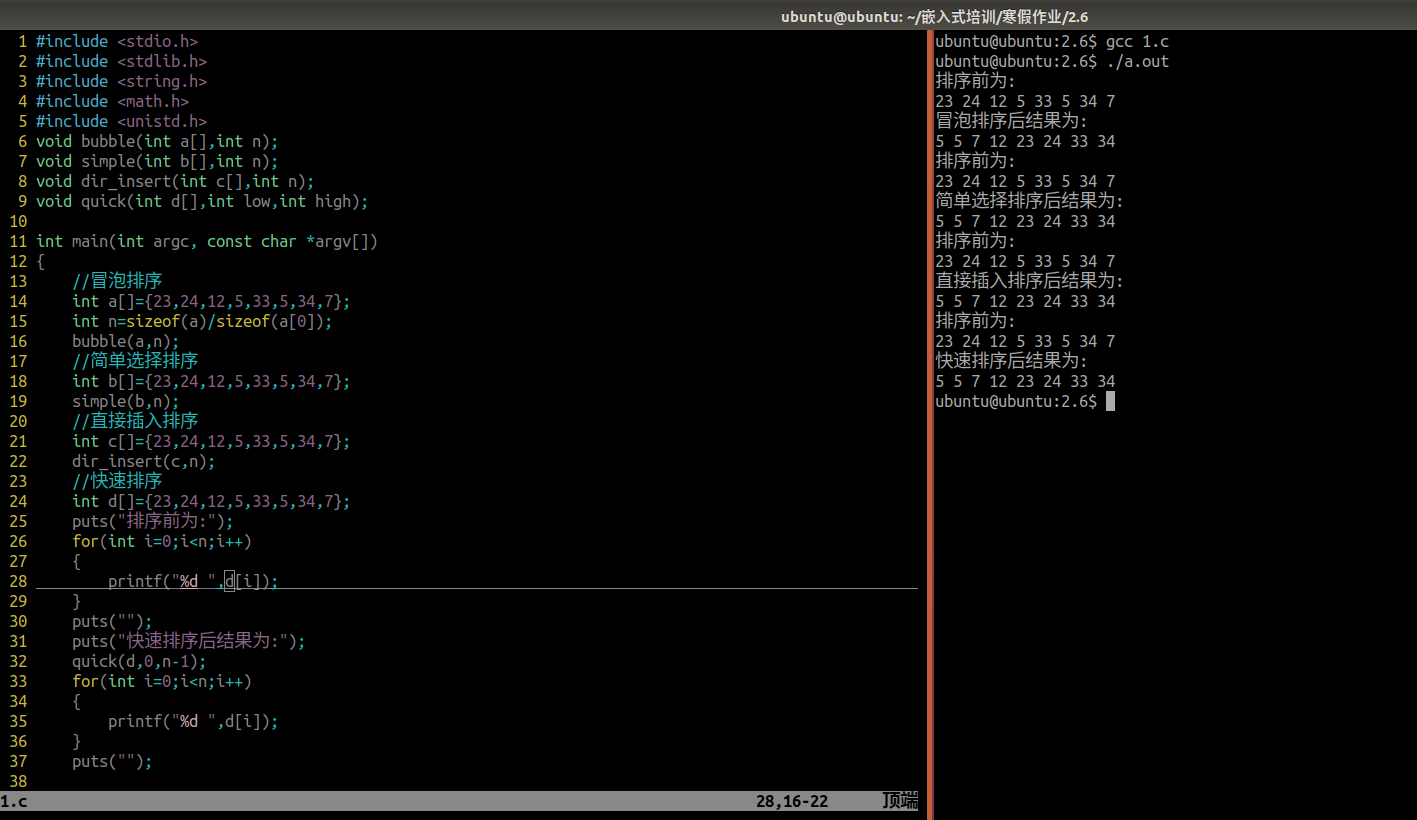
本文介绍: 函数式编程(Functional Programming)是把函数作为基本运算单元,函数可以作为变量,可以接收函数,还可以返回函数。函数也可以作为参数传递给其他函数。本文重点介绍使用Java Stream流排序器Comparator对List集合进行排序的技巧,包括复杂实体对象多字段升降序排序方法。定义一个Studen类,内部含有3个字段,调用调用sort方法可以动态实现对list集合多字段排序。进行链状流式的排序就需要搬出Stream sort方法进行排序,重写其中的Comparator。
Java 8 的 Stream 使用了函数式编程模式,它可以被用来对集合或数组进行链状流式的排序就需要搬出Stream sort方法进行排序,重写其中的Comparator。
本文重点介绍使用Java Stream流排序器Comparator对List集合进行排序的技巧,包括复杂实体对象多字段升降序排序方法。
函数式编程(Functional Programming)是把函数作为基本运算单元,函数可以作为变量,可以接收函数,还可以返回函数。对函数实例的变量引用,就像对字符串、Map 或任何其他对象的引用一样。函数也可以作为参数传递给其他函数。
利用Function把Java类中的get方法转换成Function形式, 用全局Map进行储存
static public Map<String, Function> functionMap = new HashMap<>();
<T> void init(T t) {
for (Method temp : t.getClass().getMethods()) {
String aaaa = temp.getName();
if (aaaa.startsWith("get")) {
System.out.println(aaaa);
String fieldName = aaaa.split("get")[1];
Function keyExtractosss11 = (a) -> {
try {
Object obj = temp.invoke(a, null);
return obj;
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (InvocationTargetException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
};
functionMap.put(lowerFirst(fieldName), keyExtractosss11);
}
}
}2 排序工具类方法
static public <T> List<T> sort(List<T> userList, List<String> fields) {
Function function = functionMap.get(fields.get(0));
Comparator<T> comparator = null;
for (int i = 0; i < fields.size(); i++) {
String temp = fields.get(i);
if (i == 0) {
comparator = Comparator.comparing(function);
} else {
Function function1 = functionMap.get(temp);
comparator = comparator.thenComparing(function1);
System.out.println(comparator);
}
}
userList = userList.stream().sorted(comparator).collect(Collectors.toList());
return userList;
}3 示例
定义一个Studen类,内部含有3个字段,调用调用sort方法可以动态实现对list集合多字段排序。
Method[] getMethods = Student.class.getMethods();
List<Student> userList = new ArrayList<>();
Student student3 = new Student();
student3.setId(1);
student3.setName("1");
student3.setAddress("3");
userList.add(student3);
Student student1 = new Student();
student1.setId(1);
student1.setName("1");
student1.setAddress("2");
userList.add(student1);
Student student2 = new Student();
student2.setId(1);
student2.setName("1");
student2.setAddress("1");
userList.add(student2);
List<String> fields = new ArrayList<>();
fields.add("id");
fields.add("name");
fields.add("address");
List<Student> userList111 = sort(userList, fields);
System.out.println(userList111);
for(Student temp:userList111){
System.out.println("排序"+temp.getId()+";"+temp.getName()+";"+temp.getAddress());
}原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/zhousenshan/article/details/134766687
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。
如若转载,请注明出处:http://www.7code.cn/show_38334.html
如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系代码007邮箱:suwngjj01@126.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
声明:本站所有文章,如无特殊说明或标注,均为本站原创发布。任何个人或组织,在未征得本站同意时,禁止复制、盗用、采集、发布本站内容到任何网站、书籍等各类媒体平台。如若本站内容侵犯了原著者的合法权益,可联系我们进行处理。