1. 信号和槽细节
1.1 举例
1.1.1 一个信号对应多个槽
一个信号可以绑定多个槽,先绑定哪个槽,哪个槽先执行,后绑定后执行
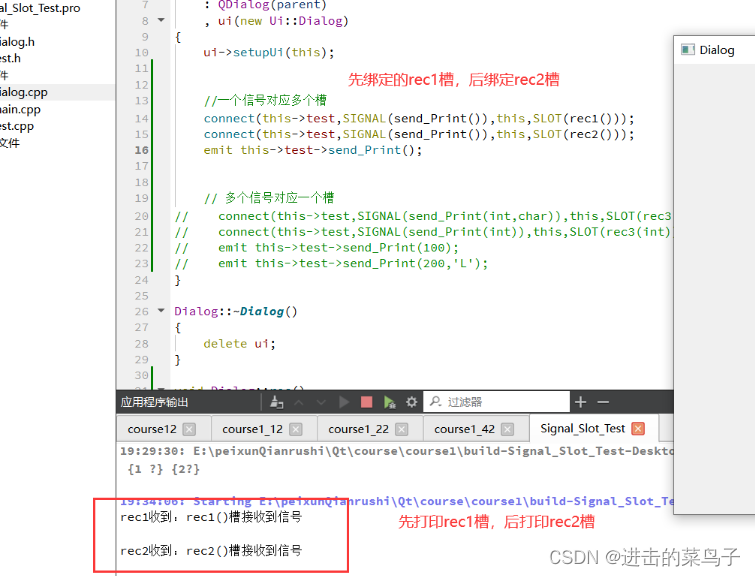
Signal_Slot_Test
信号
test.h
signals://信号函数
void send_Print();
};
绑定
dialog.cpp
//一个信号对应多个槽
connect(this->test,SIGNAL(send_Print()),this,SLOT(rec1()));
connect(this->test,SIGNAL(send_Print()),this,SLOT(rec2()));
emit this->test->send_Print();
槽
dialog.h
public slots:
void rec1();
void rec2();
dialog.cpp
void Dialog::rec1()
{
qDebug()<<"rec1收到:rec1()槽接收到信号"<<endl;
}
void Dialog::rec2()
{
qDebug()<<"rec2收到:rec2()槽接收到信号"<<endl;
}
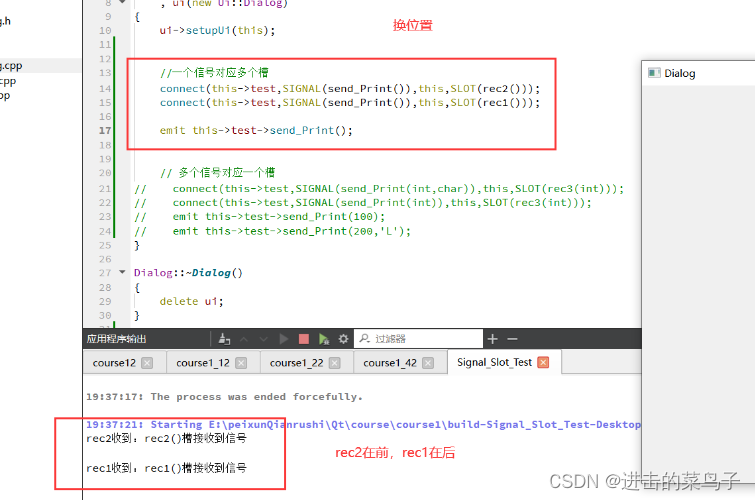
换绑rec1和rec2的位置
Signal_Slot_Test
绑定
dialog.cpp
//一个信号对应多个槽
connect(this->test,SIGNAL(send_Print()),this,SLOT(rec2()));
connect(this->test,SIGNAL(send_Print()),this,SLOT(rec1()));
emit this->test->send_Print();
1.1.2 多个信号对应一个槽
Signal_Slot_Test
信号
test.h
signals://信号函数
void send_Print(int a);
void send_Print(int a,char b);
绑定
dialog.cpp
// 多个信号对应一个槽
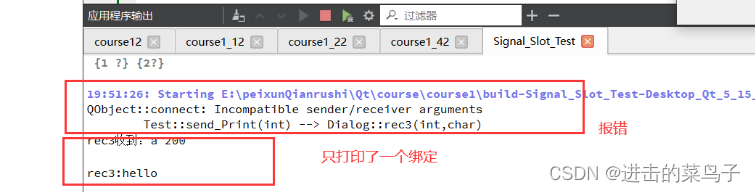
connect(this->test,SIGNAL(send_Print(int)),this,SLOT(rec3(int)));
connect(this->test,SIGNAL(send_Print(int,char)),this,SLOT(rec3(int)));
emit this->test->send_Print(100);
emit this->test->send_Print(200,'L');
槽
dialog.h
public slots:
void rec3(int a);
dialog.cpp
void Dialog::rec3(int a)
{
qDebug()<<"rec3收到:a"<<a<<endl;
qDebug()<<"rec3:hello"<<endl;
}
1.1.3 传递参数细节
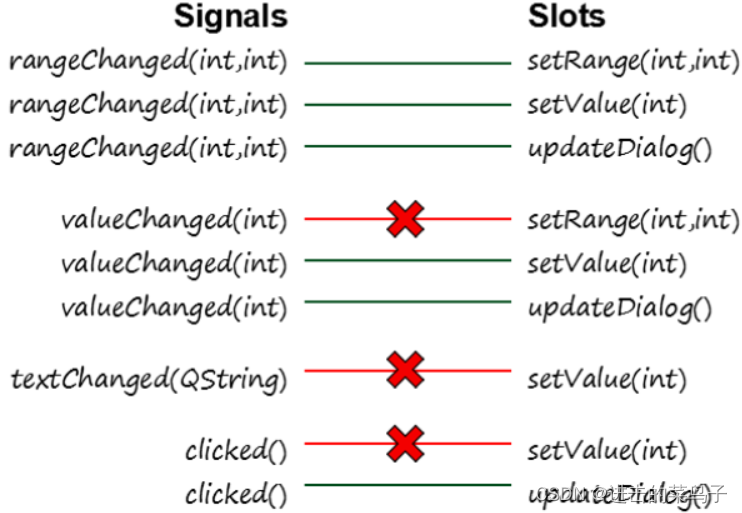
1.当槽函数的参数与信号的参数一致时,需要满足槽函数的参数类型和信号的参数类型保持一致(即一一对应)
2.信号的参数个数必须大于等于槽函数的参数个数
具体代码不写了
列举比较容易犯错的写法
Signal_Slot_Test
信号
signals://信号函数
void send_Print(int a);
void send_Print(int a,char b);
绑定
// 多个信号对应一个槽
connect(this->test,SIGNAL(send_Print(int,char)),this,SLOT(rec3(int,char)));
connect(this->test,SIGNAL(send_Print(int)),this,SLOT(rec3(int,char)));
emit this->test->send_Print(100);
emit this->test->send_Print(200,'L');
槽
public slots:
void rec3(int a,char b);
public slots:
void rec3(int a,char b);
原因是recv3有两个参数但是我们的第二个绑定只有一个参数int 槽的参数比信号函数的多了,就出错了
总之切记,槽的参数个数永远小于等于信号的参数个数
2. 自动绑定的信号与槽
用户只需要选择相应的信号——–执行转到槽操作———QT自动完成绑定的过程
2.1 以按钮为例:
按钮中的信号:
clicked()//点击按钮时出发该信号
clicked(bool)//当按钮被点击时触发。这个信号带有一个布尔值的参数,通常用于表示 按钮的点击状态。
pressed()//按下按钮时出发该信号
released()//按下按钮并释放按钮时触发该信号(即按下后松开触发)
toggled(bool)//按钮的状态取反时出发该信号(当按钮的状态发生切换时触发。这个信 号带有一个布尔值的参数,表示按钮的最新状态。)
2.1.1 基本操作
2.2 练习
2.2.1 奇数偶数交替打印
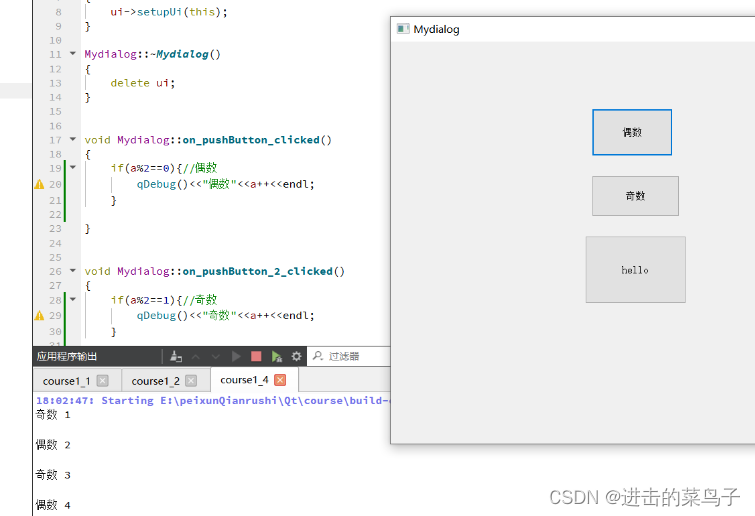
(1)使用自动绑定信号与槽(用按钮) , 实现奇偶数的交替打印
course1_4
mydialog.cpp
#include "mydialog.h"
#include "ui_mydialog.h"
Mydialog::Mydialog(QWidget *parent)
: QDialog(parent)
, ui(new Ui::Mydialog)
{
ui->setupUi(this);
}
Mydialog::~Mydialog()
{
delete ui;
}
void Mydialog::on_pushButton_clicked()
{
if(a%2==0){//偶数
qDebug()<<"偶数"<<a++<<endl;
}
}
void Mydialog::on_pushButton_2_clicked()
{
if(a%2==1){//奇数
qDebug()<<"奇数"<<a++<<endl;
}
}
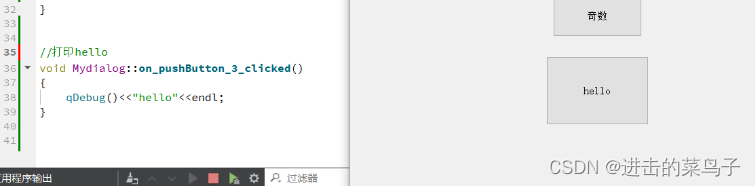
//奇数偶数交替打印
void Mydialog::on_pushButton_3_clicked()
{
qDebug()<<"hello"<<endl;
}
2.2.2 练习2
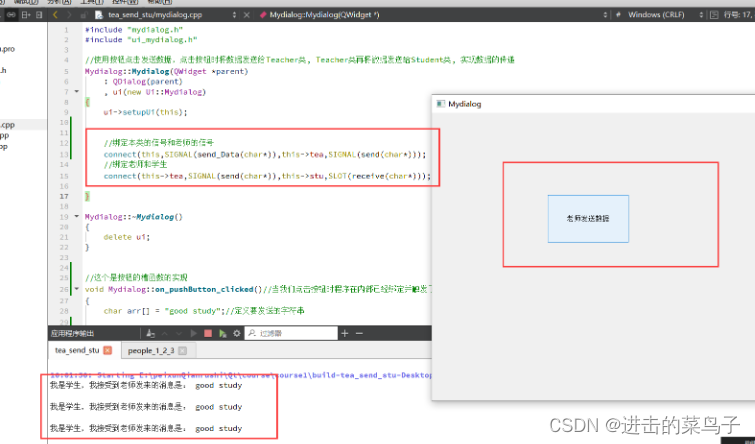
(2)使用按钮点击发送数据,点击按钮时将数据发送给Teacher类, Teacher类再将数据发送给Student类, 实现数据的传递
tea_send_stu
Teacher.h
#ifndef TEACHER_H
#define TEACHER_H
#include <QObject>
#include <QDebug>
class Teacher : public QObject
{
Q_OBJECT
public:
explicit Teacher(QObject *parent = nullptr);
signals:
void send(char* arr);//老师发送消息信号
void send();
};
#endif // TEACHER_H
Teacher.cpp
#include "teacher.h"
Teacher::Teacher(QObject *parent)
: QObject{parent}
{
}
Student.h
#ifndef STUDENT_H
#define STUDENT_H
#include <QObject>
#include <QDebug>
class Student : public QObject
{
Q_OBJECT
public:
explicit Student(QObject *parent = nullptr);
signals:
public slots://槽函数
void receive(char* arr);
};
#endif // STUDENT_H
Student.cpp
#include "student.h"
Student::Student(QObject *parent)
: QObject{parent}
{
}
void Student::receive(char* arr){//学生的槽函数实现
qDebug()<<"我是学生,我接受到老师发来的消息是:"<<arr<<endl;
}
mydialog.h
#ifndef MYDIALOG_H
#define MYDIALOG_H
#include <QDialog>
#include <teacher.h>
#include <student.h>
#include <QDebug>
QT_BEGIN_NAMESPACE
namespace Ui { class Mydialog; }
QT_END_NAMESPACE
class Mydialog : public QDialog
{
Q_OBJECT
public:
Mydialog(QWidget *parent = nullptr);
~Mydialog();
private slots:
void on_pushButton_clicked();
signals:
void send_Data(char*);//在本类中定义信号函数,用于将数据发送给teacher
private:
//实例化对象
Teacher* tea = new Teacher;
Student* stu = new Student;
Ui::Mydialog *ui;
};
#endif // MYDIALOG_H
mydialog.cpp
#include "mydialog.h"
#include "ui_mydialog.h"
//使用按钮点击发送数据,点击按钮时将数据发送给Teacher类, Teacher类再将数据发送给Student类, 实现数据的传递
Mydialog::Mydialog(QWidget *parent)
: QDialog(parent)
, ui(new Ui::Mydialog)
{
ui->setupUi(this);
//绑定本类的信号和老师的信号
connect(this,SIGNAL(send_Data(char*)),this->tea,SIGNAL(send(char*)));
//绑定老师和学生
connect(this->tea,SIGNAL(send(char*)),this->stu,SLOT(receive(char*)));
}
Mydialog::~Mydialog()
{
delete ui;
}
//这个是按钮的槽函数的实现
void Mydialog::on_pushButton_clicked()//当我们点击按钮时程序在内部已经绑定并触发了信号,所以肯定会跳到这个槽中
{
char arr[] = "good study";//定义要发送的字符串
emit this->send_Data(arr);//这里触发本类信号,将数据发送给老师
}
2.2.3 练习3
(3) 现有四个类,分别是按钮类、People1、 People2、 People3
用户点陆按钮类,将发射整形数据给People1和People3类
如果整形数据是1,则给People1类,如果整形数据是2,则给People3类
其中如果是整形数据1,则发送给People1类的时候,也需要让People2告诉People3不用进行接收;如果是整形数据2,则需要让People2告诉People3进行接收并输出收到的数据
people_1_2_3
people1.h
#ifndef PEOPLE1_H
#define PEOPLE1_H
#include <QObject>
#include <QDebug>
class People1 : public QObject
{
Q_OBJECT
public:
explicit People1(QObject *parent = nullptr);
signals:
public slots://槽
void receive_Data(int a);
};
#endif // PEOPLE1_H
people1.cpp
#include "people1.h"
People1::People1(QObject *parent)
: QObject{parent}
{
}
void People1::receive_Data(int a){
qDebug()<<"people1收到的数据"<<a<<endl;
}
people2.h
#ifndef PEOPLE2_H
#define PEOPLE2_H
#include <QObject>
class People2 : public QObject
{
Q_OBJECT
public:
explicit People2(QObject *parent = nullptr);
signals://定义信号用于通知people3
void tell_To_People3(int a);
};
#endif // PEOPLE2_H
people2.cpp
#include "people2.h"
People2::People2(QObject *parent)
: QObject{parent}
{
}
people3.h
#ifndef PEOPLE3_H
#define PEOPLE3_H
#include <QObject>
#include <QDebug>
class People3 : public QObject
{
Q_OBJECT
public:
explicit People3(QObject *parent = nullptr);
signals:
public slots://槽
void receive_Data(int a);
};
#endif // PEOPLE3_H
people3.cpp
#include "people3.h"
People3::People3(QObject *parent)
: QObject{parent}
{
}
void People3::receive_Data(int a){
if(a==1){//发来的数据是1
return;//不用打印
}
//到这发来的数据肯定不是1,需要接收打印
qDebug()<<"people3收到的数据"<<a<<endl;
}
mydialog.h
#ifndef MYDIALOG_H
#define MYDIALOG_H
#include <QDialog>
#include <people1.h>
#include <people2.h>
#include <people3.h>
QT_BEGIN_NAMESPACE
namespace Ui { class mydialog; }
QT_END_NAMESPACE
class mydialog : public QDialog
{
Q_OBJECT
public:
mydialog(QWidget *parent = nullptr);
~mydialog();
private slots:
void on_pushButton_clicked();
signals://定义本类信号,用来发送数据
void send_Data1(int a);
void send_Data3(int b);
private:
Ui::mydialog *ui;
//实例化对象
People1* people1 = new People1;
People2* people2 = new People2;
People3* people3 = new People3;
};
#endif // MYDIALOG_H
#include "mydialog.h"
#include "ui_mydialog.h"
/*
现有四个类,分别是按钮类、People1、 People2、 People3
用户点陆按钮类,将发射整形数据给People1和People3类
如果整形数据是1,则给People1类,如果整形数据是2,则给People3类
其中如果是整形数据1,则发送给People1类的时候,也需要让People2告诉People3不用进行接收;如果是整形数据2,则需要让People2告诉People3进行接收并输出收到的数据
*/
mydialog::mydialog(QWidget *parent)
: QDialog(parent)
, ui(new Ui::mydialog)
{
ui->setupUi(this);
//绑定本类信号1与people1的槽
connect(this,SIGNAL(send_Data1(int)),this->people1,SLOT(receive_Data(int)));
//绑定people2信号与people3的槽
connect(this->people2,SIGNAL(tell_To_People3(int)),this->people3,SLOT(receive_Data(int)));
}
mydialog::~mydialog()
{
delete ui;
}
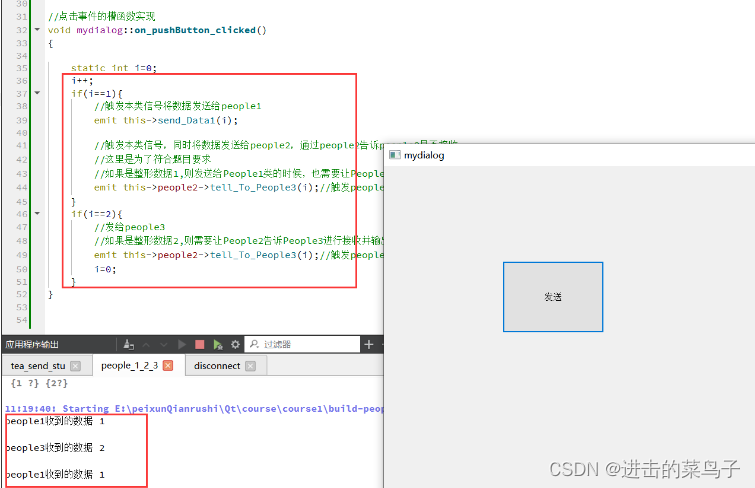
//点击事件的槽函数实现
void mydialog::on_pushButton_clicked()
{
static int i=0;
i++;
if(i==1){
//触发本类信号将数据发送给people1
emit this->send_Data1(i);
//触发本类信号,同时将数据发送给people2,通过people2告诉people3是否接收
//这里是为了符合题目要求
//如果是整形数据1,则发送给People1类的时候,也需要让People2告诉People3不用进行接收;
emit this->people2->tell_To_People3(i);//触发people2的信号
}
if(i==2){
//发给people3
//如果是整形数据2,则需要让People2告诉People3进行接收并输出收到的数据
emit this->people2->tell_To_People3(i);//触发people2的信号
i=0;
}
}
3. QT中解绑两个对象的绑定:
函数原型:
bool disconnect(对象1,对象1发出的信号,对象2,对对象1发出的信号进行处理);//解绑对象1和对象2绑定的信号和槽
3.1 解绑1:解绑指定的两个对象中的指定的信号和槽
即解绑两个特定的信号和槽
1-1 :1-1
disconnect(对象1,对象1的信号,对象2,对象2的槽);
文件diaconnect
信号
mydialog.h
signals:
void send_signal1();
void send_signal2();
绑定
mydialog.cpp
//解绑一
connect(this,SIGNAL(send_signal1()),this->people1,SLOT(slot1()));
connect(this,SIGNAL(send_signal2()),this->people1,SLOT(slot1()));
emit this->send_signal1();
//解绑指定的两个对象中的指定的信号和槽
disconnect(this,SIGNAL(send_signal2()),this->people1,SLOT(slot1()));
emit this->send_signal2();
槽
定义
people1.h
public slots:
void slot1();
void slot2();
实现
people1.cpp
void People1::slot1(){
qDebug()<<"slot1()"<<endl;
}
void People1::slot2(){
qDebug()<<"slot2()"<<endl;
}
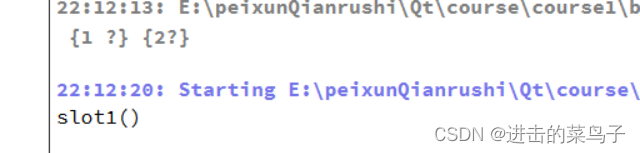
解绑前
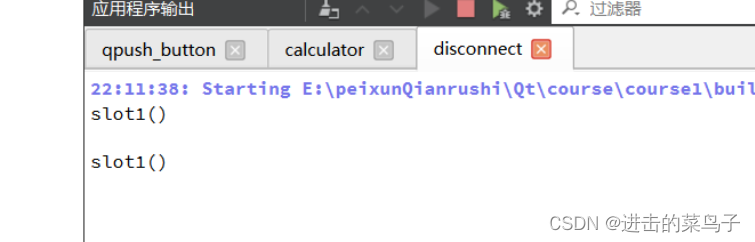
解绑后
解绑信号2和槽2
结果只输出槽1
3.2 解绑2:解绑对象1中的信号和对象2中的所有(任何)槽函数
即一个对象中的一个信号 绑定的 另一个对象的中的所有槽都会 解绑
1-1 :1-n
disconnect(对象1,对象1的信号,对象2,nullptr);
文件diaconnect
信号
mydialog.h
signals:
void send_signal1();
void send_signal2();
绑定
mydialog.cpp
//解绑二
connect(this,SIGNAL(send_signal1()),this->people1,SLOT(slot1()));
connect(this,SIGNAL(send_signal1()),this->people1,SLOT(slot2()));
//解绑对象1中的信号和对象2中的所有(任何)槽函数(即所有与这个对象绑定的槽都会解绑)
disconnect(this,SIGNAL(send_signal1()),this->people1,nullptr);
emit this->send_signal1();
emit this->send_signal2();
槽
定义
people1.h
public slots:
void slot1();
void slot2();
实现
people1.cpp
void People1::slot1(){
qDebug()<<"slot1()"<<endl;
}
void People1::slot2(){
qDebug()<<"slot2()"<<endl;
}
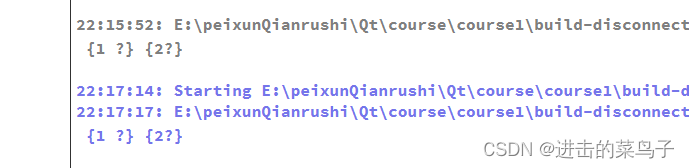
解绑前

解绑后
没输出
3.3 解绑3:解绑对象1中的信号和任何对象的槽函数的绑定
即 一个对象 的 一个信号 绑定的 任何对象 的 任何槽
1-1:n-n
disconnect(对象1,对象1的信号,nullptr,nullptr);
文件diaconnect
信号
mydialog.h
signals:
void send_signal1();
绑定
mydialog.cpp
//解绑三
connect(this,SIGNAL(send_signal1()),this->people1,SLOT(slot1()));
connect(this,SIGNAL(send_signal1()),this->people2,SLOT(people2_slot()));
//解绑对象1中的信号和任何对象的槽函数的绑定(即 一个对象 的 一个信号 绑定的 任何对象 的 任何槽)
disconnect(this,SIGNAL(send_signal1()),nullptr,nullptr);
emit this->send_signal1();
槽
定义
people1.h
public slots:
void slot1();
people2.h
public slots:
void people2_slot();
实现
people1.cpp
void People1::slot1(){
qDebug()<<"slot1()"<<endl;
}
people2.cpp
void People2::people2_slot(){
qDebug()<<"people2"<<endl;
}
解绑前

解绑后
都不会输出

7.4 解绑4:解绑对象1中的任何信号和任何对象中任何槽的绑定
即 一个对象中的 任何信号 绑定的 任何对象中的任何槽
1-n : n-n
disconnect(对象1,nullptr,nullptr,nullptr);
文件diaconnect
信号
mydialog.h
signals:
void send_signal1();
void send_signal2();
绑定
mydialog.cpp
//解绑四
//绑定信号1和people1、people2的槽
connect(this,SIGNAL(send_signal1()),this->people1,SLOT(slot1()));
connect(this,SIGNAL(send_signal1()),this->people2,SLOT(people2_slot()));
//绑定信号2和people1、people2的槽
connect(this,SIGNAL(send_signal2()),this->people1,SLOT(slot1()));
connect(this,SIGNAL(send_signal2()),this->people2,SLOT(people2_slot()));
//解绑对象1中的任何信号和任何对象中任何槽的绑定(即 一个对象中的 任何信号 绑定的 任何对象中的任何槽)
disconnect(this,nullptr,nullptr,nullptr);
emit this->send_signal1();
emit this->send_signal2();
槽
定义
people1.h
public slots:
void slot1();
people2.h
public slots:
void people2_slot();
实现
people1.cpp
void People1::slot1(){
qDebug()<<"slot1()"<<endl;
}
void People2::people2_slot(){
qDebug()<<"people2"<<endl;
}
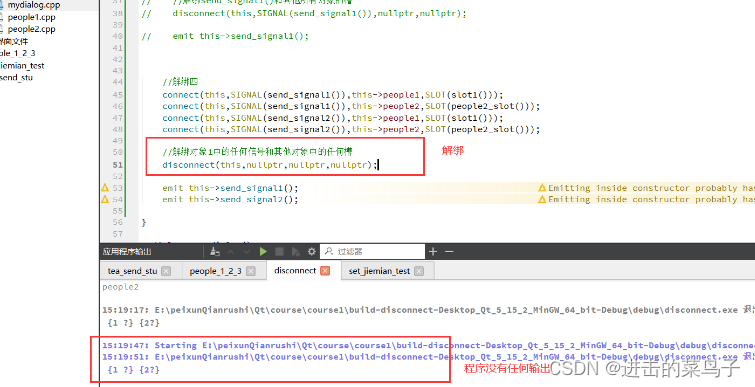
不解绑的情况

解绑的情况
原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/m0_65554471/article/details/135439943
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。
如若转载,请注明出处:http://www.7code.cn/show_53234.html
如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系代码007邮箱:suwngjj01@126.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!