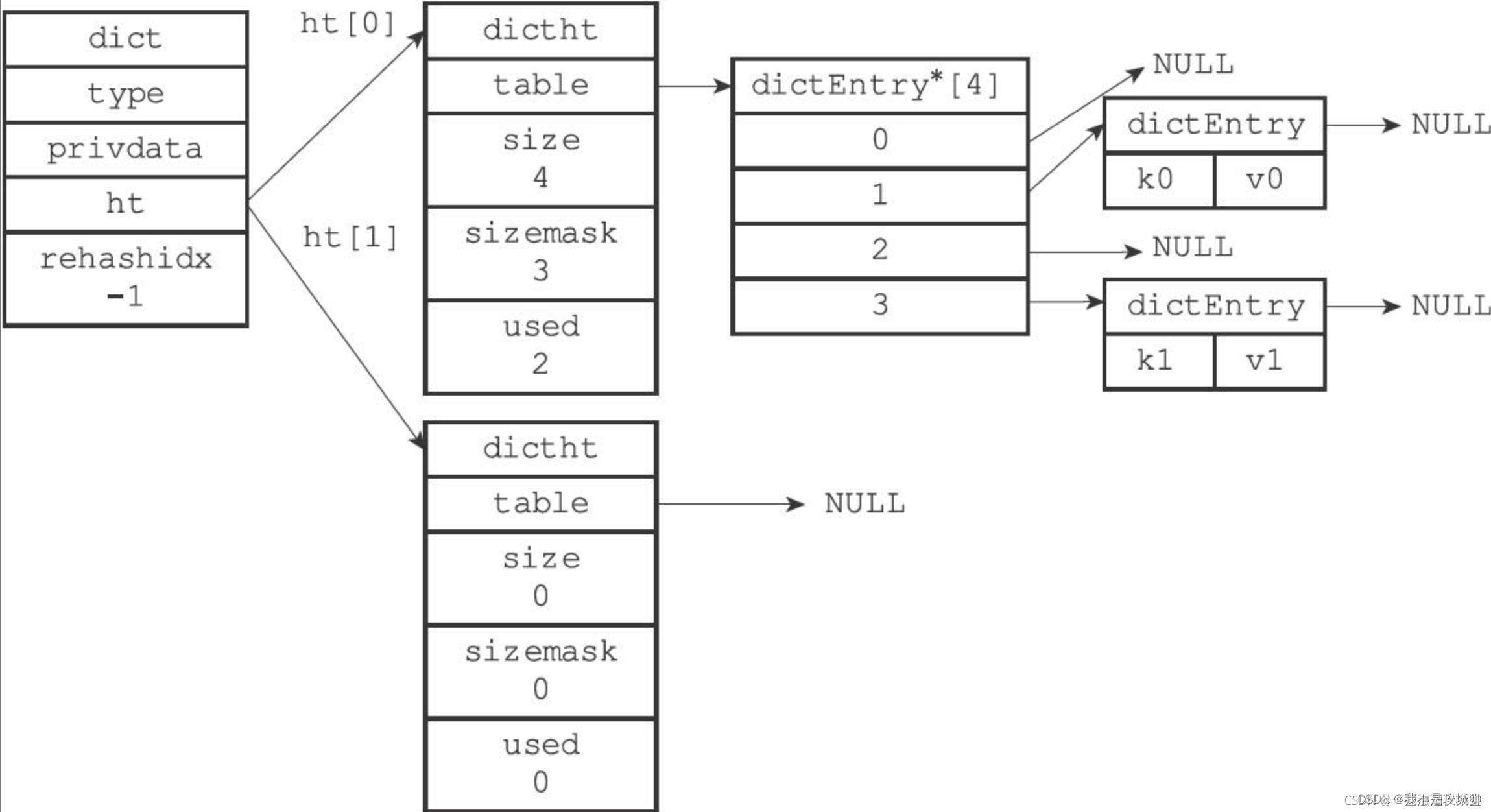
本文介绍: 2、当迁移完成后,ht[1]表供正常使用,ht[0]表指向空。如果还需要迁移,那么ht[0]表就会变成rehash那张表,ht[1]就会供正常使用。1、ht[0]供正常使用,ht[1]供rehash使用,从ht[0]迁移到ht[1]会从新计算hash位置,操作粒度是bucket级别。rehash是由ht[0]和ht[1]两个hashTable组成的,操作的粒度是hash表里面的bucket组成的。dictRelace:用来往 Hash 表中添加一个键值对,或者键值对存在时,修改键值对。
1、 整体数据结构
链式hash解决hash冲突、采用渐进式hash来完成扩容过程。
/*
* 哈希表节点
*/
typedef struct dictEntry {
// 键
void *key;
// 值
union {
void *val;
uint64_t u64;
int64_t s64;
} v;
// 指向下个哈希表节点,形成链表
struct dictEntry *next;
} dictEntry;
/*
* 字典类型特定函数
*/
typedef struct dictType {
// 计算哈希值的函数
unsigned int (*hashFunction)(const void *key);
// 复制键的函数
void *(*keyDup)(void *privdata, const void *key);
// 复制值的函数
void *(*valDup)(void *privdata, const void *obj);
// 对比键的函数
int (*keyCompare)(void *privdata, const void *key1, const void *key2);
// 销毁键的函数
void (*keyDestructor)(void *privdata, void *key);
// 销毁值的函数
void (*valDestructor)(void *privdata, void *obj);
} dictType;
/* This is our hash table structure. Every dictionary has two of this as we
* implement incremental rehashing, for the old to the new table. */
/*
* 哈希表
*
* 每个字典都使用两个哈希表,从而实现渐进式 rehash 。
*/
typedef struct dictht {
// 哈希表数组
dictEntry **table;
// 哈希表大小
unsigned long size;
// 哈希表大小掩码,用于计算索引值
// 总是等于 size - 1
unsigned long sizemask;
// 该哈希表已有节点的数量
unsigned long used;
} dictht;
/*
* 字典
*/
typedef struct dict {
// 类型特定函数
dictType *type;
// 私有数据
void *privdata;
// 哈希表:两个Hash表,里面存储的是键值对,交替使用,用于rehash操作
dictht ht[2];
// rehash 索引
// 当 rehash 不在进行时,值为 -1
int rehashidx; /* rehashing not in progress if rehashidx == -1 */
// 目前正在运行的安全迭代器的数量
int iterators; /* number of iterators currently running */
} dict;2、扩容函数
static int _dictExpandIfNeeded(dict *d)
dictRelace:用来往 Hash 表中添加一个键值对,或者键值对存在时,修改键值对。
dictAddorFind:间接调用 dictAddRaw。_dictExpandIfNeeded->_dictKeyIndex->dictAddRaw
static int _dictExpandIfNeeded(dict *d) 里面的代码片段截取
//扩容两个条件
// 1)字典已使用节点数趋近用完,并且没有开启aof和rdb两个操作
// 2)Hash表承载的元素个数已是当前大小的5倍
if (d->ht[0].used >= d->ht[0].size &&
(dict_can_resize ||
d->ht[0].used/d->ht[0].size > dict_force_resize_ratio))
{
// 新哈希表的大小至少是目前已使用节点数的两倍
// T = O(N)
return dictExpand(d, d->ht[0].used*2);
}
//以下代码可以发现,但凡开启rdb和aof两个操作,必定禁止rehash。
void dictEnableResize(void) {
dict_can_resize = 1;
}
void dictDisableResize(void) {
dict_can_resize = 0;
}
void updateDictResizePolicy(void) {
if (server.rdb_child_pid == -1 && server.aof_child_pid == -1)
dictEnableResize();
else
dictDisableResize();
}
3、rehash(渐进式hash过程)
rehash是由ht[0]和ht[1]两个hashTable组成的,操作的粒度是hash表里面的bucket组成的。
1、ht[0]供正常使用,ht[1]供rehash使用,从ht[0]迁移到ht[1]会从新计算hash位置,操作粒度是bucket级别。
2、当迁移完成后,ht[1]表供正常使用,ht[0]表指向空。如果还需要迁移,那么ht[0]表就会变成rehash那张表,ht[1]就会供正常使用。
3、迁移是一个渐进式过程,通过记录rehashidx来标记上一次执行的位置,这样的好处是可以避免一次性消耗巨大导致redis过慢,因为redis是一个单线程过程。
/* This function performs just a step of rehashing, and only if there are
* no safe iterators bound to our hash table. When we have iterators in the
* middle of a rehashing we can't mess with the two hash tables otherwise
* some element can be missed or duplicated.
*
* 在字典不存在安全迭代器的情况下,对字典进行单步 rehash 。
*
* 字典有安全迭代器的情况下不能进行 rehash ,
* 因为两种不同的迭代和修改操作可能会弄乱字典。
*
* This function is called by common lookup or update operations in the
* dictionary so that the hash table automatically migrates from H1 to H2
* while it is actively used.
*
* 这个函数被多个通用的查找、更新操作调用,
* 它可以让字典在被使用的同时进行 rehash 。
*
* T = O(1)
*/
static void _dictRehashStep(dict *d) {
if (d->iterators == 0) dictRehash(d,1);
}
/* Performs N steps of incremental rehashing. Returns 1 if there are still
* keys to move from the old to the new hash table, otherwise 0 is returned.
*
* 执行 N 步渐进式 rehash 。
*
* 返回 1 表示仍有键需要从 0 号哈希表移动到 1 号哈希表,
* 返回 0 则表示所有键都已经迁移完毕。
*
* Note that a rehashing step consists in moving a bucket (that may have more
* than one key as we use chaining) from the old to the new hash table.
*
* 注意,每步 rehash 都是以一个哈希表索引(桶)作为单位的,
* 一个桶里可能会有多个节点,
* 被 rehash 的桶里的所有节点都会被移动到新哈希表。
*
* T = O(N)
*/
int dictRehash(dict *d, int n) {
// 只可以在 rehash 进行中时执行
if (!dictIsRehashing(d)) return 0;
// 进行 N 步迁移
// T = O(N)
while(n--) {
dictEntry *de, *nextde;
/* Check if we already rehashed the whole table... */
// 如果 0 号哈希表为空,那么表示 rehash 执行完毕
// T = O(1)
if (d->ht[0].used == 0) {
// 释放 0 号哈希表
zfree(d->ht[0].table);
// 将原来的 1 号哈希表设置为新的 0 号哈希表
d->ht[0] = d->ht[1];
// 重置旧的 1 号哈希表
_dictReset(&d->ht[1]);
// 关闭 rehash 标识
d->rehashidx = -1;
// 返回 0 ,向调用者表示 rehash 已经完成
return 0;
}
/* Note that rehashidx can't overflow as we are sure there are more
* elements because ht[0].used != 0 */
// 确保 rehashidx 没有越界
assert(d->ht[0].size > (unsigned)d->rehashidx);
// 略过数组中为空的索引,找到下一个非空索引
while(d->ht[0].table[d->rehashidx] == NULL) d->rehashidx++;
// 指向该索引的链表表头节点
de = d->ht[0].table[d->rehashidx];
/* Move all the keys in this bucket from the old to the new hash HT */
// 将链表中的所有节点迁移到新哈希表
// T = O(1)
while(de) {
unsigned int h;
// 保存下个节点的指针
nextde = de->next;
/* Get the index in the new hash table */
// 计算新哈希表的哈希值,以及节点插入的索引位置
h = dictHashKey(d, de->key) & d->ht[1].sizemask;
// 插入节点到新哈希表
de->next = d->ht[1].table[h];
d->ht[1].table[h] = de;
// 更新计数器
d->ht[0].used--;
d->ht[1].used++;
// 继续处理下个节点
de = nextde;
}
// 将刚迁移完的哈希表索引的指针设为空
d->ht[0].table[d->rehashidx] = NULL;
// 更新 rehash 索引
d->rehashidx++;
}
return 1;
}原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/lyyCSDNBLOG/article/details/134755846
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。
如若转载,请注明出处:http://www.7code.cn/show_49713.html
如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系代码007邮箱:suwngjj01@126.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
声明:本站所有文章,如无特殊说明或标注,均为本站原创发布。任何个人或组织,在未征得本站同意时,禁止复制、盗用、采集、发布本站内容到任何网站、书籍等各类媒体平台。如若本站内容侵犯了原著者的合法权益,可联系我们进行处理。