本文介绍: 寻找到了 com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.transport.command.SimpleHttpCommandCenter#start 的相关收发数据逻辑。触发一次 Http 请求调用后,发现进入了 com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.init.InitExecutor#doInit 断点。这样我们在界面修改就可以持久化到nacos,这里要注意如果在nacos直接修改,控制台上是不能感知到的。关键代码 2:从 ServerSocket 的 accept 方法收数据。
sentinel
功能
- 限流 限流文档
- 直接拒绝:触发阀值直接抛弃。
- 冷启动:在一段时间内针对突发流量缓慢增长处理数量。
3)匀速器:请求以均匀的速度通过。
- 降级降级文档
1)RT 统计时间内,大于预设请求数量,且慢请求大于这个预设比例,则熔断拒绝一段时间。
2)异常比例,统计时间内,请求总数大于预设请求数,且异常比例大于预设比例,则熔断拒绝一段时间。
3)异常数,统计时间内,请求总数大于预设请求数量,且异常大于预设数值,则拒绝熔断一段时间。
手动限流案例Demo
- 根据线程活跃数量进行限流
/**
* 根据并发数量进行限流
*/
public class Flow_1_Thread_Demo {
/** 资源 methodA 所有业务逻辑处理完成的数量 **/
private static AtomicInteger pass = new AtomicInteger();
/** 资源 methodA 被拒绝的数量 **/
private static AtomicInteger block = new AtomicInteger();
/** 资源 methodA 接收到请求的总数量 **/
private static AtomicInteger total = new AtomicInteger();
/** 资源 methodA 真正开始干活时就开始计数,表示 methodA 的任务活跃数 **/
private static AtomicInteger activeThread = new AtomicInteger();
private static volatile boolean stop = false;
private static final int threadCount = 100;
/** 资源 methodA 总共被发起调用的持续时间 **/
private static int seconds = 15;
/** 资源 methodB 处理业务时需要消耗的时间,单位:毫秒 **/
private static volatile int methodBRunningTime = 2000;
/**
* 并发数限流
* 当并发数大于 5 时则进行阻断
* 反正一直保持最大活跃任务数为 5
*/
private static void initFlowRule() {
List<FlowRule> rules = new ArrayList<FlowRule>();
FlowRule rule = new FlowRule();
// 设置资源名称为:methodA
rule.setResource("methodA");
// 设置限流类型:并发数限流
rule.setGrade(RuleConstant.FLOW_GRADE_THREAD);
// 设置并发数限流,对应的限制数值
rule.setCount(5);
// 设置需要限制哪些应用,如果没有想好需要限制谁的话,那么采用 default 方式
rule.setLimitApp("default");
// 将设置好的规则,添加至列表中,并且加载到限流管理器中
rules.add(rule);
FlowRuleManager.loadRules(rules);
System.out.println("Flow_1_Thread rule loaded: " + rules);
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
System.out.println(
"MethodA will call methodB. After running for a while, methodB becomes fast, "
+ "which make methodA also become fast ");
// 开启一个线程打印统计信息
tick();
// 设置规则
initFlowRule();
// 启动现场 不停的发送请求
for (int i = 0; i < threadCount; i++) {
Thread entryThread = new Thread(new ThreadRunTask());
entryThread.setName("working thread");
entryThread.start();
}
}
private static void tick() {
Thread timer = new Thread(new TimerTask());
timer.setName("sentinel-timer-task");
timer.start();
}
/**
* 打印统计信息 每秒钟输出
*/
static class TimerTask implements Runnable {
@Override
public void run() {
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("begin to statistic!!!");
long oldTotal = 0;
long oldPass = 0;
long oldBlock = 0;
while (!stop) {
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
}
long globalTotal = total.get();
long oneSecondTotal = globalTotal - oldTotal;
oldTotal = globalTotal;
long globalPass = pass.get();
long oneSecondPass = globalPass - oldPass;
oldPass = globalPass;
long globalBlock = block.get();
long oneSecondBlock = globalBlock - oldBlock;
oldBlock = globalBlock;
System.out.print("【秒】倒计时: " + seconds + ", ");
System.out.println((new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss.SSSSSS").format(new Date()))
+ ", 每秒总请求量:" + oneSecondTotal
+ ", 每秒完成量:" + oneSecondPass
+ ", 每秒拒绝量:" + oneSecondBlock
+ ", 每秒活跃量:" + activeThread.get());
System.out.println();
if (seconds-- <= 0) {
stop = true;
}
// 倒数5秒的时候提高MethodB 方法的效率
if (seconds == 5) {
System.out.println("method B 原来执行需要花费 2000 毫秒,改造后只需要花费 20 毫秒,系统即将能处理更多的请求。n");
methodBRunningTime = 20;
}
}
long cost = System.currentTimeMillis() - start;
System.out.println("time cost: " + cost + " ms");
System.out.println("total:" + total.get() + ", pass:" + pass.get()
+ ", block:" + block.get());
System.exit(0);
}
}
static class ThreadRunTask implements Runnable {
@Override
public void run() {
while (true) {
Entry methodA = null;
try {
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(5);
// 抢占资源A
methodA = SphU.entry("methodA");
activeThread.incrementAndGet();
// 抢占资源B
Entry methodB = SphU.entry("methodB");
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(methodBRunningTime);
methodB.exit();
pass.addAndGet(1);
} catch (BlockException e1) {
// 阻塞的数量
block.incrementAndGet();
} catch (Exception e2) {
// biz exception
} finally {
// 请求总数量
total.incrementAndGet();
if (methodA != null) {
methodA.exit();
// 活跃数量减
activeThread.decrementAndGet();
}
}
}
}
}
}
- 根据QPS进行限流
/**
* 根据QPS进行限流
*/
public class Flow_2_Qps_Demo {
private static final String KEY = "methodA";
/** 资源 methodA 所有业务逻辑处理完成的数量 **/
private static AtomicInteger pass = new AtomicInteger();
/** 资源 methodA 被拒绝的数量 **/
private static AtomicInteger block = new AtomicInteger();
/** 资源 methodA 接收到请求的总数量 **/
private static AtomicInteger total = new AtomicInteger();
private static volatile boolean stop = false;
private static final int threadCount = 32;
/** 资源 methodA 总共被发起调用的持续时间 **/
private static int seconds = 15;
private static void initFlowQpsRule() {
List<FlowRule> rules = new ArrayList<FlowRule>();
FlowRule rule1 = new FlowRule();
// 设置资源名称为:methodA
rule1.setResource(KEY);
// 设置限流类型:QPS 限流
rule1.setGrade(RuleConstant.FLOW_GRADE_QPS);
// 设置 QPS 限流,对应的限制数值
rule1.setCount(5);
// 设置 QPS 限流数值满后的应对策略:直接拒绝(该策略为默认策略,可以从 setControlBehavior 方法跟踪进去看)
// public static final int CONTROL_BEHAVIOR_DEFAULT = 0;
// public static final int CONTROL_BEHAVIOR_WARM_UP = 1;
// public static final int CONTROL_BEHAVIOR_RATE_LIMITER = 2;
// public static final int CONTROL_BEHAVIOR_WARM_UP_RATE_LIMITER = 3;
// rule1.setControlBehavior()
// 设置需要限制哪些应用,如果没有想好需要限制谁的话,那么采用 default 方式
rule1.setLimitApp("default");
// 将设置好的规则,添加至列表中,并且加载到限流管理器中
rules.add(rule1);
FlowRuleManager.loadRules(rules);
System.out.println("Flow_2_Qps rule loaded: " + rules);
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
initFlowQpsRule();
tick();
// first make the system run on a very low condition
simulateTraffic();
System.out.println("===== begin to do flow control");
System.out.println("only 5 requests per second can pass");
}
private static void simulateTraffic() {
for (int i = 0; i < threadCount; i++) {
Thread t = new Thread(new RunTask());
t.setName("simulate-traffic-Task");
t.start();
}
}
private static void tick() {
Thread timer = new Thread(new TimerTask());
timer.setName("sentinel-timer-task");
timer.start();
}
static class TimerTask implements Runnable {
@Override
public void run() {
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("begin to statistic!!!");
long oldTotal = 0;
long oldPass = 0;
long oldBlock = 0;
while (!stop) {
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
}
long globalTotal = total.get();
long oneSecondTotal = globalTotal - oldTotal;
oldTotal = globalTotal;
long globalPass = pass.get();
long oneSecondPass = globalPass - oldPass;
oldPass = globalPass;
long globalBlock = block.get();
long oneSecondBlock = globalBlock - oldBlock;
oldBlock = globalBlock;
System.out.print("【秒】倒计时: " + seconds + ", ");
System.out.println((new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss.SSSSSS").format(new Date()))
+ ", 每秒总请求量:" + oneSecondTotal
+ ", 每秒完成量:" + oneSecondPass
+ ", 每秒拒绝量:" + oneSecondBlock);
System.out.println();
if (seconds-- <= 0) {
stop = true;
}
}
long cost = System.currentTimeMillis() - start;
System.out.println("time cost: " + cost + " ms");
System.out.println("total:" + total.get() + ", pass:" + pass.get()
+ ", block:" + block.get());
System.exit(0);
}
}
static class RunTask implements Runnable {
@Override
public void run() {
while (!stop) {
Entry entry = null;
try {
entry = SphU.entry(KEY);
// token acquired, means pass
pass.addAndGet(1);
} catch (BlockException e1) {
block.incrementAndGet();
} catch (Exception e2) {
// biz exception
} finally {
total.incrementAndGet();
if (entry != null) {
entry.exit();
}
}
Random random2 = new Random();
try {
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(random2.nextInt(50));
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// ignore
}
}
}
}
}
- 冷启动
也就是在一定的时间内慢慢可以达到我们处理请求的峰值。
public class Flow_3_WarmUp_Demo {
private static final String KEY = "methodA";
/** 资源 methodA 所有业务逻辑处理完成的数量 **/
private static AtomicInteger pass = new AtomicInteger();
/** 资源 methodA 被拒绝的数量 **/
private static AtomicInteger block = new AtomicInteger();
/** 资源 methodA 接收到请求的总数量 **/
private static AtomicInteger total = new AtomicInteger();
private static volatile boolean stop = false;
private static final int threadCount = 100;
/** 资源 methodA 总共被发起调用的持续时间 **/
private static int seconds = 16;
private static void initFlowRule() {
List<FlowRule> rules = new ArrayList<FlowRule>();
FlowRule rule1 = new FlowRule();
// 设置资源名称为:methodA
rule1.setResource(KEY);
// 设置限流类型:QPS 限流
rule1.setGrade(RuleConstant.FLOW_GRADE_QPS);
// 设置 QPS 限流,对应的限制数值
rule1.setCount(20);
// 设置 QPS 限流数值满后的应对策略:冷启动,即让通过的流量缓慢增加,直到增加到限制数值上限
rule1.setControlBehavior(RuleConstant.CONTROL_BEHAVIOR_WARM_UP);
// 既然设置了冷启动缓慢增长,那么这个缓慢增长到限制数值上限的时间为:10 秒
rule1.setWarmUpPeriodSec(10);
// 设置需要限制哪些应用,如果没有想好需要限制谁的话,那么采用 default 方式
rule1.setLimitApp("default");
// 将设置好的规则,添加至列表中,并且加载到限流管理器中
rules.add(rule1);
FlowRuleManager.loadRules(rules);
System.out.println("Flow_3_WarmUp rule loaded: " + rules);
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
initFlowRule();
// trigger Sentinel internal init
Entry entry = null;
try {
entry = SphU.entry(KEY);
} catch (Exception e) {
} finally {
if (entry != null) {
entry.exit();
}
}
Thread timer = new Thread(new TimerTask());
timer.setName("sentinel-timer-task");
timer.start();
//first make the system run on a very low condition
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
// WarmUpTask 控制住了调用资源 methodA 的频率,让系统处于一个低水平调用状态
Thread t = new Thread(new WarmUpTask());
t.setName("sentinel-warmup-task");
t.start();
}
Thread.sleep(5000);
/*
* Start more thread to simulate more qps. Since we use {@link RuleConstant.CONTROL_BEHAVIOR_WARM_UP} as
* {@link FlowRule#controlBehavior}, real passed qps will increase to {@link FlowRule#count} in
* {@link FlowRule#warmUpPeriodSec} seconds.
*/
for (int i = 0; i < threadCount; i++) {
// RunTask 稍微加大了调用资源 methodA 的频率,让系统处于一个相对原来处于一个较高水平调用状态
Thread t = new Thread(new RunTask());
t.setName("sentinel-run-task");
t.start();
}
}
static class TimerTask implements Runnable {
@Override
public void run() {
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("begin to statistic!!!");
long oldTotal = 0;
long oldPass = 0;
long oldBlock = 0;
while (!stop) {
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
}
long globalTotal = total.get();
long oneSecondTotal = globalTotal - oldTotal;
oldTotal = globalTotal;
long globalPass = pass.get();
long oneSecondPass = globalPass - oldPass;
oldPass = globalPass;
long globalBlock = block.get();
long oneSecondBlock = globalBlock - oldBlock;
oldBlock = globalBlock;
System.out.print("【秒】倒计时: " + seconds + ", ");
System.out.println((new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss.SSSSSS").format(new Date()))
+ ", 每秒总请求量:" + oneSecondTotal
+ ", 每秒完成量:" + oneSecondPass
+ ", 每秒拒绝量:" + oneSecondBlock);
System.out.println();
if (seconds-- <= 0) {
stop = true;
}
}
long cost = System.currentTimeMillis() - start;
System.out.println("time cost: " + cost + " ms");
System.out.println("total:" + total.get() + ", pass:" + pass.get()
+ ", block:" + block.get());
System.exit(0);
}
}
static class WarmUpTask implements Runnable {
@Override
public void run() {
while (!stop) {
Entry entry = null;
try {
entry = SphU.entry(KEY);
// token acquired, means pass
pass.addAndGet(1);
} catch (BlockException e1) {
block.incrementAndGet();
} catch (Exception e2) {
// biz exception
} finally {
total.incrementAndGet();
if (entry != null) {
entry.exit();
}
}
Random random2 = new Random();
try {
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(random2.nextInt(2000));
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// ignore
}
}
}
}
static class RunTask implements Runnable {
@Override
public void run() {
while (!stop) {
Entry entry = null;
try {
entry = SphU.entry(KEY);
pass.addAndGet(1);
} catch (BlockException e1) {
block.incrementAndGet();
} catch (Exception e2) {
// biz exception
} finally {
total.incrementAndGet();
if (entry != null) {
entry.exit();
}
}
Random random2 = new Random();
try {
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(random2.nextInt(50));
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// ignore
}
}
}
}
}
手动降级案例Demo
- 根据响应时间来限流
也就是统计慢请求超过一定的比例以后,则在我们设置的时间内停止干活儿,知道下一次请求处理小于我们设置的慢请求的时间,继续干活。
public class Degrade_1_RT_Demo {
private static final String KEY = "methodA";
private static volatile boolean stop = false;
private static int seconds = 120;
/** 资源 methodA 接收到请求的总数量 **/
private static AtomicInteger total = new AtomicInteger();
/** 资源 methodA 被拒绝的数量 **/
private static AtomicInteger block = new AtomicInteger();
/** 资源 methodA 真正开始干活时就开始计数,表示 methodA 的任务活跃数 **/
private static AtomicInteger activeThread = new AtomicInteger();
private static void initDegradeRule() {
List<DegradeRule> rules = new ArrayList<>();
DegradeRule rule = new DegradeRule();
// 设置资源名称为:methodA
rule.setResource(KEY);
// 设置熔断策略:慢调用比例策略
rule.setGrade(CircuitBreakerStrategy.SLOW_REQUEST_RATIO.getType());
// 既然策略为慢调用比例,那么设置当请求的响应时间大于 50 毫秒时,则统计为慢调用
rule.setCount(50);
// 触发熔断条件 1:最小请求数,若【统计时长】内请求数小于该值时,即使【异常比率】超出 count 阈值也不会熔断
rule.setMinRequestAmount(10);
// 触发熔断条件 2:所谓的【统计时长】是多少,即到底在多少时间内进行统计计数
rule.setStatIntervalMs(8000);
// 触发熔断条件 3:所谓的【异常比率】其实就是一个 0 到 1 之间的数值,异常数 = minRequestAmount * slowRatioThreshold
rule.setSlowRatioThreshold(0.2);
// 当熔断触发后,熔断时长(10 秒)内请求会自动被熔断
// 经过熔断时长后,若接下来的一个请求响应时间小于 RT 则结束熔断
rule.setTimeWindow(10);
// 将设置好的规则,添加至列表中,并且加载到熔断降级管理器中
rules.add(rule);
DegradeRuleManager.loadRules(rules);
System.out.println("Degrade rule loaded: " + rules);
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
initDegradeRule();
registerStateChangeObserver();
startTick();
int concurrency = 8;
for (int i = 0; i < concurrency; i++) {
Thread entryThread = new Thread(new DegradeRTTask());
entryThread.setName("sentinel-simulate-traffic-task-" + i);
entryThread.start();
}
}
private static void registerStateChangeObserver() {
EventObserverRegistry.getInstance().addStateChangeObserver("logging",
(prevState, newState, rule, snapshotValue) -> {
if (newState == State.OPEN) {
System.err.println(String.format("%s -> OPEN at %d, snapshotValue=%.2f", prevState.name(),
TimeUtil.currentTimeMillis(), snapshotValue));
} else {
System.err.println(String.format("%s -> %s at %d", prevState.name(), newState.name(),
TimeUtil.currentTimeMillis()));
}
});
}
private static void sleep(int timeMs) {
try {
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(timeMs);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// ignore
}
}
private static void startTick() {
Thread timer = new Thread(new TimerTask());
timer.setName("sentinel-timer-tick-task");
timer.start();
}
static class TimerTask implements Runnable {
@Override
public void run() {
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("Begin to run! Go go go!");
System.out.println("See corresponding metrics.log for accurate statistic data");
long oldTotal = 0;
long oldActivePass = 0;
long oldBlock = 0;
while (!stop) {
sleep(1000);
long globalTotal = total.get();
long oneSecondTotal = globalTotal - oldTotal;
oldTotal = globalTotal;
long currActivePass = activeThread.get();
long oneSecondPass = currActivePass - oldActivePass;
oldActivePass = currActivePass;
long globalBlock = block.get();
long oneSecondBlock = globalBlock - oldBlock;
oldBlock = globalBlock;
System.out.print("【秒】倒计时: " + seconds + ", ");
System.out.println((new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss.SSSSSS").format(new Date()))
+ ", 每秒总请求量:" + oneSecondTotal
+ ", 每秒活跃量:" + oneSecondPass
+ ", 每秒拒绝量:" + oneSecondBlock);
if (seconds-- <= 0) {
stop = true;
}
}
long cost = System.currentTimeMillis() - start;
System.out.println("time cost: " + cost + " ms");
System.out.println("total: " + total.get() + ", pass:" + activeThread.get()
+ ", block:" + block.get());
System.exit(0);
}
}
static class DegradeRTTask implements Runnable {
@Override
public void run() {
while (true) {
Entry entry = null;
try {
entry = SphU.entry(KEY);
activeThread.incrementAndGet();
// RT: [40ms, 80ms)
sleep(ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextInt(40, 80));
} catch (BlockException e) {
block.incrementAndGet();
sleep(ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextInt(5, 10));
} finally {
total.incrementAndGet();
if (entry != null) {
entry.exit();
}
}
}
}
}
}
- 异常比例
也就是异常超过我们预设的比例,接下来我们设置的时间内都不干活,知道我们后面成功处理了一个请求接着干活。
public class Degrade_2_ExceptionRatio_Demo {
private static final String KEY = "methodA";
private static AtomicInteger total = new AtomicInteger();
private static AtomicInteger pass = new AtomicInteger();
private static AtomicInteger block = new AtomicInteger();
private static AtomicInteger bizException = new AtomicInteger();
private static volatile boolean stop = false;
private static int seconds = 120;
private static void initDegradeRule() {
List<DegradeRule> rules = new ArrayList<>();
DegradeRule rule = new DegradeRule();
// 设置资源名称为:methodA
rule.setResource(KEY);
// 设置熔断策略:异常比例策略
rule.setGrade(CircuitBreakerStrategy.ERROR_RATIO.getType());
// 既然策略为异常比例,出现业务异常则统计异常数量,当异常比例大于 50% 时,则触发熔断
rule.setCount(0.5d);
// 触发熔断条件 1:最小请求数,若【统计时长】内请求数小于该值时,即使【异常比例】超出 count 阈值也不会熔断
rule.setMinRequestAmount(10);
// 触发熔断条件 2:所谓的【统计时长】是多少,即到底在多少时间内进行统计计数
rule.setStatIntervalMs(10000);
// 当熔断触发后,熔断时长(10 秒)内请求会自动被熔断
// 经过熔断时长后,若接下来的一个请求成功返回,则结束熔断
rule.setTimeWindow(10);
// 将设置好的规则,添加至列表中,并且加载到熔断降级管理器中
rules.add(rule);
DegradeRuleManager.loadRules(rules);
System.out.println("Degrade rule loaded: " + rules);
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
initDegradeRule();
registerStateChangeObserver();
startTick();
final int concurrency = 8;
for (int i = 0; i < concurrency; i++) {
Thread entryThread = new Thread(new DegradeErrorRatioTask());
entryThread.setName("sentinel-simulate-traffic-task-" + i);
entryThread.start();
}
}
private static void registerStateChangeObserver() {
EventObserverRegistry.getInstance().addStateChangeObserver("logging",
(prevState, newState, rule, snapshotValue) -> {
if (newState == State.OPEN) {
System.err.println(String.format("%s -> OPEN at %d, snapshotValue=%.2f", prevState.name(),
TimeUtil.currentTimeMillis(), snapshotValue));
} else {
System.err.println(String.format("%s -> %s at %d", prevState.name(), newState.name(),
TimeUtil.currentTimeMillis()));
}
});
}
private static void sleep(int timeMs) {
try {
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(timeMs);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// ignore
}
}
private static void startTick() {
Thread timer = new Thread(new TimerTask());
timer.setName("sentinel-timer-tick-task");
timer.start();
}
static class TimerTask implements Runnable {
@Override
public void run() {
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("Begin to run! Go go go!");
System.out.println("See corresponding metrics.log for accurate statistic data");
long oldTotal = 0;
long oldPass = 0;
long oldBlock = 0;
long oldBizException = 0;
while (!stop) {
sleep(1000);
long globalTotal = total.get();
long oneSecondTotal = globalTotal - oldTotal;
oldTotal = globalTotal;
long globalPass = pass.get();
long oneSecondPass = globalPass - oldPass;
oldPass = globalPass;
long globalBlock = block.get();
long oneSecondBlock = globalBlock - oldBlock;
oldBlock = globalBlock;
long globalBizException = bizException.get();
long oneSecondBizException = globalBizException - oldBizException;
oldBizException = globalBizException;
// System.out.println(TimeUtil.currentTimeMillis() + ", oneSecondTotal:" + oneSecondTotal
// + ", oneSecondPass:" + oneSecondPass
// + ", oneSecondBlock:" + oneSecondBlock
// + ", oneSecondBizException:" + oneSecondBizException);
System.out.print("【秒】倒计时: " + seconds + ", ");
System.out.println((new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss.SSSSSS").format(new Date()))
+ ", 每秒总请求量:" + oneSecondTotal
+ ", 每秒完成量:" + oneSecondPass
+ ", 每秒拒绝量:" + oneSecondBlock
+ ", 每秒业务异常量:" + oneSecondBizException);
if (seconds-- <= 0) {
stop = true;
}
}
long cost = System.currentTimeMillis() - start;
System.out.println("time cost: " + cost + " ms");
System.out.println("total: " + total.get() + ", pass:" + pass.get()
+ ", block:" + block.get() + ", bizException:" + bizException.get());
System.exit(0);
}
}
static class DegradeErrorRatioTask implements Runnable {
@Override
public void run() {
while (true) {
Entry entry = null;
try {
entry = SphU.entry(KEY);
sleep(ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextInt(5, 10));
pass.addAndGet(1);
// Error probability is 45%
if (ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextInt(0, 100) > 55) {
// biz code raise an exception.
throw new RuntimeException("oops");
}
} catch (BlockException e) {
block.addAndGet(1);
sleep(ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextInt(5, 10));
} catch (Throwable t) {
bizException.incrementAndGet();
// It's required to record exception here manually.
Tracer.traceEntry(t, entry);
} finally {
total.addAndGet(1);
if (entry != null) {
entry.exit();
}
}
}
}
}
}
直接使用框架
- Sentinel 控制台
参考官方文档

下载jar以后可以创建一个命令启动文件:startup.cmd
java -Dserver.port=9999 -Dcsp.sentinel.dashboard.server=localhost:9999 -Dproject.name=sentinel-dashboard -jar sentinel-dashboard.jar
然后有这样一个控制台:
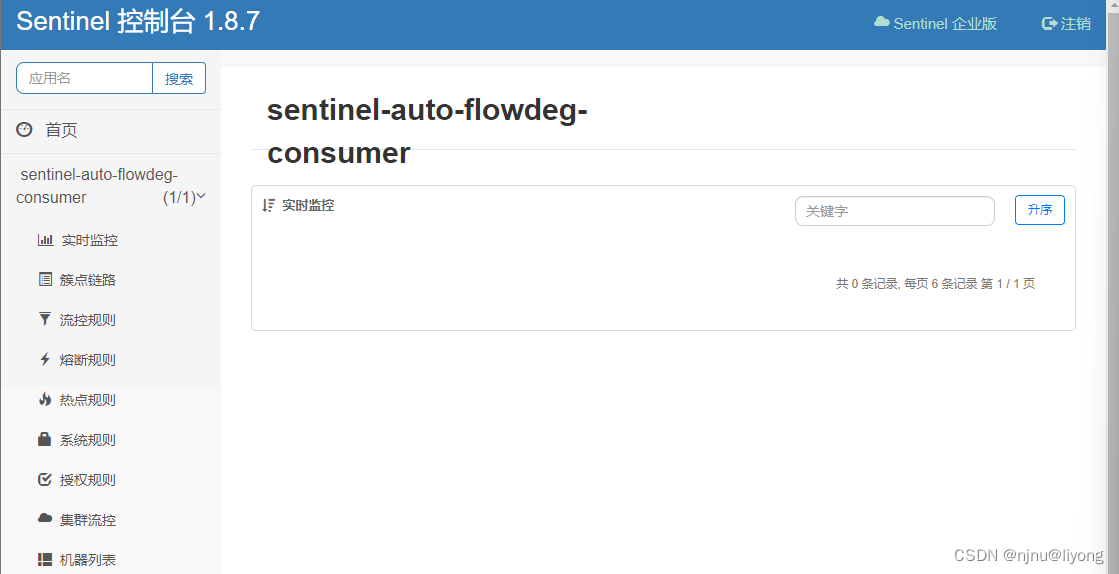
- Sentinel 服务端
父POM
<dependencyManagement>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-alibaba-dependencies</artifactId>
<version>${com.alibaba.cloud.version}</version>
<type>pom</type>
<scope>import</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-dependencies</artifactId>
<version>${com.cloud.version}</version>
<type>pom</type>
<scope>import</scope>
</dependency>
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/com.alibaba.cloud/spring-cloud-starter-dubbo -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-dubbo</artifactId>
<version>${com.dubbo.version}</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</dependencyManagement>
工程POM
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-alibaba-sentinel</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>

接入Nacos
工程pom
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-alibaba-sentinel</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-alibaba-nacos-config</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-alibaba-nacos-discovery</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba.csp</groupId>
<artifactId>sentinel-datasource-nacos</artifactId>
</dependency>
spring:
application:
name: sentinel-online-flowdeg-consumer
cloud:
nacos:
discovery:
server-addr: 111.229.199.181:8848
sentinel:
transport:
port: 8719
dashboard: 127.0.0.1:9999
datasource:
r1:
nacos:
# nacos地址
server-addr: 111.229.199.181:8848
# nacos中配置文件的data-id
data-id: sentinel-online-flowdeg-consumer
# nacos 分组
group-id: DEFAULT_GROUP
data-type: json
# 规则类型 流控
rule-type: flow
namespace: 05b6571e-7791-4af9-9522-f8097beac3d7
server:
port: 9064
nacos 配置
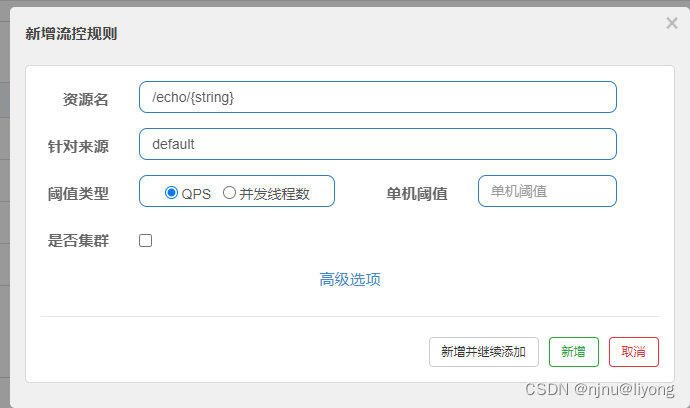
[
{
"limitApp": "default",
"resource": "/echo/{string}",
"grade": 1,
"count": 20,
"strategy": 0,
"refResource": null,
"controlBehavior": 0,
"warmUpPeriodSec": null,
"maxQueueingTimeMs": null,
"clusterMode": false,
"clusterConfig":
{
"flowId": null,
"thresholdType": 0,
"fallbackToLocalWhenFail": true,
"strategy": 0,
"sampleCount": 10,
"windowIntervalMs": 1000,
"resourceTimeout": 2000,
"resourceTimeoutStrategy": 0,
"acquireRefuseStrategy": 0,
"clientOfflineTime": 2000
},
"gmtCreate": "2024-01-05T06:03:30.663+00:00",
"gmtModified": "2024-01-05T06:03:30.663+00:00"
}
]
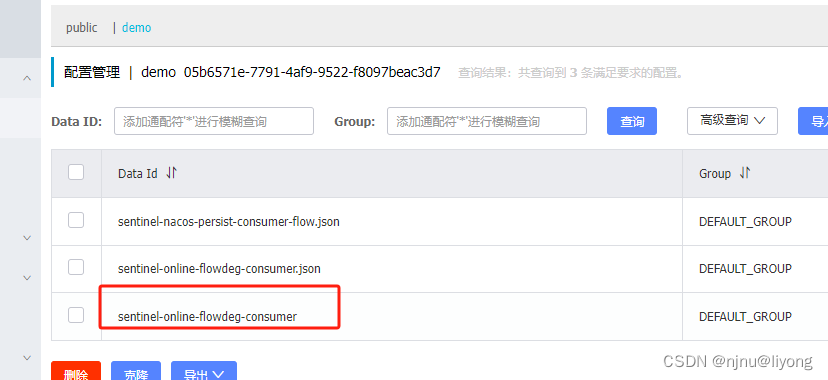
Nacos Sentinel持久化

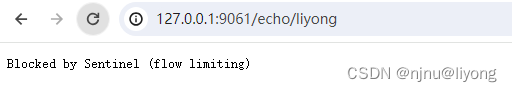
触发一次 Http 请求调用后,发现进入了 com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.init.InitExecutor#doInit 断点
循环逻辑代码块分析
for (InitFunc initFunc : loader) {
RecordLog.info("[InitExecutor] Found init func: " + initFunc.getClass().getCanonicalName());
insertSorted(initList, initFunc);
}
for (OrderWrapper w : initList) {
w.func.init();
RecordLog.info(String.format("[InitExecutor] Executing %s with order %d",
w.func.getClass().getCanonicalName(), w.order));
}
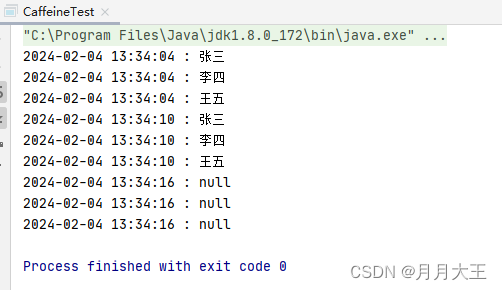
寻找到了 com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.transport.command.SimpleHttpCommandCenter#start 的相关收发数据逻辑
关键代码 1:开启服务端层面的线程
socketReference = serverSocket;
executor.submit(new ServerThread(serverSocket));
success = true;
port = serverSocket.getLocalPort();
关键代码 2:从 ServerSocket 的 accept 方法收数据
socket = this.serverSocket.accept();
setSocketSoTimeout(socket);
HttpEventTask eventTask = new HttpEventTask(socket);
bizExecutor.submit(eventTask);
数据源处理核心代码
if (FLOW_RULE_TYPE.equalsIgnoreCase(type)) {
List<FlowRule> flowRules = JSONArray.parseArray(data, FlowRule.class);
FlowRuleManager.loadRules(flowRules);
if (!writeToDataSource(getFlowDataSource(), flowRules)) {
result = WRITE_DS_FAILURE_MSG;
}
return CommandResponse.ofSuccess(result);
}
基于上面的源码分析
我们写下面两个类,来完成限流配置的持久化。
@Configuration
public class NacosLinkSentinelConfig implements InitializingBean {
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {
}
@PostConstruct
public void init() throws Exception {
NacosWritableDataSource ds = new NacosWritableDataSource(
"sentinel-nacos-persist-consumer-flow.json",
"DEFAULT_GROUP",
"ip",
"05b6571e-7791-4af9-9522-f8097beac3d7"
);
WritableDataSourceRegistry.registerFlowDataSource(ds);
}
}
public class NacosWritableDataSource<T> implements WritableDataSource<T> {
private String dataId;
private String group;
private ConfigService configService;
public NacosWritableDataSource(String dataId,
String group,
String serverAddr,
String namespace) throws Exception {
this.dataId = dataId;
this.group = group;
Properties properties = new Properties();
properties.setProperty(PropertyKeyConst.SERVER_ADDR, serverAddr);
properties.setProperty(PropertyKeyConst.NAMESPACE, namespace);
properties.setProperty(PropertyKeyConst.USERNAME, "nacos");
properties.setProperty(PropertyKeyConst.PASSWORD, "nacos");
configService = NacosFactory.createConfigService(properties);
}
@Override
public void write(T t) throws Exception {
configService.publishConfig(this.dataId, this.group, JSON.toJSONString(t), "json");
}
@Override
public void close() throws Exception {
}
}
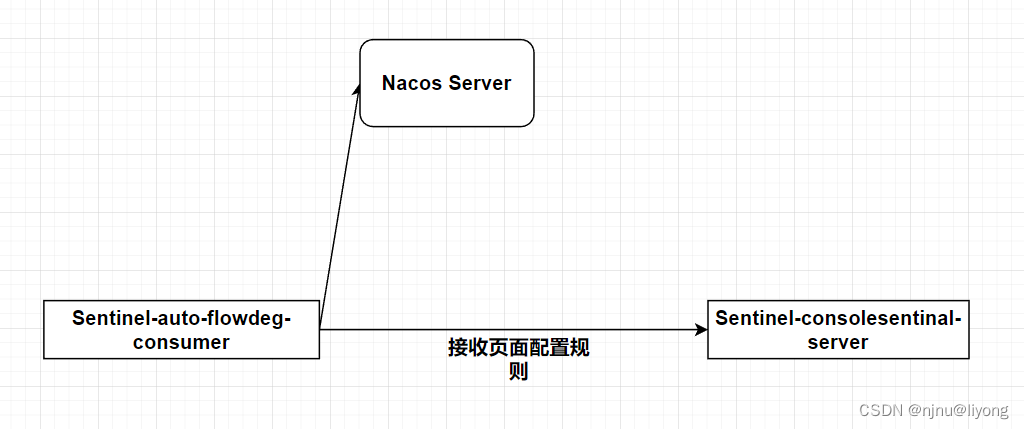
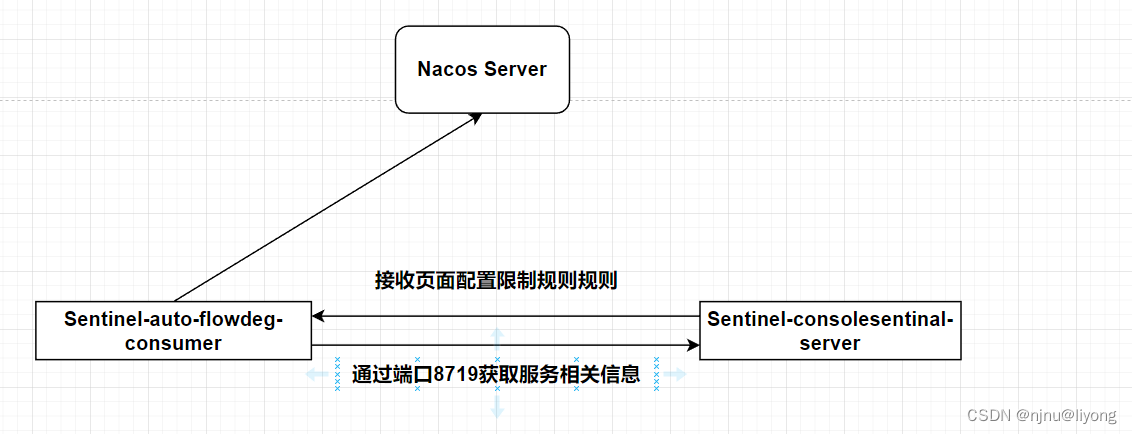
这样我们在界面修改就可以持久化到nacos,这里要注意如果在nacos直接修改,控制台上是不能感知到的。
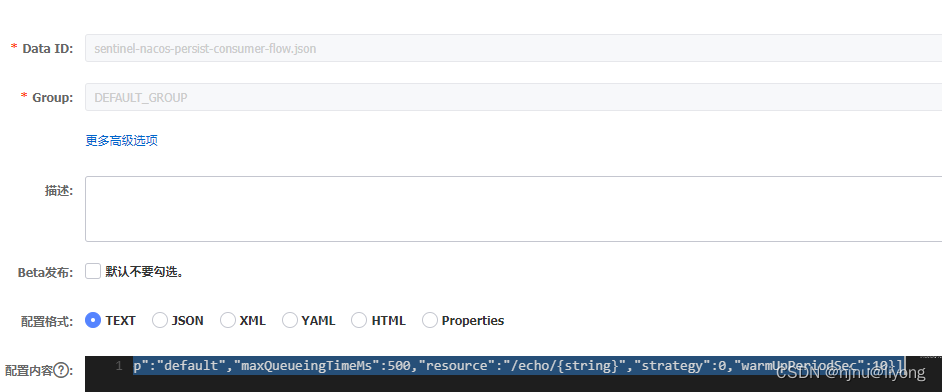
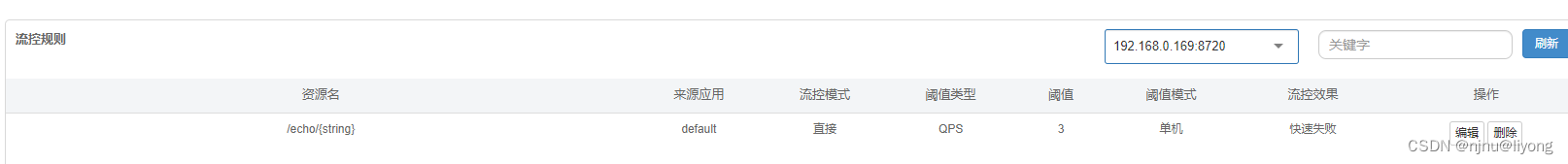
下次重启控制台,Nacos被持久化规则也会进行加载:
原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_43259860/article/details/135385265
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。
如若转载,请注明出处:http://www.7code.cn/show_53344.html
如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系代码007邮箱:suwngjj01@126.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
声明:本站所有文章,如无特殊说明或标注,均为本站原创发布。任何个人或组织,在未征得本站同意时,禁止复制、盗用、采集、发布本站内容到任何网站、书籍等各类媒体平台。如若本站内容侵犯了原著者的合法权益,可联系我们进行处理。