本文介绍: ArrayBlockingQueue 实际实现是一个环形数组,并且保护了线程安全,那么是如何保证线程安全的?ArrayBlockingQueue 实际实现是一个环形数组 先看下它咋实现的。offer如果队列满了会抛弃掉,offer方法如果满了会锁住挂起等到加入为止。先看下里面的几个参数是干嘛的。环形数组示例图片嘛,大概这样。环形数组怎么实现的?
ArrayBlockingQueue 实际实现是一个环形数组,并且保护了线程安全,那么是如何保证线程安全的?
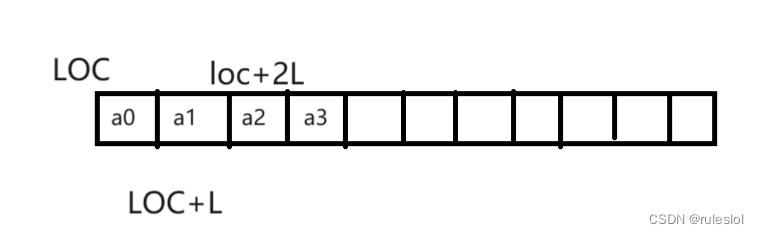
环形数组怎么实现的?
先看下里面的几个参数是干嘛的
ArrayBlockingQueue 实际实现是一个环形数组 先看下它咋实现的
offer如果队列满了会抛弃掉,offer方法如果满了会锁住挂起等到加入为止
环形数组示例图片嘛,大概这样
声明:本站所有文章,如无特殊说明或标注,均为本站原创发布。任何个人或组织,在未征得本站同意时,禁止复制、盗用、采集、发布本站内容到任何网站、书籍等各类媒体平台。如若本站内容侵犯了原著者的合法权益,可联系我们进行处理。