接下来,学习一个全新的知识,叫做正则表达式。正则表达式其实是由一些特殊的符号组成的,它代表的是某种规则。
正则表达式的作用1:用来校验字符串数据是否合法
正则表达式的作用2:可以从一段文本中查找满足要求的内容

5.1 正则表达式初体验
现在,我们就以QQ号码为例,来体验一下正则表达式的用法。注意:现在仅仅只是体验而已,我们还没有讲正则表达式的具体写法。
- 不使用正则表达式,校验QQ号码代码是这样的
public static boolean checkQQ(String qq){
// 1、判断qq号码是否为null
if(qq == null || qq.startsWith("0") || qq.length() < 6 || qq.length() > 20){
return false;
}
// 2、qq至少是不是null,不是以0开头的,满足6-20之间的长度。
// 判断qq号码中是否都是数字。
// qq = 2514ghd234
for (int i = 0; i < qq.length(); i++) {
// 根据索引提取当前位置处的字符。
char ch = qq.charAt(i);
// 判断ch记住的字符,如果不是数字,qq号码不合法。
if(ch < '0' || ch > '9'){
return false;
}
}
// 3、说明qq号码肯定是合法
return true;
}
- 用正则表达式代码是这样的
public static boolean checkQQ1(String qq){
return qq != null && qq.matches("[1-9]\d{5,19}");
}
我们发现,使用正则表达式,大大简化的了代码的写法。这个代码现在不用写,体验到正则表达式的优势就可以了。
5.2 正则表达式书写规则
前面我们已经体验到了正则表达式,可以简化校验数据的代码书写。这里需要用到一个方法叫matches(String regex)。这个方法时属于String类的方法。

这个方法是用来匹配一个字符串是否匹配正则表达式的规则,参数需要调用者传递一个正则表达式。但是正则表达式不能乱写,是有特定的规则的。
下面我们就学习一下,正则表达式的规则。从哪里学呢?在API中有一个类叫做Pattern,我们可以到API文档中搜索,关于正则表达式的规则,这个类都告诉我们了。我这里把常用的已经给大家整理好了。
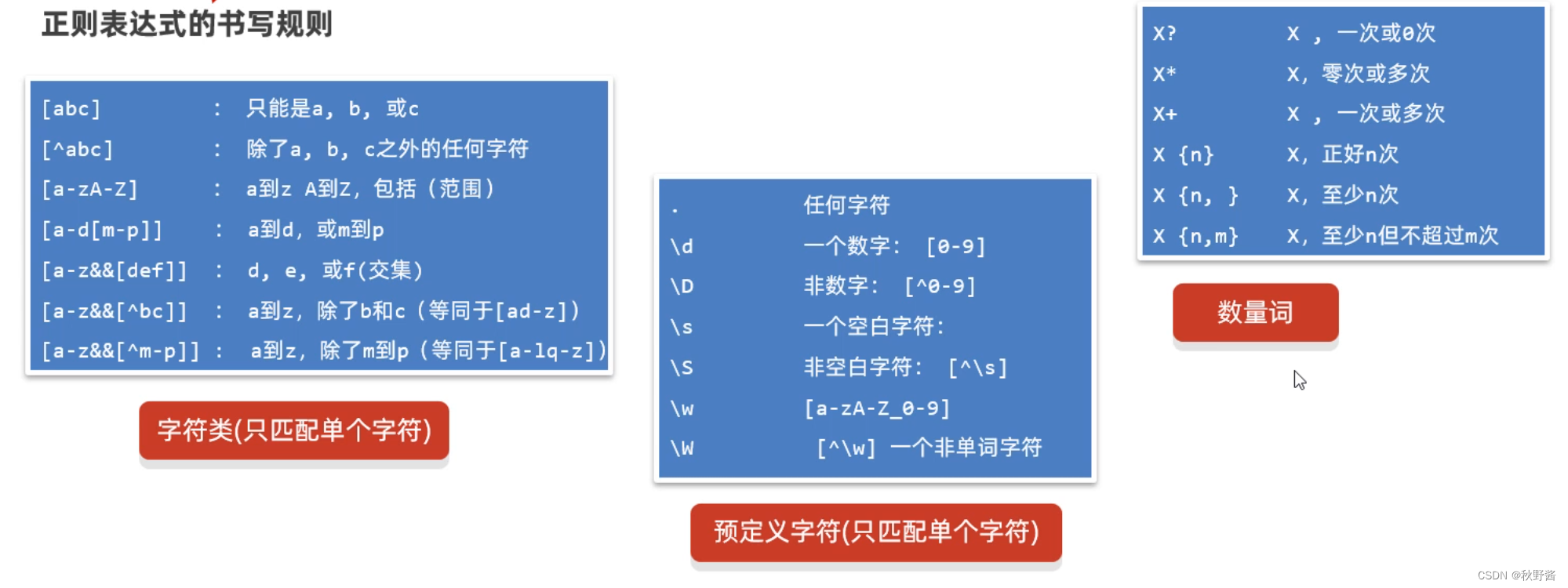
我们将这些规则,在代码中演示一下
/**
* 目标:掌握正则表达式的书写规则
*/
public class RegexTest2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 1、字符类(只能匹配单个字符)
System.out.println("a".matches("[abc]")); // [abc]只能匹配a、b、c
System.out.println("e".matches("[abcd]")); // false
System.out.println("d".matches("[^abc]")); // [^abc] 不能是abc
System.out.println("a".matches("[^abc]")); // false
System.out.println("b".matches("[a-zA-Z]")); // [a-zA-Z] 只能是a-z A-Z的字符
System.out.println("2".matches("[a-zA-Z]")); // false
System.out.println("k".matches("[a-z&&[^bc]]")); // : a到z,除了b和c
System.out.println("b".matches("[a-z&&[^bc]]")); // false
System.out.println("ab".matches("[a-zA-Z0-9]")); // false 注意:以上带 [内容] 的规则都只能用于匹配单个字符
// 2、预定义字符(只能匹配单个字符) . d D s S w W
System.out.println("徐".matches(".")); // .可以匹配任意字符
System.out.println("徐徐".matches(".")); // false
// 转义
System.out.println(""");
// n t
System.out.println("3".matches("\d")); // d: 0-9
System.out.println("a".matches("\d")); //false
System.out.println(" ".matches("\s")); // s: 代表一个空白字符
System.out.println("a".matches("s")); // false
System.out.println("a".matches("\S")); // S: 代表一个非空白字符
System.out.println(" ".matches("\S")); // false
System.out.println("a".matches("\w")); // w: [a-zA-Z_0-9]
System.out.println("_".matches("\w")); // true
System.out.println("徐".matches("\w")); // false
System.out.println("徐".matches("\W")); // [^w]不能是a-zA-Z_0-9
System.out.println("a".matches("\W")); // false
System.out.println("23232".matches("\d")); // false 注意:以上预定义字符都只能匹配单个字符。
// 3、数量词: ? * + {n} {n, } {n, m}
System.out.println("a".matches("\w?")); // ? 代表0次或1次
System.out.println("".matches("\w?")); // true
System.out.println("abc".matches("\w?")); // false
System.out.println("abc12".matches("\w*")); // * 代表0次或多次
System.out.println("".matches("\w*")); // true
System.out.println("abc12张".matches("\w*")); // false
System.out.println("abc12".matches("\w+")); // + 代表1次或多次
System.out.println("".matches("\w+")); // false
System.out.println("abc12张".matches("\w+")); // false
System.out.println("a3c".matches("\w{3}")); // {3} 代表要正好是n次
System.out.println("abcd".matches("\w{3}")); // false
System.out.println("abcd".matches("\w{3,}")); // {3,} 代表是>=3次
System.out.println("ab".matches("\w{3,}")); // false
System.out.println("abcde徐".matches("\w{3,}")); // false
System.out.println("abc232d".matches("\w{3,9}")); // {3, 9} 代表是 大于等于3次,小于等于9次
// 4、其他几个常用的符号:(?i)忽略大小写 、 或:| 、 分组:()
System.out.println("abc".matches("(?i)abc")); // true
System.out.println("ABC".matches("(?i)abc")); // true
System.out.println("aBc".matches("a((?i)b)c")); // true
System.out.println("ABc".matches("a((?i)b)c")); // false
// 需求1:要求要么是3个小写字母,要么是3个数字。
System.out.println("abc".matches("[a-z]{3}|\d{3}")); // true
System.out.println("ABC".matches("[a-z]{3}|\d{3}")); // false
System.out.println("123".matches("[a-z]{3}|\d{3}")); // true
System.out.println("A12".matches("[a-z]{3}|\d{3}")); // false
// 需求2:必须是”我爱“开头,中间可以是至少一个”编程“,最后至少是1个”666“
System.out.println("我爱编程编程666666".matches("我爱(编程)+(666)+"));
System.out.println("我爱编程编程66666".matches("我爱(编程)+(666)+"));
}
}
5.3 正则表达式应用案例
学习完正则表达式的规则之后,接下来我们再利用正则表达式,去校验几个实际案例。
-
正则表达式校验手机号码
/**
* 目标:校验用户输入的电话、邮箱、时间是否合法。
*/
public class RegexTest3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
checkPhone();
}
public static void checkPhone(){
while (true) {
System.out.println("请您输入您的电话号码(手机|座机): ");
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
String phone = sc.nextLine();
// 18676769999 010-3424242424 0104644535
if(phone.matches("(1[3-9]\d{9})|(0\d{2,7}-?[1-9]\d{4,19})")){
System.out.println("您输入的号码格式正确~~~");
break;
}else {
System.out.println("您输入的号码格式不正确~~~");
}
}
}
}
- 使用正则表达式校验邮箱是否正确
public class RegexTest3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
checkEmail();
}
public static void checkEmail(){
while (true) {
System.out.println("请您输入您的邮箱: ");
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
String email = sc.nextLine();
/**
* dlei0009@163.com
* 25143242@qq.com
* itheima@itcast.com.cn
*/
if(email.matches("\w{2,}@\w{2,20}(\.\w{2,10}){1,2}")){
System.out.println("您输入的邮箱格式正确~~~");
break;
}else {
System.out.println("您输入的邮箱格式不正确~~~");
}
}
}
}
5.4 正则表达式信息爬取
各位小伙伴,在前面的课程中,我们学习了正则表达式的作用之一,用来校验数据格式的正确性。接下来我们学习正则表达式的第二个作用:在一段文本中查找满足要求的内容
我们还是通过一个案例给大家做演示:案例需求如下
/**
* 目标:掌握使用正则表达式查找内容。
*/
public class RegexTest4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
method1();
}
// 需求1:从以下内容中爬取出,手机,邮箱,座机、400电话等信息。
public static void method1(){
String data = " 来黑马程序员学习Java,n" +
" 电话:1866668888,18699997777n" +
" 或者联系邮箱:boniu@itcast.cn,n" +
" 座机电话:01036517895,010-98951256n" +
" 邮箱:bozai@itcast.cn,n" +
" 邮箱:dlei0009@163.com,n" +
" 热线电话:400-618-9090 ,400-618-4000,4006184000,4006189090";
// 1、定义爬取规则
String regex = "(1[3-9]\d{9})|(0\d{2,7}-?[1-9]\d{4,19})|(\w{2,}@\w{2,20}(\.\w{2,10}){1,2})"
+ "|(400-?\d{3,7}-?\d{3,7})";
// 2、把正则表达式封装成一个Pattern对象
Pattern pattern = Pattern.compile(regex);
// 3、通过pattern对象去获取查找内容的匹配器对象。
Matcher matcher = pattern.matcher(data);
// 4、定义一个循环开始爬取信息
while (matcher.find()){
String rs = matcher.group(); // 获取到了找到的内容了。
System.out.println(rs);
}
}
}
5.5 正则表达式搜索、替换
接下来,我们学习一下正则表达式的另外两个功能,替换、分割的功能。需要注意的是这几个功能需要用到Stirng类中的方法。这两个方法其实我们之前学过,只是当时没有学正则表达式而已。

/**
- 目标:掌握使用正则表达式做搜索替换,内容分割。
*/
public class RegexTest5 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 1、public String replaceAll(String regex , String newStr):按照正则表达式匹配的内容进行替换
// 需求1:请把下面字符串中的不是汉字的部分替换为 “-”
String s1 = "古力娜扎ai8888迪丽热巴999aa5566马尔扎哈fbbfsfs42425卡尔扎巴";
System.out.println(s1.replaceAll("\w+", "-"));
// 需求2(拓展):某语音系统,收到一个口吃的人说的“我我我喜欢编编编编编编编编编编编编程程程!”,需要优化成“我喜欢编程!”。
String s2 = "我我我喜欢编编编编编编编编编编编编程程程";
System.out.println(s2.replaceAll("(.)\1+", "$1"));
// 2、public String[] split(String regex):按照正则表达式匹配的内容进行分割字符串,反回一个字符串数组。
// 需求1:请把下面字符串中的人名取出来,使用切割来做
String s3 = "古力娜扎ai8888迪丽热巴999aa5566马尔扎哈fbbfsfs42425卡尔扎巴";
String[] names = s3.split("\w+");
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(names));
}
}
原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/qiuyeyyy/article/details/135688208
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。
如若转载,请注明出处:http://www.7code.cn/show_61317.html
如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系代码007邮箱:suwngjj01@126.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!