一、SpringBoot热部署
热部署,就是在应用正在运行的时候升级软件,却不需要重新启动应用。即修改完代码后不需要重启项目即可生效。在SpringBoot中,可以使用DevTools工具实现热部署
1.1 添加DevTools依赖
首先我们需要在pom文件中引入devtools的依赖,如下:
<!– 热部署工具 –>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-devtools</artifactId>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
1.2 在idea中设置自动编译
点击 File–>Settings

如上图,勾选上。
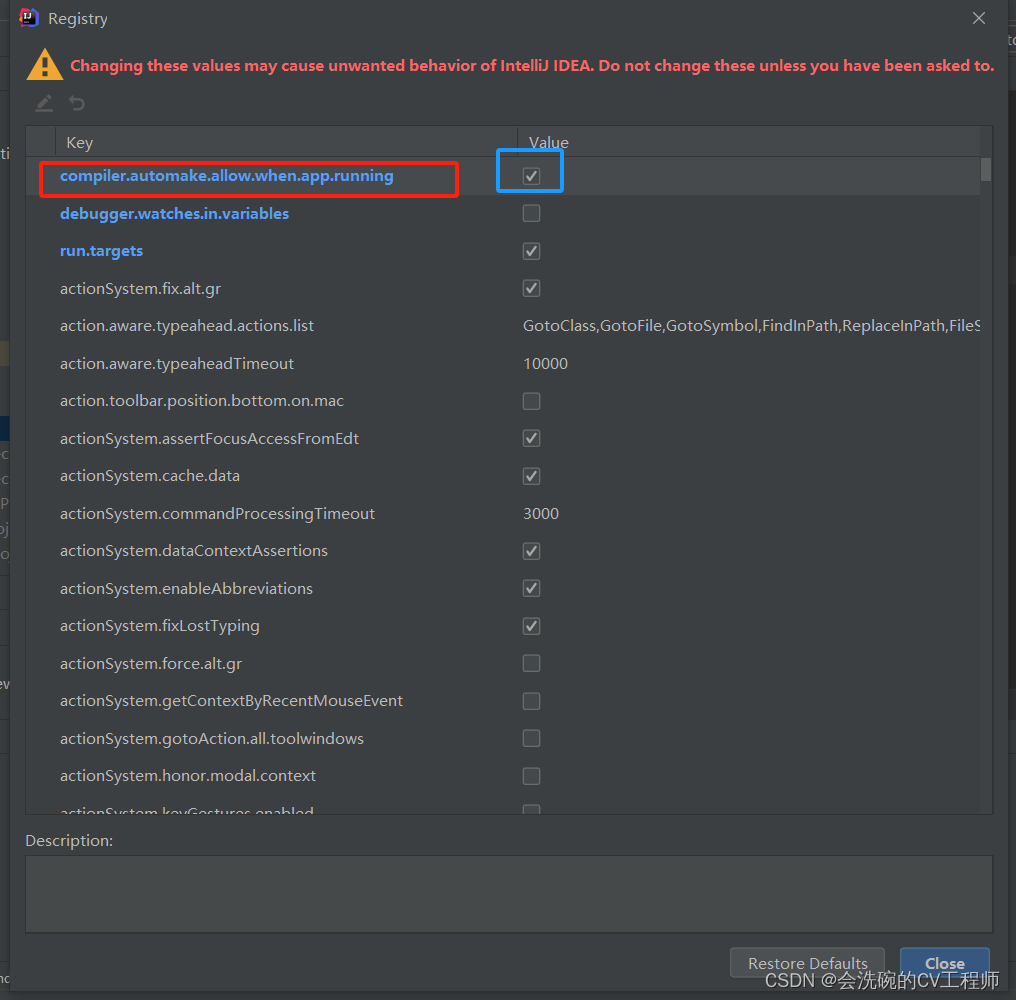
1.3 在Idea设置自动运行
快捷键 Ctrl+Shift+Alt+/ 后点击 Registry ,勾选complier.automake.allow.when.app.running
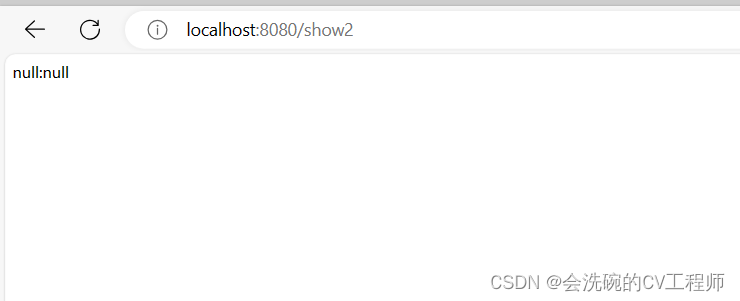
然后我们来测试一下,运行项目,然后在运行时往/show2路径修改输出看看是否不用重启项目也能发生改变。
修改之后,在控制台可以看到:重新运行了一下项目。

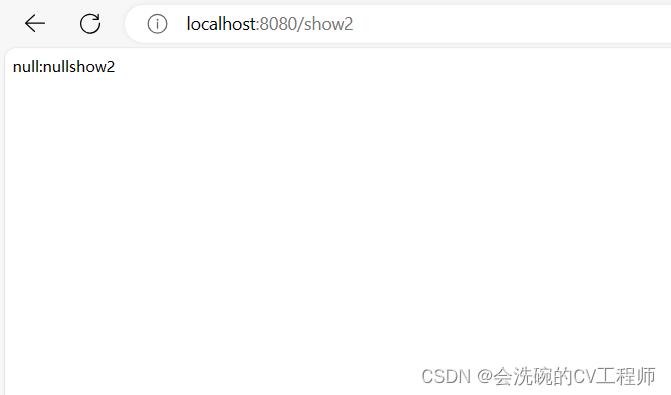
则说明我们的热部署生效
二、SpringBoot整合Mybatis
Spring整合MyBatis时需要进行大量配置,而SpringBoot整合MyBatis则可以简化很多配置:
2.1 准备数据
-- ----------------------------
-- Table structure for student
-- ----------------------------
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `student`;
CREATE TABLE `student` (
`id` int NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`name` varchar(255) CHARACTER SET utf8 COLLATE utf8_general_ci NULL DEFAULT NULL,
`sex` varchar(255) CHARACTER SET utf8 COLLATE utf8_general_ci NULL DEFAULT NULL,
`address` varchar(255) CHARACTER SET utf8 COLLATE utf8_general_ci NULL DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`) USING BTREE
) ENGINE = InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT = 3 CHARACTER SET = utf8 COLLATE = utf8_general_ci ROW_FORMAT = Dynamic;
-- ----------------------------
-- Records of student
-- ----------------------------
INSERT INTO `student` VALUES (1, 'LYL', '男', '广州');
INSERT INTO `student` VALUES (2, 'HQX', '女', '揭阳');添加pojo类:
package com.example.springbootdemo3.pojo;
public class Student {
private int id;
private String name;
private String sex;
private String address;public Student() {
}public Student(int id, String name, String sex, String address) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.sex = sex;
this.address = address;
}public int getId() {
return id;
}public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}public String getName() {
return name;
}public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}public String getSex() {
return sex;
}public void setSex(String sex) {
this.sex = sex;
}public String getAddress() {
return address;
}public void setAddress(String address) {
this.address = address;
}@Override
public String toString() {
return “Student [” +
“id=” + id +
“, name='” + name + ”’ +
“, sex='” + sex + ”’ +
“, address='” + address + ”’ +
” ]”;
}
}
2.2 添加相关依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis.spring.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis–spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>2.3.0</version>
</dependency><dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
2.3 在配置文件进行数据源配置
# 配置数据源
spring:
datasource:
driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
url: jdbc:mysql:///student?serverTimezone=UTC
username: root
password: 666666# mybatis配置
mybatis:
# 映射文件位置
mapper-locations: com/example/springbootdemo3/mapper/*Mapper.xml
# 别名
type-aliases-package: com.example.springbootdemo3.pojo#日志格式
logging:
pattern:
console: ‘%d{YYYY-MM-dd HH:mm:ss.SSS} %clr(%-5level) — [%-15thread]%cyan(%-50logger{50}):%msg%n’
2.4 编写Mapper接口和Mapper文件
然后新建一个mapper包,里面新建一个StudentMapper接口
package com.example.springbootdemo3.mapper;
import com.example.springbootdemo3.pojo.Student;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Mapper;
import java.util.List;
@Mapper
public interface StudentMapper {
List<Student> findAll();
}
这里还要在resources目录下新建一个与StudentMapper同级目录和同名的.xml文件

内容如下:
<?xml version=”1.0″ encoding=”UTF-8″?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper
PUBLIC “-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper3.0//EN”
“http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd”>
<mapper namespace=”com.example.springbootdemo3.mapper.StudentMapper”>
<select id=”findAll” resultType=”com.example.springbootdemo3.pojo.Student”>
select * from student;
</select>
</mapper>
2.5 测试
OK,从上面我们已经新建了一个查询所有的方法啊,现在在测试类我们看看能否成功获取数据库信息。测试类代码如下:
package com.example.springbootdemo3.mapper;
import com.example.springbootdemo3.pojo.Student;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import java.util.List;
@SpringBootTest
public class StudentMapperTest {
@Autowired
private StudentMapper studentMapper;
@Test
public void testFindAll(){
List<Student> students = studentMapper.findAll();
students.forEach(System.out::println);
}
}

原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_53317005/article/details/133198911
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。
如若转载,请注明出处:http://www.7code.cn/show_460.html
如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系代码007邮箱:suwngjj01@126.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!