Node.js Stream(流)(三)
1、管道流
管道提供了一个数据从输出流到输入流的机制。
我们使用管道可以从一个流中获取数据并将数据传递到另外一个流中。
举例:复制文件
我们把文件比作装水的桶,而水就是文件里的内容,我们用一根管子 (pipe) 连接两个桶使得水从一个桶流入另一个桶,这样就慢慢的实现了大文件的复制过程。
var fs = require("fs");
// 创建一个可读流
var readerStream = fs.createReadStream('input.txt');
// 创建一个可写流
var writerStream = fs.createWriteStream('output.txt');
// 管道读写操作
// 读取 input.txt 文件内容,并将内容写入到output.txt 文件中
readerStream.pipe(writerStream);2、链式流
链式是通过连接输出流到另外一个流并创建多个流操作链的机制。
pipe() 方法的返回值是目标流。
var fs = require("fs");
var zlib = require('zlib');
// 压缩 input.txt 文件为 input.txt.gz
fs.createReadStream('input.txt').pipe(zlib.createGzip()).pipe(fs.createWriteStream('input.txt.gz')
);var fs = require("fs");
var zlib = require('zlib');
// 解压 input.txt.gz 文件为 input.txt
fs.createReadStream('input.txt.gz').pipe(zlib.createGunzip()).pipe(fs.createWriteStream('input.txt'));Node.js http模块

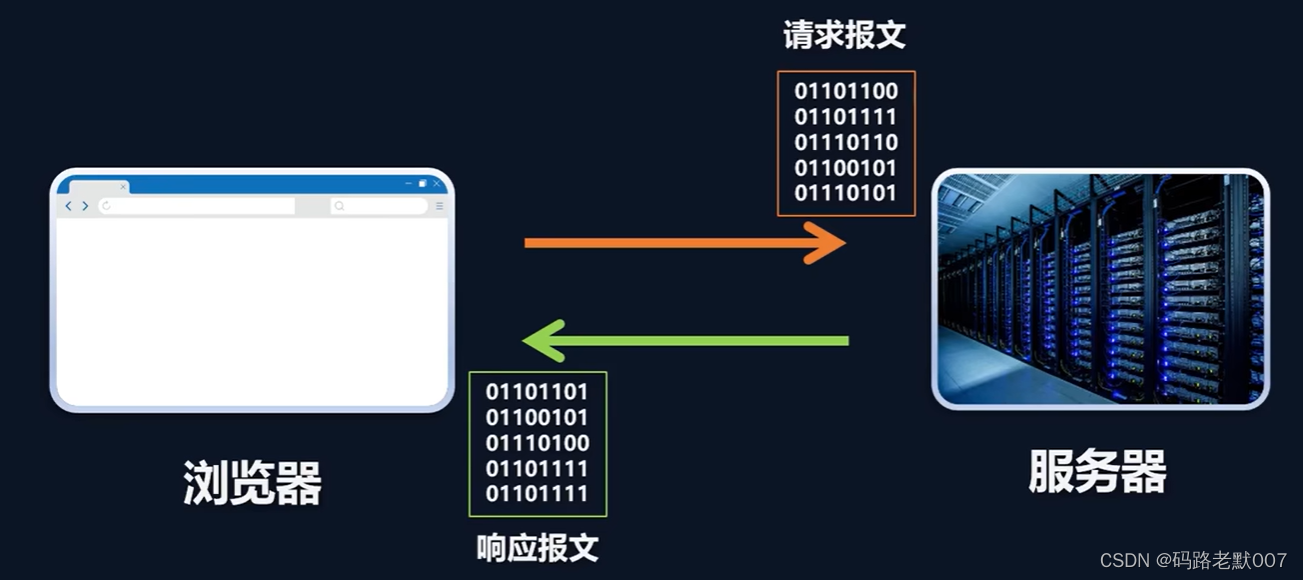
HTTP 核心模块是 Node.js 网络的关键模块。
使用该模块可以创建web服务器。
const http = require('http') //返回 http.Server 类的新实例
//req是个可读流
//res是个可写流
const server=http.createServer( function (req, res) {
res.writeHead(200, { 'Content-Type': 'text/plain; charset=utf-8' });
res.write('服务器响应了,这是响应内容')
res.end()
})server.listen('3030',function(){
console.log('服务器已做好准备,正在监听3030端口')
})Node.js GET/POST请求(一)

<!-- test.html -->
<form id="form1" action="http://localhost:3030" method="post">
姓名:<input type="text" name="name"><br />
年龄:<input type="text" name="age"><br />
<input type="submit" value="提交"
/>
</form>//test.js
const http=require('http')
const querystring = require('querystring')
const server = http.createServer((req, res) => {
var bodyStr = ''
req.on('data', function (chunk) {
bodyStr += chunk
})
req.on('end', function () {
const body = querystring.parse(bodyStr);
// 设置响应头部信息及编码
res.writeHead(200, {'Content-Type': 'text/html; charset=utf-8'});
if(body.name && body.age) {
res.write("姓名:" + body.name);
res.write("<br>");
res.write("年龄:" + body.age);
}
res.end()
});
})
server.listen('3030',function(){
console.log('服务器正在监听3030端口')
})Node.js GET/POST请求(二)

//浏览器访问地址
http://localhost:3030/?name=%27baizhan%27&&age=10const http = require('http')
const url = require('url')
const server = http.createServer(function (req, res) {
res.writeHead(200, { 'Content-Type': 'text/plain; charset=utf-8' });
//使用url.parse将路径里的参数解析出来
const { query = {} } = url.parse(req.url, true)
for ([key, value] of Object.entries(query)) {
res.write(key + ':' + value)
}
res.end();
})
server.listen('3030', function () {
console.log('服务器正在监听3030端口')
})Node.js 路由

我们要为路由提供请求的URL和其他需要的GET及POST参数,随后路由需要根据这些数据来执行相应的代码。
const http = require('http')
const url = require('url')
const server = http.createServer(function (req, res) {
//获取请求路径
const pathname = url.parse(req.url).pathname;
if (pathname == '/') {
res.end('hello')
}else if (pathname == '/getList') {
res.writeHead(200, { 'Content-Type': 'application/json; charset=utf-8' });
res.write(JSON.stringify({ recrods: [{ name: 'fyx' }] }))
res.end()
}else{
res.writeHead(200, { 'Content-Type': 'text/plain; charset=utf-8' });
res.end('默认值')
}
})
server.listen('3030', function () {
console.log('服务器正在监听3030端口')
})整理
//router.js
module.exports=(pathname,res)=>{
if (pathname == '/') {
res.end('hello')
}else if (pathname == '/getList') {
res.writeHead(200, { 'Content-Type': 'application/json; charset=utf-8' });
res.write(JSON.stringify({ recrods: [{ name: 'fyx' }] }))
res.end()
}else{
res.end('默认值')
}
}//test.js
const http = require('http')
const url = require('url')
const router = require('./router')
const server = http.createServer(function (req, res) {
const pathname = url.parse(req.url).pathname;
router(pathname,res)
})
server.listen('3030', function () {
console.log('服务器正在监听3030端口')
})Node.js 创建客户端

//client.js
var http = require('http');
// 用于请求的选项
var options = {
host: 'localhost',
port: '3030',
path: '/'
};
// 处理响应的回调函数
var callback = function(response){
// 不断更新数据
var body = '';
response.on('data', function(data) {
body += data;
});
response.on('end', function() {
// 数据接收完成
console.log(body);
});
}
// 向服务端发送请求
var req = http.request(options, callback);
req.end();//server.js
const http=require('http')
const url=require('url')
const server = http.createServer(function (req, res) {
const {pathname}=url.parse(req.url)
if (pathname == '/') {
res.write('hello')
res.write('xiaotong')
res.end()
}
})
server.listen('3030', function () {
console.log('服务器正在监听3030端口')
})
Node.js 作为中间层

//test.js
const http = require('http')
const url = require('url')
const server = http.createServer(function (req, res) {
const pathname = url.parse(req.url).pathname;
// 用于请求的选项
var options = {
host: 'localhost',
port: '8080',
path: pathname,
method:req.method,
headers:{token:'xxxxx'}
};
// 处理响应的回调函数
var callback = function (response) {
const {headers= {},statusCode}=response
res.writeHead(statusCode, {...headers})
response.pipe(res)
}
// 向服务端发送请求
var req = http.request(options, callback);
req.end();
})
server.listen('3030', function () {
console.log('服务器正在监听3030端口')
})
//server.js
const http=require('http')
const server=http.createServer((req,res)=>{
const {headers={}}=req
res.writeHead(200,{'Content-Type': 'application/json; charset=utf-8'})
if(headers.token){
res.end(JSON.stringify({code:0,message:'成功',data:[]}))
}else{
res.end(JSON.stringify({code:-1,message:'您还没有权限'}))
}
})
server.listen('8080',function(){
console.log('服务器正在监听8080端口')
}) Node.js 文件系统模块(一)

fs 模块提供了许多非常实用的函数来访问文件系统并与文件系统进行交互。
文件系统(fs 模块)模块中的方法均有异步和同步版本,例如读取文件内容的函数有异步的 fs.readFile() 和同步的 fs.readFileSync() 。
var fs = require("fs");
// 异步读取
fs.readFile('input.txt', function (err, data) {
if (err) {
return console.error(err);
}
console.log("异步读取: " + data.toString());
});
// 同步读取
var data = fs.readFileSync('input.txt');
console.log("同步读取: " + data.toString());
console.log("程序执行完毕。");原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/m0_58719994/article/details/134662801
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。
如若转载,请注明出处:http://www.7code.cn/show_5451.html
如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系代码007邮箱:suwngjj01@126.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
声明:本站所有文章,如无特殊说明或标注,均为本站原创发布。任何个人或组织,在未征得本站同意时,禁止复制、盗用、采集、发布本站内容到任何网站、书籍等各类媒体平台。如若本站内容侵犯了原著者的合法权益,可联系我们进行处理。