🎁如果感觉还不错的话请给我点赞吧!🎁🎁

一、SSM整合Redis
1.1.pom配置
在Maven或Gradle的构建文件中添加Redis相关的依赖。
注意:resources的配置必须涵盖读取.properties结尾的文件

<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>org.example</groupId>
<artifactId>ssm2</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<packaging>war</packaging>
<name>ssm2 Maven Webapp</name>
<!-- FIXME change it to the project's website -->
<url>http://www.example.com</url>
<properties>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
<maven.compiler.source>1.8</maven.compiler.source>
<maven.compiler.target>1.8</maven.compiler.target>
<maven.compiler.plugin.version>3.7.0</maven.compiler.plugin.version>
<!--添加jar包依赖-->
<!--1.spring 5.0.2.RELEASE相关-->
<spring.version>5.0.2.RELEASE</spring.version>
<!--2.mybatis相关-->
<mybatis.version>3.4.5</mybatis.version>
<!--mysql-->
<mysql.version>5.1.44</mysql.version>
<!--pagehelper分页jar依赖-->
<pagehelper.version>5.1.2</pagehelper.version>
<!--mybatis与spring集成jar依赖-->
<mybatis.spring.version>1.3.1</mybatis.spring.version>
<!--3.dbcp2连接池相关 druid-->
<commons.dbcp2.version>2.1.1</commons.dbcp2.version>
<commons.pool2.version>2.4.3</commons.pool2.version>
<!--4.log日志相关-->
<log4j2.version>2.9.1</log4j2.version>
<!--5.其他-->
<junit.version>4.12</junit.version>
<servlet.version>4.0.0</servlet.version>
<lombok.version>1.18.2</lombok.version>
<ehcache.version>2.10.0</ehcache.version>
<slf4j-api.version>1.7.7</slf4j-api.version>
<redis.version>2.9.0</redis.version>
<redis.spring.version>1.7.1.RELEASE</redis.spring.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<!--1.spring相关-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
<version>${spring.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-orm</artifactId>
<version>${spring.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-tx</artifactId>
<version>${spring.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-aspects</artifactId>
<version>${spring.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-web</artifactId>
<version>${spring.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-test</artifactId>
<version>${spring.version}</version>
</dependency>
<!--2.mybatis相关-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis</artifactId>
<version>${mybatis.version}</version>
</dependency>
<!--mysql-->
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>${mysql.version}</version>
</dependency>
<!--pagehelper分页插件jar包依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.github.pagehelper</groupId>
<artifactId>pagehelper</artifactId>
<version>${pagehelper.version}</version>
</dependency>
<!--mybatis与spring集成jar包依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-spring</artifactId>
<version>${mybatis.spring.version}</version>
</dependency>
<!--3.dbcp2连接池相关-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.commons</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-dbcp2</artifactId>
<version>${commons.dbcp2.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.commons</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-pool2</artifactId>
<version>${commons.pool2.version}</version>
</dependency>
<!--4.log日志相关依赖-->
<!--核心log4j2jar包-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.logging.log4j</groupId>
<artifactId>log4j-core</artifactId>
<version>${log4j2.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.logging.log4j</groupId>
<artifactId>log4j-api</artifactId>
<version>${log4j2.version}</version>
</dependency>
<!--web工程需要包含log4j-web,非web工程不需要-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.logging.log4j</groupId>
<artifactId>log4j-web</artifactId>
<version>${log4j2.version}</version>
</dependency>
<!--5.其他-->
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>${junit.version}</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servlet</groupId>
<artifactId>javax.servlet-api</artifactId>
<version>${servlet.version}</version>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<version>${lombok.version}</version>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-webmvc</artifactId>
<version>${spring.version}</version>
</dependency>
<!-- jsp依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servlet.jsp</groupId>
<artifactId>javax.servlet.jsp-api</artifactId>
<version>2.3.3</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>jstl</groupId>
<artifactId>jstl</artifactId>
<version>1.2</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>taglibs</groupId>
<artifactId>standard</artifactId>
<version>1.1.2</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>commons-fileupload</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-fileupload</artifactId>
<version>1.3.3</version>
</dependency>
<!-- 做服务端参数校验 JSR303 的jar包依赖 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.hibernate</groupId>
<artifactId>hibernate-validator</artifactId>
<version>6.0.7.Final</version>
</dependency>
<!-- 用来SpringMVC支持json数据转换-->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.core</groupId>
<artifactId>jackson-databind</artifactId>
<version>2.9.3</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.core</groupId>
<artifactId>jackson-core</artifactId>
<version>2.9.3</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.core</groupId>
<artifactId>jackson-annotations</artifactId>
<version>2.9.3</version>
</dependency>
<!-- shiro相关依赖 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.shiro</groupId>
<artifactId>shiro-core</artifactId>
<version>1.3.2</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.shiro</groupId>
<artifactId>shiro-web</artifactId>
<version>1.3.2</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.shiro</groupId>
<artifactId>shiro-spring</artifactId>
<version>1.3.2</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>net.sf.ehcache</groupId>
<artifactId>ehcache</artifactId>
<version>${ehcache.version}</version>
</dependency>
<!-- slf4j核心包 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.slf4j</groupId>
<artifactId>slf4j-api</artifactId>
<version>${slf4j-api.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.slf4j</groupId>
<artifactId>jcl-over-slf4j</artifactId>
<version>${slf4j-api.version}</version>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
<!--用于与slf4j保持桥接 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.logging.log4j</groupId>
<artifactId>log4j-slf4j-impl</artifactId>
<version>${log4j2.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>redis.clients</groupId>
<artifactId>jedis</artifactId>
<version>${redis.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.data</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-data-redis</artifactId>
<version>${redis.spring.version}</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<finalName>ssm2</finalName>
<resources>
<!--解决mybatis-generator-maven-plugin运行时没有将XxxMapper.xml文件放入target文件夹的问题-->
<resource>
<directory>src/main/java</directory>
<includes>
<include>**/*.xml</include>
</includes>
</resource>
<!--解决mybatis-generator-maven-plugin运行时没有将jdbc.properites文件放入target文件夹的问题-->
<resource>
<directory>src/main/resources</directory>
<includes>
<include>*.properties</include>
<include>*.xml</include>
</includes>
</resource>
</resources>
<pluginManagement><!-- lock down plugins versions to avoid using Maven defaults (may be moved to parent pom) -->
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId>
<version>${maven.compiler.plugin.version}</version>
<configuration>
<source>${maven.compiler.source}</source>
<target>${maven.compiler.target}</target>
<encoding>${project.build.sourceEncoding}</encoding>
</configuration>
</plugin>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.mybatis.generator</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-generator-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<version>1.3.2</version>
<dependencies>
<!--使用Mybatis-generator插件不能使用太高版本的mysql驱动 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>${mysql.version}</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<configuration>
<overwrite>true</overwrite>
</configuration>
</plugin>
<plugin>
<artifactId>maven-clean-plugin</artifactId>
<version>3.1.0</version>
</plugin>
<!-- see http://maven.apache.org/ref/current/maven-core/default-bindings.html#Plugin_bindings_for_war_packaging -->
<plugin>
<artifactId>maven-resources-plugin</artifactId>
<version>3.0.2</version>
</plugin>
<plugin>
<artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId>
<version>3.8.0</version>
</plugin>
<plugin>
<artifactId>maven-surefire-plugin</artifactId>
<version>2.22.1</version>
</plugin>
<plugin>
<artifactId>maven-war-plugin</artifactId>
<version>3.2.2</version>
</plugin>
<plugin>
<artifactId>maven-install-plugin</artifactId>
<version>2.5.2</version>
</plugin>
<plugin>
<artifactId>maven-deploy-plugin</artifactId>
<version>2.8.2</version>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</pluginManagement>
</build>
</project>
1.2.配置文件spring-redis.xml
这个配置文件的作用主要用于配置数据源和连接工厂还有配置序列化的用途
redis.hostName=localhost
redis.port=6379
redis.password=123456
redis.timeout=10000
redis.maxIdle=300
redis.maxTotal=1000
redis.maxWaitMillis=1000
redis.minEvictableIdleTimeMillis=300000
redis.numTestsPerEvictionRun=1024
redis.timeBetweenEvictionRunsMillis=30000
redis.testOnBorrow=true
redis.testWhileIdle=true
redis.expiration=3600<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:cache="http://www.springframework.org/schema/cache"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/cache
http://www.springframework.org/schema/cache/spring-cache.xsd">
<!-- 1. 引入properties配置文件 -->
<!--<context:property-placeholder location="classpath:redis.properties" />-->
<!-- 2. redis连接池配置-->
<bean id="poolConfig" class="redis.clients.jedis.JedisPoolConfig">
<!--最大空闲数-->
<property name="maxIdle" value="${redis.maxIdle}"/>
<!--连接池的最大数据库连接数 -->
<property name="maxTotal" value="${redis.maxTotal}"/>
<!--最大建立连接等待时间-->
<property name="maxWaitMillis" value="${redis.maxWaitMillis}"/>
<!--逐出连接的最小空闲时间 默认1800000毫秒(30分钟)-->
<property name="minEvictableIdleTimeMillis" value="${redis.minEvictableIdleTimeMillis}"/>
<!--每次逐出检查时 逐出的最大数目 如果为负数就是 : 1/abs(n), 默认3-->
<property name="numTestsPerEvictionRun" value="${redis.numTestsPerEvictionRun}"/>
<!--逐出扫描的时间间隔(毫秒) 如果为负数,则不运行逐出线程, 默认-1-->
<property name="timeBetweenEvictionRunsMillis" value="${redis.timeBetweenEvictionRunsMillis}"/>
<!--是否在从池中取出连接前进行检验,如果检验失败,则从池中去除连接并尝试取出另一个-->
<property name="testOnBorrow" value="${redis.testOnBorrow}"/>
<!--在空闲时检查有效性, 默认false -->
<property name="testWhileIdle" value="${redis.testWhileIdle}"/>
</bean>
<!-- 3. redis连接工厂 -->
<bean id="connectionFactory" class="org.springframework.data.redis.connection.jedis.JedisConnectionFactory"
destroy-method="destroy">
<property name="poolConfig" ref="poolConfig"/>
<!--IP地址 -->
<property name="hostName" value="${redis.hostName}"/>
<!--端口号 -->
<property name="port" value="${redis.port}"/>
<!--如果Redis设置有密码 -->
<property name="password" value="${redis.password}"/>
<!--客户端超时时间单位是毫秒 -->
<property name="timeout" value="${redis.timeout}"/>
</bean>
<!-- 4. redis操作模板,使用该对象可以操作redis
hibernate课程中hibernatetemplete,相当于session,专门操作数据库。
-->
<bean id="redisTemplate" class="org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate">
<property name="connectionFactory" ref="connectionFactory"/>
<!--如果不配置Serializer,那么存储的时候缺省使用String,如果用User类型存储,那么会提示错误User can't cast to String!! -->
<property name="keySerializer">
<bean class="org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.StringRedisSerializer"/>
</property>
<property name="valueSerializer">
<bean class="org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.GenericJackson2JsonRedisSerializer"/>
</property>
<property name="hashKeySerializer">
<bean class="org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.StringRedisSerializer"/>
</property>
<property name="hashValueSerializer">
<bean class="org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.GenericJackson2JsonRedisSerializer"/>
</property>
<!--开启事务 -->
<property name="enableTransactionSupport" value="true"/>
</bean>
<!-- 5.配置缓存管理器 -->
<bean id="redisCacheManager" class="org.springframework.data.redis.cache.RedisCacheManager">
<constructor-arg name="redisOperations" ref="redisTemplate"/>
<!--redis缓存数据过期时间单位秒-->
<property name="defaultExpiration" value="${redis.expiration}"/>
<!--是否使用缓存前缀,与cachePrefix相关-->
<property name="usePrefix" value="true"/>
<!--配置缓存前缀名称-->
<property name="cachePrefix">
<bean class="org.springframework.data.redis.cache.DefaultRedisCachePrefix">
<constructor-arg index="0" value="-cache-"/>
</bean>
</property>
</bean>
<!--6.配置缓存生成键名的生成规则-->
<bean id="cacheKeyGenerator" class="com.zking.ssm.redis.CacheKeyGenerator"></bean>
<!--7.启用缓存注解功能-->
<cache:annotation-driven cache-manager="redisCacheManager" key-generator="cacheKeyGenerator"/>
</beans>1.3.修改applicationContext.xml
如果spring配置文件中需要配置两个及以上的properties文件则需要在applicationContext.xml中进行配置处理,否则会出现覆盖的情况。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd">
<!--1. 引入外部多文件方式 -->
<bean id="propertyConfigurer"
class="org.springframework.beans.factory.config.PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer">
<property name="systemPropertiesModeName" value="SYSTEM_PROPERTIES_MODE_OVERRIDE" />
<property name="ignoreResourceNotFound" value="true" />
<property name="locations">
<list>
<value>classpath:jdbc.properties</value>
<value>classpath:redis.properties</value>
</list>
</property>
</bean>
<!-- 随着后续学习,框架会越学越多,不能将所有的框架配置,放到同一个配制间,否者不便于管理 -->
<import resource="applicationContext-mybatis.xml"></import>
<import resource="spring-redis.xml"></import>
<import resource="applicationContext-shiro.xml"></import>
</beans>
1.4.配置redis的key生成策略
CacheKeyGenerator.java
package com.zking.ssm.redis;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.cache.interceptor.KeyGenerator;
import org.springframework.util.ClassUtils;
import java.lang.reflect.Array;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
@Slf4j
public class CacheKeyGenerator implements KeyGenerator {
// custom cache key
public static final int NO_PARAM_KEY = 0;
public static final int NULL_PARAM_KEY = 53;
@Override
public Object generate(Object target, Method method, Object... params) {
StringBuilder key = new StringBuilder();
key.append(target.getClass().getSimpleName()).append(".").append(method.getName()).append(":");
if (params.length == 0) {
key.append(NO_PARAM_KEY);
} else {
int count = 0;
for (Object param : params) {
if (0 != count) {//参数之间用,进行分隔
key.append(',');
}
if (param == null) {
key.append(NULL_PARAM_KEY);
} else if (ClassUtils.isPrimitiveArray(param.getClass())) {
int length = Array.getLength(param);
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
key.append(Array.get(param, i));
key.append(',');
}
} else if (ClassUtils.isPrimitiveOrWrapper(param.getClass()) || param instanceof String) {
key.append(param);
} else {//Java一定要重写hashCode和eqauls
key.append(param.hashCode());
}
count++;
}
}
String finalKey = key.toString();
// IEDA要安装lombok插件
log.debug("using cache key={}", finalKey);
return finalKey;
}
}
在代码中,通过
log.debug()语句输出了生成的缓存键,方便调试和查看。注意事项:
二、Redis的注解式开发及应用场景
2.1.什么是Redis注解式
Redis的注解式是指通过使用Spring框架提供的缓存注解,在业务代码中对Redis进行读写操作的方式。这种方式可以大大简化开发人员对缓存的操作,避免了手动编写Redis API代码的繁琐操作。
通过使用这些缓存注解,开发人员可以快速方便地实现对Redis的读写操作,同时也能够灵活地控制缓存的过期时间、缓存Key的生成规则等。
2.2.为什么使用Redis注解式
使用缓存注解的主要目的是为了提高应用程序的性能和响应速度。当应用程序从数据库或其他资源中获取数据时,如果这些数据在未来的请求中可能会被多次读取,那么使用缓存可以显著减少每个请求的响应时间。缓存将数据存储在内存中,因此可以快速读取,而不需要每次都访问数据库或其他资源。
使用缓存注解还可以减少对数据库或其他资源的负载,从而减少应用程序的资源消耗。当数据被缓存时,应用程序不需要每次都访问数据库或其他资源,从而减轻了这些资源的负载。
在使用缓存注解时,需要注意该注解的生命周期和缓存策略。缓存的生命周期指定了数据在缓存中存储的时间,而缓存策略则指定了何时应将数据从缓存中删除。通过选择适当的生命周期和缓存策略,可以优化缓存的性能和效率。
总之,使用缓存注解可以显著提高应用程序的性能和响应速度,减少对数据库或其他资源的负载,并优化缓存的性能和效率。
2.3.Redis注解式的应用
package com.zking.ssm.biz;
import com.zking.ssm.model.Clazz;
import com.zking.ssm.util.PageBean;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.CacheEvict;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.CachePut;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
public interface ClazzBiz {
@CacheEvict(value = "xx",key = "'cid:'+#cid",allEntries = true)
int deleteByPrimaryKey(Integer cid);
int insert(Clazz record);
int insertSelective(Clazz record);
// xx=cache-cid:1
// key的作用改变原有的key生成规则
// @Cacheable(value = "xx",key = "'cid:'+#cid")
@CachePut(value = "xx",key = "'cid:'+#cid",condition = "#cid > 6")
Clazz selectByPrimaryKey(Integer cid);
int updateByPrimaryKeySelective(Clazz record);
int updateByPrimaryKey(Clazz record);
List<Clazz> listPager(Clazz clazz, PageBean pageBean);
List<Map> listMapPager(Clazz clazz, PageBean pageBean);
}①Cacheable
使用该注解会将查询结果放入Redis中下一次同样的查询就不会走数据库,而是走Redis.
@Cacheable(value = "xx",key = "'cid:'+#cid",condition = "#cid > 6")
Clazz selectByPrimaryKey(Integer cid);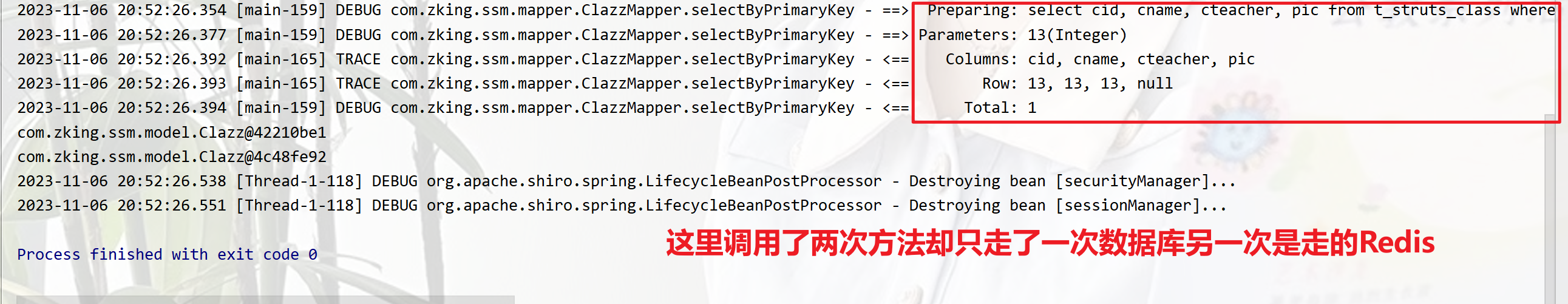
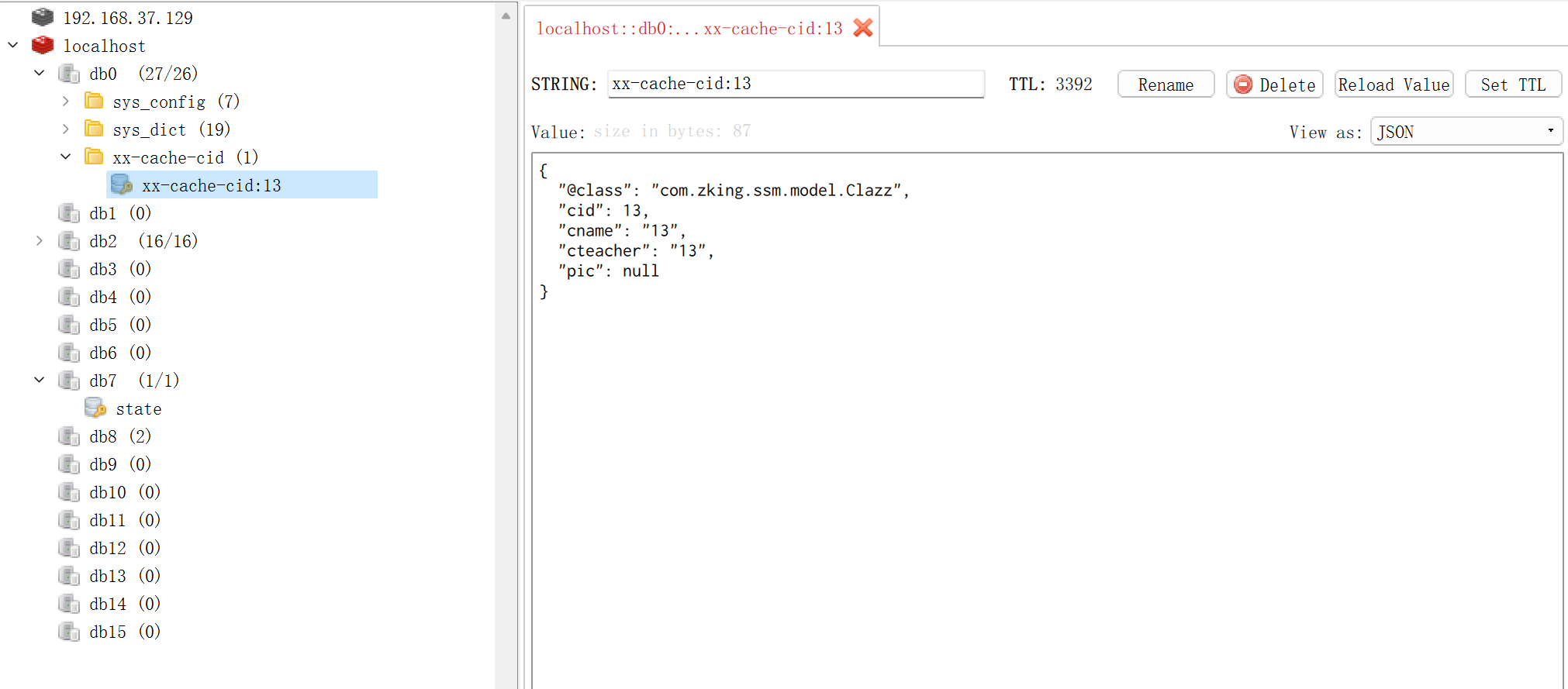
value:缓存位置的一段名称,不能为空
key:缓存的key,默认为空,表示使用方法的参数类型及参数值作为key,支持SpEL
condition:触发条件,满足条件就加入缓存,默认为空,表示全部都加入缓存,支持SpEL
②CachePut
该注解会将查询结果放入Redis中,类似于更新操作,即每次不管缓存中有没有结果,都从数据库查找结果,并将结果更新到缓存,并返回结果
@CachePut(value = "xx",key = "'cid:'+#cid")
Clazz selectByPrimaryKey(Integer cid);
value:缓存的名称,在 spring 配置文件中定义,必须指定至少一个
key:缓存的 key,可以为空,如果指定要按照 SpEL 表达式编写,如果不指定,则缺省按照方法的所有参数进行组合
condition:缓存的条件,可以为空,使用 SpEL 编写,返回 true 或者 false,只有为 true 才进行缓存
③CacheEvict
@CacheEvict(value = "xx",key = "'cid:'+#cid",allEntries = true)
int deleteByPrimaryKey(Integer cid);value:缓存位置的一段名称,不能为空
key:缓存的key,默认为空,表示使用方法的参数类型及参数值作为key,支持SpEL
condition:触发条件,满足条件就加入缓存,默认为空,表示全部都加入缓存,支持SpEL
allEntries:true表示清除value中的全部缓存,默认为false
2.4.CachePut和Cacheable的区别
Cacheable和CachePut都是Spring框架中用于缓存的注解,它们的主要区别是:
-
Cacheable用于获取缓存中的数据,如果缓存不存在,就会执行方法并将返回值放入缓存中;而CachePut用于更新缓存中的数据,它每次都会执行方法,并将返回值放入缓存中。
-
Cacheable和CachePut的key生成方式不同,Cacheable默认使用方法的参数作为key,可以通过key属性指定key的生成方式或使用SpEL表达式自定义key的生成方式;而CachePut默认使用Cacheable的默认key生成方式,也可以通过key属性指定key的生成方式。
-
Cacheable和CachePut的Sync属性也不同,Cacheable默认为false,即异步处理;而CachePut默认为true,即同步处理。
因此,Cacheable适用于需要从缓存中获取数据的场景,比如读取数据库中的数据;而CachePut适用于需要更新缓存中的数据的场景,比如写入数据库或者删除数据。
在具体应用场景中,可以根据实际需求选择合适的注解。例如,当我们需要查询用户信息时,可以使用Cacheable注解将查询结果缓存起来,下一次查询同样的信息时,直接从缓存中读取,避免了频繁访问数据库,提高了响应速度;当我们需要修改用户信息时,可以使用CachePut注解将修改后的信息更新缓存,保证缓存与数据库的一致性。
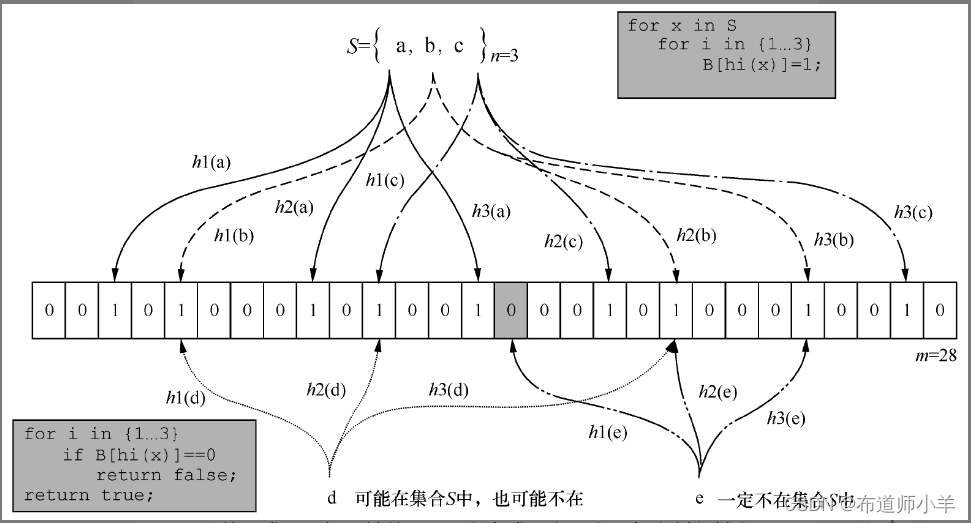
三、Redis中的击穿、穿透、雪崩的三种场景
3.1.缓存穿透
首先,我们来说说缓存穿透。什么是缓存穿透呢?缓存穿透问题在一定程度上与缓存命中率有关。如果我们的缓存设计的不合理,缓存的命中率非常低,那么,数据访问的绝大部分压力都会集中在后端数据库层面。
1.什么是缓存穿透?
如果在请求数据时,在缓存层和数据库层都没有找到符合条件的数据,也就是说,在缓存层和数据库层都没有命中数据,那么,这种情况就叫作缓存穿透。
我们可以使用下图来表示缓存穿透的现象。
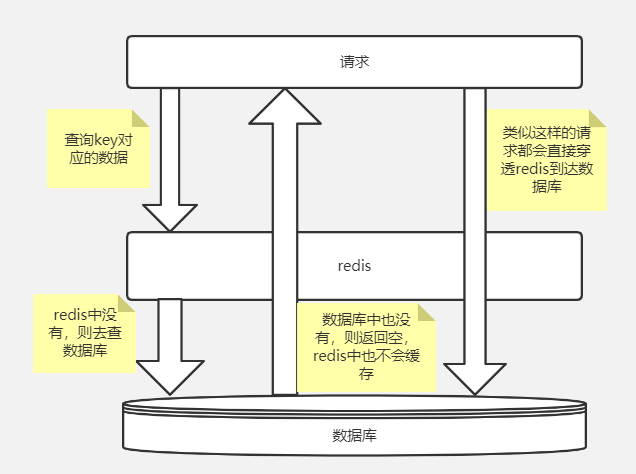
造成缓存穿透的主要原因就是:查询某个Key对应的数据,Redis缓存中没有相应的数据,则直接到数据库中查询。数据库中也不存在要查询的数据,则数据库会返回空,而Redis也不会缓存这个空结果。这就造成每次通过这样的Key去查询数据都会直接到数据库中查询,Redis不会缓存空结果。这就造成了缓存穿透的问题。
2.如何解决缓存穿透问题?
既然我们知道了造成缓存穿透的主要原因就是缓存中不存在相应的数据,直接到数据库查询,数据库返回空结果,缓存中不存储空结果。
那我们就自然而然的想到了第一种解决方案:就是把空对象缓存起来。当第一次从数据库中查询出来的结果为空时,我们就将这个空对象加载到缓存,并设置合理的过期时间,这样,就能够在一定程度上保障后端数据库的安全。
第二种解决缓存穿透问题的解决方案:就是使用布隆过滤器,布隆过滤器可以针对大数据量的、有规律的键值进行处理。一条记录是不是存在,本质上是一个Bool值,只需要使用 1bit 就可以存储。我们可以使用布隆过滤器将这种表示是、否等操作,压缩到一个数据结构中。比如,我们最熟悉的用户性别这种数据,就非常适合使用布隆过滤器来处理。
3.2.缓存击穿
如果我们为缓存中的大部分数据设置了相同的过期时间,则到了某一时刻,缓存中的数据就会批量过期。
1.什么是缓存击穿?
如果缓存中的数据在某个时刻批量过期,导致大部分用户的请求都会直接落在数据库上,这种现象就叫作缓存击穿。
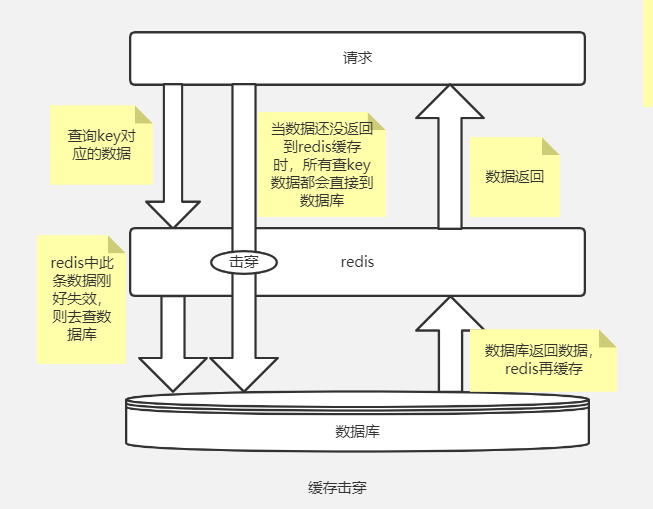
造成缓存击穿的主要原因就是:我们为缓存中的数据设置了过期时间。如果在某个时刻从数据库获取了大量的数据,并设置了相同的过期时间,这些缓存的数据就会在同一时刻失效,造成缓存击穿问题。
2.如何解决缓存击穿问题?
对于比较热点的数据,我们可以在缓存中设置这些数据永不过期;也可以在访问数据的时候,在缓存中更新这些数据的过期时间;如果是批量入库的缓存项,我们可以为这些缓存项分配比较合理的过期时间,避免同一时刻失效。
还有一种解决方案就是:使用分布式锁,保证对于每个Key同时只有一个线程去查询后端的服务,某个线程在查询后端服务的同时,其他线程没有获得分布式锁的权限,需要进行等待。不过在高并发场景下,这种解决方案对于分布式锁的访问压力比较大。
3.3.缓存雪崩
1.什么是缓存雪崩?
如果在某一时刻缓存集中失效,或者缓存系统出现故障,所有的并发流量就会直接到达数据库。数据存储层的调用量就会暴增,用不了多长时间,数据库就会被大流量压垮,这种级联式的服务故障,就叫作缓存雪崩。
我们可以用下图来表示缓存雪崩的现象。
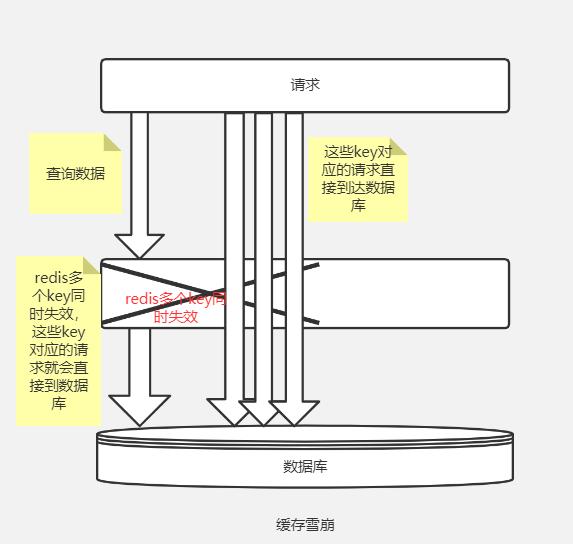
造成缓存雪崩的主要原因就是缓存集中失效,或者缓存服务发生故障,瞬间的大并发流量压垮了数据库。
2.如何解决缓存雪崩问题?
解决缓存雪崩问题最常用的一种方案就是保证Redis的高可用,将Redis缓存部署成高可用集群(必要时候做成异地多活),可以有效的防止缓存雪崩问题的发生。
为了缓解大并发流量,我们也可以使用限流降级的方式防止缓存雪崩。例如,在缓存失效后,通过加锁或者使用队列来控制读数据库写缓存的线程数量。具体点就是设置某些Key只允许一个线程查询数据和写缓存,其他线程等待。则能够有效的缓解大并发流量对数据库打来的巨大冲击。
另外,我们也可以通过数据预热的方式将可能大量访问的数据加载到缓存,在即将发生大并发访问的时候,提前手动触发加载不同的数据到缓存中,并为数据设置不同的过期时间,让缓存失效的时间点尽量均匀,不至于在同一时刻全部失效。

💖如果觉得有用的话还请点个赞吧 💖

原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_74318097/article/details/134252504
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。
如若转载,请注明出处:http://www.7code.cn/show_50459.html
如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系代码007邮箱:suwngjj01@126.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!