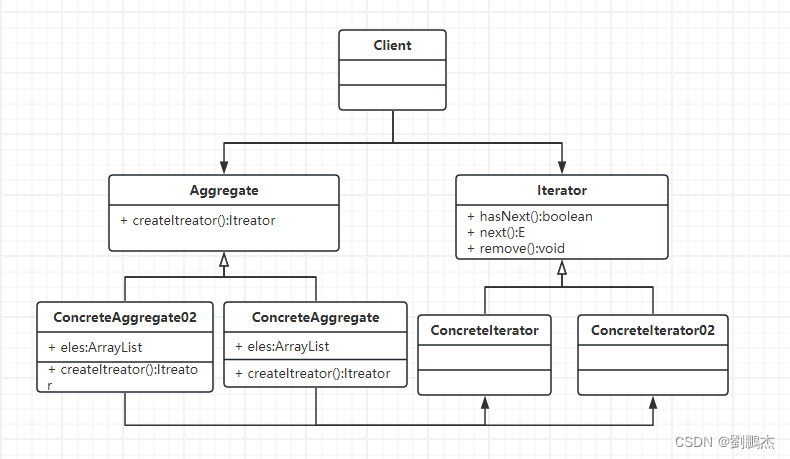
1:完成以下填空:
Collection 接口的特点是 存放list与set共性内容 没有直接实现类 没有明确的存储特点要求 ;
2:List 接口的特点是元素 有 (有|无)顺序, 可 (可以|不可以)重复;
Set 接口的特点是元素 无 (有|无)顺序,不可 (可以|不可以)重复;
3:(Set)关于Set 集合描述正确的是()
A.可以利用Set 创建集合对象,存储多个对象
B.可以利用下标操作集合中的数据
C.Set 集合中所有方法继承于父接口Collection
D.以上描述都不正确
4:(List、Set)仔细阅读以下程序,关于程序描述正确的是()

A.编译不通过 B. 编译通过,运行时异常
C. 编译运行都正常,输出 3 D. 编译运行都正常,输出 4
5:(Set)仔细阅读以下代码,将不正确的代地方进行改正。

hashCode里面的salary 前面加强转(int)
Equals 里面
Public boolean equals (Object o){
If(this == o) return true;
If(this.getClass != o.getClass || o == null) return false;
Worker w = (Worker)o;
return name.equals(o.Name) && salary == w.salary && age ==w.age;
}
将第三个add的0删掉,set的集合不能用下标赋值
6:(Set)编程:创建一个商品(Product)类,属性:商品名,商品单价,商品的数量,商品产地。
①创建多个商品对象,存储在 Set 集合中,集合中不能出现重复商品,商品名相同即为重复,在 Product 类中添加必要的方法;
②显示所有的商品信息;
③打印输出商品价格 > 1000 的所有商品信息;
④打印售空的商品的信息;
⑤打印输出商品产地为”北京”的商品信息;
⑥输入一个商品名,查询出此类商品的信息,如果不存在,则打印商品”商场无此商品!!!”
⑦输入一个价格段,查询出集合中所有在这个价格区间的所有商品信息。
public class Product {
private String goosName;
private double price;
private int quantity;//数量
private String area;
public Product() {
}
public Product(String goosName, double price, int quantity, String area) {
this.goosName = goosName;
this.price = price;
this.quantity = quantity;
this.area = area;
}
public String getGoosName() {
return goosName;
}
public void setGoosName(String goosName) {
if(!this.goosName.equals(goosName)){
this.goosName = goosName;
}
}
public double getPrice() {
return price;
}
public void setPrice(double price) {
this.price = price;
}
public int getQuantity() {
return quantity;
}
public void setQuantity(int quantity) {
this.quantity = quantity;
}
public String getArea() {
return area;
}
public void setArea(String area) {
this.area = area;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Produtor{" +
"goosName='" + goosName + ''' +
", price=" + price +
", quantity=" + quantity +
", area='" + area + ''' +
'}';
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (this == o) return true;
if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) return false;
Product product = (Product) o;
return goosName.equals(product.getGoosName());
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return goosName.hashCode();
}
}
public class zy_6 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Set<Product> set = new HashSet<>();
set.add(new Product("小米",1000,100,"北京"));
set.add(new Product("小米",2000,99,"beijing"));
set.add(new Product("红米",3000,100,"杭州"));
set.add(new Product("锤子",4000,0,"苏州"));
set.forEach(p -> System.out.println(p));
for (Product product : set) {
if(product.getPrice()>1000){
System.out.println(product);
}
}
for (Product product : set) {
if(product.getQuantity() ==0){
System.out.println(product);
}
}
for (Product product : set) {
if(product.getArea().equals("北京")){
System.out.println(product);
}
}
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("输入要查找的手机品牌");
String name = sc.next();
boolean flag = false;
for (Product product : set) {
if(product.getGoosName().equals(name)){
System.out.println(product);
flag = true;
}
}
if(!flag){
System.out.println("商场无此商品!!!");
}
System.out.println("7======================");
System.out.println("输入要查找的价格区间例如:1000-2000");
String price = sc.next();
String[] split = price.split("-");
int price1 = Integer.parseInt(split[0]);
int price2 = Integer.parseInt(split[1]);
boolean flag2 = false;
for (Product product : set) {
double d = product.getPrice();
if(d > price1 && d<price2){
System.out.println(product);
flag2 = true;
}
}
if(!flag2){
System.out.println("商场没有这个区间的商品!!!");
}
}
}
7;(Set)编程:随机产生 10 个 0~50 之间的整数,存储在集合中,要求集合中的数据不能重复。知识补充: Random rd= new Random(); //Random 位于 java.util 包中
int n = rd.nextInt(n); //0~n -1之间的整数
public class zy_7 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Set<Integer> set = new HashSet<>();
Random r = new Random();
while (set.size()<50){
int n = r.nextInt(50+1);
set.add(n);
}
System.out.println(set.size());
}
}
8;(Set)编程:键盘输入一个字符串,利用集合去除其重复字符,打印输出最终不同的字符。
package com.by.homework4;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.LinkedHashSet;
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.util.Set;
public class Test8 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入字符串");
String str=sc.next();
String []strs=str.split("");
Set<String> set=new LinkedHashSet<>();
for (int i = 0; i < strs.length; i++) {
set.add(strs[i]);
}
set.forEach(s -> System.out.print(s));
}
}
9:使用Set集合完成List练习题的最后一题
public class zy_9 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Set<Student> set = new HashSet<>();
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
while (true){
System.out.println("输入学生信息,格式为:张三/18/男/99.5 输入:0退出");
String s = sc.next();
if(s.equals("0")){
break;
}
String[] ss = s.split("/");
Double score = ss[3].equals("null") ? null : Double.valueOf(ss[3]);
set.add(new Student(ss[0],Integer.parseInt(ss[1]),ss[2],score));
}
System.out.println("1===================");
for (Student s : set) {
if(s.getScore() != null && s.getScore()>=80){
System.out.println(s);
}
}
System.out.println("2===================");
for (Student s : set) {
if(s.getScore() == null){
System.out.println("没有参加考试的学生:"+s);
}
}
System.out.println("5===================");
Set<Student> set2 = new TreeSet<>(new Comparator<Student>() {
@Override
public int compare(Student o1, Student o2) {
if(o1.getScore()<o2.getScore()){
return 1;
}else if(o1.getScore()>o2.getScore()){
return -1;
}else {
return 0;
}
}
});
set2.addAll(set);
for (Student student : set2) {
System.out.println(student);
}
}
}
原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/zhzjn/article/details/135453353
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。
如若转载,请注明出处:http://www.7code.cn/show_55456.html
如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系代码007邮箱:suwngjj01@126.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!