1线程池中提交一个任务得流程是怎样的
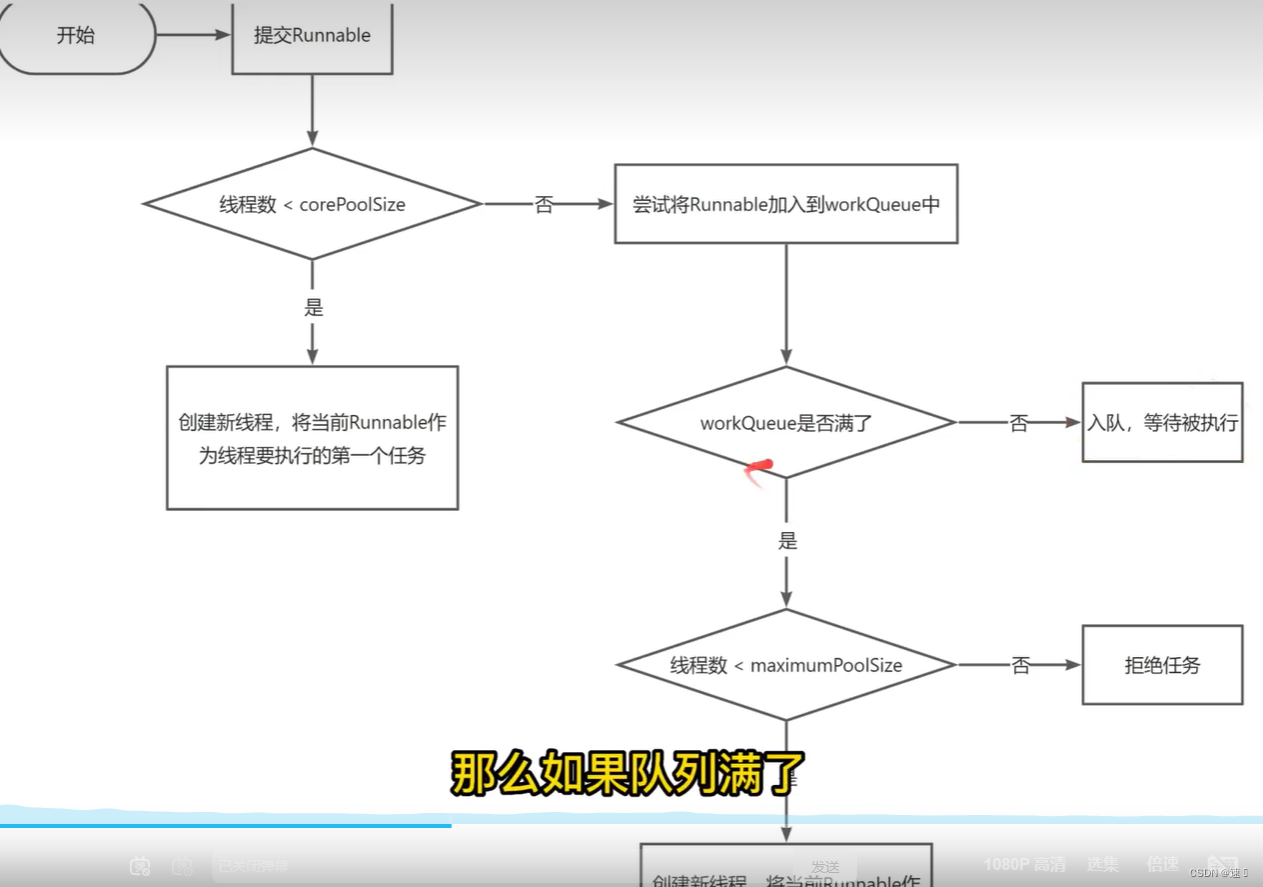
public void execute(Runnable command) {
if (command == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
/*
* Proceed in 3 steps:
*
* 1. If fewer than corePoolSize threads are running, try to
* start a new thread with the given command as its first
* task. The call to addWorker atomically checks runState and
* workerCount, and so prevents false alarms that would add
* threads when it shouldn't, by returning false.
*
* 2. If a task can be successfully queued, then we still need
* to double-check whether we should have added a thread
* (because existing ones died since last checking) or that
* the pool shut down since entry into this method. So we
* recheck state and if necessary roll back the enqueuing if
* stopped, or start a new thread if there are none.
*
* 3. If we cannot queue task, then we try to add a new
* thread. If it fails, we know we are shut down or saturated
* and so reject the task.
*/
int c = ctl.get();
if (workerCountOf(c) < corePoolSize) {
if (addWorker(command, true))
return;
c = ctl.get();
}
if (isRunning(c) && workQueue.offer(command)) {
int recheck = ctl.get();
if (! isRunning(recheck) && remove(command))
reject(command);
else if (workerCountOf(recheck) == 0)
addWorker(null, false);
}
else if (!addWorker(command, false))
reject(command);
}2 线程池中有几种状态?分别是如何变化的?
状态:
2 SHUTDOWN:不会接收新任务并且会处理队列中的任务,任务处理完后会中断所有线程
3 STOP: 不会接收新任务并且不会处理队列中的任务,并且会直接中断所有线程
4 TIDYING:所有线程都停止之后,线程池的状态会转为TIDYING,一旦达到此状态,就会调用线程池的terminated()
5 TERMINATED: terminated()执行完之后就会转变为TERMINATED
源码:
private final AtomicInteger ctl = new AtomicInteger(ctlOf(RUNNING, 0));
private static final int COUNT_BITS = Integer.SIZE - 3;
private static final int CAPACITY = (1 << COUNT_BITS) - 1;
// runState is stored in the high-order bits
private static final int RUNNING = -1 << COUNT_BITS;
private static final int SHUTDOWN = 0 << COUNT_BITS;
private static final int STOP = 1 << COUNT_BITS;
private static final int TIDYING = 2 << COUNT_BITS;
private static final int TERMINATED = 3 << COUNT_BITS;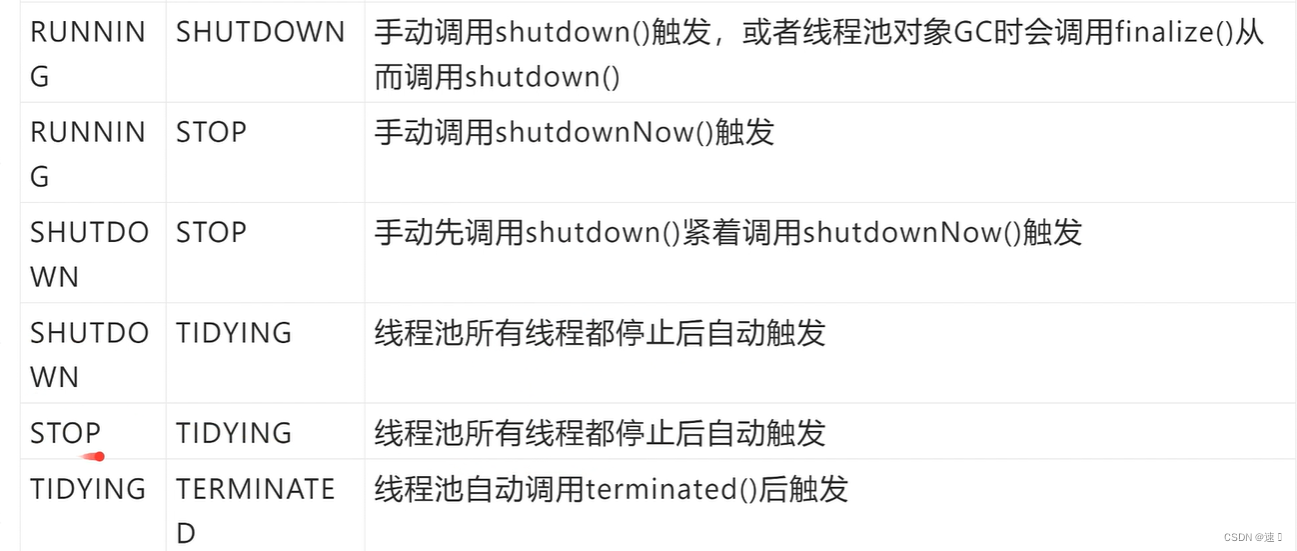
3 如何优雅的停止一个线程
stop():stop()会释放线程占用的synchronized锁,而不会自动释放ReentranLock锁
interrupt(): 该方法只是在目标线程中设置一个标志,表示它已经被中断,线程是否中断,取决于线程本身,
4 线程池的核心线程数,最大线程数如何设置?
cpu核心数 * (1 + 线程等待时间 / 线程运行总时间 )
corePoolSize: 核心线程数,表示线程中的常驻线程个数
maximumPoolSize: 最大线程数,表示线程池总能开辟的最大线程个数
核心应用():核心线程数 = maximumPoolSize = 压测出来的个数,
非核心线程:核心线程数设置少点,maximumPoolSize=压测个数
5 如何理解java并发中的可见性
java 并发可见性是指多线程并发访问共享变量时,对变量的更改能够被其他线程及时感知
6 如何理解Java并发中的原子性?
线程在执行一段代码的时候,要么全部执行成功,要么全部不执行,不能执行到一半就结束了
7 如何理解Java并发中的有序性
java并发有序性指的是多个线程执行的指令和操作,按照开发者编写程序的顺序或预定的顺序进行执行。多线程并发执行时,可能会发生指令的重排,导致程序的执行顺序与预期不一致,从而出现数据竞争和线程安全问题
8JDK JRE JVMM之间的关系
JDK : java标准开发包,他提供了编译,运行Java程序所需的各种工具和资源,包括java编译器, java运行时环境,以及常用的java类库等
JVM:JAVA虚拟机,是jre的一部分,他是整个java实现跨平最核心的部分,负责运行字节码文件
9 hashCode()和 equals()之间的关系
在java的一些集合类的实现中,在比较两个对象是否相等时,会先调用对象的hashCode()方法得到hashCode进行比较,如果hashCode不相同,就可以认为这两个对象不相同,如果hashcode相同,就会调用equals方法进行比较
10 String StringBuffer StringBuilder的区别
1 String是常量不可变,StringBuilder StringBuffer是可变的
2 StringBuilder线程不安全,StringBuffer线程安全
原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_61743064/article/details/134756250
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。
如若转载,请注明出处:http://www.7code.cn/show_36080.html
如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系代码007邮箱:suwngjj01@126.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!



![[设计模式Java实现附plantuml源码~行为型]请求的链式处理——职责链模式](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/699aac3ed0c446d088772a0ed4c444ed.png)
![[设计模式Java实现附plantuml源码~结构型]处理多维度变化——桥接模式](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/8e811a73550d49e6a55c49a070a733e8.png)