1.SpringBoot
1.1springboot是什么
1.2springboot的优点
2.Springboot入门
2.1版本控制
2.2创建maven工程

2.3导入父工程依赖
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<version>2.7.14</version>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
</parent>2.4添加springboot依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>2.5创建主程序类
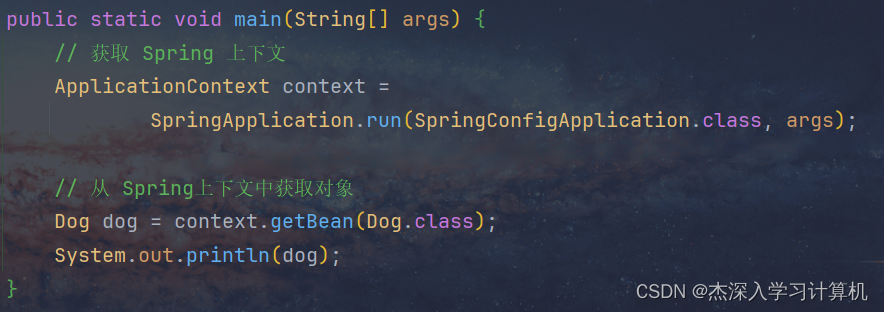
@SpringBootApplication
public class MainApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(MainApplication.class,args);
}
}2.6controller
@RestController
public class HelloController {
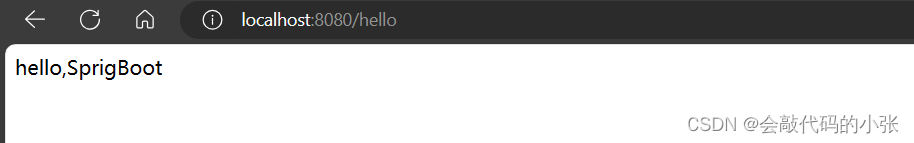
@RequestMapping("/hello")
public String hello(){
return "hello,SprigBoot";
}
}2.7测试结果
2.8总结
2.SpringBoot帮我们配置好了所有的web开发的常用场景
@SpringBootConfiguration、@EnableAutoConfiguration、ComponentScan
3.相关注解的使用
3.1.@Configuration+@Bean
注意:
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
public class MyConfig {
@Bean
public User user01() {
return new User("张三", "123456");
}
}3.2.@Import
@Import({User.class})
@Configuration
public class MyConfig {
@Bean
public User user01() {
return new User("张三", "123456");
}
} 
3.3.@ImprotResource
@ImportResource("classpath:bean.xml")
@Configuration
public class MyConfig {
@Bean
public User user01() {
return new User("张三", "123456");
}
}3.4.@ConfigurationProperties

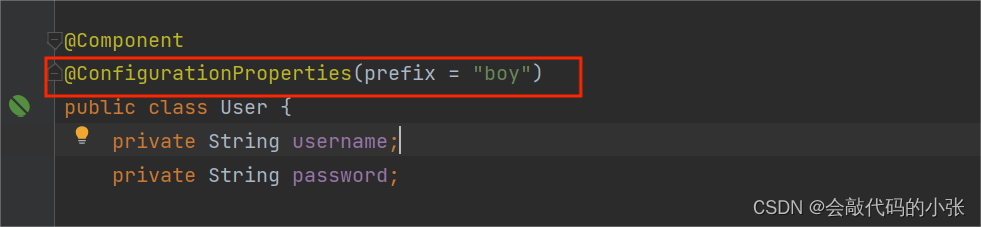
3.5.@EnableConfigurationProperties
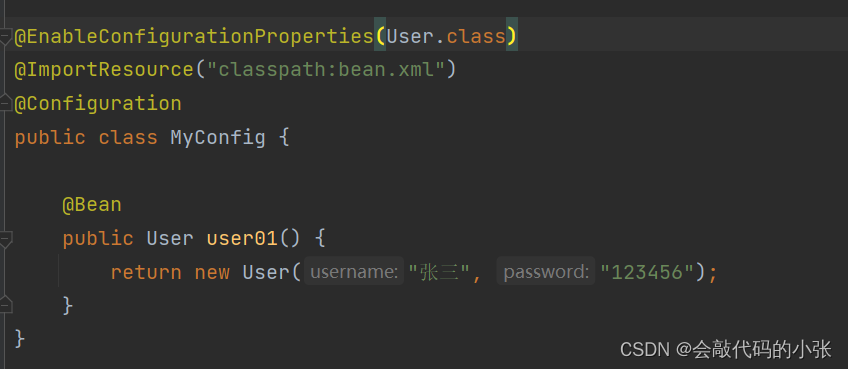
4.自动配置原理
@SpringBootApplication等价于:@SprignBootConfiguration+@EnableAutoConfiguration+@ComponentScan
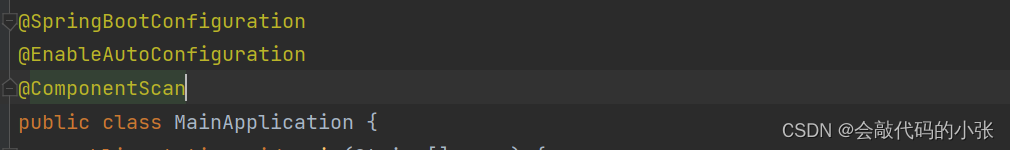
4.1@SpringBootConfiguration
@Configuration
@Indexed
public @interface SpringBootConfiguration {
@AliasFor(
annotation = Configuration.class
)
boolean proxyBeanMethods() default true;
}4.2@ComponentScan
4.3@EnableAutoConfiguration
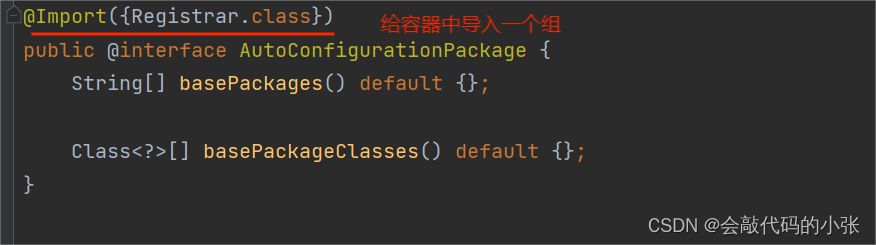
- 1.@Import:利用getAutoConfigurationEntry(annotationMetadata)給容器中批量导入一些组件.
- 2.调用List<String> configurations = getCandidateConfigurations(annotationMetadata, attributes)获取到所有导入到容器中的配置类.
- 3.利用工厂加载Map<String, List<String>> loadSpringFactories(@Nullable ClassLoader classLoader):得到所有的组件.
- 4.从META-INF/spring.factories位置来加载一个文件。默认扫描我们当前系统里面所有META-INF/spring.factories位置的文件spring–boot–autoconfigure-2.3.4.RELEASE.jar包里面也有META-INF/spring.factories.
@AutoConfigurationPackage
@Import({AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class})
public @interface EnableAutoConfiguration {
String ENABLED_OVERRIDE_PROPERTY = "spring.boot.enableautoconfiguration";
Class<?>[] exclude() default {};
String[] excludeName() default {};
}
4.4总结
5.简化开发
5.1Lombok
5.1.1导入依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
</dependency>5.1.2安装lombok插件
5.1.3实例
@Data
@ToString
@NoArgsConstructor
@AllArgsConstructor
public class User {
private String username;
private String password;
public User(String username) {
this.username = username;
}
}5.2dev–tools
spring为开发者提供了一个名为spring-boot-devtools的模块来使Spring Boot应用支持热部署。
5.2.1引入依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-devtools</artifactId>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>说明:ctrl+F9–重启,只要请求路径或类变化,无需重新部署。
5.3Spring Initailizr
5.3.1新建模块
5.3.2添加依赖项
5.3.3模块结构
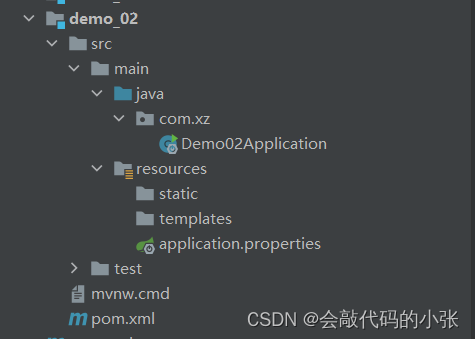
5.4yaml
YAML 是 “YAML Ain’t Markup Language” (YAML 不是一种标记语言)的递归缩写。在开发的这种语言时,YAML 的意思其实是: “Yet Another Markup Language” (仍是一种标记语言)。
5.4.1基本语法
5.4.2数据类型
#或
k:
k1: v1
k2: v2
k3: v3
#或
k:
– v1
– v2
– v3
5.4.3实例
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "user")//与配置文件进行绑定
@Component //放到容器中
@Data
@ToString
@NoArgsConstructor
@AllArgsConstructor
public class User {
private String username;
private String pwd;
private String sex;
private Integer age;
private Pet pet;
}@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "pet")
@Component
@Data
@ToString
@NoArgsConstructor
@AllArgsConstructor
public class Pet {
private String pName;
private Integer age;
}user:
username: jack
pwd: 123
sex: man
age: 18
loves:
- sql
- php
- java
pet:
pName: tom
age: 2
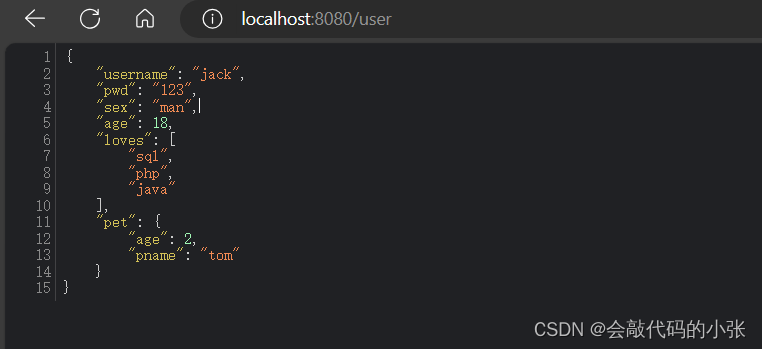
@RestController
public class HelloController {
@Autowired
private User user;
@RequestMapping("/user")
public User user(){
return user;
}
}结果:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-configuration-processor</artifactId>
</dependency>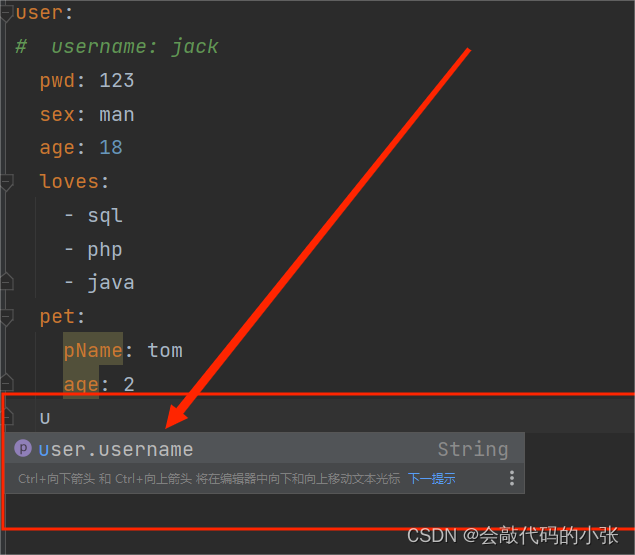
注意:
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<configuration>
<excludes>
<exclude>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
</exclude>
<exclude>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-configuration-processor</artifactId>
</exclude>
</excludes>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>6.Web开发
6.1静态资源访问
6.1.1.静态资源目录
6.1.2.静态资源访问前缀
6.1.3.欢迎页
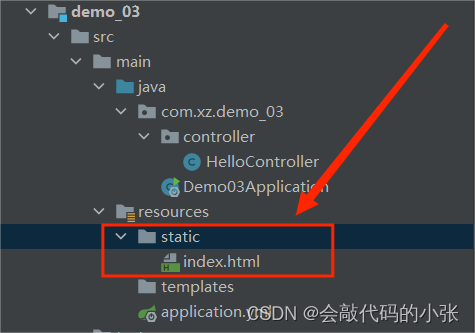
6.1.4静态配置原理
@AutoConfiguration(
after = {DispatcherServletAutoConfiguration.class, TaskExecutionAutoConfiguration.class, ValidationAutoConfiguration.class}
)
@ConditionalOnWebApplication(
type = Type.SERVLET
)
@ConditionalOnClass({Servlet.class, DispatcherServlet.class, WebMvcConfigurer.class})
@ConditionalOnMissingBean({WebMvcConfigurationSupport.class})
@AutoConfigureOrder(-2147483638)
public class WebMvcAutoConfiguration {
public static final String DEFAULT_PREFIX = "";
public static final String DEFAULT_SUFFIX = "";
public static final PathPatternParser pathPatternParser = new PathPatternParser();
private static final String SERVLET_LOCATION = "/";WebMvcAutoConfiguration生效给容器中配置了什么呢?
@Configuration( proxyBeanMethods = false ) @Import({WebMvcAutoConfiguration.EnableWebMvcConfiguration.class}) @EnableConfigurationProperties({WebMvcProperties.class, WebProperties.class}) @Order(0) public static class WebMvcAutoConfigurationAdapter implements WebMvcConfigurer, ServletContextAware { private static final Log logger = LogFactory.getLog(WebMvcConfigurer.class); private final Resources resourceProperties; private final WebMvcProperties mvcProperties; private final ListableBeanFactory beanFactory; private final ObjectProvider<HttpMessageConverters> messageConvertersProvider; private final ObjectProvider<DispatcherServletPath> dispatcherServletPath; private final ObjectProvider<ServletRegistrationBean<?>> servletRegistrations; private final WebMvcAutoConfiguration.ResourceHandlerRegistrationCustomizer resourceHandlerRegistrationCustomizer; private ServletContext servletContext;
配置类只有一个有参构造器:有参构造器所有参数的值都会从容器中找
public WebMvcAutoConfigurationAdapter(WebProperties webProperties, WebMvcProperties mvcProperties, ListableBeanFactory beanFactory, ObjectProvider<HttpMessageConverters> messageConvertersProvider, ObjectProvider<WebMvcAutoConfiguration.ResourceHandlerRegistrationCustomizer> resourceHandlerRegistrationCustomizerProvider, ObjectProvider<DispatcherServletPath> dispatcherServletPath, ObjectProvider<ServletRegistrationBean<?>> servletRegistrations) { this.resourceProperties = webProperties.getResources(); this.mvcProperties = mvcProperties; this.beanFactory = beanFactory; this.messageConvertersProvider = messageConvertersProvider; this.resourceHandlerRegistrationCustomizer = (WebMvcAutoConfiguration.ResourceHandlerRegistrationCustomizer)resourceHandlerRegistrationCustomizerProvider.getIfAvailable(); this.dispatcherServletPath = dispatcherServletPath; this.servletRegistrations = servletRegistrations; this.mvcProperties.checkConfiguration(); }
- ResourceProperties resourceProperties;获取和spring.resources绑定的所有的值的对象
- WebMvcProperties mvcProperties获取和spring.mvc绑定的所有的值的对象
- ListableBeanFactory beanFactory Spring的beanFactory
- HttpMessageConverters 找到所有的HttpMessageConverters6 ResourceHandlerRegistrationCustomizer 找到 资源处理器的自定义器
- DispatcherServletPath8 //ServletRegistrationBean给应用注册Servlet、FilterI
public void addResourceHandlers(ResourceHandlerRegistry registry) { if (!this.resourceProperties.isAddMappings()) { logger.debug("Default resource handling disabled"); } else { this.addResourceHandler(registry, "/webjars/**", "classpath:/META-INF/resources/webjars/"); this.addResourceHandler(registry, this.mvcProperties.getStaticPathPattern(), (registration) -> { registration.addResourceLocations(this.resourceProperties.getStaticLocations()); if (this.servletContext != null) { ServletContextResource resource = new ServletContextResource(this.servletContext, "/"); registration.addResourceLocations(new Resource[]{resource}); } }); } }spring: web: resources: add-mappings: false
6.1.5rest风格
默认不开起
@Bean @ConditionalOnMissingBean({HiddenHttpMethodFilter.class}) @ConditionalOnProperty( prefix = "spring.mvc.hiddenmethod.filter", name = {"enabled"} ) public OrderedHiddenHttpMethodFilter hiddenHttpMethodFilter() { return new OrderedHiddenHttpMethodFilter(); }spring: mvc: hiddenmethod: filter: enabled: true
- 表单提交会带上_method=PUT
- 请求过来被HiddenHttpMethodFilter拦截
- 请求是否正常,并且是POST
- 获取到_method的值。兼容以下请求:PUT,DELETE,PATCH
- 原生request (post),包装模式requesWrapper重写了getMethod方法,返回的是传入的值。
- 过滤器链放行的时候用wrapper,以后的方法调用getMethod是调用requesWrapper的。
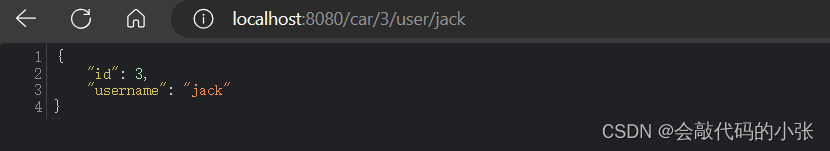
<a href="/car/3/user/jack">测试@PathVarable</a>
6.2普通参数与基本注解
6.2.1@PathVarable
<a href="/car/3/user/jack">测试@PathVarable</a>@GetMapping("/car/{id}/user/{username}")
public Map<String, Object> getCar(@PathVariable("id") Integer id, @PathVariable("username") String username,) {
Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("id", id);
map.put("username", username);
return map;
}
6.2.2@RequestBody
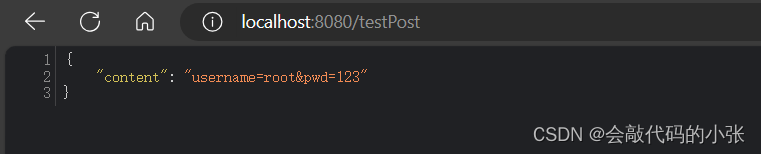
<form action="/testPost" method="post">
用户名:<input type="text" name="username"><br>
密码: <input type="text" name="pwd"><br>
<input type="submit" value="提交"><br>
</form>@PostMapping("/testPost")
public Map<String,Object> postMethod(@RequestBody String content){
Map<String,Object> map=new HashMap<>();
map.put("content",content);
return map;
}
6.2.3@RequestAttribute
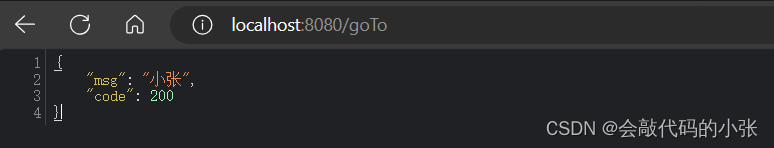
@RequestAttribute 获取请求域中的值
@GetMapping("/goTo")
public String goToPage(HttpServletRequest request) {
request.setAttribute("msg","小张");
request.setAttribute("code",200);
return "forward:/success";
}
@GetMapping("/success")
@ResponseBody
public Map<String, Object> success(@RequestAttribute("msg") String msg, @RequestAttribute("code") Integer code){
Map<String,Object> map=new HashMap<>();
map.put("msg",msg);
map.put("code",code);
return map;
}
6.2.4@MatrixVaribale
1.方式一:使用@Bean注解,给容器注入WebMvcConfigurer
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
public class WebConfig {
@Bean
public WebMvcConfigurer webMvcConfigurer() {
return new WebMvcConfigurer() {
@Override
public void configurePathMatch(PathMatchConfigurer configurer) {
UrlPathHelper urlPathHelper = new UrlPathHelper();
//设置为不移除分号后面的内容,矩阵变量生效
urlPathHelper.setRemoveSemicolonContent(false);
configurer.setUrlPathHelper(urlPathHelper);
}
};
}
}2.方式二:实现接口WebMvcConfigurer
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
public class WebConfig implements WebMvcConfigurer {
@Override
public void configurePathMatch(PathMatchConfigurer configurer) {
UrlPathHelper urlPathHelper = new UrlPathHelper();
//设置为不移除分号后面的内容,矩阵变量生效
urlPathHelper.setRemoveSemicolonContent(false);
configurer.setUrlPathHelper(urlPathHelper);
}
}3.测试情况一:无相同的请求属性
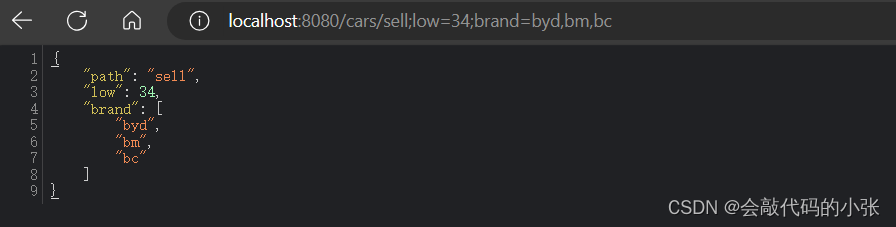
<a href="/cars/sell;low=34;brand=byd,bm,bc">测试@MatrixVarable</a> @ResponseBody
@GetMapping("/cars/{path}")
public Map<String, Object> carsSell(@MatrixVariable("low") Integer low,
@MatrixVariable("brand") List<String> brand,
@PathVariable("path") String path) {
Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("low", low);
map.put("brand", brand);
map.put("path", path);
return map;
}
3.测试情况二:相同的请求属性
<a href="/boss/1;id=10/2;id=20">测试@MatrixVarable=====情况二</a><br> @ResponseBody
@RequestMapping("/boss/{bossId}/{empId}")
public Map<String, Object> boss(@MatrixVariable(value = "id", pathVar = "bossId") Integer bossId,
@MatrixVariable(value = "id", pathVar = "empId") Integer empId) {
Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("bossId",bossId);
map.put("empId",empId);
return map;
}
6.3视图解析与模板引擎
6.3.1视图解析
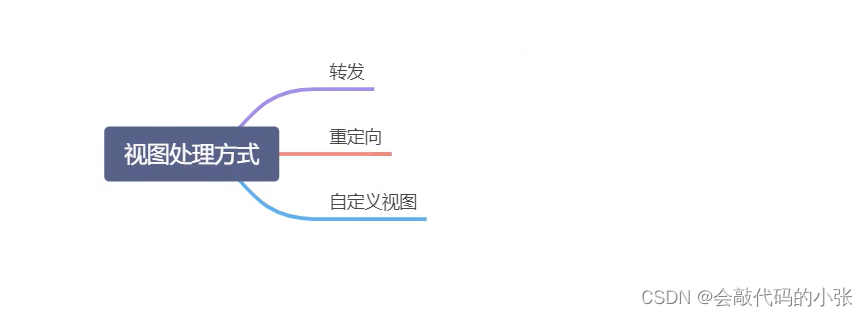
6.3.2Thymeleaf使用
1.引入依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf</artifactId>
</dependency>2.springboot已经自动配置好了thymeleaf
@AutoConfiguration(
after = {WebMvcAutoConfiguration.class, WebFluxAutoConfiguration.class}
)
@EnableConfigurationProperties({ThymeleafProperties.class})
@ConditionalOnClass({TemplateMode.class, SpringTemplateEngine.class})
@Import({ReactiveTemplateEngineConfiguration.class, DefaultTemplateEngineConfiguration.class})
public class ThymeleafAutoConfiguration {3.开发的页面存放位置
public class ThymeleafProperties {
private static final Charset DEFAULT_ENCODING;
public static final String DEFAULT_PREFIX = "classpath:/templates/";
public static final String DEFAULT_SUFFIX = ".html";4.实例
@Controller
public class ViewController {
@RequestMapping("/view")
public String view(Model model){
model.addAttribute("mgs","小张呀");
return "success";
}
}<html lang="en" xml:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" xml:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>success</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1 th:text="${mgs}"></h1>
</body>
</html>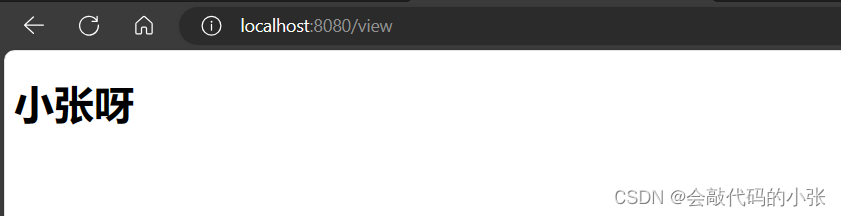
6.4拦截器
6.4.1.编写拦截器实现Handlerceptor接口
public class LoginInterceptor implements HandlerInterceptor {
/**
* 目标方法执行之前
*/
@Override
public boolean preHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler) throws Exception {
System.out.println("控制器方法执行前");
return false;
}
/**
* 目标方法执行以后
*/
@Override
public void postHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, ModelAndView modelAndView) throws Exception {
System.out.println("控制器方法执行后");
}
/**
* 页面渲染以后
*/
@Override
public void afterCompletion(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, Exception ex) throws Exception {
System.out.println("视图渲染后");
}
}
6.4.2.拦截器注册到容器中
@Configuration
public class WebConfig {
/**
* 拦截器
*/
@Bean
public WebMvcConfigurer addInterceptors() {
return new WebMvcConfigurer() {
@Override
public void addInterceptors(InterceptorRegistry registry) {
registry.addInterceptor(new LoginInterceptor())
.addPathPatterns("/**")//所有请求都会被拦截,包括静态资源
.excludePathPatterns("/");//放行的请求
}
};
}6.5文件上传
spring: servlet: multipart: max-file-size: 10MB max-request-size: 100MB
<form th:action="@{/form}" method="post" enctype="multipart/form-data">
头像:<input type="file" name="photo"><br>
<input type="submit" value="上传">
</form>@Controller
public class FormController {
@RequestMapping("/form")
public String form(@RequestPart("photo") MultipartFile photo) throws IOException {
if (!photo.isEmpty()) {
String filename = photo.getOriginalFilename();
photo.transferTo(new File("F:\" + filename));
}
return "form";
}
}6.6Web原生组件
2.使用@WebServlet注解
@WebServlet(urlPatterns = "/mv")
public class MyServlet extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
resp.getWriter().write("9999");
}
}@ServletComponentScan(basePackages = "com.xz.demo_03")
@SpringBootApplication
public class Demo03Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Demo03Application.class, args);
}
}7.数据访问
7.1数据源自动配置
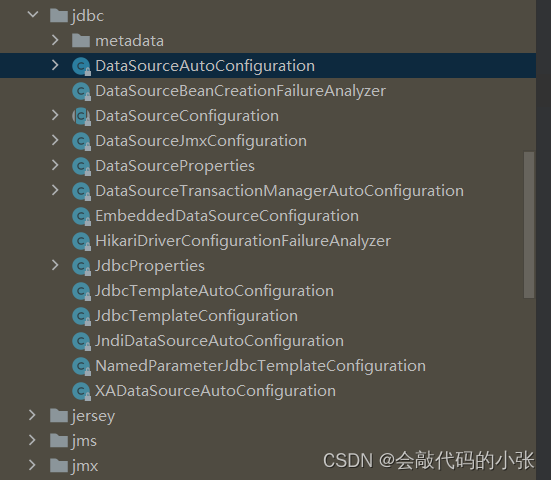
自动配置的类:
- DataSourceAutoConfiguration:数据源的自动配置
1.导入jdbc场景
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-jdbc</artifactId>
</dependency>
2.导入Mysql驱动
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>8.0.33</version>
</dependency>3.application.yml配置
spring:
datasource:
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mybatis
password: 123456
username: root
driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
7.2使用Druid数据源
1.引入依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>druid-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>1.2.16</version>
</dependency>2.自动配置分析
- 扩展配置项 spring.datasource.druid
- DruidSpringAopConfiguration.class,监控SpringBean的;配置项: spring.datasource.druid.aop–patterns
- DruidStatViewServletConfiguration.class,监控页的配置: spring.datasource.druid.stat-view–servlet;默认开启
- DruidWebStatFilterConfiguration.class, web监控配置; spring.datasource.druid.web-stat-filter;默认开启
- DruidFilterConfiguration.class))所有Druid自己filter的配置
3.application.yml
spring:
datasource:
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mybatis
password: 123456
username: root
driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
druid:
stat-view-servlet:
enabled: true
login-username: admin
login-password: admin
reset-enable: false
web-stat-filter:
enabled: true
url-pattern: /*
exclusions: '*.jsp,*.gif,*.jpg,*.png,*.css,*.ioc,/druid/*'
7.3整合mybatis
1.引入依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis.spring.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>2.3.1</version>
</dependency>2.配置模式
3.配置流程
#配置mybatis
mybatis:
# config-location: classpath:mybatis/mybatis-config.xml #全局配置文件位置,
#映射文件位置
mapper-locations: classpath:mybatis/mapper/*.xml
#指定 mybatis全局配置文件的相关配置
configuration:
#开启驼峰映射
map-underscore-to-camel-case: true4.实例
@Controller
@ResponseBody
public class UserController {
@Autowired
private UserService userService;
@GetMapping("/getAllUser")
public List<User> getUser(){
return userService.getAllUser();
}
}@Service
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService {
@Autowired
private UserMapper userMapper;
@Override
public List<User> getAllUser() {
return userMapper.getAllUser();
}
}
dao:
注意@Mapper注解
@Mapper
public interface UserMapper {
/**
* 查询所有用户
* @return
*/
List<User> getAllUser();
}映射文件:
<mapper namespace="com.xz.mapper.UserMapper">
<select id="getAllUser" resultType="com.xz.pojo.User">
select * from t_user
</select>
</mapper>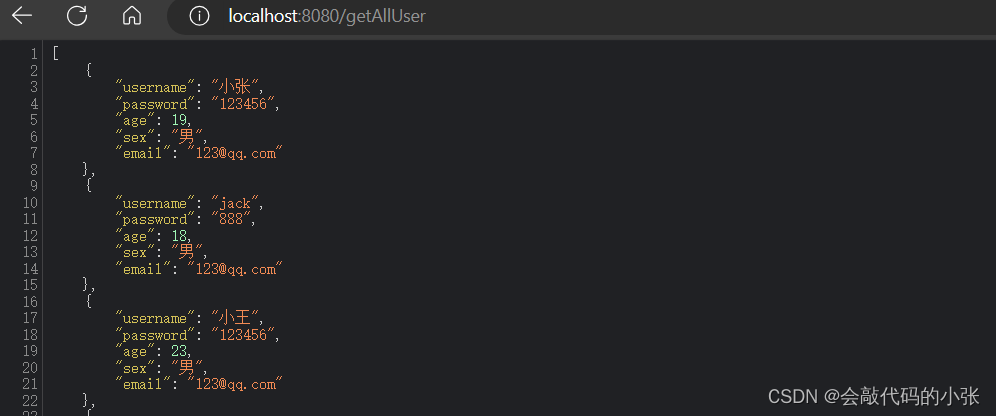
5.纯注解Mybatis
mapper:直接在mapper的方法使用查询类型的注解@Select即可
@Mapper
public interface EmpMapper {
@Select("select * from t_emp")
List<Emp> getAllEmp();
}6.总结
@MapperScan("com.xz.mapper")
@SpringBootApplication
public class Demo04Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Demo04Application.class, args);
}
}原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/dfdg345/article/details/134174496
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。
如若转载,请注明出处:http://www.7code.cn/show_50429.html
如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系代码007邮箱:suwngjj01@126.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!