字符序列(CharSequence)
1、相关接口
2、java.lang.String
2.1、概念:String 是个类 character strings 才是字符串
1、在 Java 语言中 直接使用 “” 引起来的多个字符就是 字符串 (character strings) 2、在 Java 源代码中 直接使用 “” 引起来的字符串 都是 java.lang.String 的实例 3、String 类 是个 不可变类 将来创建的 每个 String 实例 都是不可变的对象【Strings are constant】
[Java 8及之前] public final class String { private char[] value; // 使用 char 数组保存字符序列 }
[Java 9 之后] public final class String { private final byte[] value; // 使用 byte 数组保存字节序列 } 字节序列是字符序列根据某种编码转换而来
java.lang.String 类的主要字段 Java 11
public final class String implements Serializable, Comparable<String>, CharSequence {
private final byte[] value;
private final byte coder;
private int hash;
public String(String original) {
this.value = original.value;
this.coder = original.coder;
this.hash = original.hash;
}
}
String t = new String(“abc123”);
// 三个字段
byte[] value:0xA1B2C3 // 通过创建堆内存的 byte[] 来存取 "abc123" 数组变量value 存放数组的引用
byte coder:0
int hash:-1424436592
{97,98,99,49,50,51} // 假设地址为 0xA1B2C3
当我们在堆内存中 new String( s ) 这时调用 String 类的构造方法
public String(String original) {
this.value = original.value;
this.coder = original.coder;
this.hash = original.hash;
}
将 常量池的值复制一份过来
但 String t = new String(“abc123”);
如果 String s1 = “abc123”; 和 String s2 = “abc123”;
2.2、new String( s ) 的内存图
注但凡是出现了 “” 引起来的内容,这部分内容一定放在 String 常量池中
String t = new String(“abc123”);
创建一个 “abc123” 对应 String 实例 并添加到常量池中
在堆内存创建 String 实例 并将 “abc123” 的 value / hash / coder 拷贝到新创建的 String 实例中
3、String 的部分实例变量
4、String 内部的一些方法
- public String(byte[] bytes)
- public String(byte[] bytes, int offset, int length)
- public byte[] getBytes()
类变量
类方法
实例方法
1、char charAt(int) 获取指定索引的单个字符 2、int length() 获取字符串长度 3、public boolean contains(CharSequence s) 判断指定的字符序列是否存在于 当前字符串中 4、int indexOf(int ch) 查询指定字符 在当前字符串中 首次出现的位置 存在返回索引 不存在 -1 5、int indexOf(String s) 6、int lastIndexOf(int ch) 7、int lastIndexOf(String s)
package CharSequence;
/**
* 1、char charAt(int) 获取指定索引的单个字符
* 2、int length() 获取字符串长度
* 3、public boolean contains(CharSequence s) 判断指定的字符序列是否存在于 当前字符串中
* 4、int indexOf(int ch) 查询指定字符 在当前字符串中 首次出现的位置 存在返回索引 不存在 -1
* 5、int indexOf(String s)
* 6、int lastIndexOf(int ch)
* 7、int lastIndexOf(String s)
* */
public class StringTestA {
public static void main(String[] args) {
final String s = "今天天气好晴朗处处好风光好风光";
for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) {
char ch = s.charAt(i);
System.out.print(ch);
System.out.print(i<s.length() - 1 ? "," : "n");
}
// 因为 String 类实现了 CharSequence接口
CharSequence cs = "好风光"; // 所以用 CharSequence 类型的引用变量指向了 String 实例是可以的
boolean z = s.contains(cs);
System.out.println(z);
// 整个字符串中的每个字符的索引 一样 从 ”左“ 开始统计 与数组相同
int index = s.indexOf('天');// 获取 天 在变量 s 所指向的字符串首次出现的位置(索引)
System.out.println(index);
index = s.indexOf("好风光");
System.out.println(index); // 获取 好风光 在变量 s 所指向的字符串首次出现的位置(索引) 好的位置
int lastIndex = s.lastIndexOf('天'); // 获取 天 在变量 s 所指向的字符串最后出现的位置(索引)
System.out.println(lastIndex);
lastIndex = s.lastIndexOf("好风光"); // 获取 好风光 在变量 s 所指向的字符串最后出现的位置(索引) 还是好的位置
System.out.println(lastIndex);
}
}
int indexOf( String s , int from )
int lastIndexOf( int ch , int from )
int lastIndexOf( String s , int from )
package CharSequence;
/**
* 1、 int indexOf( int ch , int from )
* 从 当前字符串中 指定位置(from) 开始寻找 指定字符 ( ch ) 首次出现的位置,若存在即返回该索引,否则返回 -1
* 2、int indexOf( String s , int from )
* 从 当前字符串中 指定位置(from) 开始寻找 指定字符串 ( s ) 首次出现的位置,若存在即返回该索引,否则返回 -1
* 3、int lastIndexOf( int ch , int from )
* 从 当前字符串中 指定位置(from) 开始反向寻找 指定字符 ( ch ) 最后一次出现的位置,若存在即返回该索引,否则返回 -1
* 即获取在 from 处及其之前 ch 最后一次出现的位置是什么
* ( 反向寻找的顺序是 from 、from - 1 、from - 2 、........ )
* 4、int lastIndexOf( String s , int from )
* 从 当前字符串中 指定位置(from) 开始反向寻找 指定字符串 ( s ) 最后一次出现的位置,若存在即返回该索引,否则返回 -1
* 即获取在 from 处及其之前 s 最后一次出现的位置是什么
*/
public class StringTestB {
public static void main(String[] args) {
final String s = "http://www.ecut.edu.cn:8080/soft/java/beginner/string/test.html" ;
int index ;
int last ;
index = s.indexOf( '/' ) ;
last = s.lastIndexOf( '/' );
System.out.println( index + " , " + last );
System.out.println( "~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~" );
index = s.indexOf( '/' , 10 ); // 从 索引 10 开始 向后寻找 '/' 字符首次出现的位置
last = s.lastIndexOf( '/' , 37 ); // 从 索引 37 处开始 反向寻找 '/' 字符 最后一次出现的位置
System.out.println( index + " , " + last );
}
}
1、String concat(String) 将当前字符串 与 参数给定的字符串拼接起来 并返回一个新的 字符串 2、String toUpperCase() 3、String toLowerCase() 4、equalsIgnoreCase() 忽略大小写 5、a.contentEquals(b) 用于比较参数指定的 字符序列 是否与当前String
package CharSequence;
/**
* 1、String concat(String) 将当前字符串 与 参数给定的字符串拼接起来 并返回一个新的 字符串
* 2、String toUpperCase()
* 3、String toLowerCase()
* 4、equalsIgnoreCase() 忽略大小写
* 5、a.contentEquals(b) 用于比较参数指定的 字符序列 是否与当前String
*/
public class StringTestC {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s = "abc";
String x = s.concat("123");
System.out.println(s); // "abc"
System.out.println(x); // "abc123"
System.out.println("~~~~~~~~");
String t = s.toUpperCase();
final String a = "hello";
final String b = "Hello";
System.out.println(a.equals(b)); // String 重写后的 equals 比较大小
System.out.println(a.equalsIgnoreCase(b)); // true 忽略大小写
System.out.println(a.contentEquals(b)); // 区分大小写
System.out.println("~~~~~~~~~~~~");
// 用于比较两个字符串的 “大小”
System.out.println(a.compareTo(b)); //
// 相等 返回 0 否则 非0整数
System.out.println(a.compareToIgnoreCase(b)); //
}
}
1、int length() boolean isEmpty() 是否为空 value.length 是否为0 boolean isBlank() 用于判断 是否为空 (空白 仅仅包含了 空格 tab 等字符) String trim() 剔除首尾空白 不包括 中间的空白
package CharSequence;
/**
* 1、int length()
* boolean isEmpty() 是否为空 value.length 是否为0
* boolean isBlank() 用于判断 是否为空 (空白 仅仅包含了 空格 tab 等字符)
* String trim() 剔除首尾空白 不包括 中间的空白
* */
public class StringTestD {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s = ""; // 空串 不是 空格 不是 制表符(Tab) 也不是 null 和 /u0000
System.out.println(s);
System.out.println("length:" + s.length());
System.out.println("empty:" + s.isEmpty());
System.out.println("~~~~~~~~~~~~~~");
String t = " "; // 有空格 和 tab
System.out.println("length:" + s.length());
System.out.println("empty:" + s.isEmpty());
System.out.println("is blank" + t.isBlank());
String x = " ecut ";
String trim = x.trim(); // 删除首尾空白 不包括中间的空白返回新的 String 实例
System.out.println(x.length());
System.out.println(trim.length());
}
}
1、boolean startsWith(String) 对应的字符串 是否以 参数 字符串 开始
2、boolean endsWith(String) 对应的字符串 是否以 参数 字符串 结束
package CharSequence;
import java.util.Arrays;
/**
* 1、boolean startsWith(String) 对应的字符串 是否以 参数 字符串 开始
* 2、boolean endsWith(String) 对应的字符串 是否以 参数 字符串 结束
*
* */
public class StringTestE {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String path = "D:/java-beginner/char-sequence/StringHelper.java";
System.out.println(path.startsWith("D:")); // true path 对应的字符串 是否以 D: 开始
System.out.println(path.endsWith(".java")); // true
System.out.println("~~~~~~~~~~~");
System.out.println(path.startsWith("/",10)); // 从 10 开始 是否 是 以 / 开始的
char[] array = new char[10];
String str = "沧海一声笑滔滔两岸潮";
// 将 str 所指向的 String 实例中 所包含的字符串[5,10) 之间的字符 拷贝到 数组 array 中
str.getChars(5,10,array,5);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(array));
String substring = str.substring(5); // [5,length() - 1]
System.out.println(substring);
}
}
5、代码解释 String 实例的创建过程
package CharSequence;
/**
* 1、在 Java 语言中 直接使用 “” 引起来的多个字符就是 字符串 (character strings)
* 2、在 Java 源代码中 直接使用 “” 引起来的字符串 都是 java.lang.String 的实例
* 3、String 类 是个 不可变类 将来创建的 每个 String 实例 都是不可变的对象【Strings are constant】
*
* [Java 8及之前]
* public final class String {
* private char[] value; // 使用 char 数组保存字符序列
* }
*
* [Java 9 之后]
* public final class String {
* private final byte[] value; // 使用 byte 数组保存字节序列
* }
* 字节序列是字符序列根据某种编码转换而来
*
* */
public class StringTest2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 变量 s 直接引用了 字符串常量池中的 String实例
String s = "中国是世界上最伟大的国家,没有之一";
// 变量 t 引用的是在 堆内存重新创建的 String 实例
String t = new String("中国是世界上最伟大的国家,没有之一");
System.out.println(s == t);
System.out.println(s.equals(t)); // true String 重写后的 equals
}
}
6、编码 和 解码
编码(encode):将字符串按照某种字符集 转换成字节序列
例如:比如 “中国”UTF-8>{-28, -72, -83, -27, -101, -67}
解码( decode ):将字节序列按照某种字符集 转换成字符串
例如:比如 {-28, -72, -83, -27, -101, -67}UTF-8>“中国”
7、常用字符集
Unicode:万国码
-
范围是 U+0000-U+10FFFF
-
UTF-8
-
UTF-16
- UTF-16
- UTF-16BE
- UTF-16LE
-
UTF-32
- UTF-32
- UTF-32BE
- UTF-32LE
8、String 内部的 byte 数组编码格式
package CharSequence;
import java.nio.charset.Charset;
import java.util.Arrays;
/** 1、在 String 实例内部封装的 byte 数组中存储的字节序列是字符串 按照 UTF-16LE 编码 编码后的字节序列
* 2、在通过 String 实例的 getBytes 方法获取字节序列时,可以确定任意字符集
* 3、将一组字节序列构成 String 实例时 必须指定 将 字符串编码为字节序列时所采用的的字符串 才能保证不乱码
*
* */
public class StringTest9 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
final String s = "中国威武";
StringHelper.perspective(s);
System.out.println("~~~~~~~~~~~");
Charset utf = Charset.forName("UTF-16LE"); // 16 bit
byte[] bytes = s.getBytes(utf); // UTF-16
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(bytes));
byte[] array = {45, 78, -3, 86, 1, 90, 102, 107};
String x = new String(array,utf); //不使用 UTF-16LE 会乱码
System.out.println(x);
}
}
转自:https://www.cnblogs.com/zachyoung/p/13019479.html
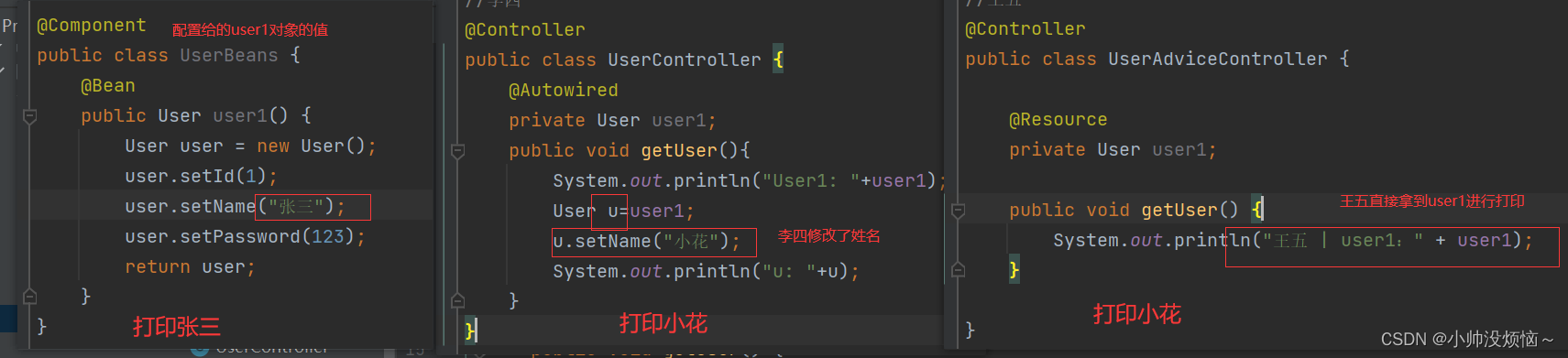
CharSequence是一个接口,表示char值的一个可读序列。此接口对许多不同种类的char序列提供统一的自读访问。此接口不修改该equals和hashCode方法的常规协定,因此,通常未定义比较实现 CharSequence 的两个对象的结果。他有几个实现类:CharBuffer、String、StringBuffer、StringBuilder。
-
CharSequence类是java.lang包下的一个接口,此接口对多种不同的对char访问的统一接口,像String、StringBuffer、StringBuilder类都是CharSequence的子接口;
-
CharSequence类和String类都可以定义字符串,但是String定义的字符串只能读,CharSequence定义的字符串是可读可写的;
-
CharSequence 接口中重新定义了 toString()方法,表示实现它的类必须重写该方法。
public String toString();
CharSequence是一个描述字符串结构的接口,在这个接口里面一般发现有三种常用的子类:
- String类
public final class String
extends Object
implements Serializable, Comparable<String>, CharSequence
- StringBuffer类
public final class StringBuffer
extends Object
implements Serializable, CharSequence
- StringBuilder类
public final class StringBuilder
extends Object
implements Serializable, CharSequence
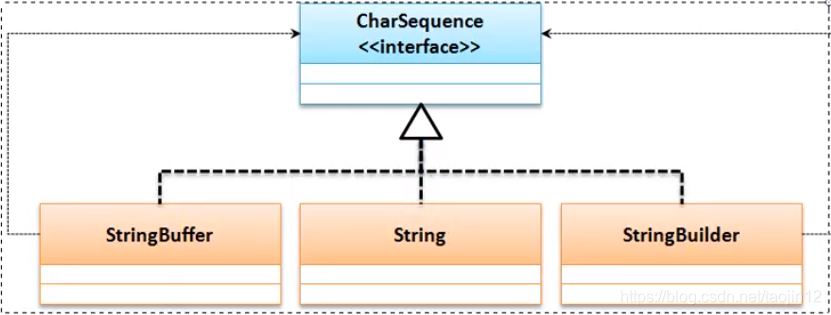
现在只要有字符串就可以为CharSequence实例化,CharSequence本身是一个接口,在该接口中有如下方法:
- 获取指定索引的字符:public char charAt?(int index);
- 获取字符串长度:public int length?();
- 截取部分字符串:public CharSequence subSequence?(int start, int end);
范例:字符串截取
public static void main(String[] args) {
CharSequence str = "hello world";
CharSequence sub = str.subSequence(6,11);
System.out.println(sub);
}
CharSequence描述的就是一个字符串,以后见到就不要感觉的陌生了。
原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_43842093/article/details/130277922
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。
如若转载,请注明出处:http://www.7code.cn/show_46156.html
如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系代码007邮箱:suwngjj01@126.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!



![[设计模式Java实现附plantuml源码~行为型]请求的链式处理——职责链模式](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/699aac3ed0c446d088772a0ed4c444ed.png)
![[设计模式Java实现附plantuml源码~结构型]处理多维度变化——桥接模式](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/8e811a73550d49e6a55c49a070a733e8.png)