本文介绍: 对于一个序列,对应图上每条边都是起点在终点前面易知,如果存在环的话,就一定不存在拓扑序列所以,有向无环图又被称为拓扑图入度为0的点可以作为起点,所以,拓扑排序步骤如下:把所有入度为0的点入队。
DFS和BFS
- DFS,深度优先搜索,
- 数据结构:stack
- 空间:Oh
- 不具有最短性
- BFS,宽度优先搜索
- queue
- O2^h
- 具有最短性(当图的所有边权重都是相同的时,bfs搜到的一定是最短路,只有这时候才能用bfs求最短路,一般情况下都用最短路算法求最短路,最短路算法的时间复杂度比较高)
DFS搜索应用
n-皇后问题
将n个皇后放到n*n的棋盘上,使任意两个皇后不能在同一行,同一列,同一斜线上
解法一:
按照全排列方式解,一行一行的放,放的时候保证同一列,同一斜线都没有其他皇后(由于是按行放的,同一行一定没有其他皇后),放完标记这一列,这一斜线有皇后,直到把n行都放完,不断向前回溯,找新的放法
public class Main{
static final int N = 20;
static char[][]q = new char[N][N];
static boolean[]col = new boolean[N];
static boolean[]dg = new boolean[N];//斜线 y = x + b
static boolean[]udg = new boolean[N];//反斜线 y = -x + b
static int n;
static void dfs(int u) {
if(u == n) {
for(int i = 0;i < n;i++) {
for(int j = 0;j < n;j++) System.out.print(q[i][j]);
System.out.println();
}
System.out.println();
}else {
for(int i = 0;i < n;i++) {
if(!col[i] && !dg[u + i] && !udg[u - i + n]) {//这里udg +n是为了防止索引为负数
q[u][i] = 'Q';
col[i] = dg[u+i] = udg[u - i + n] = true;
dfs(u + 1);
col[i] = dg[u+i] = udg[u - i + n] = false;
q[u][i] = '.';
}
}
}
}
public static void main(String[]args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
n = sc.nextInt();
for(int i = 0;i < n;i++) {
Arrays.fill(q[i],'.');
}
dfs(0);
}
}
解法二:
一个格子一个格子枚举,每个格子对应两个分支,放或不放,同时记录当前放的皇后个数,如果枚举完最后一行,且放的皇后有n个的话,收获一个结果
public class Main{
static final int N = 20;
static char[][]g = new char[N][N];
static boolean[]row = new boolean[N];
static boolean[]col = new boolean[N];
static boolean[]dg = new boolean[N];
static boolean[]udg = new boolean[N];
static int n;
/**
* @param x 第几行
* @param y 第几列
* @param s 当前放了几个皇后
*/
static void dfs(int x,int y,int s) {
if(y == n) {
y = 0;
x++;
}
if(x == n) {
if(s == n) {
for(int i = 0;i < n;i++) {
for(int j = 0;j < n;j++) System.out.print(g[i][j]);
System.out.println();
}
System.out.println();
}
}else {
//不放皇后
dfs(x,y + 1,s);
//放皇后
if(!row[x] && !col[y] && !dg[x + y] && !udg[n + x - y]) {
g[x][y] = 'Q';
row[x] = col[y] = dg[x + y] = udg[x - y + n] = true;
dfs(x,y + 1,s + 1);
row[x] = col[y] = dg[x + y] = udg[x - y + n] = false;
g[x][y] = '.';
}
}
}
public static void main(String[]args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
n = sc.nextInt();
for(int i = 0;i < n;i++) {
Arrays.fill(g[i],'.');
}
dfs(0,0,0);
}
}
树和图的存储
**重边:**两个点之间有两条边
树是无环连通图
无向图就是一种特殊的有向图
模版:
//图的存储邻接表
int[]h = new int[N];
int[]e = new int[N];
int[]w = new int[N];//如果带权重
int[]ne = new int[N];
int idx;
void add(int a,int b,int c) {
e[idx] = b;
ne[idx] = h[a];
w[idx] = c;
h[a] = idx++;
}
//图的存储邻接矩阵
int[][]g = new int[N][N];
//存储a指向b
void add(int a,int b) {
g[a][b] = 1;
}
DFS遍历
可以算出来每个子树的大小
//使用邻接表存储树
public class Main{
static final int N = 100010;//节点数量
static final int M = N * 2;//n个节点的树最多有n - 1条边,因为是无向图,需要*2
static int[]h = new int[N];//指向第i个节点的第一条边
static int[]e = new int[M];//第idx条边的终点
static int[]ne = new int[M];//表示与第idx条边同起点的另一条边
static boolean[]st = new boolean[N];//某节点是否被访问过
static int idx;
//添加a指向b
static void add(int a,int b){
e[idx] = b;
ne[idx] = h[a];
h[a] = idx++;
}
//dfs遍历
static void dfs(int u) {
st[u] = true;
for(int i = h[u];i != -1;i = ne[i]) {
int j = e[i];
if(!st[j]) dfs(j);
}
}
public static void main(String[]args) {
Arrays.fill(h,-1);
}
}
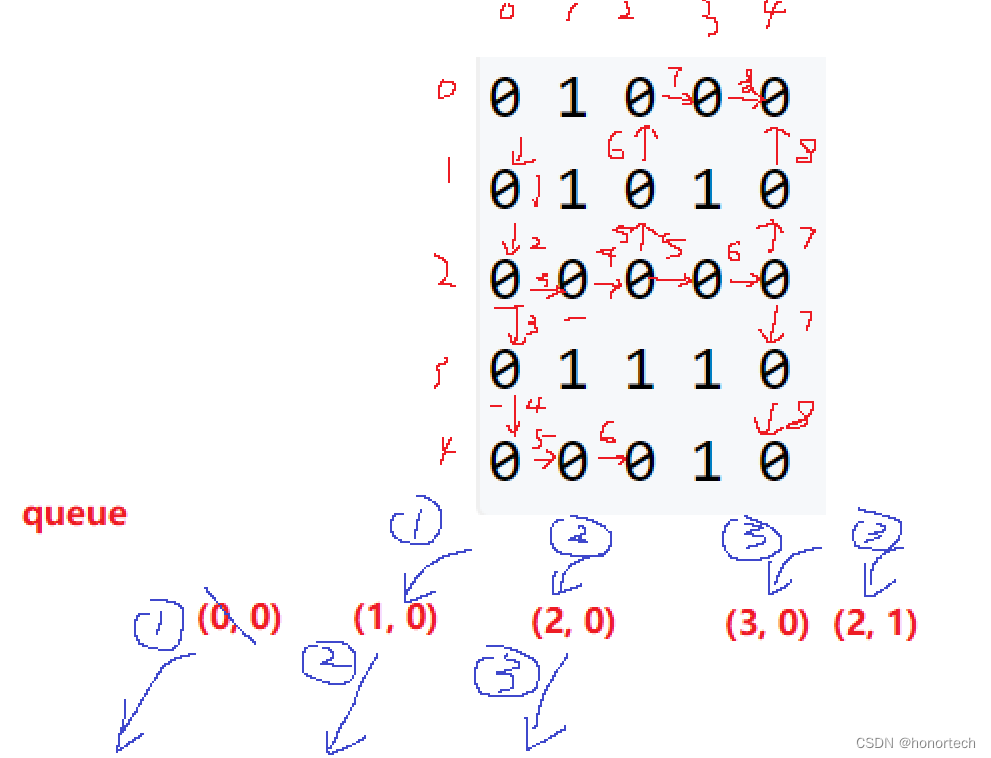
BFS遍历
while queue 不为空 {
poll 队头t
拓展 t 的所有邻点 x
if x 未被遍历
x offer进队列
d【x】= d【t】+ 1;
}
public class Main{
static final int N = 100010;
static int[]h = new int[N];
static int[]e = new int[N];
static int[]ne = new int[N];
static int idx;
static int n;
static int[]d = new int[N];//1号点到n号点的距离
static int[]q = new int[N];
public static void main(String[]args) {
Arrays.fill(h,-1);
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
n = sc.nextInt();
int m = sc.nextInt();
for(int i = 0;i < m;i++) {
int a = sc.nextInt();
int b = sc.nextInt();
add(a,b);
}
System.out.println(bfs());
}
public static int bfs() {
Arrays.fill(d,-1);
int hh = 0;
int tt = -1;
q[++tt] = 1;
d[1] = 0;
while(hh <= tt) {
int t = q[hh++];
for(int i = h[t];i != -1;i = ne[i]) {
int j = e[i];
if(d[j] == -1) {
d[j] = d[t] + 1;
q[++tt] = j;
}
}
}
return d[n];
}
public static void add(int a,int b) {
e[idx] = b;
ne[idx] = h[a];
h[a] = idx++;
}
}
应用
拓扑排序
一定是针对有向图的
定义:
对于一个序列,对应图上每条边都是起点在终点前面
易知,如果存在环的话,就一定不存在拓扑序列
所以,有向无环图又被称为拓扑图
入度为0的点可以作为起点,所以,拓扑排序步骤如下:
把所有入度为0的点入队
//类似与bfs过程 while queue不空 { t = poll队头; 枚举所有t的出边 t -> j 删掉 t -> j; d[j]--;//j的入度减一 if(d[j] == 0) 将j入队 }如果一个图没有环,我们一定可以找到入度为0的点,就可以写出拓扑序列
例如:
import java.util.*;
public class Main{
static final int N = 100010;
static int[]h = new int[N];
static int[]e = new int[N];
static int[]ne = new int[N];
static int idx;
static int n;
static int[]q = new int[N];
static int[]d = new int[N];//存入度
public static void add(int a,int b) {
e[idx] = b;
ne[idx] = h[a];
h[a] = idx++;
d[b]++;
}
public static boolean topSort() {
int hh = 0;
int tt = -1;
for(int i = 1;i <= n;i++) {
if(d[i] == 0) q[++tt] = i;
}
while(tt >= hh) {
int p = q[hh++];
for(int i = h[p];i != -1;i = ne[i]) {
int j = e[i];
d[j]--;
if(d[j] == 0) q[++tt] = j;
}
}
return tt == n - 1;//如果全部元素如果都入过队,说明图中没有环
}
public static void main(String[]args) {
Arrays.fill(h,-1);
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
n = sc.nextInt();
int m = sc.nextInt();
for(int i = 0;i < m;i++) {
int x = sc.nextInt();
int y = sc.nextInt();
add(x,y);
}
if(topSort()) {
for(int i = 0;i < n;i++) {
System.out.print(q[i]+" ");
}
}else System.out.println("-1");
}
}
原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/GJ_863/article/details/135314174
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。
如若转载,请注明出处:http://www.7code.cn/show_52548.html
如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系代码007邮箱:suwngjj01@126.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
主题授权提示:请在后台主题设置-主题授权-激活主题的正版授权,授权购买:RiTheme官网
声明:本站所有文章,如无特殊说明或标注,均为本站原创发布。任何个人或组织,在未征得本站同意时,禁止复制、盗用、采集、发布本站内容到任何网站、书籍等各类媒体平台。如若本站内容侵犯了原著者的合法权益,可联系我们进行处理。