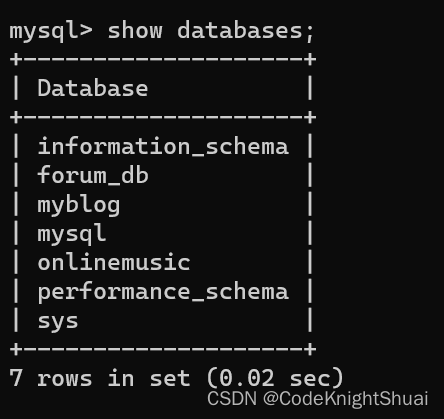
在项目中我们时常需要写SQL语句,或简单的使用注解直接开发,或使用XML进行动态SQL之类的相对困难的SQL,并在IDEA中操控我们的SQL,但网上大都图方便或者觉得太简单了,完全没一个涵盖两个方面的讲解。
单表:
DDL(表操作):
创表语句:

约束:

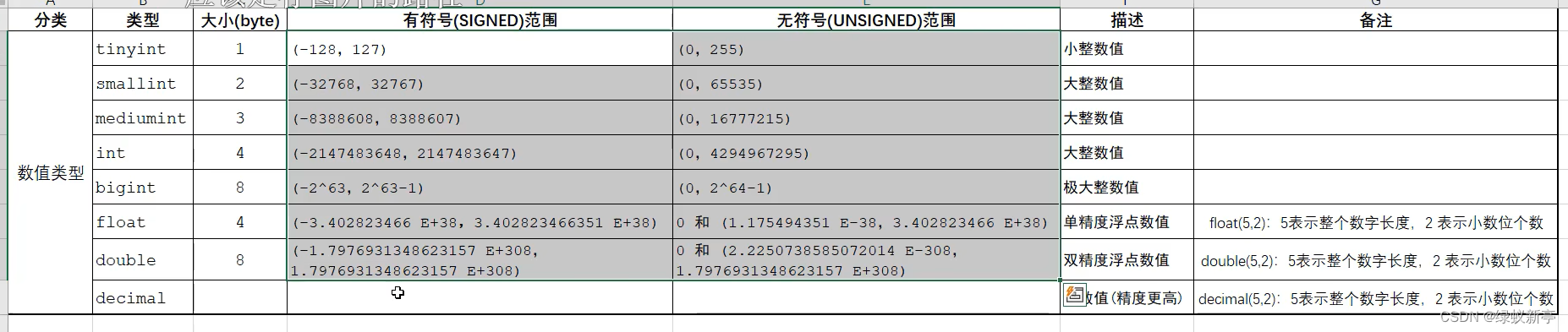
常见的数据类型:


for example(例子):
create table address_book
(
id bigint auto_increment comment '主键'
primary key,
user_id bigint not null comment '用户id',
consignee varchar(50) null comment '收货人',
sex varchar(2) null comment '性别',
phone varchar(11) not null comment '手机号',
province_code varchar(12) charset utf8mb4 null comment '省级区划编号',
province_name varchar(32) charset utf8mb4 null comment '省级名称',
city_code varchar(12) charset utf8mb4 null comment '市级区划编号',
city_name varchar(32) charset utf8mb4 null comment '市级名称',
district_code varchar(12) charset utf8mb4 null comment '区级区划编号',
district_name varchar(32) charset utf8mb4 null comment '区级名称',
detail varchar(200) charset utf8mb4 null comment '详细地址',
label varchar(100) charset utf8mb4 null comment '标签',
is_default tinyint(1) default 0 not null comment '默认 0 否 1是'
)
comment '地址簿' collate = utf8mb3_bin;查询语句:

修改语句:
 那么IDEA中是如何操作DDL语句的呢?
那么IDEA中是如何操作DDL语句的呢? 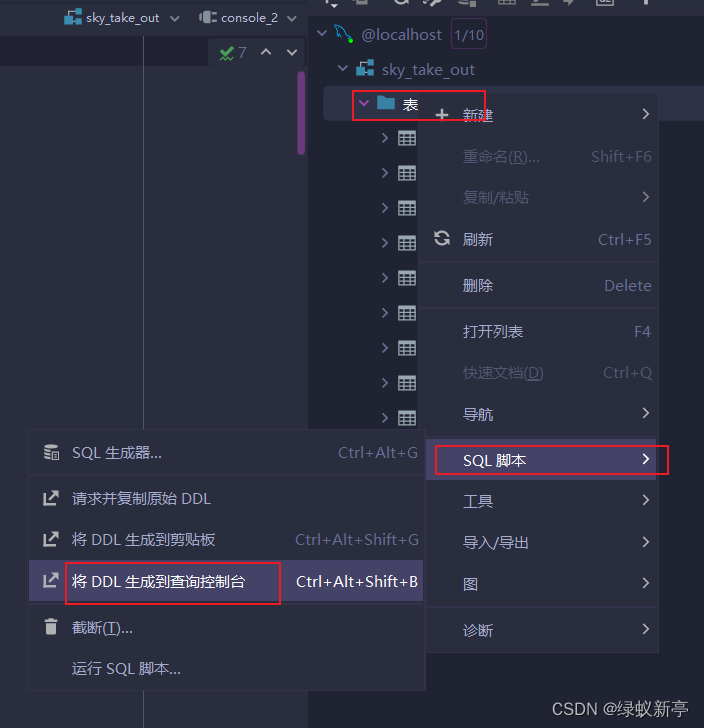
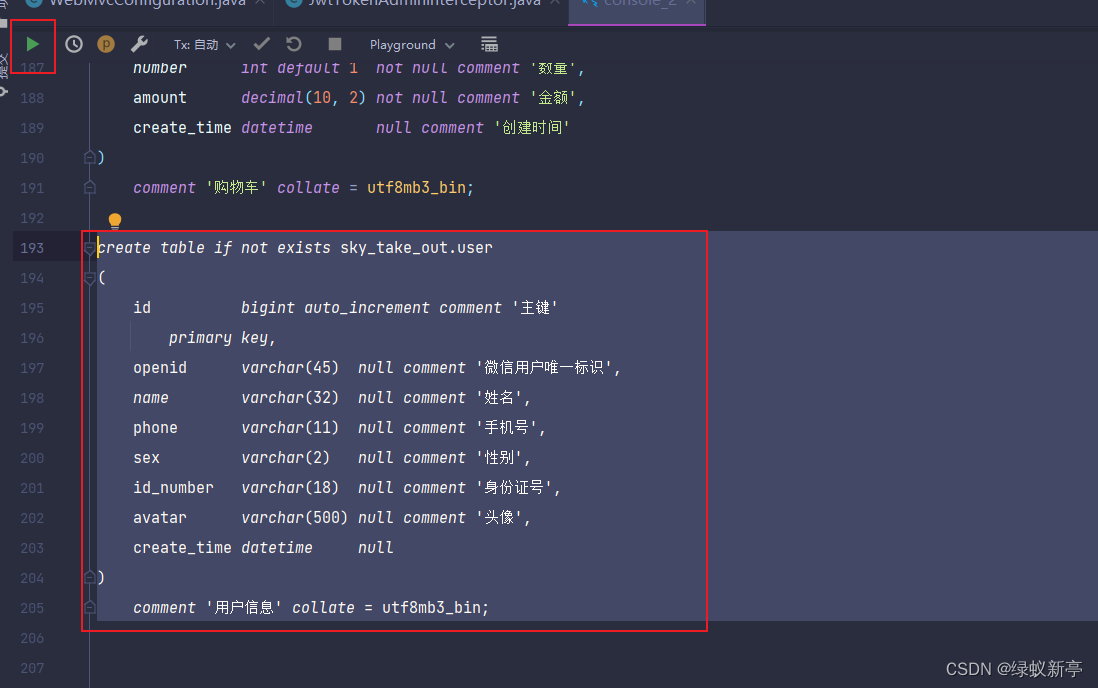 需要特别说的是,IDEA中想执行哪部分代码,就左键选中代码块变色,再点击绿色的执行按钮
需要特别说的是,IDEA中想执行哪部分代码,就左键选中代码块变色,再点击绿色的执行按钮
DML :
insert

@Insert("insert into category(type, name, sort, status, create_time, update_time, create_user, update_user)" +
" VALUES" +
" (#{type}, #{name}, #{sort}, #{status}, #{createTime}, #{updateTime}, #{createUser}, #{updateUser})")<insert id="insertBacth">
insert into dish_flavor (dish_id, name, value)
value
<foreach collection="flavors" item="df" separator=",">
(#{df.dishId},#{df.name},#{df.value})
</foreach>
</insert>Update

<update id="update">
# yml中配置文件加的开启驼峰命名,只是java中Employee 类的 成员变量的驼峰命名 可以对应 数据库中的 参数名
update employee
<set>
<if test="name != null ">
name = #{name},
</if>
<if test="username != null ">
username = #{username},
</if>
<if test="password != null ">
password = #{password},
</if>
<if test="phone != null">
phone =#{phone},
</if>
<if test="sex != null ">
sex = #{sex},
</if>
<if test="idNumber != null ">
id_Number = #{idNumber},
</if>
<if test="status != null ">
status = #{status},
</if>
<if test="updateTime != null">
update_Time = #{updateTime},
</if>
<if test="updateUser != null ">
update_User = #{updateUser},
</if>
</set>
where id = #{id}
</update>项目里一般都是动态SQL编辑数据,简单的update直接使用MP,根本没必要写
Delete

@Delete("delete from dish_flavor where dish_id = #{dishid}")
void deleteByDishId(Long dishid);<delete id="deleteByIds">
delete from dish_flavor where dish_id in
<foreach collection="dishIds" item="dishId" open="(" close=")" separator=",">
#{dishId}
</foreach>
</delete>DQL:

基本查询:

注意:代码中*是通配符,即查询所有
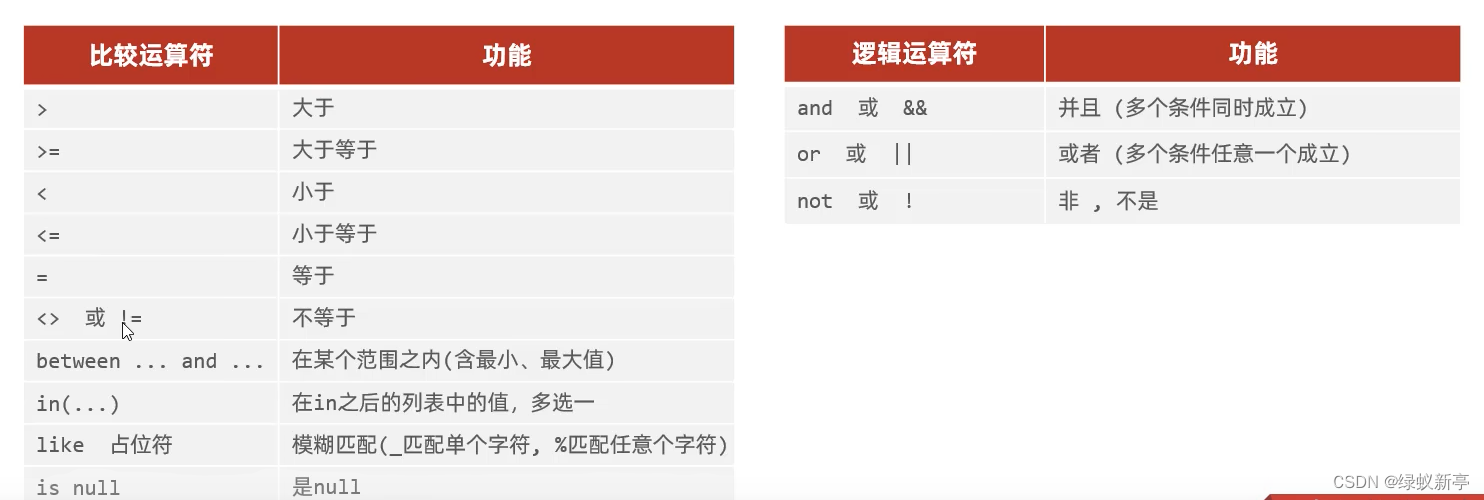
条件查询:
聚合函数:

分组查询:

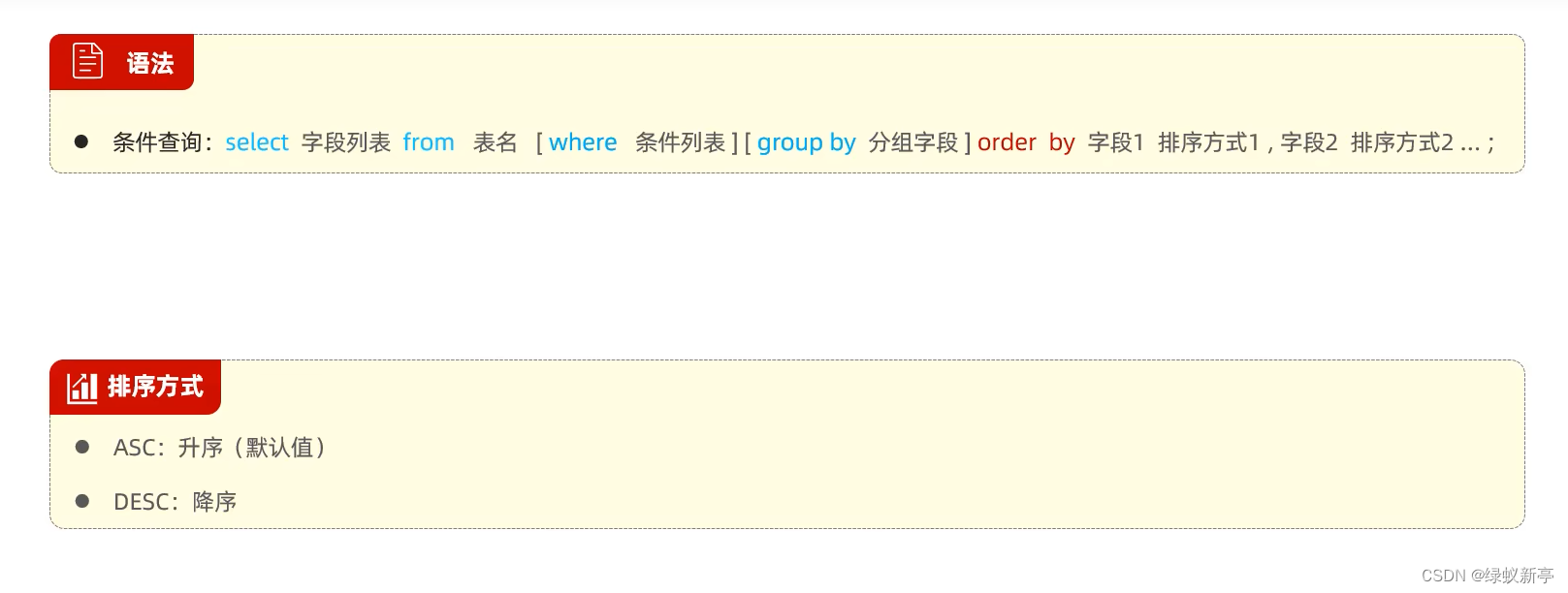
排序查询:
分页查询:

但分页查询,不同于其他的DQL查询方式,它是项目较为重要的部分,我们一般会使用PageHelper这个插件,来简化我们的代码,以下是
分页查询的三点重要的步骤:
First:
先pom.xml导入maven对应依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>com.github.pagehelper</groupId>
<artifactId>pagehelper-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
</dependency>Second:
在impl中写模板式代码
public PageResult pageQuery( EmployeePageQueryDTO employeePageQueryDTO) {
// select * from employee limit 0,10
// 开始分页查询
PageHelper.startPage(employeePageQueryDTO.getPage(),employeePageQueryDTO.getPageSize());
// 这个是强制要求名字叫”page“,不能改,所以这需要创建对象
Page<Employee> page = employeeMapper.pageQuery(employeePageQueryDTO);
// long total1 = employeeMapper.pageQuery(employeePageQueryDTO).getTotal();
// List<Employee> records1 = employeeMapper.pageQuery(employeePageQueryDTO).getResult();
long total = page.getTotal();
List<Employee> records = page.getResult();
return new PageResult(total,records);
}Third:
<select id="pageQuery" resultType="com.sky.entity.Employee">
select * from employee
<where>
<if test="name != null and name != ''">
and name like concat('%',#{name},'%')
</if>
</where>
order by create_time desc
</select>
多表:
分为逻辑外键和物理外键,见名知意,前者并没有物理层面的约束,后者则是有着物理层面的约束
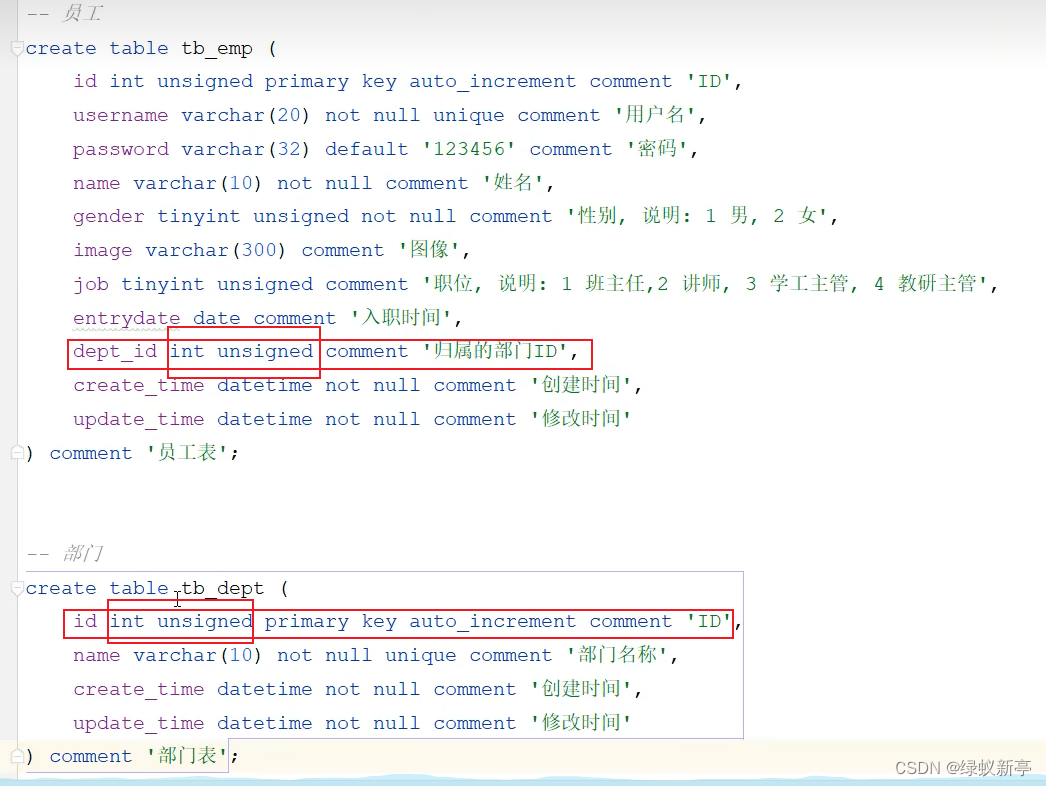
以上是一份逻辑关联的SQL语句,这应该是企业最常用的方式
但,此方法也有缺点,若你没考虑周全,可能会误操作,所以物理外键可能更利于你保持数据完整性和同一性。
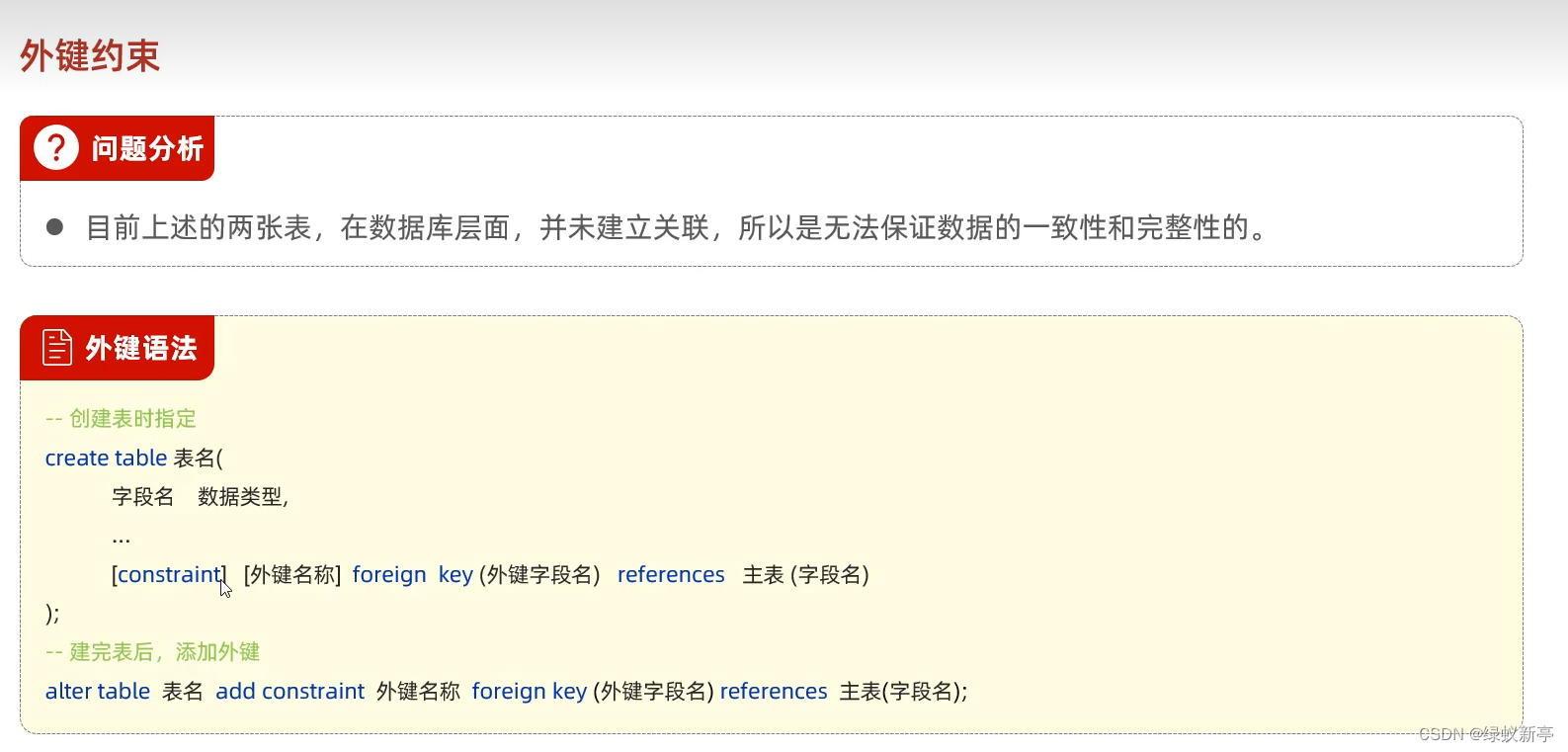
IDEA修改方法:
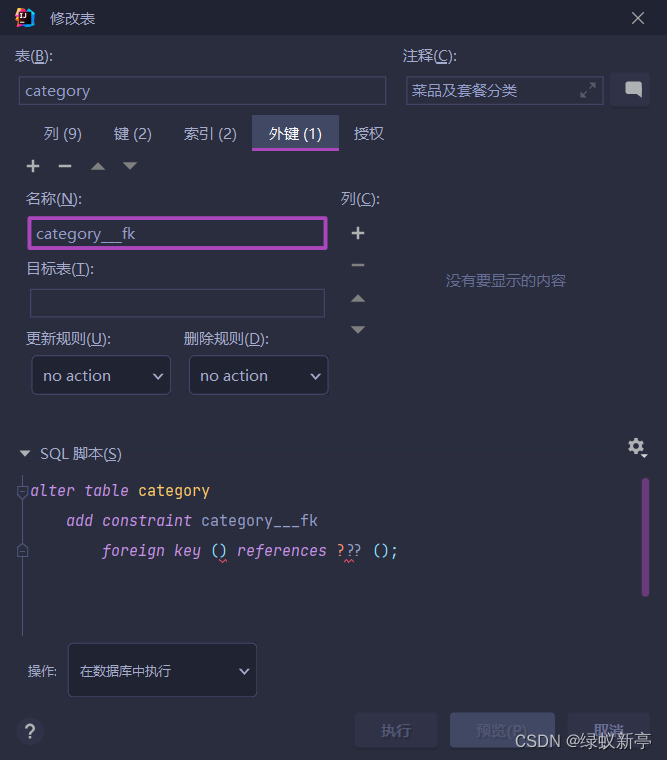
根据名称,进行添加,修改外键
多表查询:
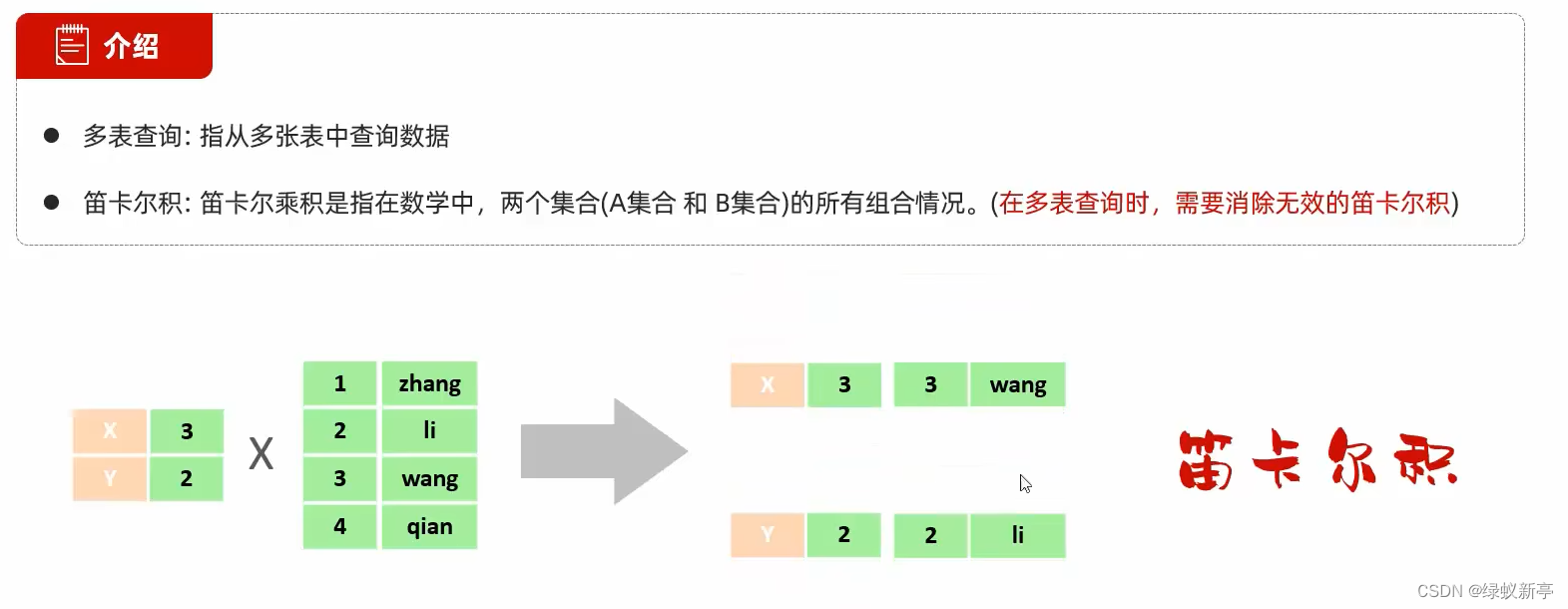
先简单介绍一下笛卡尔积,两个集合一个集合数据量为2,另一个数据量为4,两个相乘则为8条,这就是笛卡尔积,
而我们肯定不需要冗余数据,所以需要消除冗余项
分类:

内连接就是取并集,外连接就是取AorB,子查询则是查询蓝色or橘色部分
内连接:
外连接:

子查询:

总结代码:
<select id="pageQuery" resultType="com.sky.vo.DishVO">
select d.* , c.name as category_name from dish d left outer join category c on d.category_id = c.id
<where>
<if test = "name!=null">
and d.name like concat('%',#{name},'%')
</if>
<if test = "categoryId != null">
and d.category_id = #{categoryId}
</if>
<if test = "status != null">
and d.status = #{status}
</if>
</where>
order by d.create_time desc
</select>事务:


注意:
● 默认MySQL的事务是自动提交的,也就是说,当执行一条DML语句, MySQL会 立即隐式的提交事务。

索引:
当数据库的表中数据量很大时,DML等SQL语句会有很长的时耗。
索引(index)是帮助数据库高效获取数据的数据结构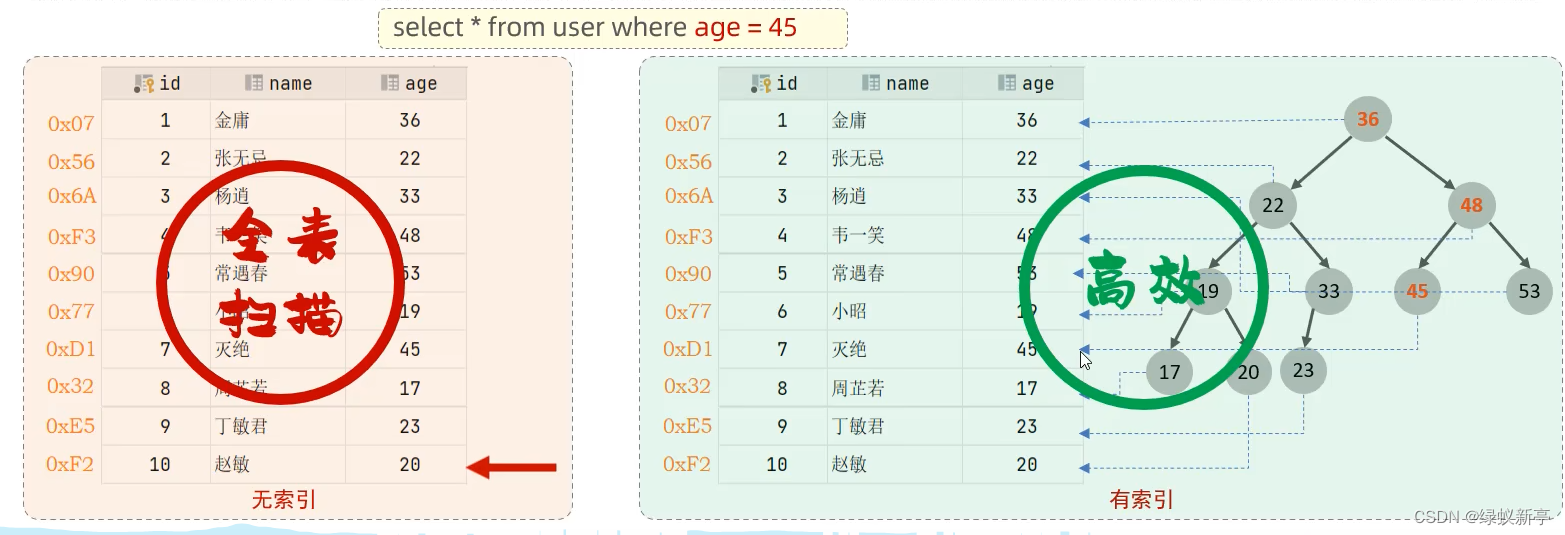
。
..
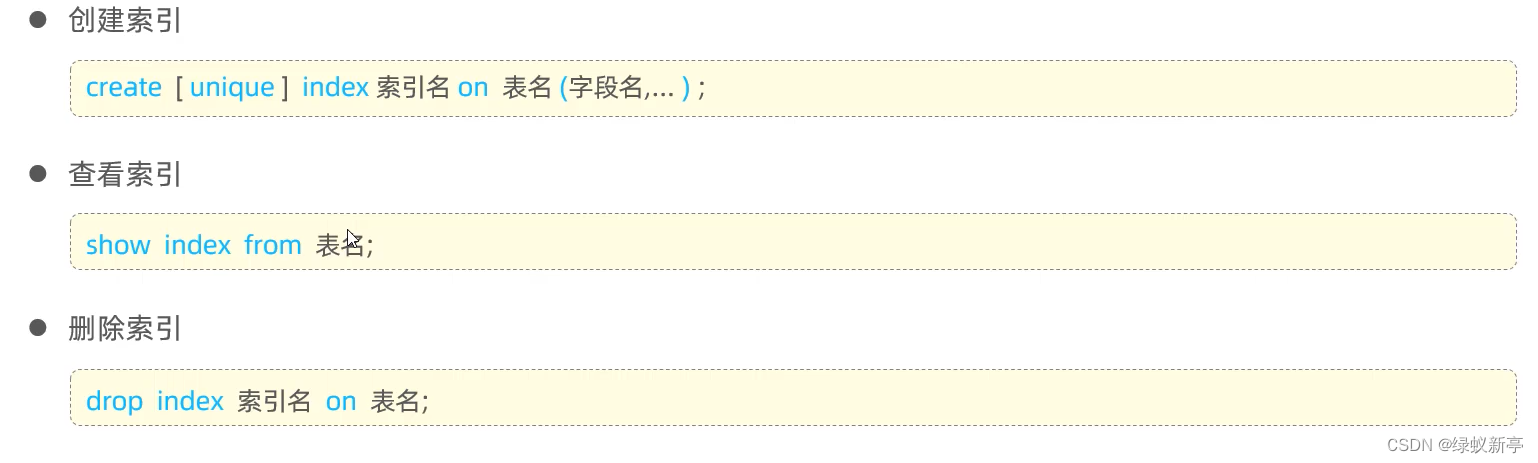
语法:
原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/lvyixinniang_/article/details/135460425
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。
如若转载,请注明出处:http://www.7code.cn/show_54162.html
如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系代码007邮箱:suwngjj01@126.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!