本文介绍: 最快的版本(比其他版本快30至300倍)直接使用C语言编写,但需要数组作为输入(使用双精度类型),并且(可选地)通过将max_dist设置为欧几里得距离的上界来剪枝计算。这个其实和我们前面的warping_path是一样的。距离函数具有线性空间复杂度但二次时间复杂度。可以将ds转化成上三角矩阵的值,节省空间。输入为一个列表的列表。
1 介绍
2 DTW举例
2.1 绘制warping 路径
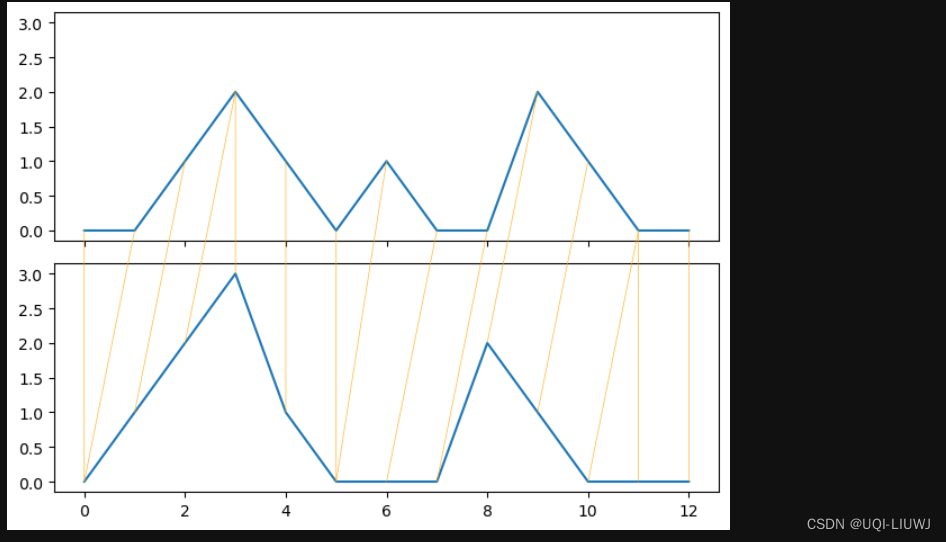
2.2 计算dtw距离
2.3 快速版本计算dtw距离
最快的版本(比其他版本快30至300倍)直接使用C语言编写,但需要数组作为输入(使用双精度类型),并且(可选地)通过将max_dist设置为欧几里得距离的上界来剪枝计算
2.4 降低DTW 复杂度
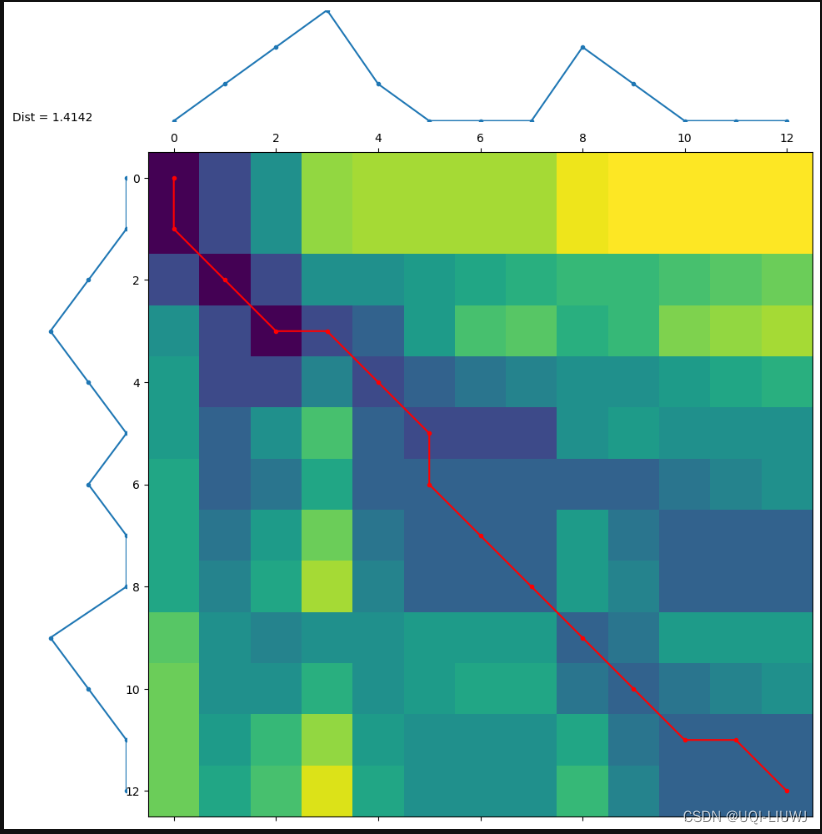
2.5 得到累计成本矩阵并绘制之
2.5.1 求最佳路径
2.5.2 可视化结果
2.6 多个时间序列的DTW
2.6.1 compact=True
声明:本站所有文章,如无特殊说明或标注,均为本站原创发布。任何个人或组织,在未征得本站同意时,禁止复制、盗用、采集、发布本站内容到任何网站、书籍等各类媒体平台。如若本站内容侵犯了原著者的合法权益,可联系我们进行处理。

![[Lucene]核心类和概念介绍](http://www.7code.cn/wp-content/uploads/2023/11/ee6748cbc735e6105405f8a984d954c804b93f34bc916-Z0IqTf_fw1200.png)