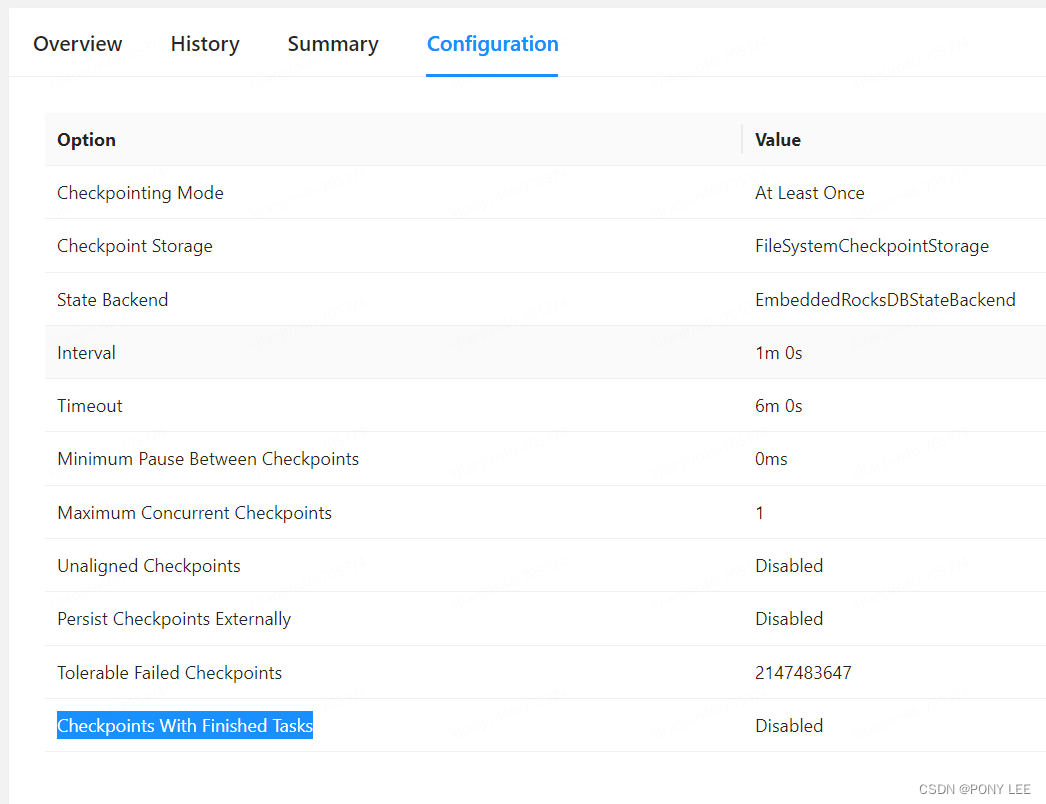
MutableSet怎么能调用indexOf去获取它的插入顺序呢?参考官网Collections overview | Kotlin Documentation![]() https://kotlinlang.org/docs/collections-overview.html#set翻不了墙的看下面 (MutableSet的默认实现是LinkedHashSet,LinkedHashSet是有保留元素插入的顺序)
https://kotlinlang.org/docs/collections-overview.html#set翻不了墙的看下面 (MutableSet的默认实现是LinkedHashSet,LinkedHashSet是有保留元素插入的顺序)
Set
Set<T> stores unique elements; their order is generally undefined. null elements are unique as well: a Set can contain only one null. Two sets are equal if they have the same size, and for each element of a set there is an equal element in the other set.()
val numbers = setOf(1, 2, 3, 4)
println("Number of elements: ${numbers.size}")
if (numbers.contains(1)) println("1 is in the set")
val numbersBackwards = setOf(4, 3, 2, 1)
println("The sets are equal: ${numbers == numbersBackwards}")
Number of elements: 4
1 is in the set
The sets are equal: trueMutableSet is a Set with write operations from MutableCollection.
The default implementation of MutableSet – LinkedHashSet – preserves the order of elements insertion. Hence, the functions that rely on the order, such as first() or last(), return predictable results on such sets.
val numbers = setOf(1, 2, 3, 4) // LinkedHashSet is the default implementation
val numbersBackwards = setOf(4, 3, 2, 1)
println(numbers.first() == numbersBackwards.first())
println(numbers.first() == numbersBackwards.last())
println(numbersBackwards.indexOf(2))
false
true
2An alternative implementation – HashSet – says nothing about the elements order, so calling such functions on it returns unpredictable results. However, HashSet requires less memory to store the same number of elements.
原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_50675668/article/details/135403859
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。
如若转载,请注明出处:http://www.7code.cn/show_53796.html
如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系代码007邮箱:suwngjj01@126.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!