/*
* Copyright 2002-2020 the original author or authors.
*
* Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
* you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
* You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* https://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/
package org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.lookup;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.Map;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.InitializingBean;
import org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.AbstractDataSource;
import org.springframework.lang.Nullable;
import org.springframework.util.Assert;
import org.springframework.util.CollectionUtils;
/**
* Abstract {@link javax.sql.DataSource} implementation that routes {@link #getConnection()}
* calls to one of various target DataSources based on a lookup key. The latter is usually
* (but not necessarily) determined through some thread-bound transaction context.
*
* @author Juergen Hoeller
* @since 2.0.1
* @see #setTargetDataSources
* @see #setDefaultTargetDataSource
* @see #determineCurrentLookupKey()
*/
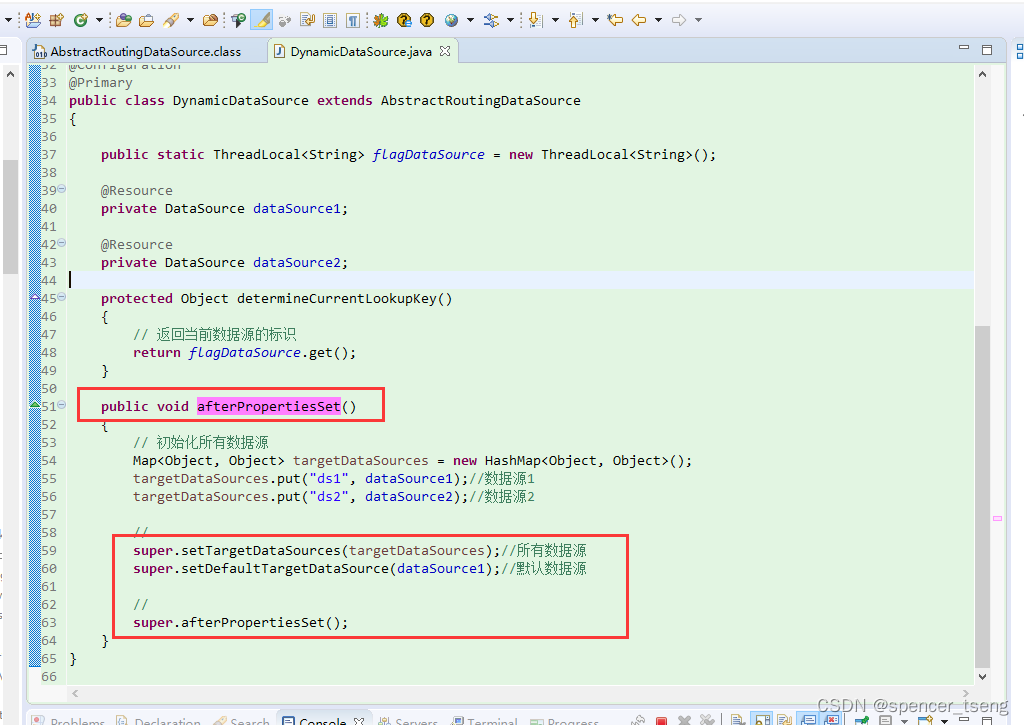
public abstract class AbstractRoutingDataSource extends AbstractDataSource implements InitializingBean {
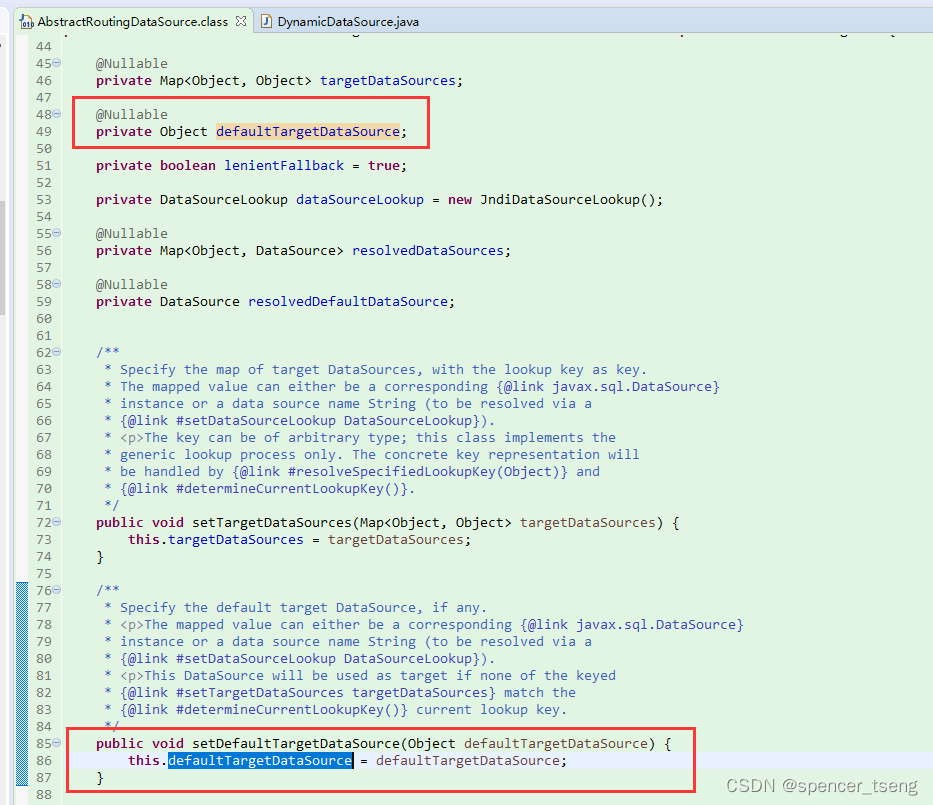
@Nullable
private Map<Object, Object> targetDataSources;
@Nullable
private Object defaultTargetDataSource;
private boolean lenientFallback = true;
private DataSourceLookup dataSourceLookup = new JndiDataSourceLookup();
@Nullable
private Map<Object, DataSource> resolvedDataSources;
@Nullable
private DataSource resolvedDefaultDataSource;
/**
* Specify the map of target DataSources, with the lookup key as key.
* The mapped value can either be a corresponding {@link javax.sql.DataSource}
* instance or a data source name String (to be resolved via a
* {@link #setDataSourceLookup DataSourceLookup}).
* <p>The key can be of arbitrary type; this class implements the
* generic lookup process only. The concrete key representation will
* be handled by {@link #resolveSpecifiedLookupKey(Object)} and
* {@link #determineCurrentLookupKey()}.
*/
public void setTargetDataSources(Map<Object, Object> targetDataSources) {
this.targetDataSources = targetDataSources;
}
/**
* Specify the default target DataSource, if any.
* <p>The mapped value can either be a corresponding {@link javax.sql.DataSource}
* instance or a data source name String (to be resolved via a
* {@link #setDataSourceLookup DataSourceLookup}).
* <p>This DataSource will be used as target if none of the keyed
* {@link #setTargetDataSources targetDataSources} match the
* {@link #determineCurrentLookupKey()} current lookup key.
*/
public void setDefaultTargetDataSource(Object defaultTargetDataSource) {
this.defaultTargetDataSource = defaultTargetDataSource;
}
/**
* Specify whether to apply a lenient fallback to the default DataSource
* if no specific DataSource could be found for the current lookup key.
* <p>Default is "true", accepting lookup keys without a corresponding entry
* in the target DataSource map - simply falling back to the default DataSource
* in that case.
* <p>Switch this flag to "false" if you would prefer the fallback to only apply
* if the lookup key was {@code null}. Lookup keys without a DataSource
* entry will then lead to an IllegalStateException.
* @see #setTargetDataSources
* @see #setDefaultTargetDataSource
* @see #determineCurrentLookupKey()
*/
public void setLenientFallback(boolean lenientFallback) {
this.lenientFallback = lenientFallback;
}
/**
* Set the DataSourceLookup implementation to use for resolving data source
* name Strings in the {@link #setTargetDataSources targetDataSources} map.
* <p>Default is a {@link JndiDataSourceLookup}, allowing the JNDI names
* of application server DataSources to be specified directly.
*/
public void setDataSourceLookup(@Nullable DataSourceLookup dataSourceLookup) {
this.dataSourceLookup = (dataSourceLookup != null ? dataSourceLookup : new JndiDataSourceLookup());
}
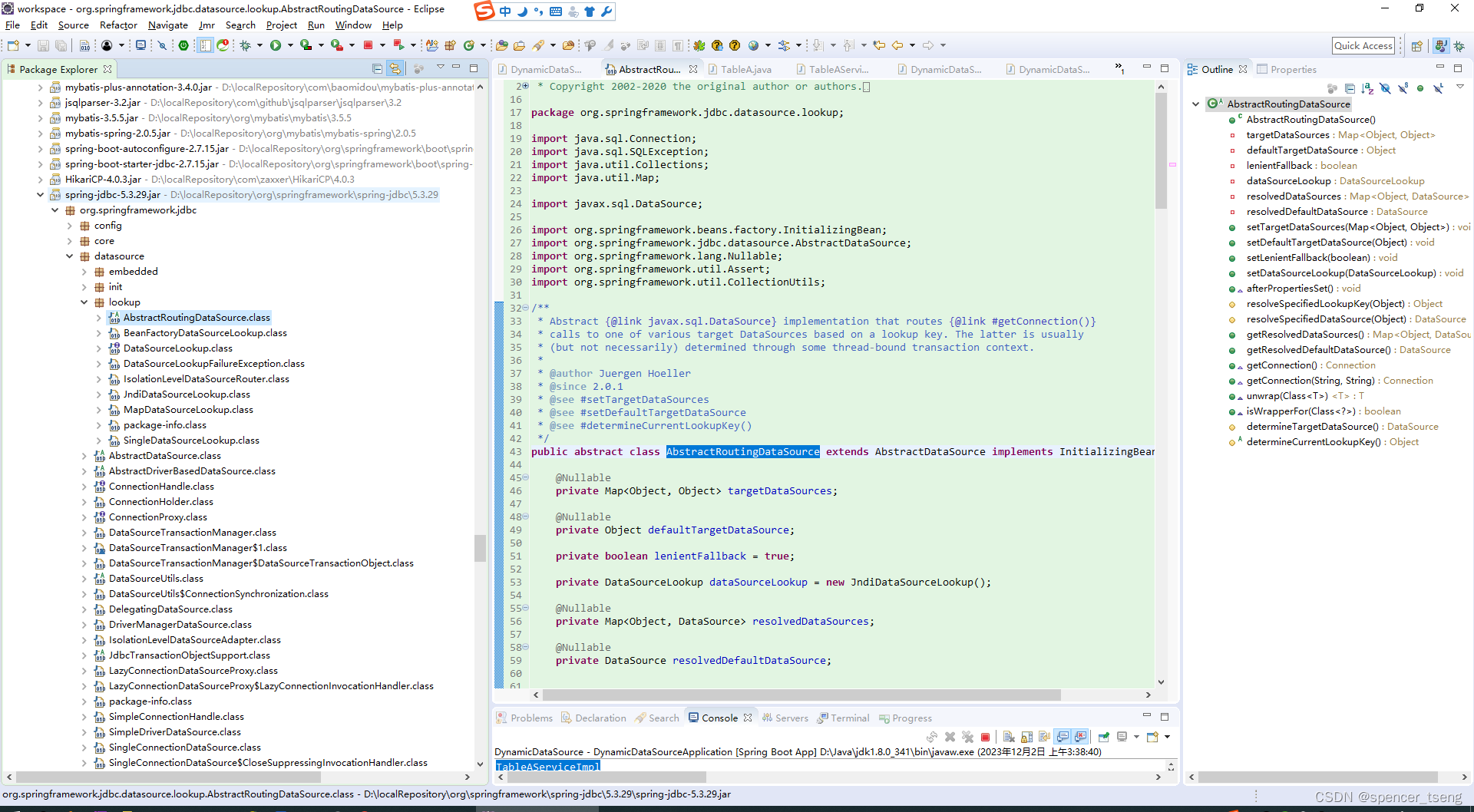
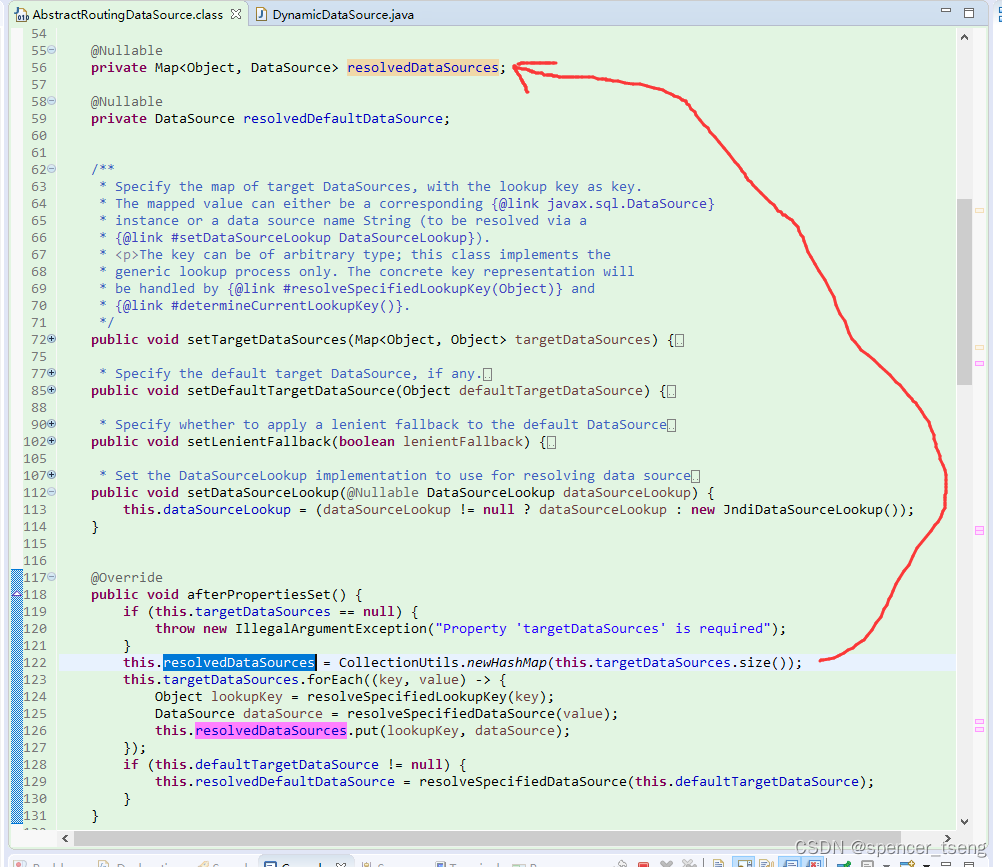
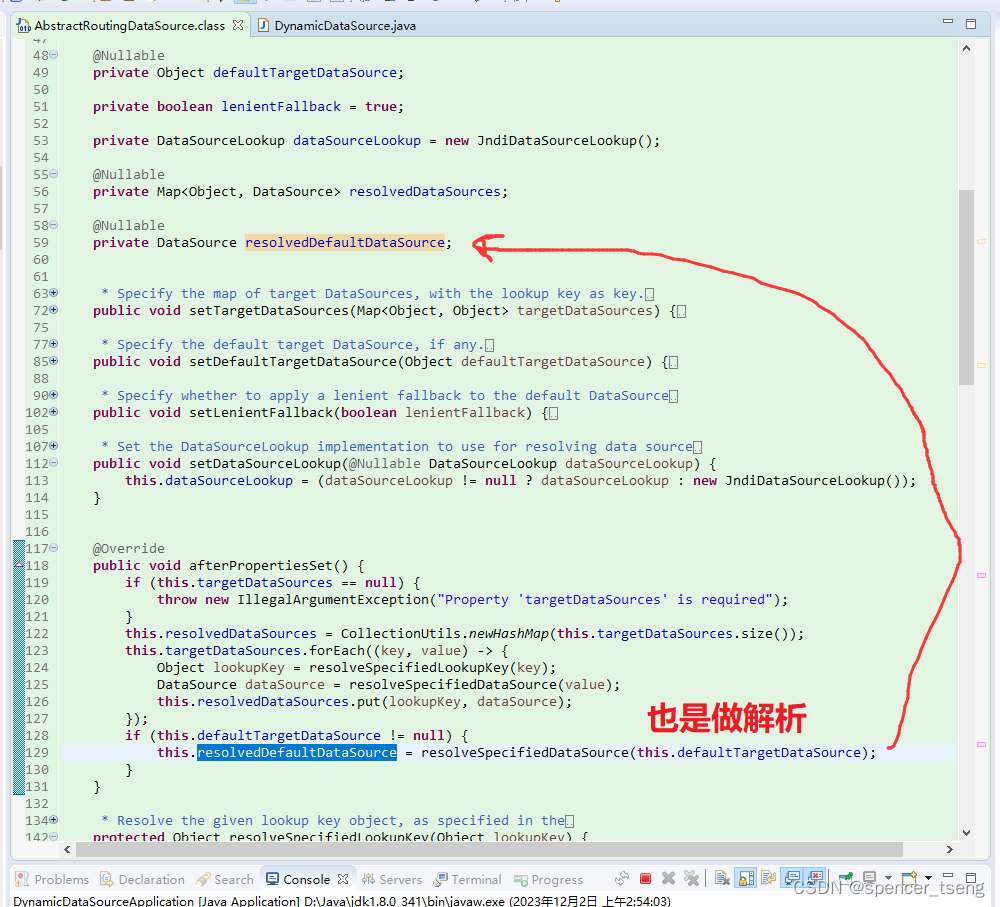
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() {
if (this.targetDataSources == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Property 'targetDataSources' is required");
}
this.resolvedDataSources = CollectionUtils.newHashMap(this.targetDataSources.size());
this.targetDataSources.forEach((key, value) -> {
Object lookupKey = resolveSpecifiedLookupKey(key);
DataSource dataSource = resolveSpecifiedDataSource(value);
this.resolvedDataSources.put(lookupKey, dataSource);
});
if (this.defaultTargetDataSource != null) {
this.resolvedDefaultDataSource = resolveSpecifiedDataSource(this.defaultTargetDataSource);
}
}
/**
* Resolve the given lookup key object, as specified in the
* {@link #setTargetDataSources targetDataSources} map, into
* the actual lookup key to be used for matching with the
* {@link #determineCurrentLookupKey() current lookup key}.
* <p>The default implementation simply returns the given key as-is.
* @param lookupKey the lookup key object as specified by the user
* @return the lookup key as needed for matching
*/
protected Object resolveSpecifiedLookupKey(Object lookupKey) {
return lookupKey;
}
/**
* Resolve the specified data source object into a DataSource instance.
* <p>The default implementation handles DataSource instances and data source
* names (to be resolved via a {@link #setDataSourceLookup DataSourceLookup}).
* @param dataSource the data source value object as specified in the
* {@link #setTargetDataSources targetDataSources} map
* @return the resolved DataSource (never {@code null})
* @throws IllegalArgumentException in case of an unsupported value type
*/
protected DataSource resolveSpecifiedDataSource(Object dataSource) throws IllegalArgumentException {
if (dataSource instanceof DataSource) {
return (DataSource) dataSource;
}
else if (dataSource instanceof String) {
return this.dataSourceLookup.getDataSource((String) dataSource);
}
else {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
"Illegal data source value - only [javax.sql.DataSource] and String supported: " + dataSource);
}
}
/**
* Return the resolved target DataSources that this router manages.
* @return an unmodifiable map of resolved lookup keys and DataSources
* @throws IllegalStateException if the target DataSources are not resolved yet
* @since 5.2.9
* @see #setTargetDataSources
*/
public Map<Object, DataSource> getResolvedDataSources() {
Assert.state(this.resolvedDataSources != null, "DataSources not resolved yet - call afterPropertiesSet");
return Collections.unmodifiableMap(this.resolvedDataSources);
}
/**
* Return the resolved default target DataSource, if any.
* @return the default DataSource, or {@code null} if none or not resolved yet
* @since 5.2.9
* @see #setDefaultTargetDataSource
*/
@Nullable
public DataSource getResolvedDefaultDataSource() {
return this.resolvedDefaultDataSource;
}
@Override
public Connection getConnection() throws SQLException {
return determineTargetDataSource().getConnection();
}
@Override
public Connection getConnection(String username, String password) throws SQLException {
return determineTargetDataSource().getConnection(username, password);
}
@Override
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public <T> T unwrap(Class<T> iface) throws SQLException {
if (iface.isInstance(this)) {
return (T) this;
}
return determineTargetDataSource().unwrap(iface);
}
@Override
public boolean isWrapperFor(Class<?> iface) throws SQLException {
return (iface.isInstance(this) || determineTargetDataSource().isWrapperFor(iface));
}
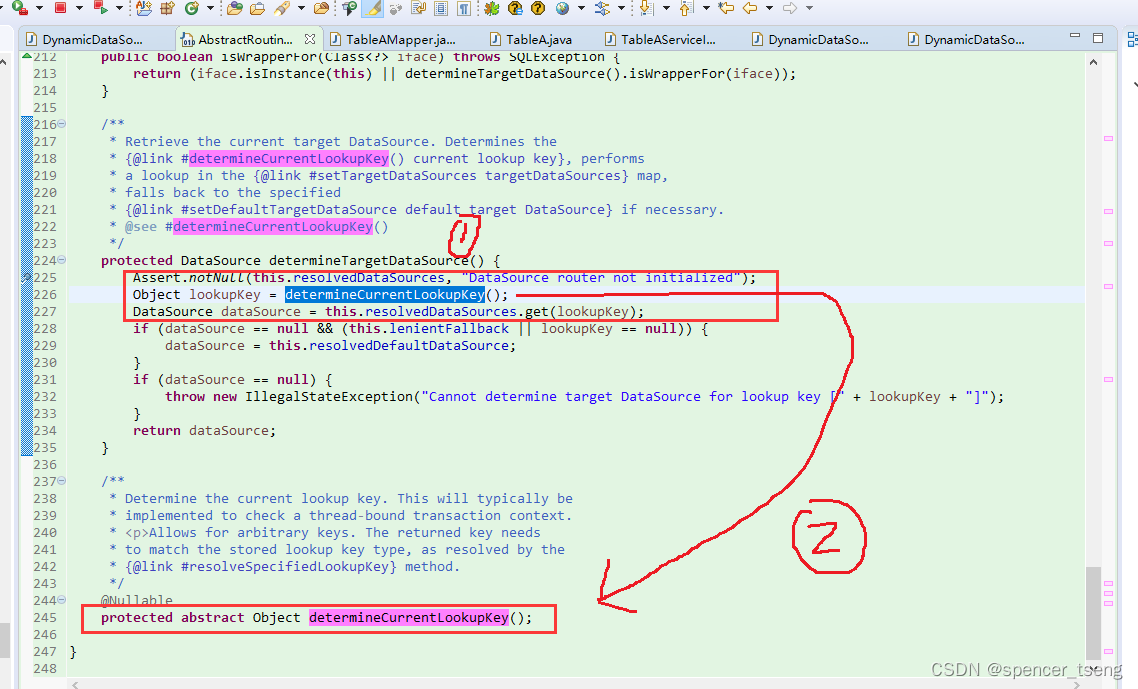
/**
* Retrieve the current target DataSource. Determines the
* {@link #determineCurrentLookupKey() current lookup key}, performs
* a lookup in the {@link #setTargetDataSources targetDataSources} map,
* falls back to the specified
* {@link #setDefaultTargetDataSource default target DataSource} if necessary.
* @see #determineCurrentLookupKey()
*/
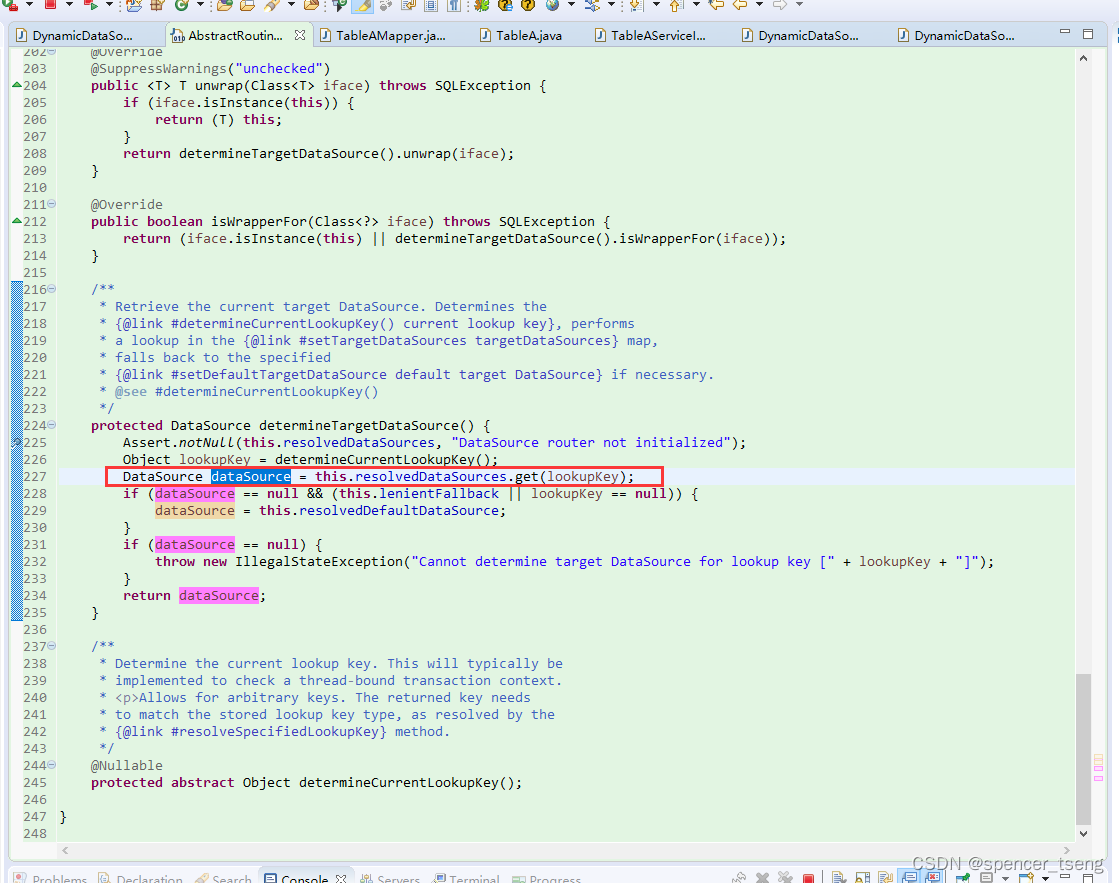
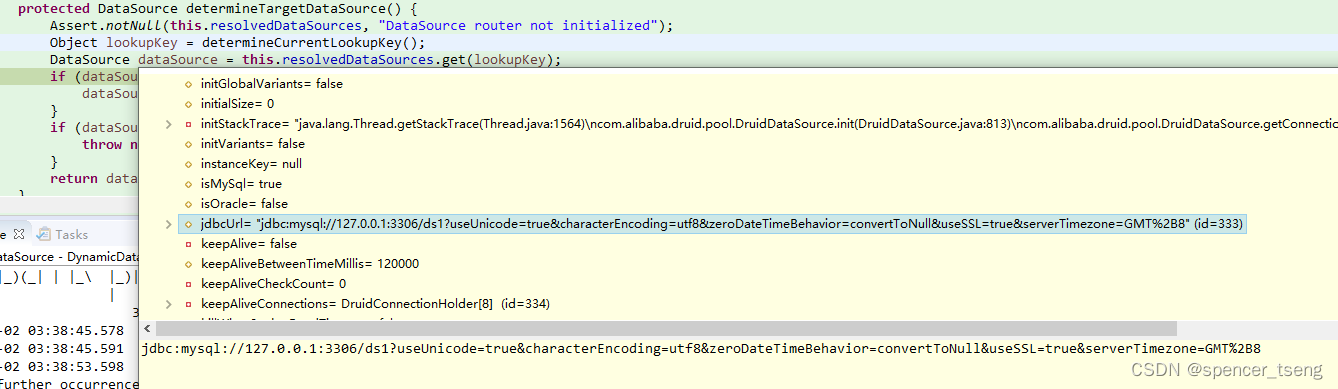
protected DataSource determineTargetDataSource() {
Assert.notNull(this.resolvedDataSources, "DataSource router not initialized");
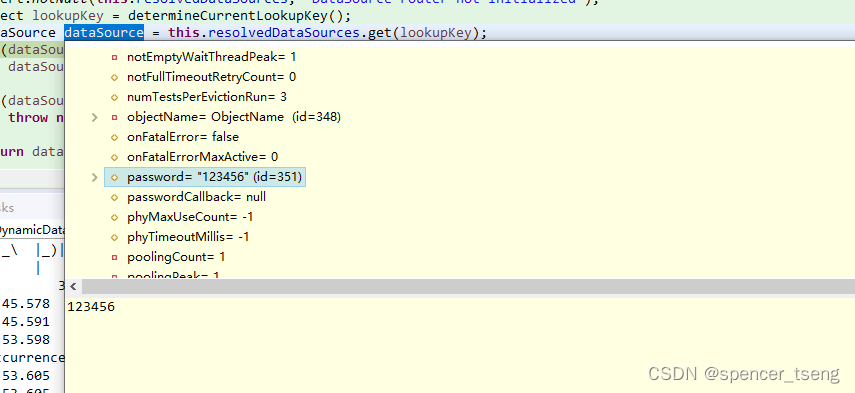
Object lookupKey = determineCurrentLookupKey();
DataSource dataSource = this.resolvedDataSources.get(lookupKey);
if (dataSource == null && (this.lenientFallback || lookupKey == null)) {
dataSource = this.resolvedDefaultDataSource;
}
if (dataSource == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Cannot determine target DataSource for lookup key [" + lookupKey + "]");
}
return dataSource;
}
/**
* Determine the current lookup key. This will typically be
* implemented to check a thread-bound transaction context.
* <p>Allows for arbitrary keys. The returned key needs
* to match the stored lookup key type, as resolved by the
* {@link #resolveSpecifiedLookupKey} method.
*/
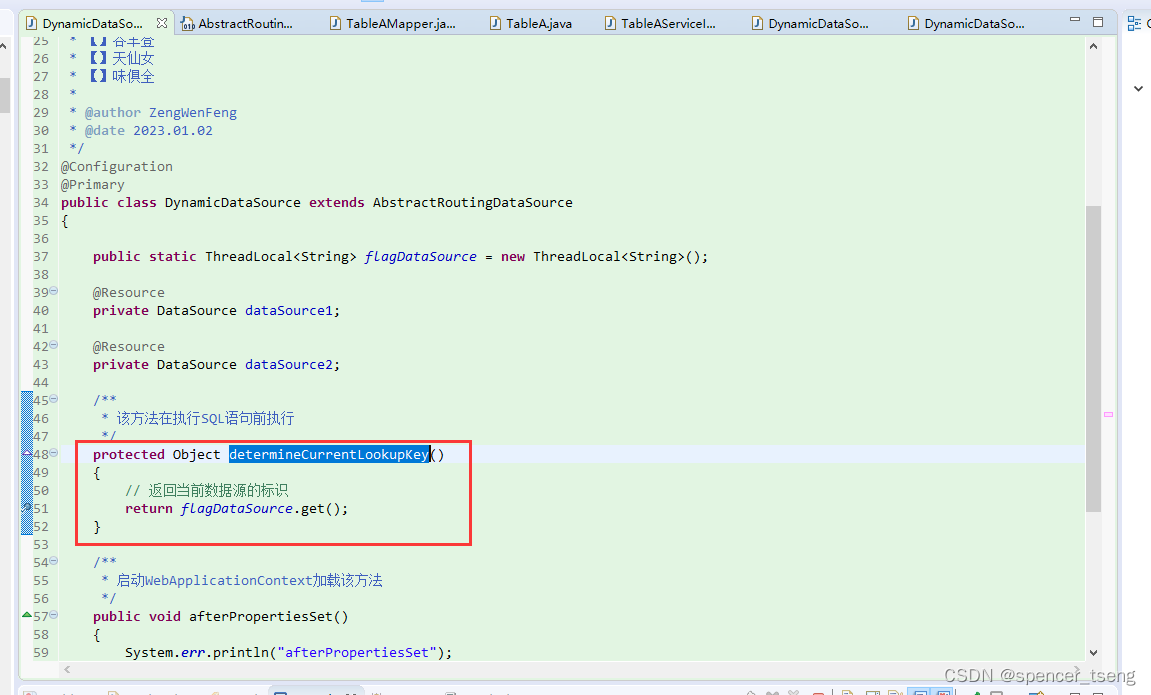
@Nullable
protected abstract Object determineCurrentLookupKey();
}


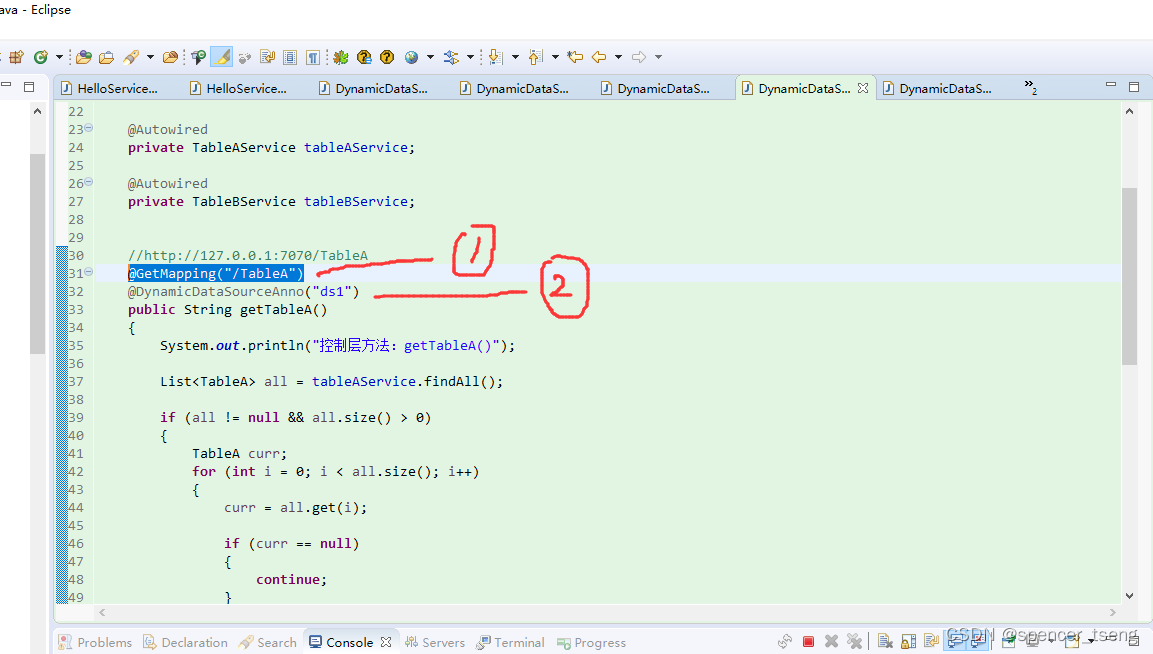
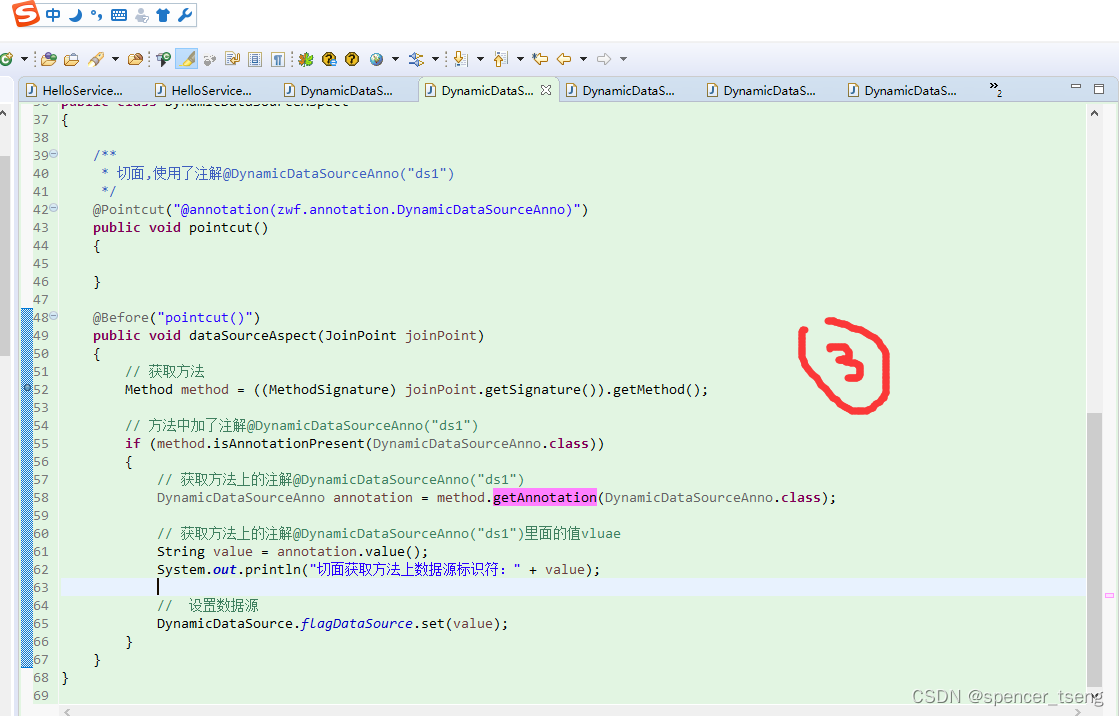
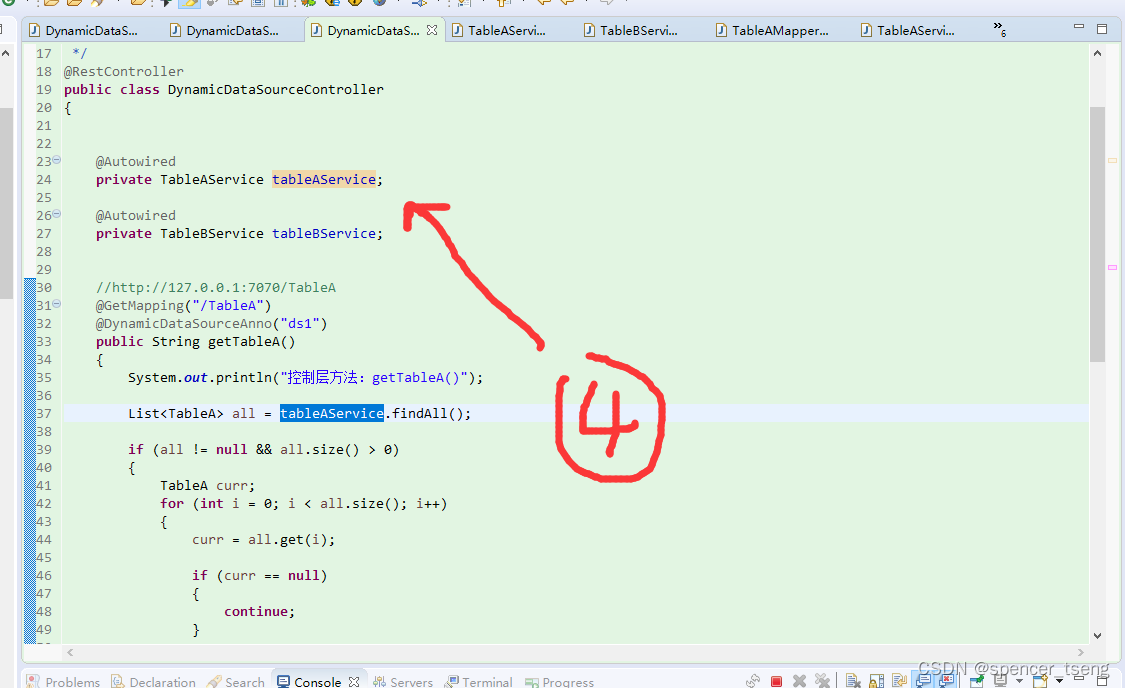
原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/spencer_tseng/article/details/134746920
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。
如若转载,请注明出处:http://www.7code.cn/show_34034.html
如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系代码007邮箱:suwngjj01@126.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
主题授权提示:请在后台主题设置-主题授权-激活主题的正版授权,授权购买:RiTheme官网
声明:本站所有文章,如无特殊说明或标注,均为本站原创发布。任何个人或组织,在未征得本站同意时,禁止复制、盗用、采集、发布本站内容到任何网站、书籍等各类媒体平台。如若本站内容侵犯了原著者的合法权益,可联系我们进行处理。


![[Lucene]核心类和概念介绍](http://www.7code.cn/wp-content/uploads/2023/11/ee6748cbc735e6105405f8a984d954c804b93f34bc916-Z0IqTf_fw1200.png)