前言:
本文使用栈以非递归的形式遍历整颗二叉树,我是通过数组模拟栈来实现的,如果对用数组模拟栈不太熟悉,你可以直接使用Stack类作为栈实现。
前序(先序)遍历:
思路:每次弹出一个节点就添加到结果集,如果节点的右孩子不为空,就让右孩子入栈、如果节点的左孩子不为空,就让左孩子进栈;栈会帮我们控制节点的弹出顺序。
题目链接:144. 二叉树的前序遍历 – 力扣(LeetCode)
class Solution {
//题目规定节点个数在100以内
public static int MAX = 101;
public static TreeNode [] stack = new TreeNode[MAX];
//栈中的元素个数
public static int size;
public List<Integer> preorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
//空树直接返回空集合
if(root == null)
return List.of();
//一开始栈中没有元素
size = 0;
//头节点入栈
stack[size++] = root;
List<Integer> ans = new ArrayList<>();
//只要栈不为空,一直弹出节点
while(size > 0){
TreeNode node = stack[--size];
ans.add(node.val);
//先让右孩子入栈、再让左孩子入栈
//栈弹出节点时,左孩子先出栈、右孩子后出栈
if(node.right != null)
stack[size++] = node.right;
if(node.left != null)
stack[size++] = node.left;
}
return ans;
}
}
中序遍历:
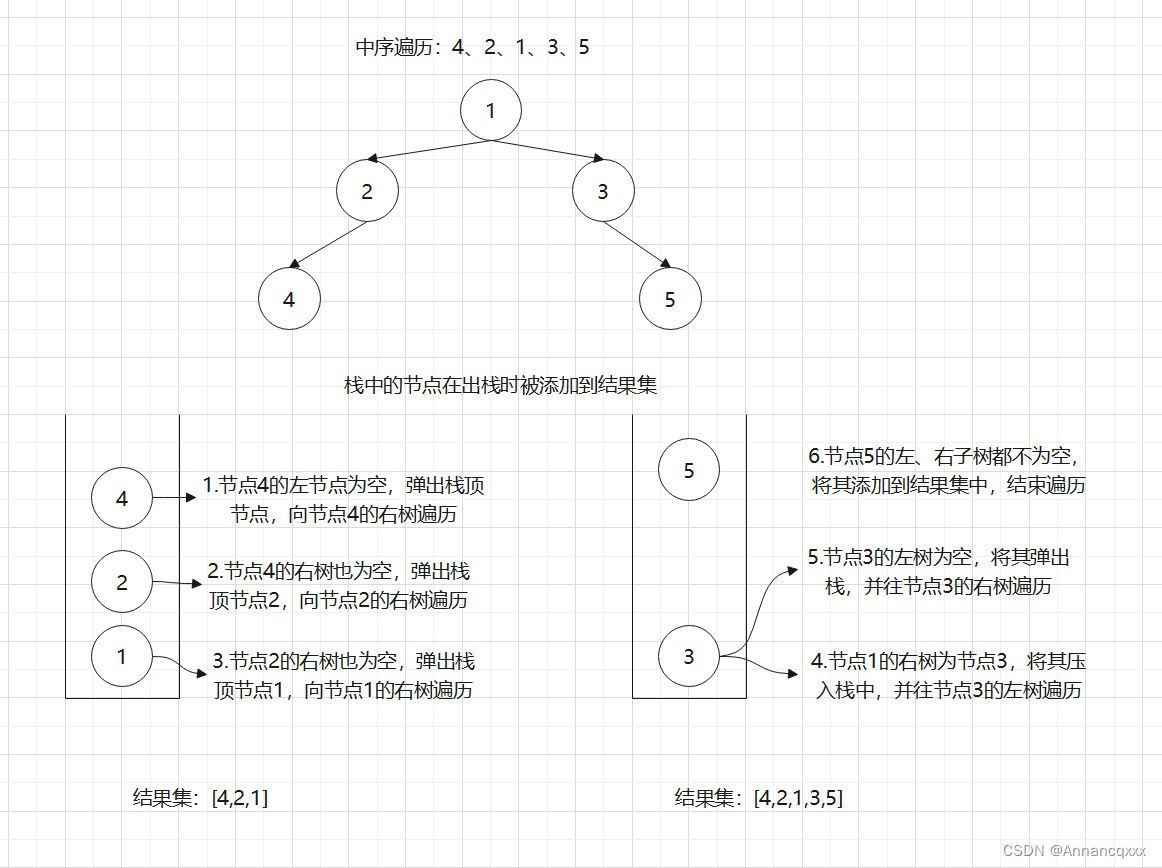
思路:指针p从根节点开始,不断向左子树遍历,遍历过程中将节点添加到栈中,当碰到空节点时,弹出此时处于栈顶的节点,将其添加到结果集中,并让指针p指向弹出节点的右节点,如果其右节点不为空,那么它会重复第一步的逻辑(不断向其左子树遍历),这样就能保证在处理完左树后,再去处理右树。
题目链接:94. 二叉树的中序遍历 – 力扣(LeetCode)
class Solution {
public static int MAX = 101;
public static TreeNode [] stack = new TreeNode[MAX];
public static int size;
public List<Integer> inorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null)
return List.of();
size = 0;
List<Integer> ans = new ArrayList<>();
TreeNode p = root;
while(size > 0 || p != null){
//只要指针p指向的节点不为null,就往其左子树遍历
//并在遍历过程中,将节点添加到栈中
if(p != null){
stack[size++] = p;
p = p.left;
//当指针p指向的节点为null时,弹出栈顶节点
//将栈顶节点添加到结果集
//并让p指针指向栈顶节点的右子树
}else{
TreeNode node = stack[--size];
ans.add(node.val);
p = node.right;
}
}
return ans;
}
}图解:
后序遍历:
思路:前序遍历通过先添加右节点、再添加左节点实现中、左、右的遍历顺序,那我们先让左节点入栈,再让右节点入栈不就可以实现中、右、左的遍历顺序吗?最后再另起一个栈,将前一个栈的结果装到新启的栈中,就实现了左、右、中的遍历顺序。
题目链接:145. 二叉树的后序遍历 – 力扣(LeetCode)
Code:
class Solution {
public static int MAX = 101;
//栈1
public static TreeNode [] stack = new TreeNode[MAX];
//栈2
public static TreeNode [] collect = new TreeNode[MAX];
//栈1的元素个数
public static int size1;
//栈2的元素个数
public static int size2;
public List<Integer> postorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
//空树返回空集合
if(root == null)
return List.of();
//初始化两个栈的大小
size1 = size2 = 0;
//让头结点进入栈1
stack[size1++] = root;
//遍历栈1
while(size1 > 0){
//弹出栈1中的元素
TreeNode node = stack[--size1];
//放入栈2中
collect[size2++] = node;
//如果左节点不为空,就放入栈1
if(node.left != null)
stack[size1++] = node.left;
//如果右节点不为空,就放入栈2
if(node.right != null)
stack[size1++] = node.right;
}
List<Integer> ans = new ArrayList<>();
//遍历栈2,不断弹出栈2中的元素添加到结果集
while(size2 > 0){
TreeNode node = collect[--size2];
ans.add(node.val);
}
return ans;
}
}原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/Annancqxxx/article/details/134762354
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。
如若转载,请注明出处:http://www.7code.cn/show_37110.html
如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系代码007邮箱:suwngjj01@126.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!