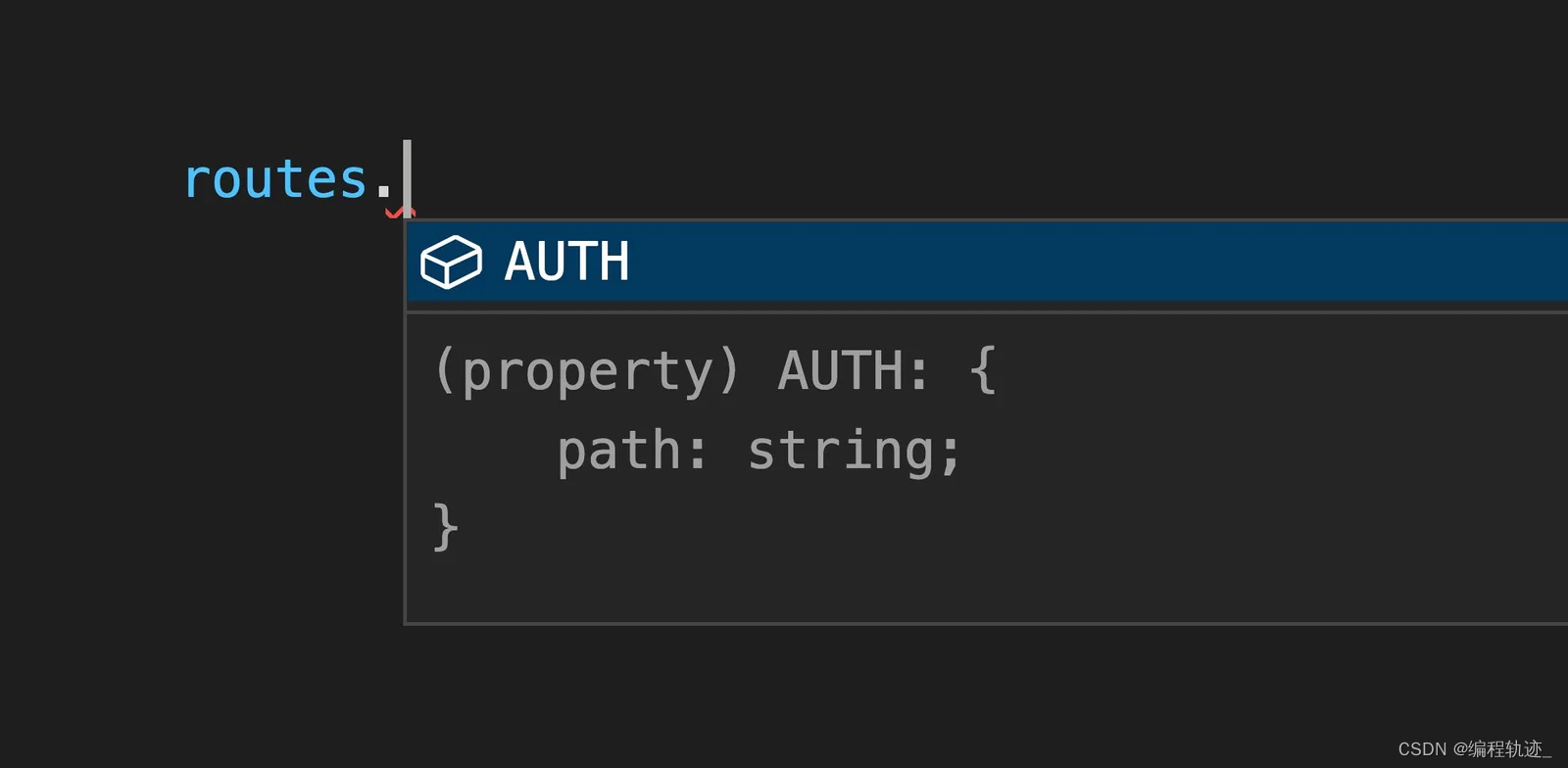
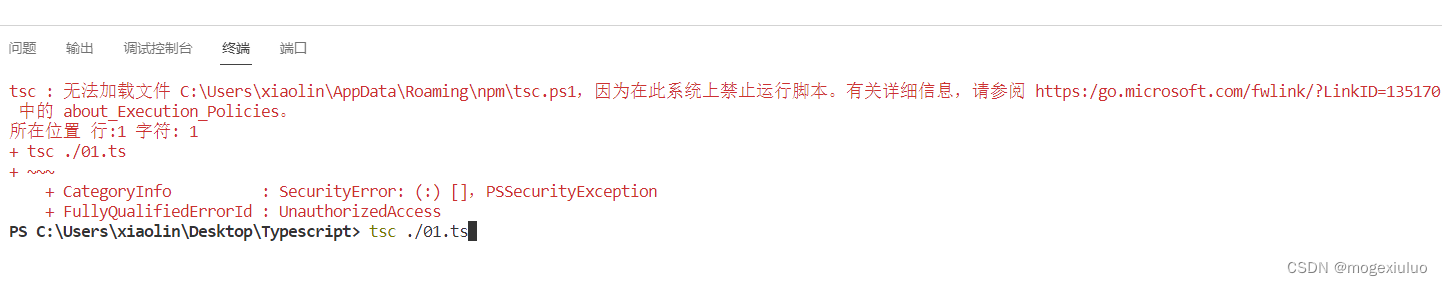
本文介绍: 在上面的示例中,我给出了satisfies的使用示例,但是我并没有解释那样做的原因。现在,是该给你解释解释了。children?AUTH : {这看起来似乎没有什么呀,很正常,IDE 也会自动帮我们进行自动补齐。但是,当我们使用routes对象时,因为 IDE 并不知道实际配置的路由是什么。routes . NONSENSE . path // TypeScript 报错:发现这个路由属性不存在为什么会这样?这是因为我们的Routes类型可以接受任何字符串作为键。
现在,随着 TS 4.9 的发布,在 TypeScript 中有了一种新的、更好的方式来做类型安全校验。它就是 satisfies :
为什么是 satisfies
在上面的示例中,我给出了 satisfies 的使用示例,但是我并没有解释那样做的原因。现在,是该给你解释解释了。
让我们从使用 TS 的标准类型声明重写上面的示例来进行一个对比:
这看起来似乎没有什么呀,很正常,IDE 也会自动帮我们进行自动补齐。
但是,当我们使用 routes 对象时,因为 IDE 并不知道实际配置的路由是什么。
Satisfies
与 as const 结合
声明:本站所有文章,如无特殊说明或标注,均为本站原创发布。任何个人或组织,在未征得本站同意时,禁止复制、盗用、采集、发布本站内容到任何网站、书籍等各类媒体平台。如若本站内容侵犯了原著者的合法权益,可联系我们进行处理。