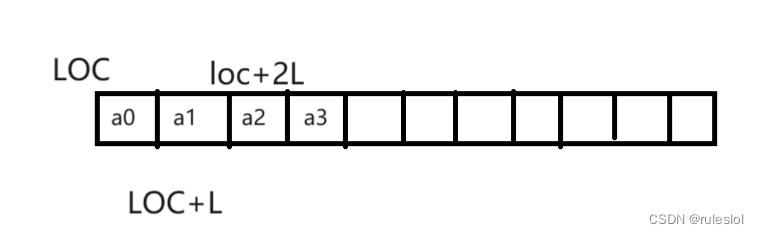
本文介绍: 给定一个排序数组和一个目标值,在数组中找到目标值,并返回其索引。如果目标值不存在于数组中,返回它将会被按顺序插入的位置。示例 1: 输入: nums = [1,3,5,6], target = 5 输出: 2示例 2: 输入: nums = [1,3,5,6], target = 2 输出: 1示例 3: 输入: nums = [1,3,5,6], target = 7 输出: 4解题思路:二分搜索。
搜索插入位置
给定一个排序数组和一个目标值,在数组中找到目标值,并返回其索引。如果目标值不存在于数组中,返回它将会被按顺序插入的位置。
有效数独
请你判断一个 9 x 9 的数独是否有效。只需要 根据以下规则 ,验证已经填入的数字是否有效即可。
数字 1-9 在每一行只能出现一次。
数字 1-9 在每一列只能出现一次。
数字 1-9 在每一个以粗实线分隔的 3×3 宫内只能出现一次。
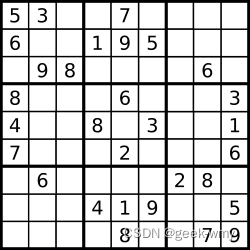
解数独
编写一个程序,通过填充空格来解决数独问题。
数独的解法需 遵循如下规则:
数字 1-9 在每一行只能出现一次。
数字 1-9 在每一列只能出现一次。
数字 1-9 在每一个以粗实线分隔的 3×3 宫内只能出现一次。
组合总和
给你一个 无重复元素 的整数数组 candidates 和一个目标整数 target ,找出 candidates 中可以使数字和为目标数 target 的 所有 不同组合 ,并以列表形式返回。你可以按 任意顺序 返回这些组合。
candidates 中的 同一个 数字可以 无限制重复被选取 。如果至少一个数字的被选数量不同,则两种组合是不同的。
组合总和2
声明:本站所有文章,如无特殊说明或标注,均为本站原创发布。任何个人或组织,在未征得本站同意时,禁止复制、盗用、采集、发布本站内容到任何网站、书籍等各类媒体平台。如若本站内容侵犯了原著者的合法权益,可联系我们进行处理。