址:lighteningchain(1)
创建项目
使用goland创建项目,取名为lighteningchain,并使用go mod init lighteningchain初始化项目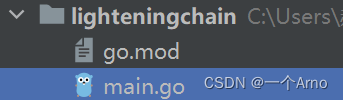
区块结构
每个区块应该包含头部(head)信息用于总结性的描述这个区块,然后在区块的数据存放区(body)中存放要保存的重要数据
首先定义区块结构体和区块链的结构体
计算哈希
information变量是将区块的各项属性串联之后的字节串。bytes.Join可以将多个字节串连接,第二个参数是将字节串连接时的分隔符,这里设置为[]byte{}即为空。
创建区块和区块链
main函数编写运行测试区块链
总结
参考资料
声明:本站所有文章,如无特殊说明或标注,均为本站原创发布。任何个人或组织,在未征得本站同意时,禁止复制、盗用、采集、发布本站内容到任何网站、书籍等各类媒体平台。如若本站内容侵犯了原著者的合法权益,可联系我们进行处理。