本文介绍: 在编写自动化测试用例的时候经常会遇到需要编写流程性测试用例的场景,一般流程性的测试用例的测试步骤比较多,我们在测试用例中添加详细的步骤会提高测试用例的可阅读性。allure提供的装饰器@allure.step()是allure测试报告框架非常有用的功能,它能帮助我们在测试用例中对测试步骤进行详细的描述。
前言
在编写自动化测试用例的时候经常会遇到需要编写流程性测试用例的场景,一般流程性的测试用例的测试步骤比较多,我们在测试用例中添加详细的步骤会提高测试用例的可阅读性。
allure提供的装饰器@allure.step()是allure测试报告框架非常有用的功能,它能帮助我们在测试用例中对测试步骤进行详细的描述。
@allure.step的使用例子:
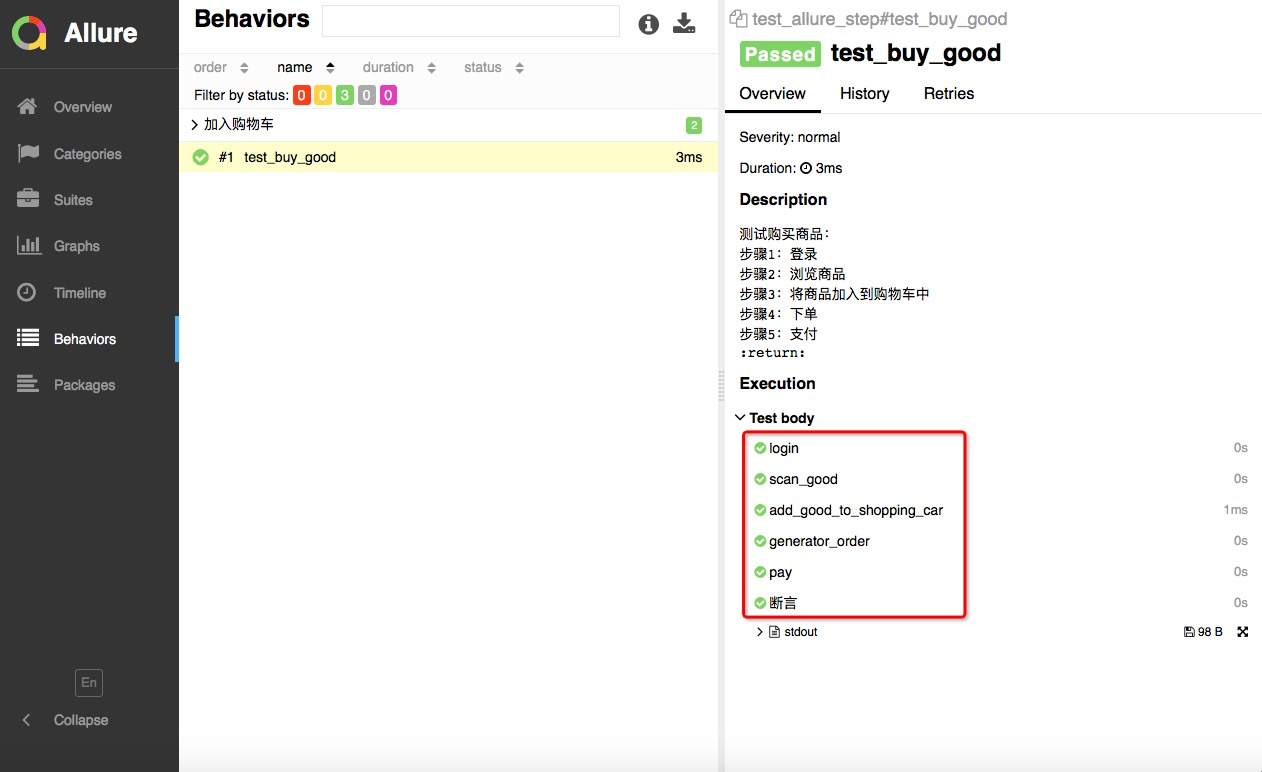
实现一个购物的场景:1.登录;2.浏览商品;3.将商品加入到购物车中;4.下单;5.支付订单;
执行命令:
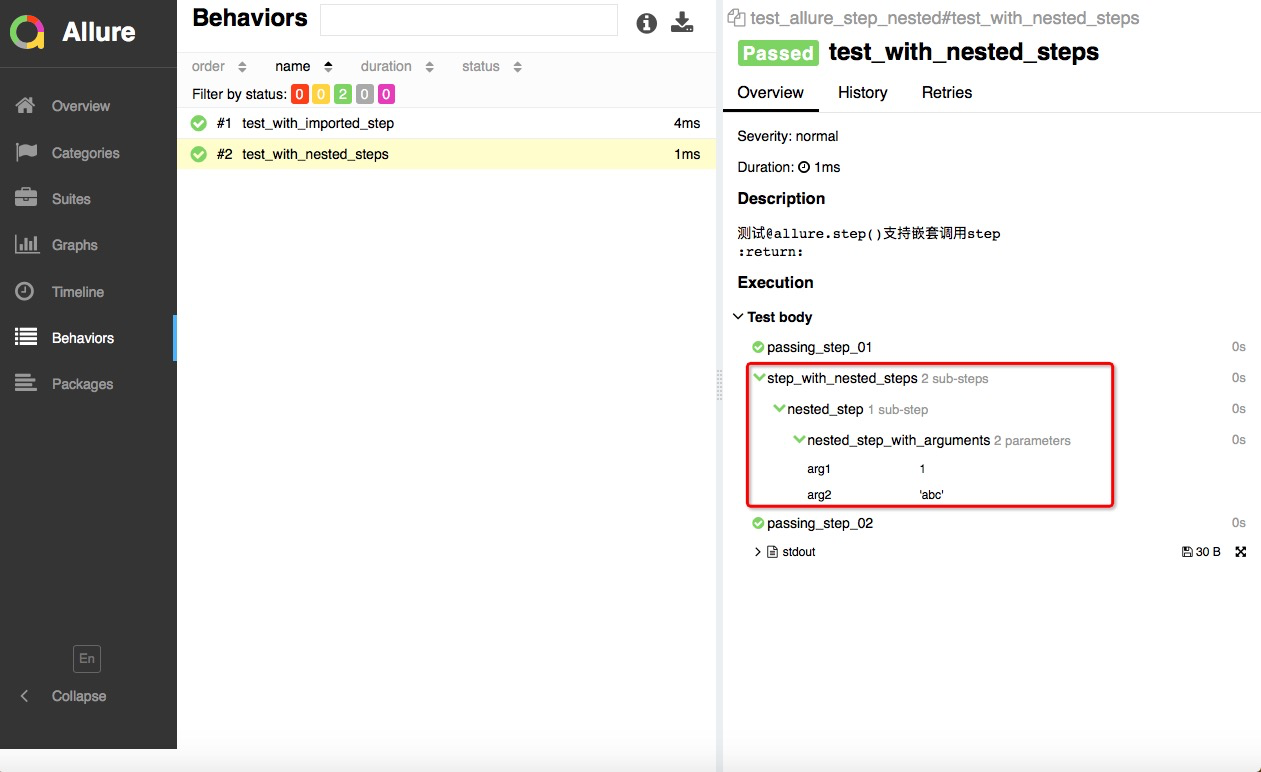
@allure.step支持嵌套,step中调用step
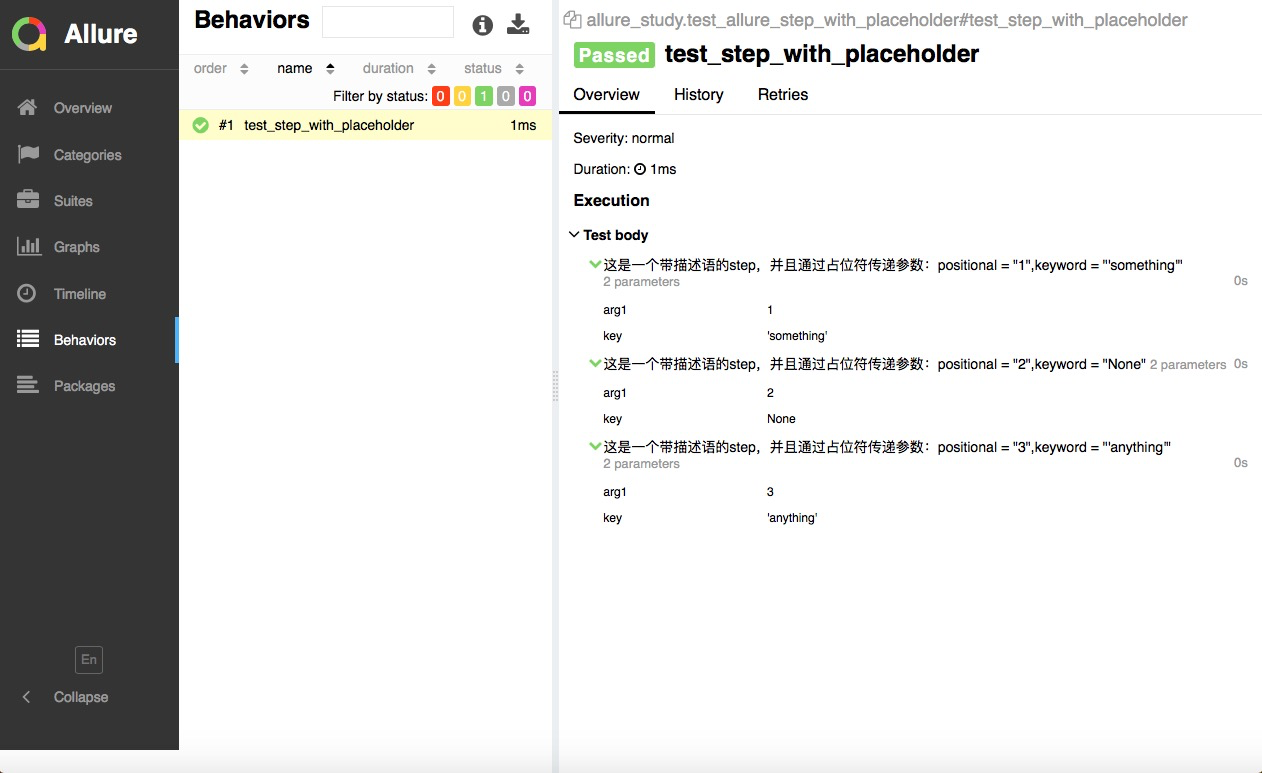
@allure.step支持添加描述且通过占位符传递参数
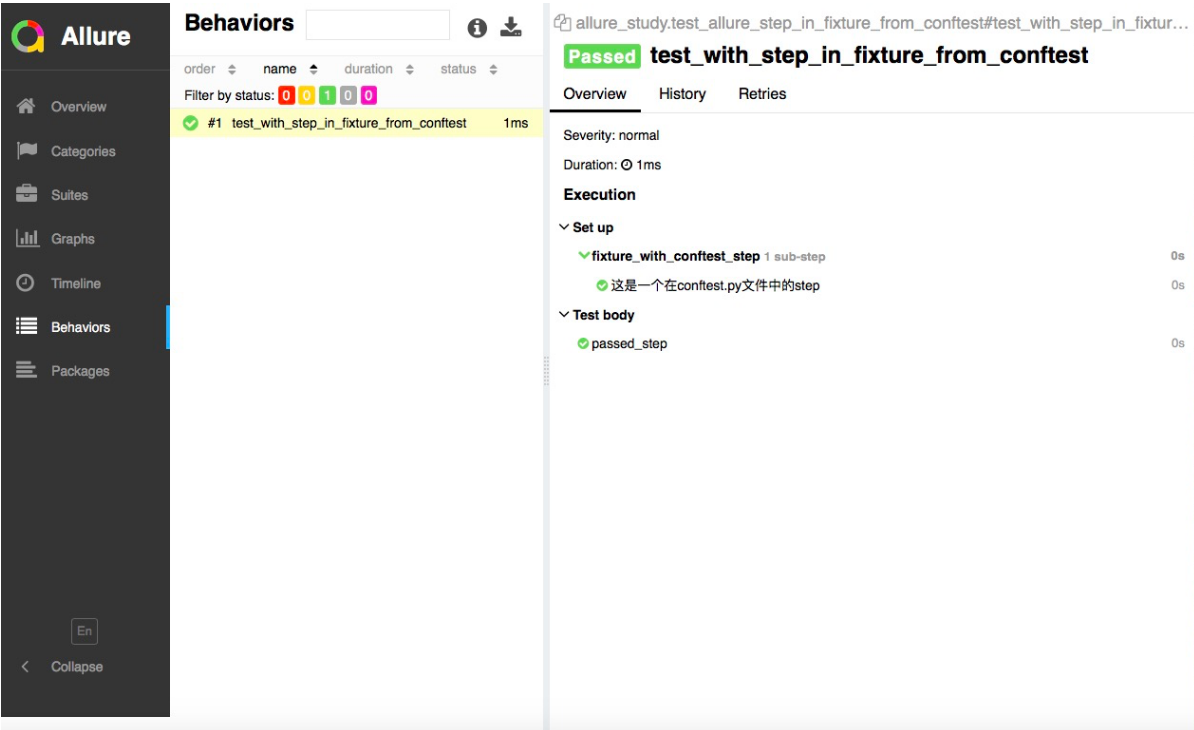
在conftest.py文件中定义@allure.step
声明:本站所有文章,如无特殊说明或标注,均为本站原创发布。任何个人或组织,在未征得本站同意时,禁止复制、盗用、采集、发布本站内容到任何网站、书籍等各类媒体平台。如若本站内容侵犯了原著者的合法权益,可联系我们进行处理。